38 fundamental diagram of traffic flow
Fundamental Speed-Flow-Density Relationships Author: Austroads Subject: This module introduces the basic macroscopic traffic variables, speed, flow, and density. Furthermore, the fundamental relationships between these variables are explored. Finally, fundamental diagrams and experimental observations are linked to the macros copic traffic ... In particular, a s-shaped three-parameter (S3) fundamental diagram model is proposed where vf, kc and m are the free-flow speed, the critical density, and the flatness-of-curve parameter respectively. Figure 1: An illustration of the S3 model when vf = 110 km/hr and kc = 25 veh/km/ln. Some calibration results are shown as follows:
Specifications of Fundamental Diagrams for Dynamic Traffic Modeling By Konstantinos Gkiotsalitis and Andy Chow Stochastic Evolutions of Dynamic Traffic Flow: Modelling and Application
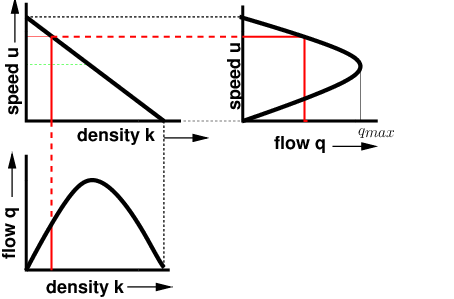
Fundamental diagram of traffic flow
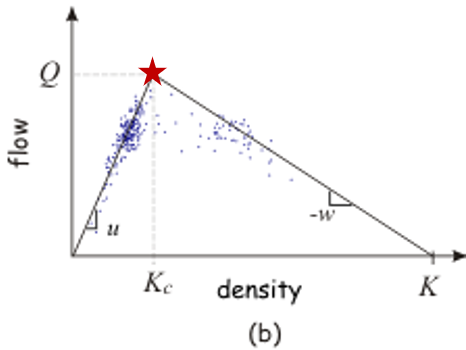
Traffic Flow Fundamentals Introduction. 2. TYPES OF FLOW Traffic flow is usually classified as either a. Uninterrupted Flow b. Interrupted Flow. 3. A. UNINTERRUPTED FLOW - flow occurring at long sections of road where vehicles are not required to stop by any cause external to the traffic stream. 4. (2013) Constructing set-valued fundamental diagrams from Jamiton solutions in second order traffic models. Networks and Heterogeneous Media 8 :3, 745-772. (2013) Riemann problems and exact solutions to a traffic flow model. The wide scattering nature of the fundamental diagram (FD) with observed flow-density data may be associated with the dynamical traffic flow process, especially on signalized intersection. To describe the uncertainty of FD, in this work we established stochastic fundamental diagram (SFD) which is defined by the distributions of shockwave speed.
Fundamental diagram of traffic flow. Fundamental Diagram of Traffic Flow: New Identification Scheme and Further Evidence from Empirical Data Show all authors. Jia Li. Jia Li. 1001 Ghausi Hall, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of California, Davis, 1 Shields Avenue, Davis, CA 95616. fundamental diagram is a useful modern concept to characterize an urban traffic network. In previous practice, traffic engineers analyze each link of a large network but they don't have any idea about the traffic flow characteristics of whole network. With individual link characteristic About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ... traffic regulations, etc. In traffic flow theory the relations between the macroscopic characteristics of a flow are called 'fundamental diagram(s)'.18 pages
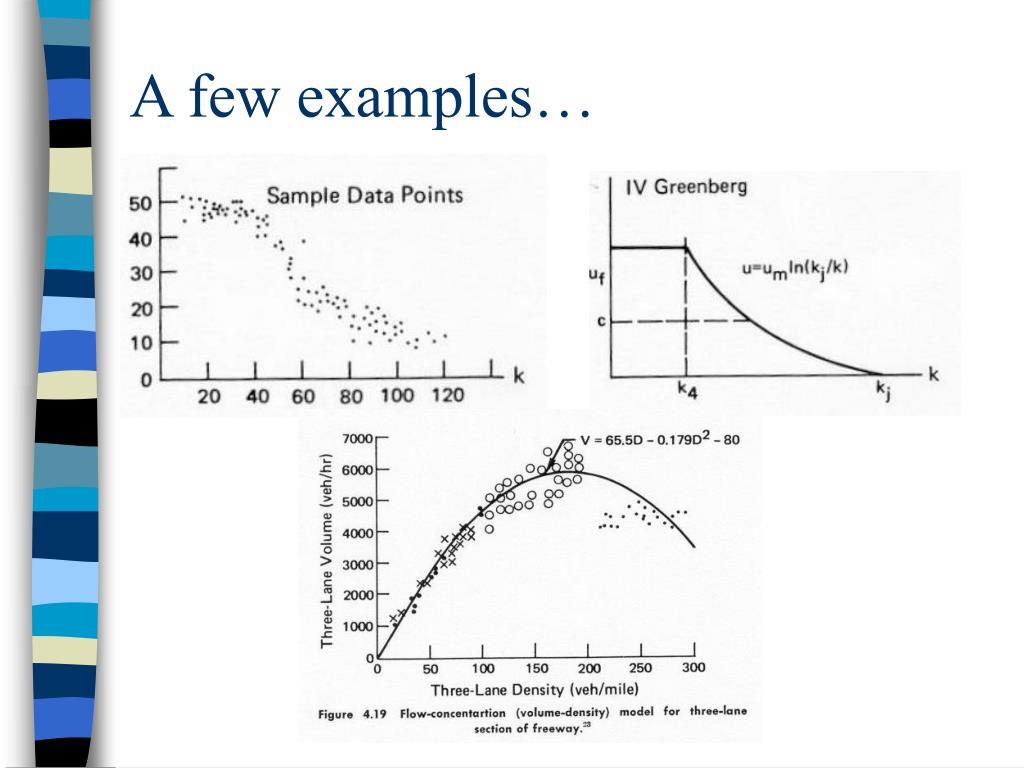
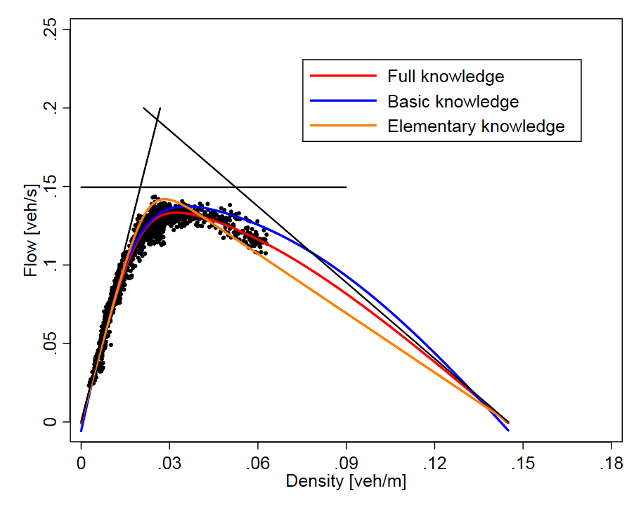
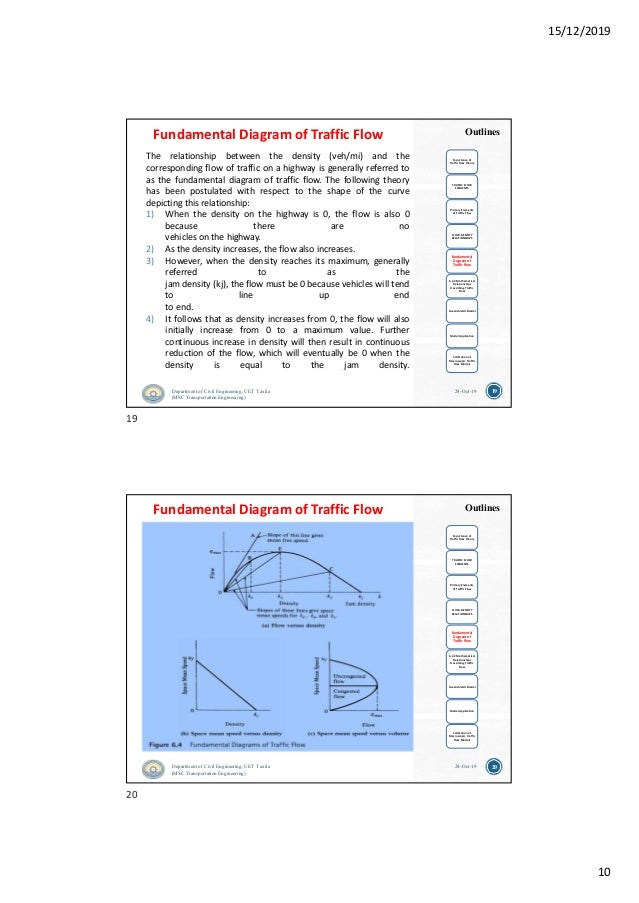
The fundamental diagram of traffic flow is a diagram that gives a relation between the traffic flux (cars/hour) and the traffic density (cars/km). A macroscopic traffic model involving traffic flux, traffic density and velocity forms the basis of the fundamental diagram. It can be used to predict the capability of a road system, or its behaviour when applying inflow regulation or speed limits. 15/12/2019 10 19 Fundamental Diagram of Traffic Flow Department of Civil Engineering,UET Taxila (MSC Transportation Engineering) 24-Oct-19 The relationship between the density (veh/mi) and the corresponding flow of traffic on a highway is generally referred to as the fundamental diagram of traffic flow. The following theory has been postulated ... by H Yu · 2020 — Fundamental diagrams (FDs) show the speed-density or flow–density relationship, which has been considered as the foundation of traffic flow ... This repository aims to provide open-source codes and test data sets for calibrating a wide range of speed-density fundamental diagrams. In particular, a s-shaped three-parameter (S3) fundamental diagram model is proposed where vf, kc and m are the free-flow speed, the critical density, and the flatness-of-curve parameter respectively.
The Fundamental diagram of traffic flow describes the relationship between flow (vehicles per hour) and density (vehicles per km). Both measures can be obtained from edgeData-output. The density value measures vehicles per km and the flow can be computed from entered * 3600 / freq where freq is the specified aggregation interval of the output. The fundamental diagram of traffic flow is a diagram that gives a relation between road traffic flux (vehicles/hour) and the traffic density (vehicles/km). A macroscopic traffic model involving traffic flux, traffic density and velocity forms the basis of the fundamental diagram. It can be used to predict the capability of a road system, or its behaviour when applying inflow regulation or ... Fundamental Diagram of Traffic Flow New Identification Scheme and Further Evidence from Empirical Data Jia Li and H. Michael Zhang A systematic approach is developed to identify the bivariate relation of two fundamental traffic variables, traffic volume and density, from single-loop detector data. The approach is motivated by the observation fundamental diagram of traffic flow is established. On the application side, the stochastic speed-density relationship model can potentially be used for real-time on-line prediction and to explain phenomenons (i.e., capacity drop, spontaneous congestion, and traffic hysteresis) in a similar manner. This enables dynamic control and
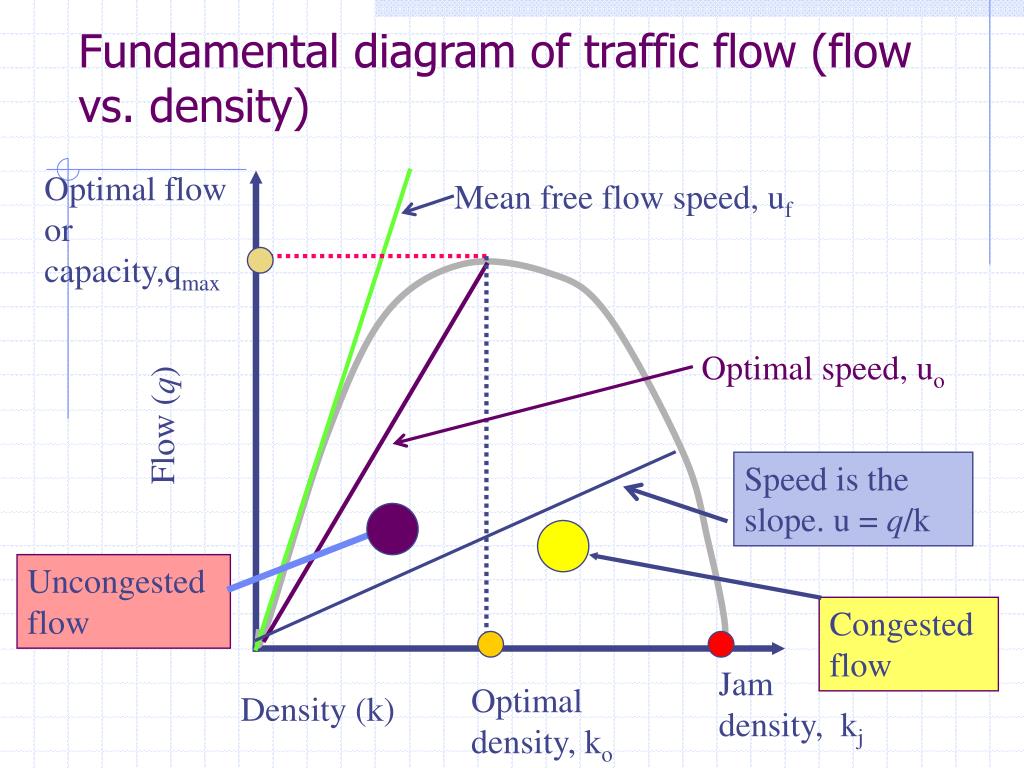
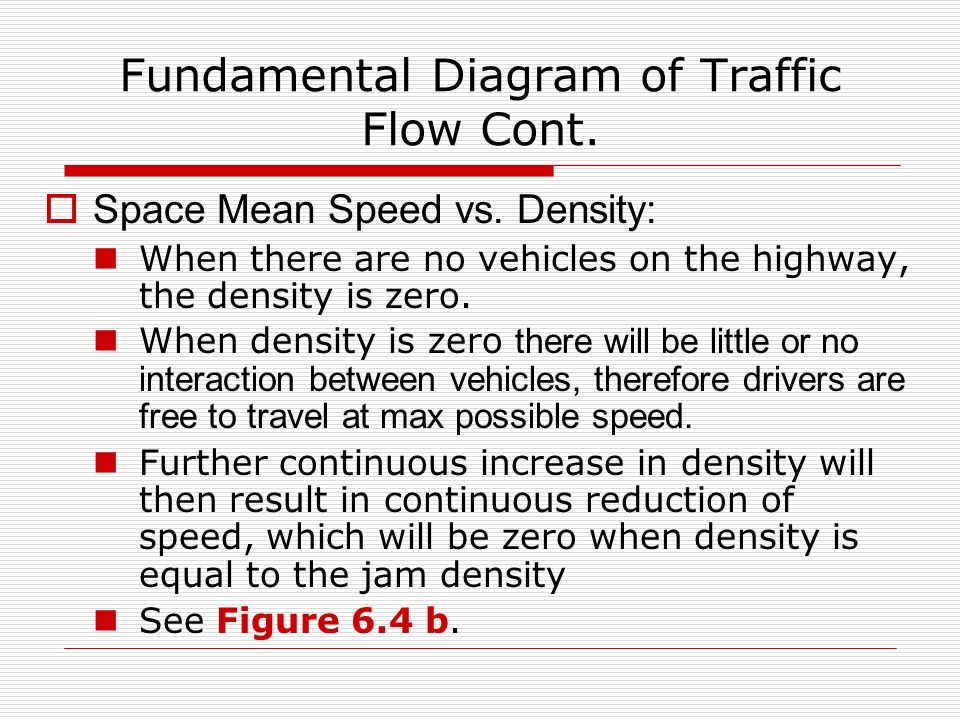
The fundamental diagrams of traffic flow are vital tools which enables analysis of fundamental relationships. There are three diagrams - speed-density, speed-flow and flow-density. They can be together combined in a single diagram as discussed in the last section of the chapter.
Most traffic flow models are able to reproduce the main features of the observed fundamental diagram; in particular, traffic congestion is understood to be closely connected to the instability of the equation of motion (Bando, Hasebe, Nakayama, Shibata, Sugiyama, 1995, Ben-Naim, Krapivsky, Redner, 1994, Kerner, Konhauser, 1993, Komatsu, Sasa ...
Dec 11, 2018 — The fundamental diagram of traffic flow is a diagram that gives a relation between the traffic flux (vehicles/hour) and the traffic density ...
FLOW, SPEED, and DENSITY. The fundamental traffic flow characteristics are flow, speed, and density. We define flow as the number of vehicles passing a point in a given time period. Speed is a vehicle's rate of motion. We define traffic density as the number of vehicles occupying a unit length of roadway at an instant in time.
The flow and capacity at which this point occurs is the optimum flow and optimum density, respectively. The flow density diagram is used to give the traffic condition of a roadway. With the traffic conditions, time-space diagrams can be created to give travel time, delay, and queue lengths of a road segment.
A systematic approach is developed to identify the bivariate relation of two fundamental traffic variables, traffic volume and density, from single-loop detector data. The approach is motivated by the observation of a peculiar feature of traffic fluctuations. That is, in a short time, traffic usually experiences fluctuations without a significant change in speed.
by T Seo · 2019 · Cited by 24 — The fundamental diagram (FD), also known as the flow–density relation, is one of the most fundamental concepts in the traffic flow theory.
- describe the traffic on a microscopic and macroscopic level - apply the relationship q=ku - draw the fundamental diagram, i.e. q=q(k) - argue the differences and similarities between relationships on the network level and road level - explain the steps in numerical traffic flow models
Experimental studies on vehicular traffic provide data on quantities like density, flux, and mean speed of the vehicles. However, the diagrams relating these variables (the fundamental and speed ...
Fundamental traffic flow diagrams and traffic flow modeling are among the widely researched topics in traffic engineering. However, the literature in modeling macroscopic and microscopic traffic flow parameters for the heterogeneous and undisciplined traffic streams is lacking. This study, for the first time, developed a multimodal speed ...
In addition, this relationship can be represented in graphical form resulting in the fundamental diagrams of traffic flow. 31.2 Time mean speed (vt).8 pages

Fundamental Diagram For Spatial Analysis Of Urban Traffic Flow In Nyeri 978 613 9 82811 1 6139828112 9786139828111 By Josphat Mwatelah Edwin Maraoro Lekairap Zachary Abiero Gariy
flow rate function Q(r) [Fundamental Diagram of Tra c Flow] Benjamin Seibold (Temple University) Mathematical Intro to Tra c Flow Theory 09/09{11/2015, IPAM Tutorials 14 / 69. Fundamentals of Tra c Flow Theory Fundamental Diagram Fundamental Diagram (FD) of tra c ow (sensor data) 0 1 2 3
title: Foundations of Traffic Flow Theory—The Fundamental Diagram. Kühne and Gartner discussed Greenshields' contributions in highway traffic and urban streets, Benekohal discussed Treiterer's legacy, and Kerner presented modern approaches to traffic flow modeling. The four
by LH Immers · 2002 · Cited by 107 — 3.2 The fundamental diagrams. Road traffic is always in a specific state that is characterised by the flow rate, the density and the mean speed.39 pages
Macroscopic traffic flow theory relates traffic flow, running speed, and density. Analogizing traffic to a stream, it has principally been developed for limited access roadways (Leutzbach 1988). The fundamental relationship "q=kv" (flow (q) equals density (k) multiplied by speed (v)) is illustrated by the fundamental diagram.

Estimating Traffic Flow Rate On Freeways From Probe Vehicle Data And Fundamental Diagram Semantic Scholar
Applying our code to a wide variety of initial data, we find the observed inverse-$\lambda$ shape of the fundamental diagram of traffic flow. Dependence of the relaxation time˜Ttime˜ time˜T on ...
Media in category "Fundamental diagrams of traffic flow". The following 7 files are in this category, out of 7 total. Basisdiagram 1L - 4.04.jpg 1,000 × 800; 210 KB. Basisdiagram.png 430 × 299; 32 KB. Fundamental Diagram.PNG 647 × 910; 54 KB. Fundamentaldiagram.JPG 1,024 × 742; 67 KB.
The wide scattering nature of the fundamental diagram (FD) with observed flow-density data may be associated with the dynamical traffic flow process, especially on signalized intersection. To describe the uncertainty of FD, in this work we established stochastic fundamental diagram (SFD) which is defined by the distributions of shockwave speed.
(2013) Constructing set-valued fundamental diagrams from Jamiton solutions in second order traffic models. Networks and Heterogeneous Media 8 :3, 745-772. (2013) Riemann problems and exact solutions to a traffic flow model.
Traffic Flow Fundamentals Introduction. 2. TYPES OF FLOW Traffic flow is usually classified as either a. Uninterrupted Flow b. Interrupted Flow. 3. A. UNINTERRUPTED FLOW - flow occurring at long sections of road where vehicles are not required to stop by any cause external to the traffic stream. 4.
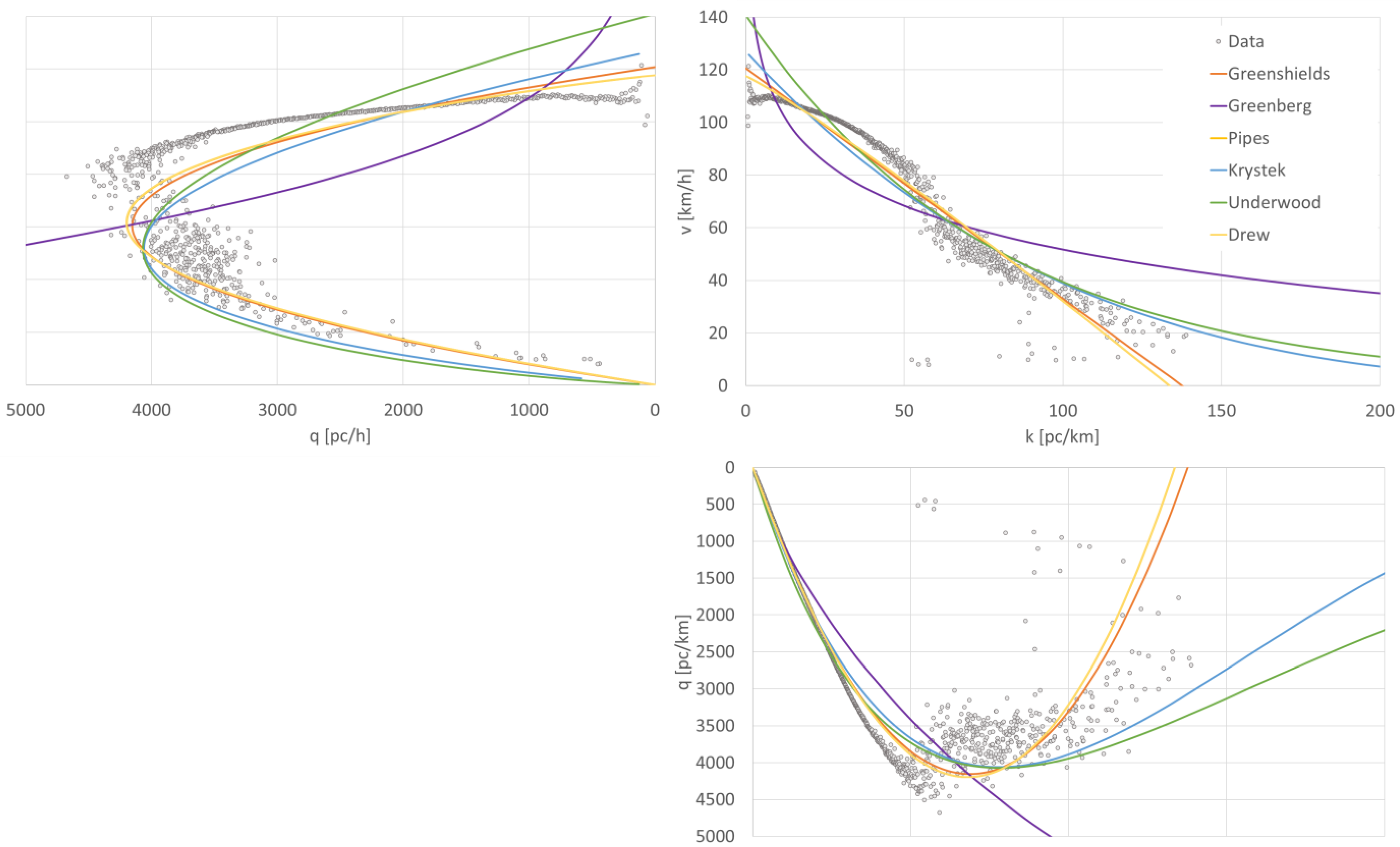
Applied Sciences Free Full Text Comparison Of Traffic Flow Models With Real Traffic Data Based On A Quantitative Assessment Html
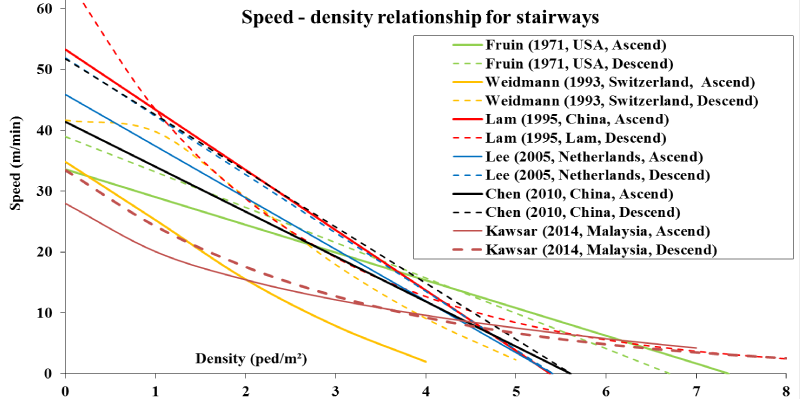
A Review Of Pedestrian Flow Characteristics And Level Of Service Over Different Pedestrian Facilities Banerjee Collective Dynamics
A New Cellular Automata Model Of Traffic Flow With Negative Exponential Weighted Look Ahead Potential
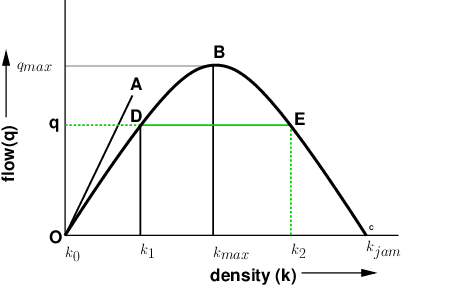
















0 Response to "38 fundamental diagram of traffic flow"
Post a Comment