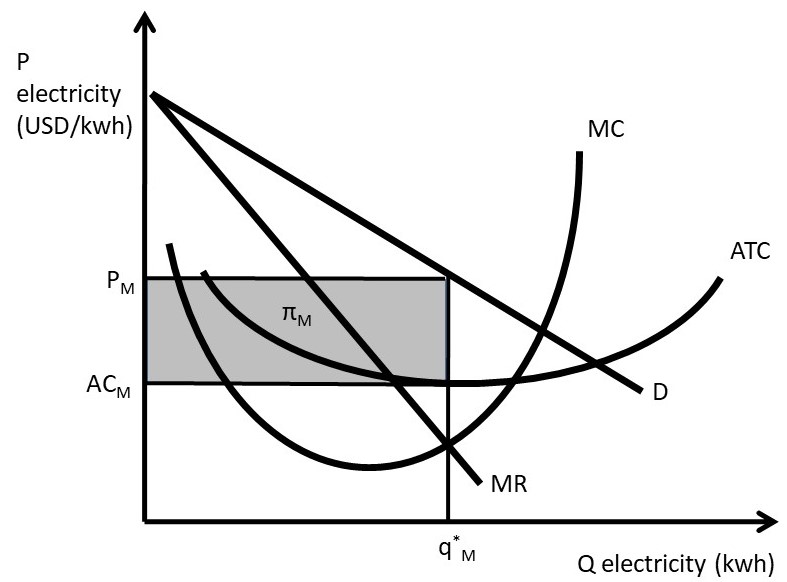
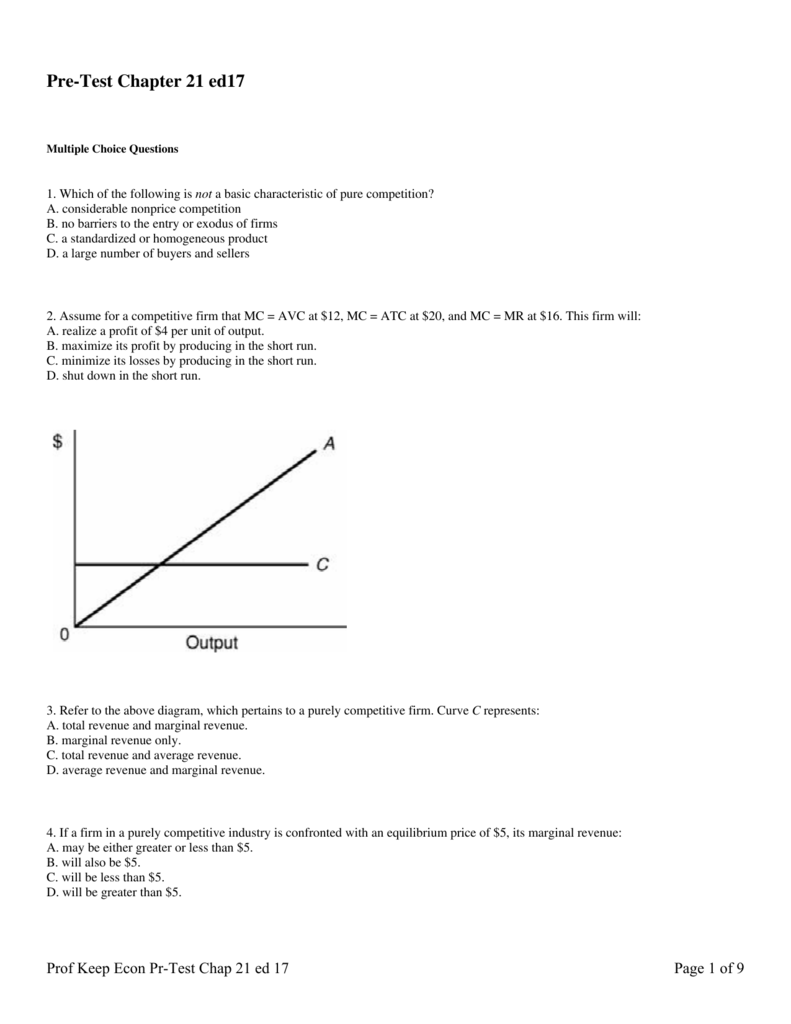
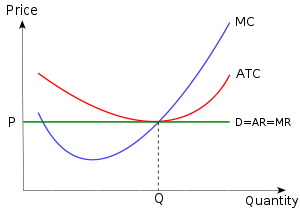
38 refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. curve c represents
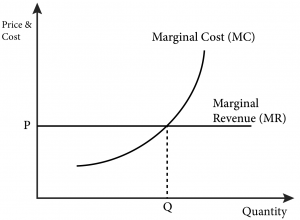
Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve A represents: A. total revenue and marginal revenue. B. Marginal revenue only. C. Total revenue and average revenue. D. Total revenue only. 10. Marginal revenue is the: A. Change in product price associated with the sale of one more unit of output. B. Refer to the diagram which pertains to a purely competitive firm curve c represents. A firm is producing an output such that the benefit from one more unit is more than the cost of producing that additional unit. Purely competitive firms monopolistically competitive firms and pure monopolies all earn zero economic profits in the long run. Producing less output than allocative efficiency ...
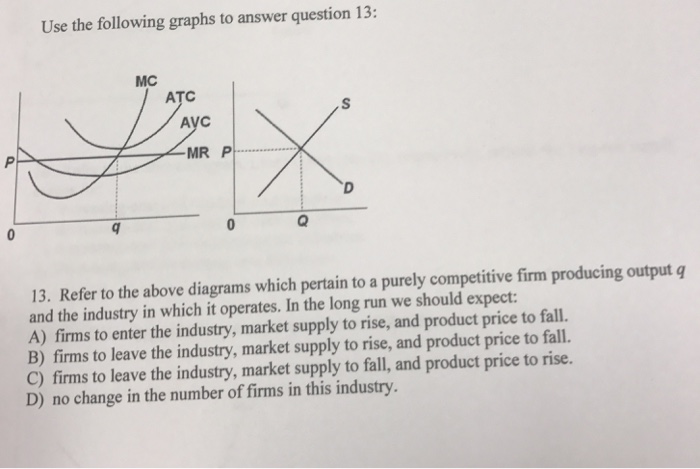
Refer To The Diagram Which Pertains To A Purely Competitive Firm Curve C Represents Ditulis oleh Susan W Nexon. Jumat, 08 November 2019 Tambah Komentar Edit. Firms to enter the industry market supply to rise and product price to fall. Refer to the above diagram which pertains to a purely competitive firm. These Sample Questions Are Based On The Textbook Material In the long run we should ...
Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. curve c represents
Ctotal revenue and average revenue. Refer to the above diagram which pertains to a purely competitive firm. In the short run a purely competitive firm. Daverage revenue and marginal revenue. The demand curves are perfectly elastic for both a purely competitive firm and a purely competitive industry. Refer to the diagram which pertains to a purely competitive firm curve a represents. For a purely competitive firm. Curve 2 horizontal line in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms. The demand curves are perfectly elastic for both a purely competitive firm and a purely competitive industry. Total revenue and average revenue d. Exam 060205rr product markets. Each firm in an oligopoly ... Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve C represents: Average revenue and marginal revenue.
Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. curve c represents. Curve 2 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms 45. A total cost curve. Key points for pure competition in the long run. Convey how purely competitive firms maximize profits or minimize losses in the short run. Quantity curve 4 in the diagram is a purely competitive firms. For a purely competitive firm. Chapter 011 Pure Competition in the Short Run AACSB: Reflective Thinking Type: Graph Refer To: 8_28 [Question] 29. Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve C represents: A. to tal revenue and marginal revenue. B. marginal revenue only. C. to tal revenue and average revenue. D. average revenue and marginal ... 29. Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve represents: C A. total revenue and marginal revenue. B. marginal revenue only. C. total revenue and average revenue.D.average revenue and marginal revenue. 30. Get the detailed answer: Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. What does curve c represent? a) total revenue and marginal reve
Figure 6.21 "The Supply Curve of an Individual Firm" reveals something remarkable: the individual supply curve How much output a firm in a perfectly competitive market will supply at any given price. It is the same as a firm's marginal cost curve. of the firm is the marginal cost curve. They are the same thing. Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve C represents: D. average revenue and marginal revenue. 63. A purely competitive seller's average revenue curve coincides with: C. both its demand and marginal revenue curves. 64. Refer to the above short-run data. Refer to the diagram which pertains to a purely competitive firm curve c represents. The demand curves of firms are kinked at the prevailing price. The firm will earn an economic profit. If product price is p3 a. The demand curves are perfectly elastic for both a purely competitive firm and a purely competitive industry. Ctotal revenue and average revenue. Atotal revenue and marginal revenue ... A purely competitive firm's short-run supply curve is upsloping and equal to the portion of the marginal cost curve that lies above the average variable cost curve. A purely competitive firm should produce in the short run if its total revenue is sufficient to cover its:
20. Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve A represents: A. total revenue and marginal revenue. B. marginal revenue only. C. total revenue and average revenue. D. total revenue only. 21. Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve C represents: A. total revenue and marginal revenue. B. marginal revenue only. C. total revenue and average revenue. D. average revenue and marginal revenue. Refer to Figure 8.4 for a perfectly competitive market and firm. Which of the following is most likely to occur, ceteris paribus? A) The firm will exit in the long run. B) The firm will shutdown in the short run. C) The firm will increase output. D) The firm will raise its price. Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve C represents: average revenue and marginal revenue. In the short run, a purely competitive firm will earn a normal profit when: P = ATC. A purely competitive firm's short-run supply curve is:
D) The demand curves are perfectly elastic for both a purely competitive firm and a purely competitive industry. Answer: A. Use the following to answer questions 30-31: Type: G Topic: 2 E: 416 MI: 172 30. Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve A represents: A) total revenue and marginal revenue.
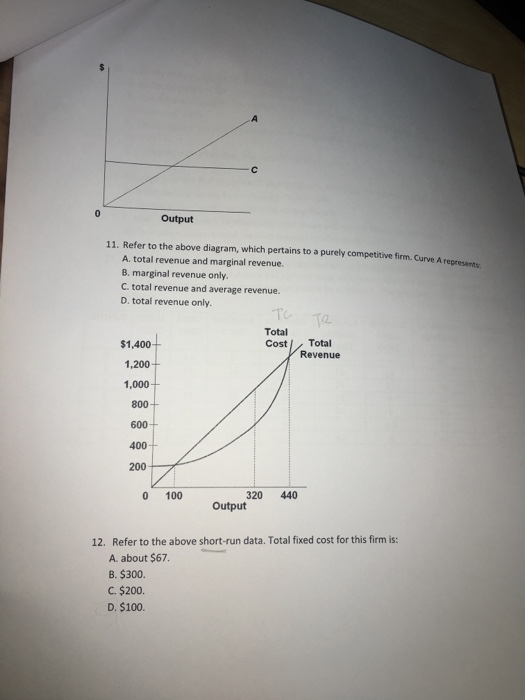
The answer is D-) Total revenue only. Beca …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: 0 Output 11. Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve A represents A. total revenue and marginal revenue. B. marginal revenue only. C. total revenue and average revenue D. total revenue only. TC Total.
Marginal Cost and the Firm's Supply Curve. For a perfectly competitive firm, the marginal cost curve is identical to the firm's supply curve starting from the minimum point on the average variable cost curve. To understand why this perhaps surprising insight holds true, first think about what the supply curve means.

Toward A Conceptual Framework For Macroeconomic Evaluation Of Public Enterprise Performance In Mixed Economies In Public Enterprise In Mixed Economies
Refer to the diagram which pertains to a purely competitive firm curve c represents. Total revenue and marginal revenue. If product price is p3 a. Exam 060205rr product markets. Total revenue and marginal revenue. Curve a represents a. Refer to the above diagram which pertains to a purely ...
A purely competitive firm finds that the market price for its product is $25.00. It has a fixed cost of $100.00 and a variable cost of $15.00 per unit for the first 50 units and then $30.00 per uni...
Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve C represents: A. total revenue and marginal revenue. B. marginal revenue only. C. total revenue and average revenue. Correct D. average revenue and marginal revenue. D. average revenue and marginal revenue.
Curve C represents... average revenue and marginal revenue. Image: Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve.
Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve A represents. total revenue only. Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. If product price is P3. economic profit will enter this industry. Curve 4 in the above diagram is a purely competitive ...
Gravity. Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve C represents: Click card to see definition 👆. Tap card to see definition 👆. average revenue and marginal revenue. Click again to see term 👆. Tap again to see term 👆.
Refer to the diagram which pertains to a purely competitive firm curve c represents. Refer to the above diagram which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Atotal revenue and marginal revenue. Both its demand and marginal revenue curves. Refer to the above short run data. Refer to the above diagram which pertains to a purely. Refer to the above diagram which pertains to a purely competitive ...
A monopolistically competitive firm faces a demand for its goods that is between monopoly and perfect competition. Figure 8.4a offers a reminder that the demand curve as faced by a perfectly competitive firm is perfectly elastic or flat, because the perfectly competitive firm can sell any quantity it wishes at the prevailing market price. In ...
Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. The shutdown point is at a price of . P2. P1. P3. P4. A purely competitive firm is precluded from making economic profits in the long run because. there are no barriers to enter the industry. Refer to the diagrams. At price b and quantity a, diagram (A) represents. the pure monopoly model.
Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve A represents Multiple Choice A. total revenue only. B. marginal revenue only. C. total revenue and marginal revenue. D. total revenue and average revenue.

Disruptive Innovation An Intellectual History And Directions For Future Research Christensen 2018 Journal Of Management Studies Wiley Online Library
Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve A represents: asked Aug 14, 2018 in Economics by Rebecca. A. total revenue and marginal revenue. B. marginal revenue only. C. total revenue and average revenue. D. total revenue only. principles-of-economics 0 Answers.
21. Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve represents: C A. total revenue and marginal revenue. B. marginal revenue only.C. total revenue and average revenue. D. average revenue and marginal revenue. 22. Marginal revenue is the: A. change in product price associated with the sale of one more unit of ...
A) Both purely competitive and monopolistic firms are "price takers." B) Both purely competitive and monopolistic firms are "price makers."; C) A purely competitive firm is a "price taker," while a monopolist is a "price maker." D) A purely competitive firm is a "price maker," while a monopolist is a "price taker."
Refer to the two diagrams for individual firms. Figure 2 pertains to a purely competitive seller. Refer to the two diagrams for individual firms. In Figure 2 the firm's demand and marginal revenue curves are represented by lines B and C, respectively. The demand curve faced by a pure monopolist is less elastic than that faced by a single purely ...
Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve C represents. answer choices . total revenue and marginal revenue. marginal revenue only. total revenue and average revenue. average revenue and marginal revenue. Tags: Question 20 .
Chapter 011 Pure Competition in the Short Run AACSB: Reflective Thinking Type: Graph Refer To: 8_28 [Question] 29. Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve C represents: A. total revenue and marginal revenue. B. marginal revenue only. C. total revenue and average revenue. D. average revenue and marginal revenue.
Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve C represents: D. Average revenue and marginal revenue. Average revenue equals marginal revenue. 8) Firms seek to maximize: C. Total Profit.
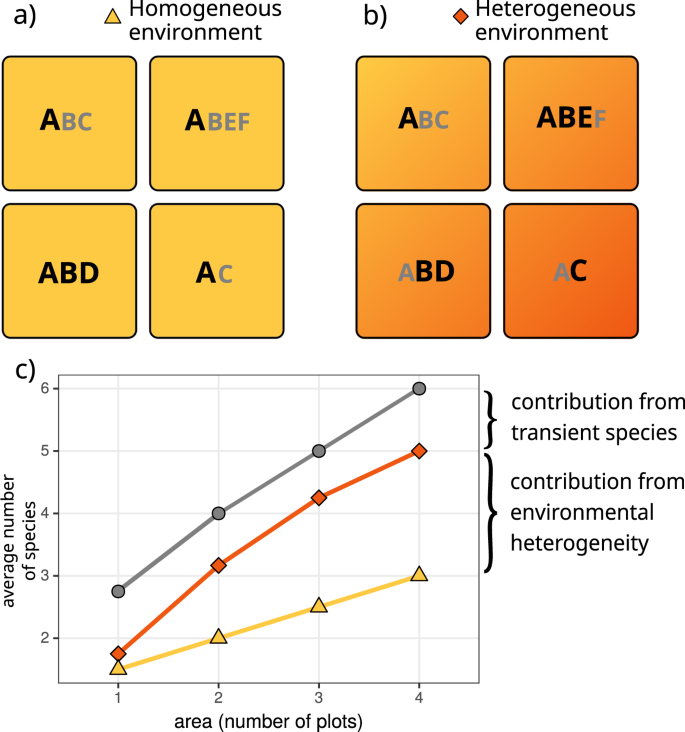
The Spatial Configuration Of Biotic Interactions Shapes Coexistence Area Relationships In An Annual Plant Community Nature Communications
• Question 1 1 out of 1 points Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve represents: C Answer. Selected Answer: average revenue and marginal revenue. Correct Answer: average revenue and marginal revenue.
The demand curve for a purely competitive firm is perfectly elastic, but the demand curve for a purely competitive industry is downsloping · 20. Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve A represents:
Get the detailed answer: Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. What does curve c represent? a) total revenue and marginal reve
2. the equilibrium position of a competitive firm in the long run. 3. a competitive firm that is realizing an economic profit. 4. the loss-minimizing position of a competitive firm in the short run. 9. Refer to the above diagram. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: 1. suffer an economic loss. 2. earn a normal profit.
Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve C represents: Average revenue and marginal revenue.
Refer to the diagram which pertains to a purely competitive firm curve a represents. For a purely competitive firm. Curve 2 horizontal line in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms. The demand curves are perfectly elastic for both a purely competitive firm and a purely competitive industry. Total revenue and average revenue d. Exam 060205rr product markets. Each firm in an oligopoly ...
Ctotal revenue and average revenue. Refer to the above diagram which pertains to a purely competitive firm. In the short run a purely competitive firm. Daverage revenue and marginal revenue. The demand curves are perfectly elastic for both a purely competitive firm and a purely competitive industry.

Opec Unconventional Oil And Climate Change On The Importance Of The Order Of Extraction Sciencedirect

European Flag European Commission Brussels 14 7 2021 Swd 2021 621 Final Commission Staff Working Document Impact Assessment Report Accompanying The Proposal For A Directive Of The European Parliament And The Council

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Guns-and-ButterCurve-f52db04559864b0ebce64aec2db5fe09.png)




/MinimumEfficientScaleMES2-c9372fffba0a4a1ab4ab0175600afdb6.png)



0 Response to "38 refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. curve c represents"
Post a Comment