39 the greater the area between the lorenz curve and the diagonal in the lorenz curve diagram, the
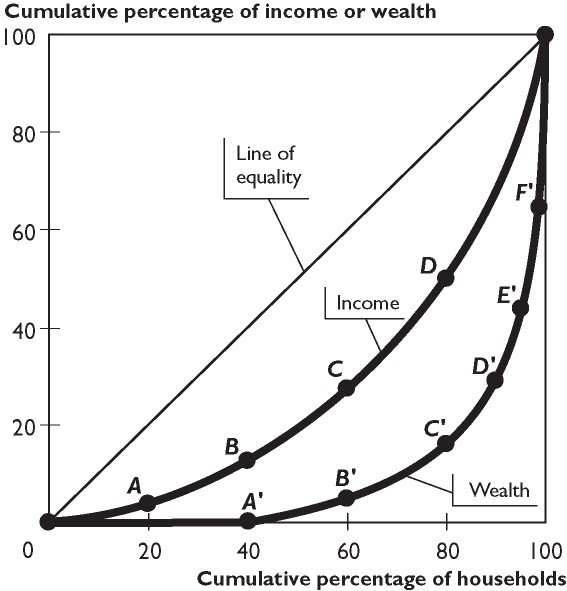
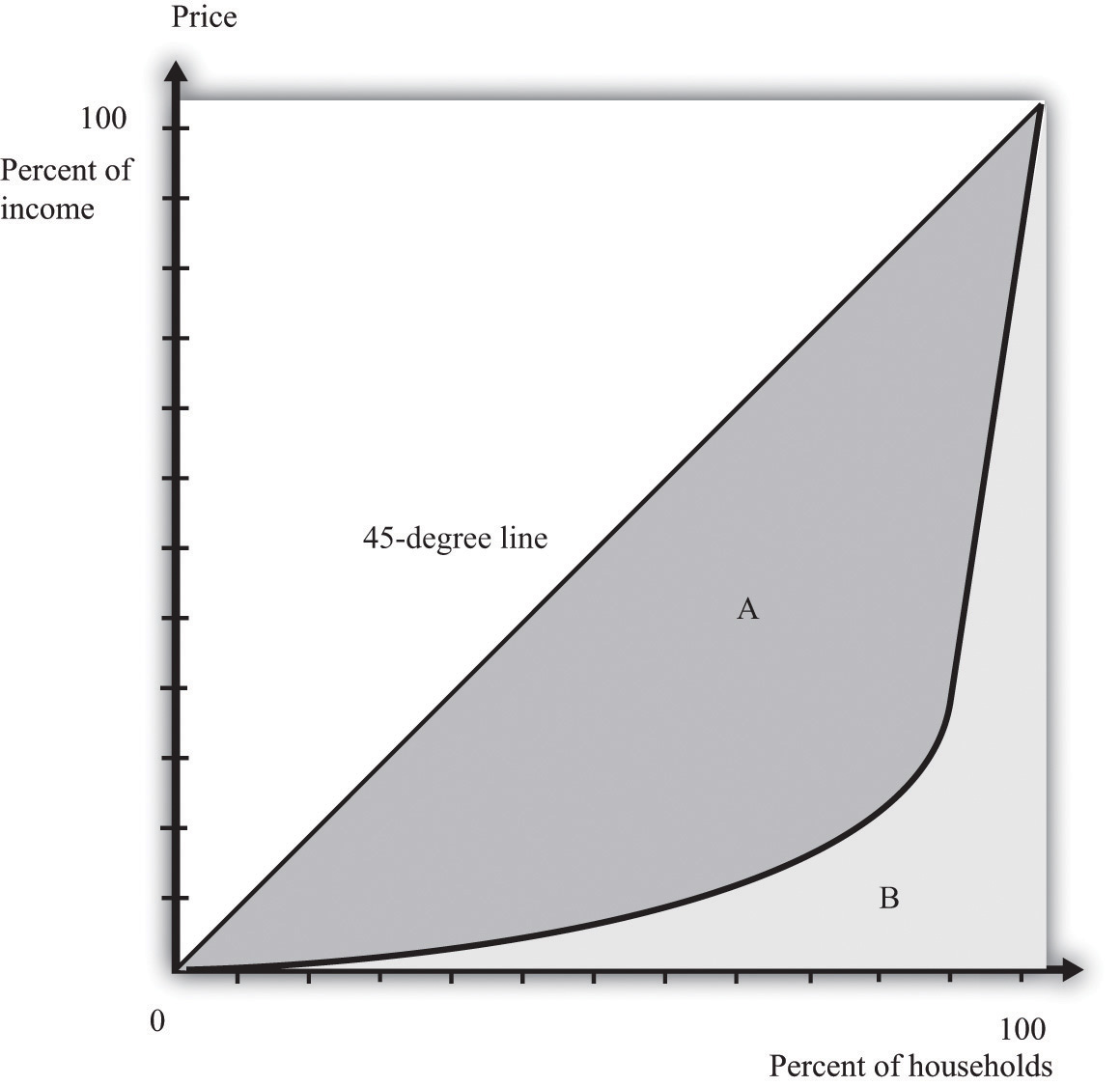
The degree of inequality in a country can be obtained by calculating the ratio of the "area between the diagonal and the Lorenz Curve as compared to the total, area of the half square in which the curve lies". Thus in Fig. 4: "The ratio of the shaded area EA to the total area of the triangle BCD". Ellie Tragakes · 2011 · Juvenile NonfictionThe diagonal line in the diagram represents perfect equality in income ... The Lorenz curve plots the actual relationship between percentages of the ...
The greater the area between the Lorenz curve and the diagonal in the Lorenz curve diagram the: A: smaller is the Gini ratio and the greater is the degree of income inequality. B: larger is the Gini ratio and the greater is the degree of income inequality. C: smaller is the Gini ratio and the lesser is the degree of income inequality.
The greater the area between the lorenz curve and the diagonal in the lorenz curve diagram, the
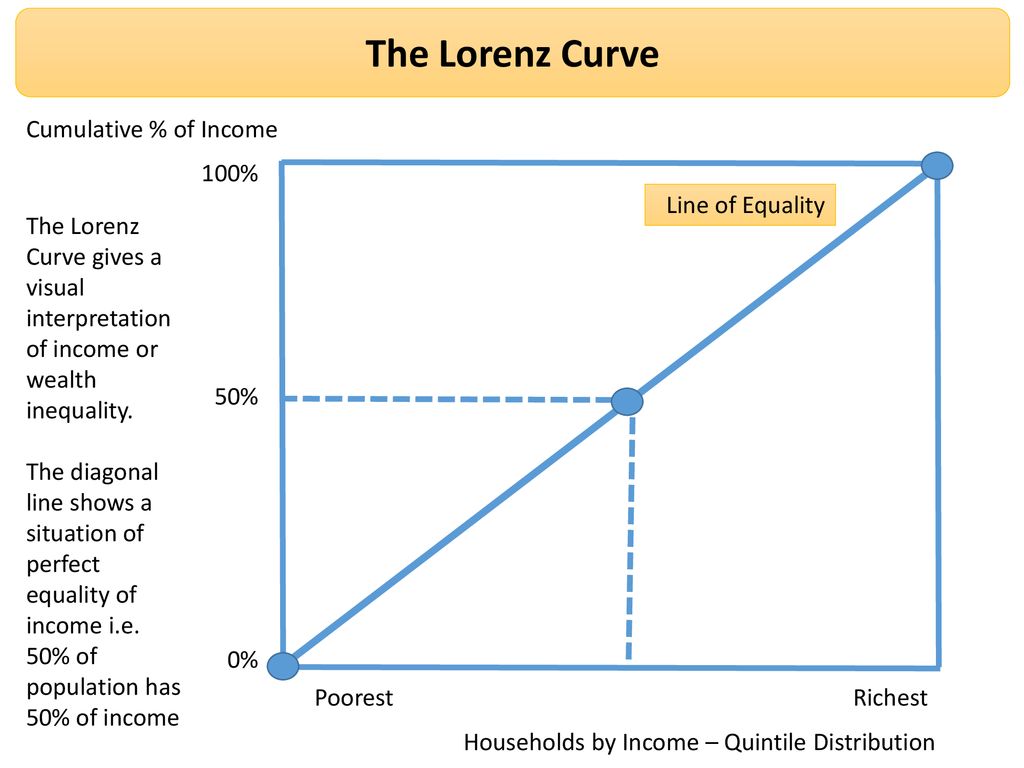
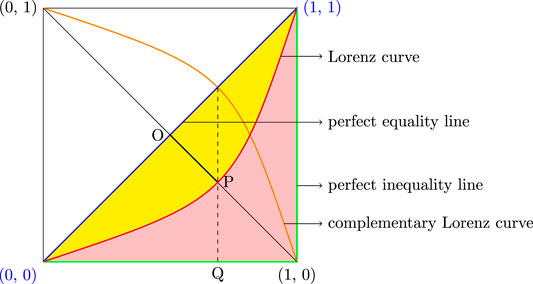
In economics, the Lorenz curve is a graphical representation of the distribution of income or of wealth.It was developed by Max O. Lorenz in 1905 for representing inequality of the wealth distribution.. The curve is a graph showing the proportion of overall income or wealth assumed by the bottom x% of the people, although this is not rigorously true for a finite population (see below). Subaru's FB20 was a 2.0-litre horizontally-opposed (or 'boxer') four-cylinder petrol engine. Effectively replacing the EJ204 engine, the FB20 engine was a member of Subaru's third generation 'FB' boxer engine family which also included the FB25, FA20D, FA20E and FA20F engines.The FB20 engine first offered in Australia in 2012 Subaru GP/GJ Impreza. The Lorenz curve is represented by a straight diagonal line, which represents perfect equality in income or wealth distribution; the Lorenz curve lies beneath it, showing estimated distribution. The area that is between the straight line and the curved line is the Gini coefficient .
The greater the area between the lorenz curve and the diagonal in the lorenz curve diagram, the. Answer (1 of 3): The Lorenz curve is a graphical representation of the distribution of some measure - income, consumption, education, etc. -- among a population of people, households, or other units. The Gini coefficient is a numerical measure of inequality, which can be easily related to the Lor... Donald T. Rowland · 2003 · Social ScienceIt 'measures the proportion of the total area under the diagonal that lies in the area between the diagonal and the Lorenz curve' (White 1986: 204). The Gini coefficient is defined as a ratio of the areas on the Lorenz curve diagram. If the area between the line of perfect equality and Lorenz curve is A, and the area under the Lorenz curve is B, then the Gini coefficient is A/(A+B). Since A+B = 0.5, the Gini coefficient, G = 2A = 1-2B. If the Lorenz curve is represented by the Lorenz Curve. Definition: The Lorenz curve is a way of showing the distribution of income (or wealth) within an economy. It was developed by Max O. Lorenz in 1905 for representing wealth distribution. The Lorenz curve shows the cumulative share of income from different sections of the population. If there was perfect equality - if everyone ...
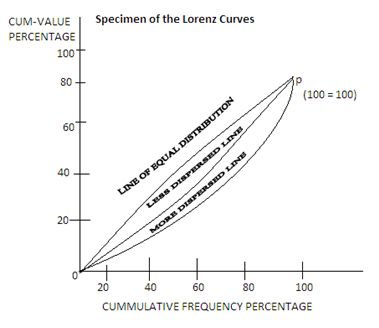
(the Lorenz curve coincides with the diagonal in Figure 2) and 1 perfect inequality. If the Gini coefficient for some variable (e.g., income) in a country has increased over time, it means that the distribution of that The Gini ratio can't exceed 1 because if the Lorenz curve is as far as possible from the diagonal (line of equality), the area between the curve and the diagonal will equal the total area below the diagonal. The equality will result in a Gini ratio of 1. A decline in the Gini ratio implies less income inequality; and it would be graphically ... Also available as an addition to this 2S manual is a set of 11 large electrical drawings including Control Box Connection Diagram, Connection Diagram for Knee Limit Switch, 2 Diagrams for Automatic Sequence, Wiring Diagram for Automatic Plate, Wiring Diagram of Master Plate for Automatic and Manual Machines. £85 (order under reference MA445ME) Answer: The relationship between the Lorenz curve and the Gini coefficient is that you need the former in order to calculate the latter. The Lorenz curve (see graph below) is an indication of the income distribution in a population. At one extreme and unrealistic case, we would have the perfect ...
The degree of inequality in a country can be obtained by calculating the ratio of the "area between the diagonal and the Lorenz Curve as compared to the total, area of the half square in which the curve lies". Thus in Fig. 4: "The ratio of the shaded area EA to the total area of the triangle BCD". Lorenz Curve Definition. Lorenz Curve, named after American Economist Max O. Lorenz, is a graphical representation of an economic inequality Economic Inequality Economic inequality is the inequality in wealth distribution and opportunities among people belonging to different groups, communities or countries. Its increasing trend indicates more disparity, appropriately expressed with the ... The ratio between the areas X and Y on the graph is known as the Gini coefficient. Thus G=x/y . where G is the Gini coefficient; X is the area between the Lorenz curve and the diagonal and Y is the area above the diagonal. If there is a completely equal distribution of income, the G=0 and the Lorenz curve is a diagonal line. 1.4 The area between the Lorenz curve of a country and the diagonal of perfect equality represents: A. The area of equality B. The cumulative percentage of the population. C. The Gini coefficient D. The quantile ratio E. Difference Between Equality and Reality. 1.5 Which one of the following is not part of the BOP accounts?
James M. Cypher · 2020 · Business & EconomicsFrom the Lorenz curve diagram, the Gini coefficient can be calculated. It is equal to the area A (the area between the Lorenz curve and the diagonal “line ...
The greater the area between the Lorenz curve and the diagonal in the Lorenz Curve diagram, the: larger is the Gini ratio and the greater is the degree of income inequality. Which of the following is correct? Income is a flow and wealth is a stock concept. Wealth:
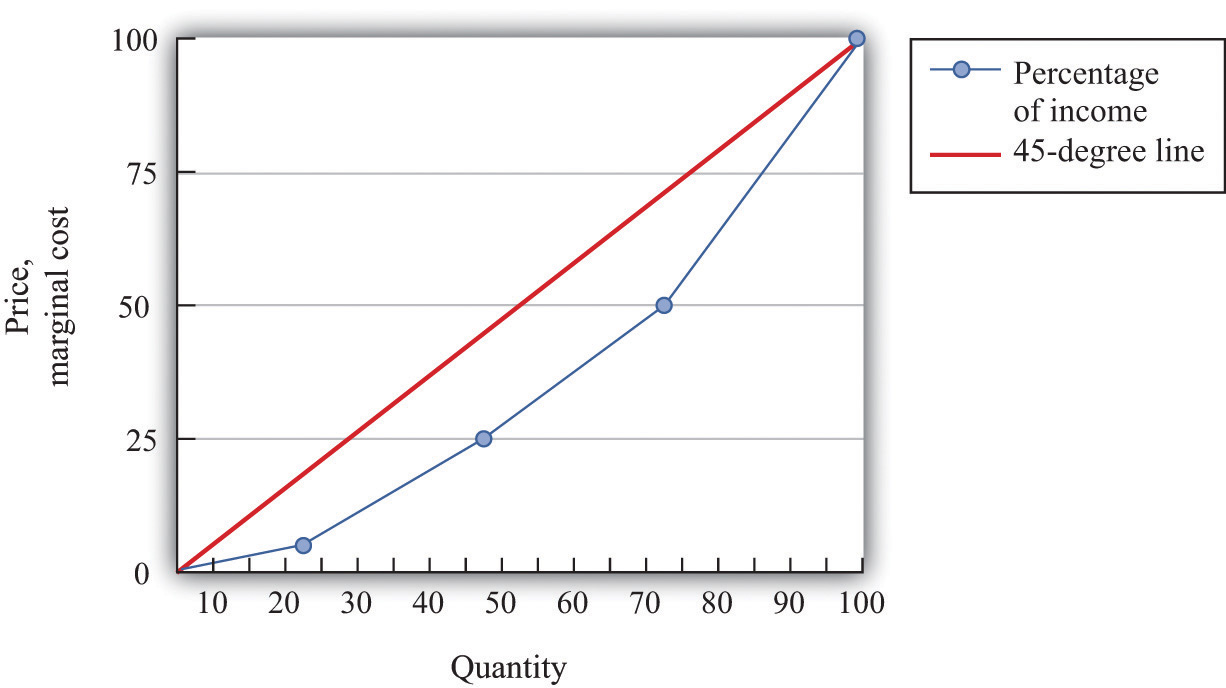
The greater inequality of the U.S. income distribution between 1980 and 2013 is illustrated in this figure because the Lorenz curve for 2013 is farther from the 45-degree line than the Lorenz curve for 1980. The Lorenz curve is a useful way of presenting the quintile data that provides an image of all the quintile data at once.
25. As the area between the Lorenz curve and diagonal gets larger, the Gini ratio: A. Rises to reflect greater equality B.Rises to reflect greater inequality C. Falls to reflect greater inequality D. Falls to reflect greater equality AACSB: Analytic Bloom's: Knowledge Learning Objective: 11-1 Level: Moderate Topic: Income inequality; Lorenz ...

Contributory Inequality Alters Assessment Of Academic Output Gap Between Comparable Countries Sciencedirect
The greater the area between the Lorenz curve and the diagonal line of absolute equality, the more inequality exists. asked Aug 24, 2019 in Economics by Janessa Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
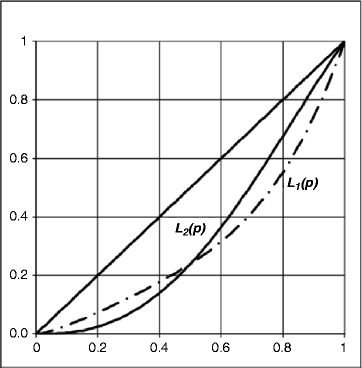
by A Byrtusová · Cited by 1 — The Lorenz curve describes the actual state of income distribution in a society. Generally speaking, the more the Lorenz curve approaches the diagonal, the ...8 pages
The Gini index is equal to twice the area between the Equality and Lorenz curves. Note that the area under the Equality curve is 0.5 and the area under the Lorenz curve can be approximated by adding the areas of trapezoids as described in ROC Data Analysis Tool. The area of the 10 trapezoids used for Example 1 are shown in column K of Figure 1.
The Gini coefficient, or Gini index, is derived from the Lorenz curve, and like the Lorenz curve, it measures the degree of economic equality across a given population and simplifies this reality into a single number.. How Does the Gini Coefficient Work? The Gini coefficient can vary from 0 (perfect equality, also represented as 0%) to 1 (perfect inequality, also represented as 100%).
Economic Development, 11th Edition (The Pearson Series in Economics) by Michael P. Todaro, Stephen C. Smith
The area between the Lorenz curve of a country and the diagonal of perfect equality represents: A. the area of equality. B. the area of inequality. C. The Gini coefficient. D. The quantile ratio. E. the cumulative percentage of the population. Question 17. Which of the following is recorded on the financial account of the balance of payments? A.
Password requirements: 6 to 30 characters long; ASCII characters only (characters found on a standard US keyboard); must contain at least 4 different symbols;
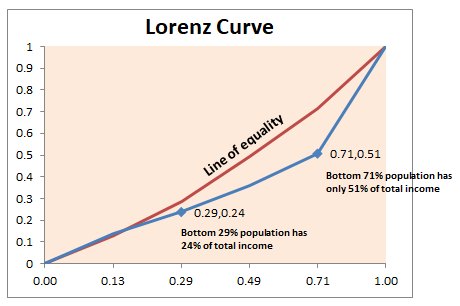
The Lorenz curve shows the actual quantitative relationship between the percentage of income recipients and the percentage of the total income they did in fact receive during, say, a given year. The more the Lorenz curve line is away from the diagonal (perfect equality), the greater the degree of inequality represented.
in this video we're going to discuss income inequality which is something that is often debated thinking about comparing countries thinking about whether it's an issue or not and how to address it and to appreciate what income inequality is let's imagine two different countries let's imagine first country a and there's two people in country a so you have person one here who makes $1000 a year ...
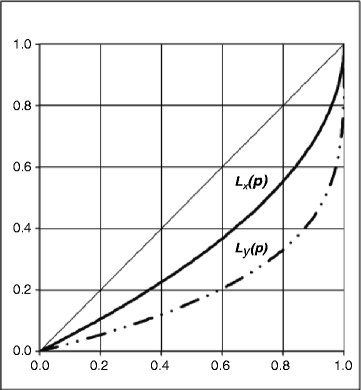
As you can see, in the. graph, the curve starts from coordinates (0,0), as a zero fraction of the population owns. a zero fraction of income. Since the Lorenz C urve records cumulative proportions ...
To estimate the income Gini coefficient for Haiti in 2012, we would find the area below its Lorenz curve: around 0.2. Subtracting that figure from 0.5 (the area under the line of equality), we get ...
Ray Powell, James Powell · 2016 · Study AidsLorenz curve a graph on which the cumulative percentage of total national ... coefficient measures the area between the Lorenz curve and the diagonal as a ...

Methods For Measuring Health Inequalities Part Iii Maria Cristina Schneider Carlos Castillo Salgado Jorge Bacallao Enrique Loyola Oscar J Mujica Manuel Vidaurre And Anne Roca Gini Coefficient And Lorenz Curve The Gini Coefficient Is Based On The
23/02/2004 · [prev in list] [next in list] [prev in thread] [next in thread] List: llvm-commits Subject: [llvm-commits] CVS: llvm/test/Programs/MultiSource/Benchmarks/MallocBench ...
21.The greater the area between the Lorenz curve and the diagonal in the Lorenz curve diagram, the: A. smaller is the Gini ratio and the greater is the degree ...
The Lorenz coefficient is defined in terms of a plot of Fm versus Hm, shown in Figure 4.6. The Lorenz coefficient Lc is two times the area enclosed between the Lorenz curve ABC in the figure and the diagonal AC. The range of the Lorenz coefficient is 0 ≤ L c ≤ 1. For a homogeneous reservoir, the Lorenz coefficient satisfies the equality Lc = 0.
Uncertainty quantification (UQ) currently underpins many critical decisions, and predictions made without UQ are usually not trustworthy. To understand the deep learning (DL) , process life cycle, we need to comprehend the role of UQ in DL. DL models start with a collection of the most comprehensive and potentially relevant datasets available for the decision making process.
Can you explain why the Lorenz curve could not lie above or to the left of the diagonal at any point? It is because percentage population and percentage income are represented in cumulative percentages on the diagram. Gini Coefficients and Aggregate Measures of Inequality A very common measure of inequality can be obtained by calculating the ratio of the area between the diagonal and the ...

Characterizing Forest Structural Types And Shelterwood Dynamics From Lorenz Based Indicators Predicted By Airborne Laser Scanning
In a Lorenz curve diagram, the size of the area between the Lorenz curve and the diagonal line represents A) the dollar incomes of the bottom 40% of families. B) the percentage of income received by the bottom 20% of families. C) the degree of inequality in the distribution of income. D) complete income equality. E)
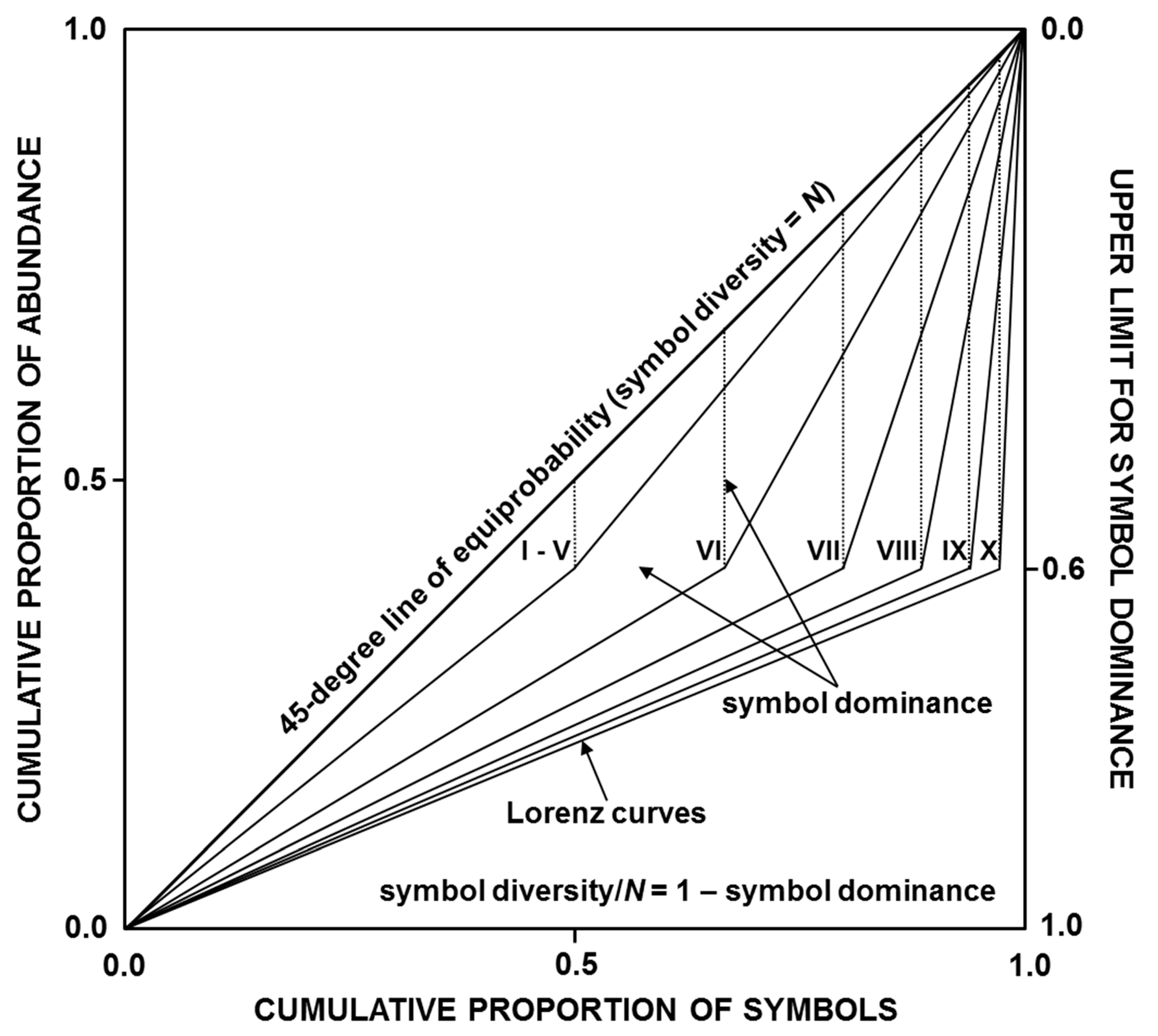
Entropy Free Full Text The Lorenz Curve A Proper Framework To Define Satisfactory Measures Of Symbol Dominance Symbol Diversity And Information Entropy Html
In other words, it is double the area between the Lorenz curve and the line of perfect equality. Another way of thinking about the Gini coefficient is as a measure of deviation from perfect equality. The further a Lorenz curve deviates from the perfectly equal straight line (which represents a Gini coefficient of 0), the higher the Gini ...
Plotted as a Lorenz curve, complete equality would be a straight diagonal line with a slope of 1 (the area between this curve and itself is 0, so the Gini coefficient is 0).
The Lorenz curve is represented by a straight diagonal line, which represents perfect equality in income or wealth distribution; the Lorenz curve lies beneath it, showing estimated distribution. The area that is between the straight line and the curved line is the Gini coefficient .
Subaru's FB20 was a 2.0-litre horizontally-opposed (or 'boxer') four-cylinder petrol engine. Effectively replacing the EJ204 engine, the FB20 engine was a member of Subaru's third generation 'FB' boxer engine family which also included the FB25, FA20D, FA20E and FA20F engines.The FB20 engine first offered in Australia in 2012 Subaru GP/GJ Impreza.
In economics, the Lorenz curve is a graphical representation of the distribution of income or of wealth.It was developed by Max O. Lorenz in 1905 for representing inequality of the wealth distribution.. The curve is a graph showing the proportion of overall income or wealth assumed by the bottom x% of the people, although this is not rigorously true for a finite population (see below).

















0 Response to "39 the greater the area between the lorenz curve and the diagonal in the lorenz curve diagram, the"
Post a Comment