36 enzyme reaction coordinate diagram
This video contains detailed explanations of reaction coordinate diagram with outstanding examples in a very simple way.
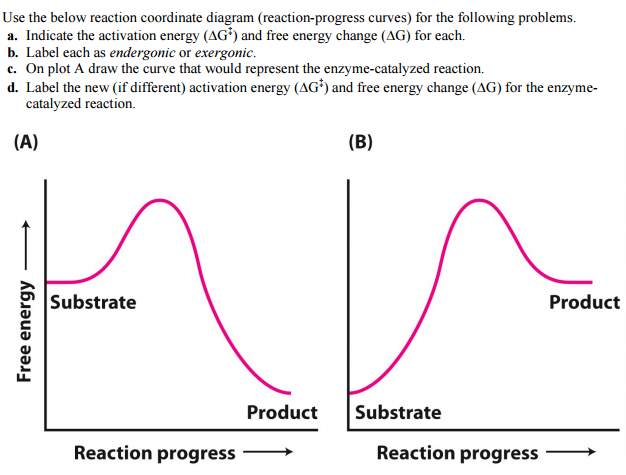
1i. Draw an energy vs reaction coordinate diagram to illustrate a reaction in which the energy of the products is greater than the energy of the reactants. Label all quantities as per Fig. 1. See diagram (3) in sample exercise 14.10 on pg 595 of Brown and LeMay, 11th ed.
Transcribed image text: Use the reaction coordinate diagram of an enzyme catalyzed reaction shown below to answer Questions 5 through 10 From this diagram you can conclude: (A) The forward reaction is endergonic. (B) The forward reaction is exothermic. (C) The forward reaction is endothermic. (D) The forward reaction is at equilibrium.
Enzyme reaction coordinate diagram
Enzymes as biological catalysts, activation energy, the active site, and environmental effects on enzyme activity.
Professor Patricia Shapley, University of Illinois, 2012
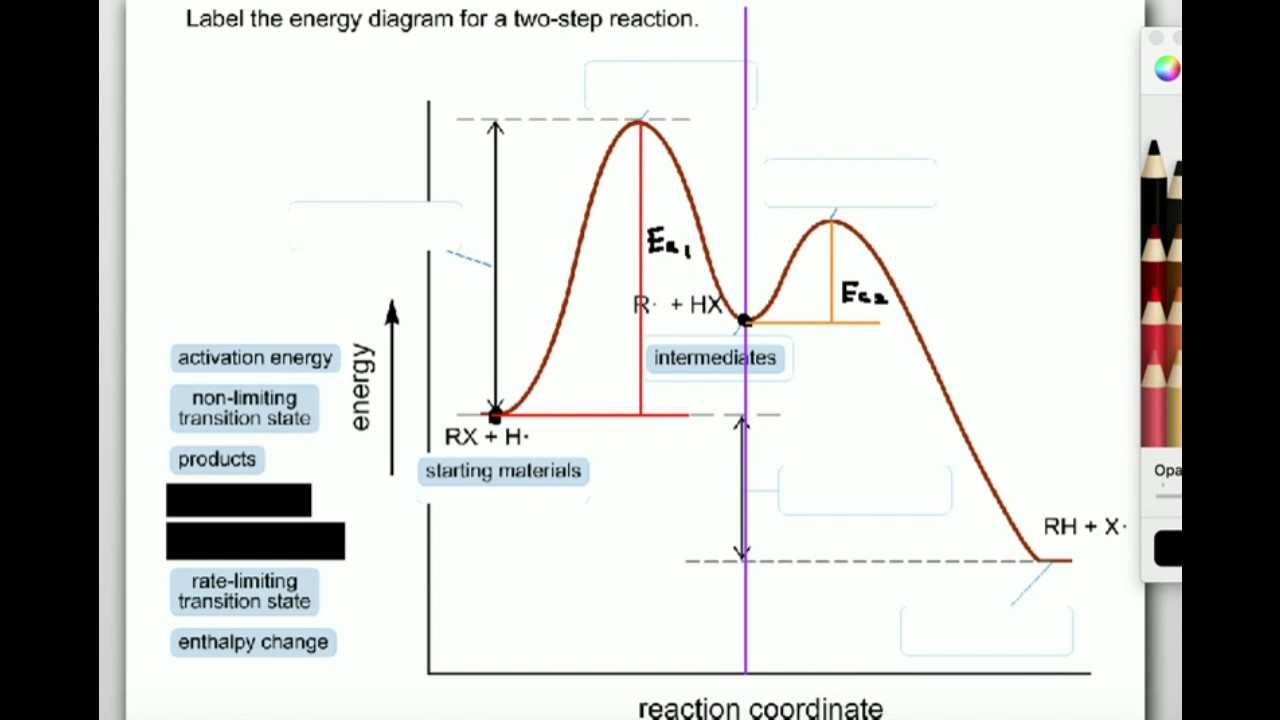
12) Which of the following is seen in a reaction coordinate diagram for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction that uses covalent catalysis? A) an intermediate B) two distinct transition states C) reactants that are lower in energy than an intermediate D) products that are lower in energy than an intermediate E) all of the above
Enzyme reaction coordinate diagram.
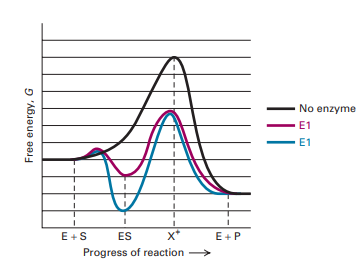
b. Enzymes can also increase the effective local concentration of reacting species by directing reacting groups toward an optimal geometry in a process termed orbital steering. c. Enzymes can promote desolvation. 3. The reaction coordinate diagram for an enzyme catalyzed reaction contains an additional step representing substrate binding.
Reaction coordinate diagrams show the energetic consequences of complementarity to substrate versus complementarity to transition state. The term ΔGM represents the energy contributed by the magnetic interactions between the stick and stickase. When the enzyme is complementary to the substrate, ...
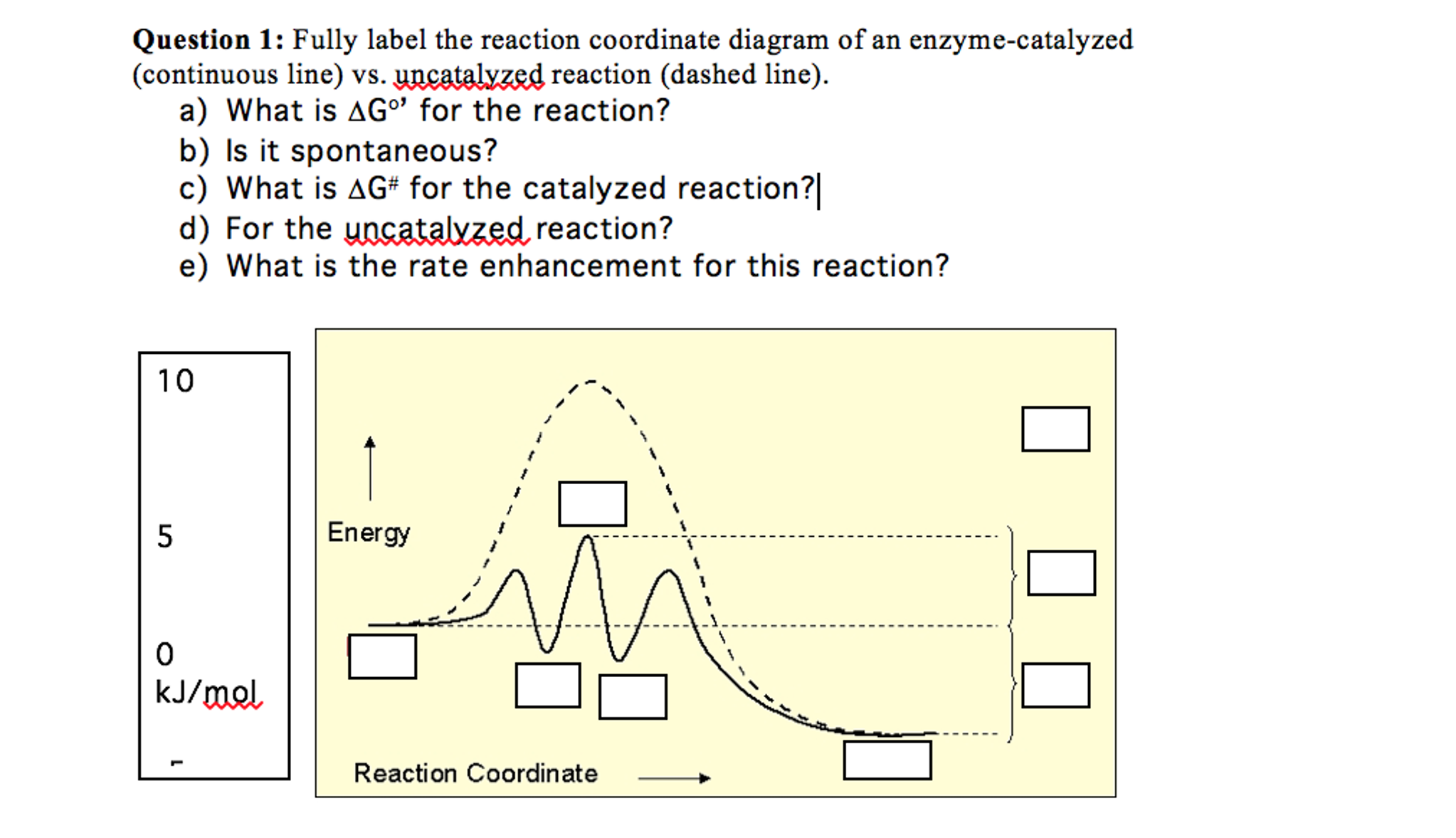
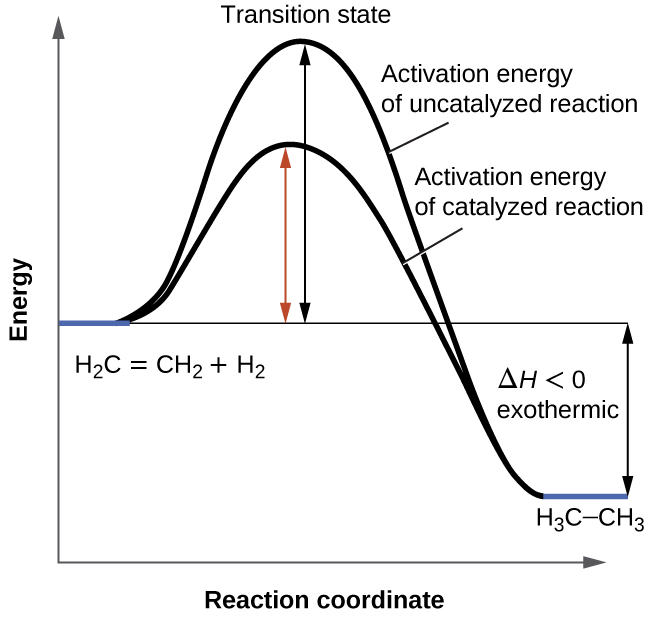
A comparison of the reaction coordinate diagrams (also known as energy diagrams) for catalyzed and uncatalyzed alkene hydrogenation is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1. This graph compares the reaction coordinates for catalyzed and uncatalyzed alkene hydrogenation.
November 8, 2016 - If the formation of the ES complex is thermodynamically favorable, it would be represented on a reaction coordinate diagram at a lower level along the energy axis. The next step, representing the enzyme-bound S-to-P conversion, which we show here as resulting in formation of a enzyme-product ...
Now, we can look at the process of this reaction using something called a reaction coordinate diagram. And here, we'll plot the energy state of our molecules against the progress of the reaction. So essentially, using this graph, we'll follow the energy level of molecule A as it's converted to molecule B. Remember that a molecule's energy level ...
Enzyme kinetics is the study of the rates of enzyme-catalysed chemical reactions.In enzyme kinetics, the reaction rate is measured and the effects of varying the conditions of the reaction are investigated. Studying an enzyme's kinetics in this way can reveal the catalytic mechanism of this enzyme, its role in metabolism, how its activity is controlled, and how a drug or a modifier (inhibitor ...
September 4, 2017 - Cookies are disabled for this browser. Wiley Online Library requires cookies for authentication and use of other site features; therefore, cookies must be enabled to browse the site. Detailed information on how Wiley uses cookies can be found in our Privacy Policy · Your password has been changed
Enzymes have high substrate specificity, and can even show regiospecificity that leads to the generation of stereospecific products. Figure 7.1 Effect of an enzyme on reducint the activation energy required to start a reaction where (a) is uncatalyzed and (b) is an enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Figure from Peter K. Robinson.
A reaction coordinate diagram comparing an uncatalyzed reaction with an enzyme-catalyzed reaction can directly illustrate that the enzyme _____, but will not directly illustrate that the enzyme _____. 1. stabilizes the transition state; orients the substrates appropriately for the reaction to occur
Reaction Coordinate Diagram. ... transition state of the reaction - Enzymes bind transition states better than substrates - Stronger/additional interactions with the transition ...
March 25, 2021 - Reaction coordinate of an exothermic reaction with and without an enzyme. The enzyme reduced the EA to facilitate the likelihood that the reaction occurs. This catabolic reaction breaks complex things down, thus increasing entropy and releasing energy into the system.
This course is a short introduction to important topics in biophysics. The course is structured as a series of self-contained seminars; each seminar is devoted to a particular topic in biophysics, or to a topic in biology as seen through the eyes of a physicist · For those parts of the course ...
Export articles to Mendeley · Get article recommendations from ACS based on references in your Mendeley library
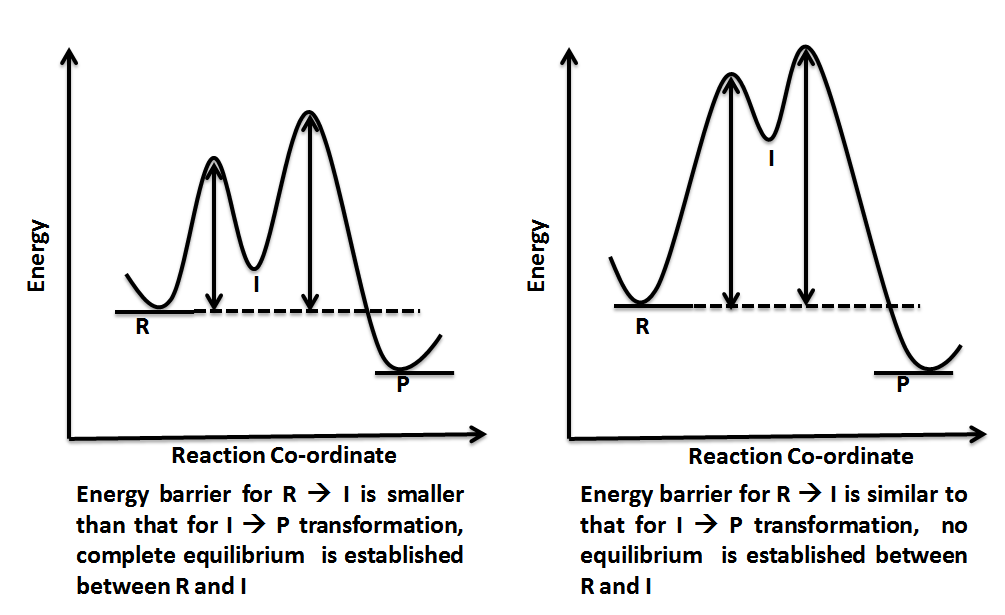
Reaction coordinate diagrams. The intrinsic reaction coordinate (IRC), derived from the potential energy surface, is a parametric curve that connects two energy minima in the direction that traverses the minimum energy barrier (or shallowest ascent) passing through one or more saddle point(s). However, in reality if reacting species attains enough energy it may deviate from the IRC to some extent.
Reaction coordinate diagrams clearly show that the energy of an enzyme bound to a transition state is higher than the energies of the E + S, E + P, and ES that occur along the same reaction coordinate. The energy of an enzyme bound to a transition state analog would lie _____ in the diagram. a. above the E + S but below the transition state
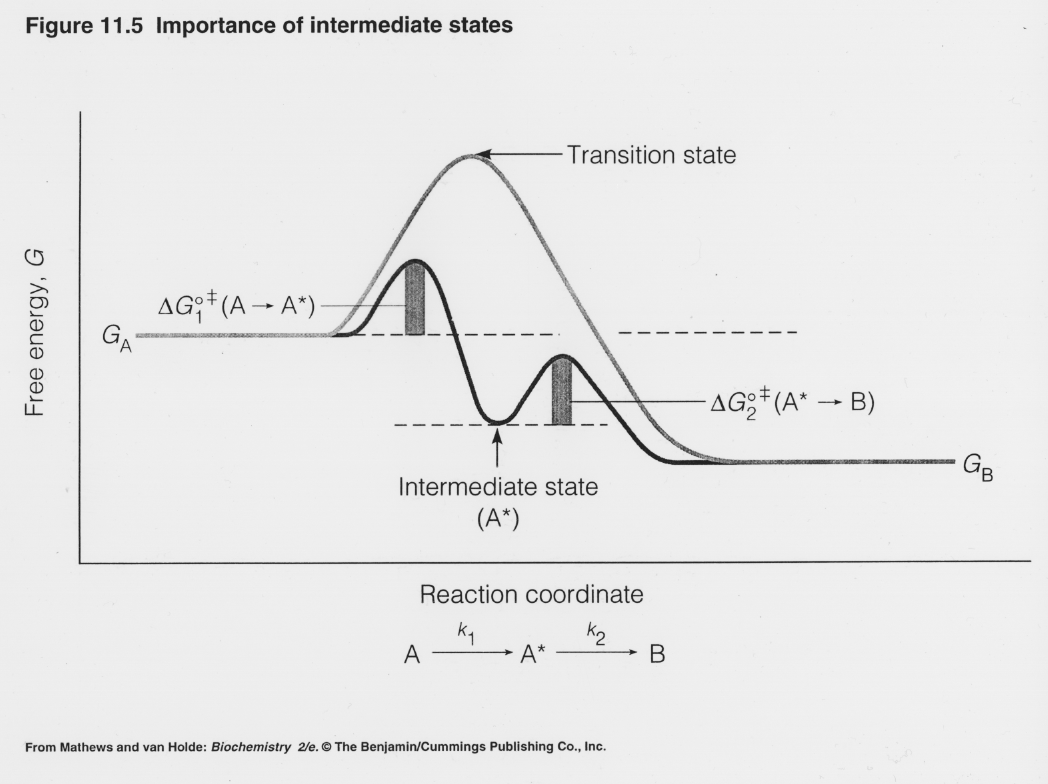
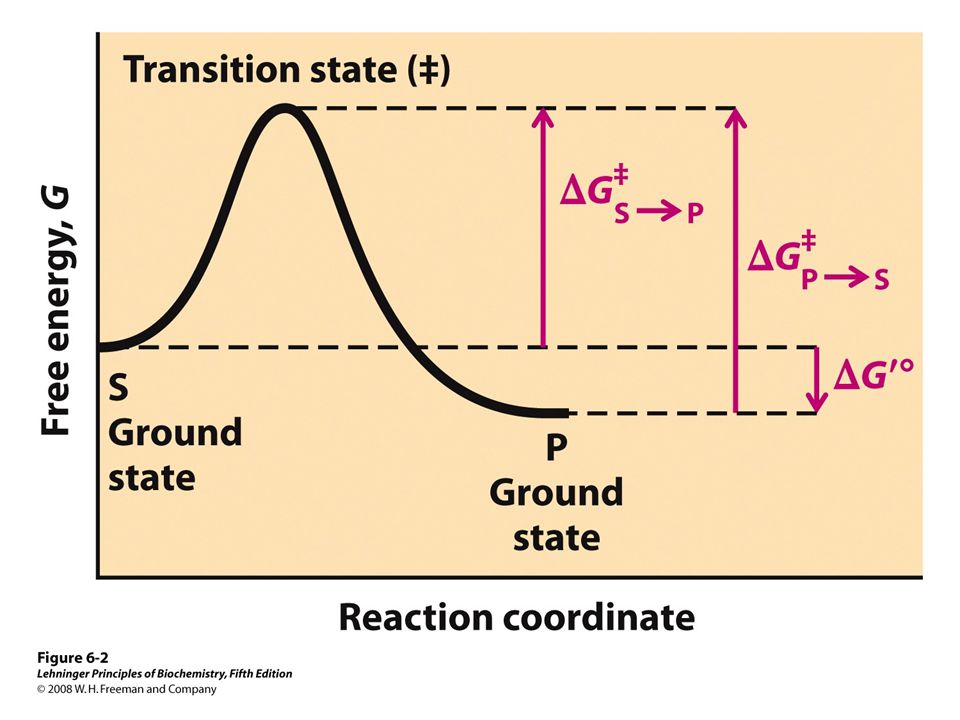
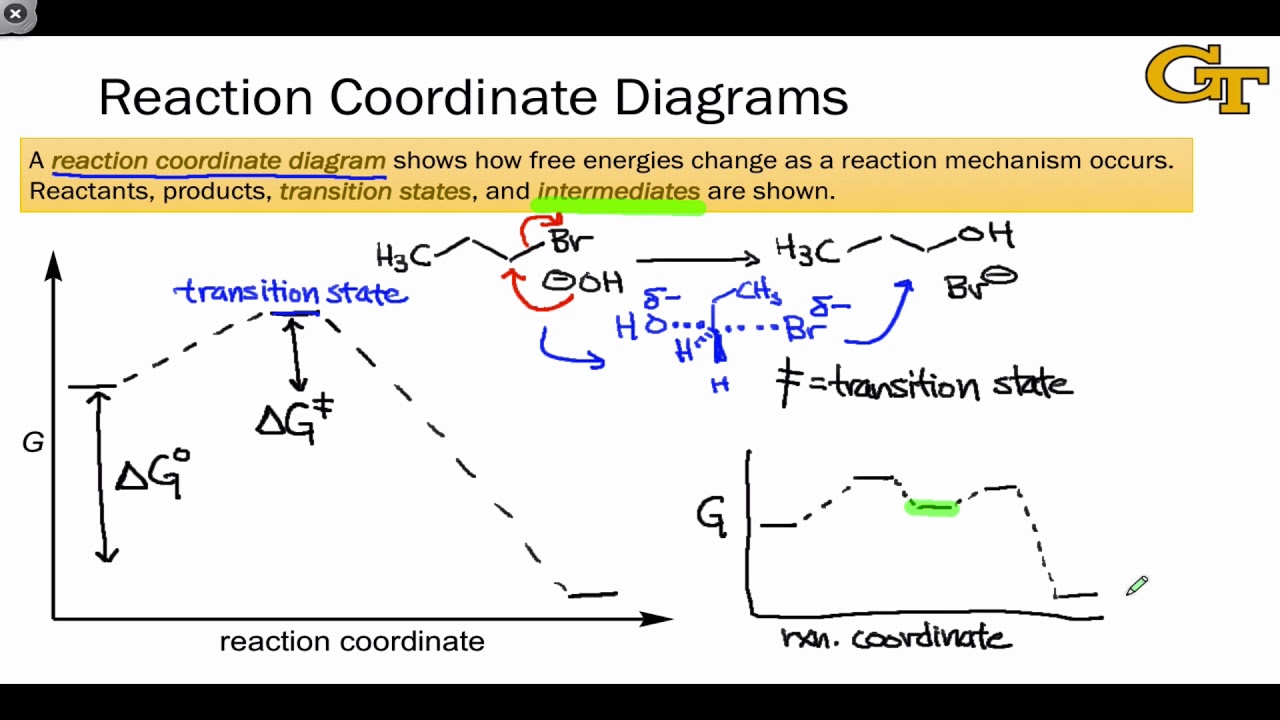
Fig. 1 Reaction coordinate diagram for a chemical reaction Fig. 2 Reaction coordinate diagram comparing enzyme-catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions. 3 of 16 As shown in Fig. 1, from starting material to product, the highest point in terms of energy is called transition
The reaction coordinate diagram shown to the left is for the mitochondrial enzyme ATP synthase. Use this diagram to answers Questions 1 - 4 From this diagram you can conclude: (A) ATP synthesis is endergonic. (B) The reaction is at equilibrium. (C) ATP synthesis is exergonic. (D) ATP synthesis is endothermic. (E) ATP synthesis is exothermic.
Export articles to Mendeley · Get article recommendations from ACS based on references in your Mendeley library
Transition state diagram/reaction coordinate diagram: Plot of free energy versus the reaction coordinate. Transition State Diagram (Symetrical)! Substrate! Product! Transition ... Enzymes catalyze reactions by preferentially binding the transition state An enzyme may binds the transition state of the
by JC Aledo · 2003 · Cited by 20 — Energy diagrams for enzyme-catalyzed reactions: Concepts and ... decrease in the Gibbs energy when moving through the reaction coordinate, ...
General structure of a reaction coordinate diagram, including transition states and intermediates. Overall free energy change and activation energy. Definiti...
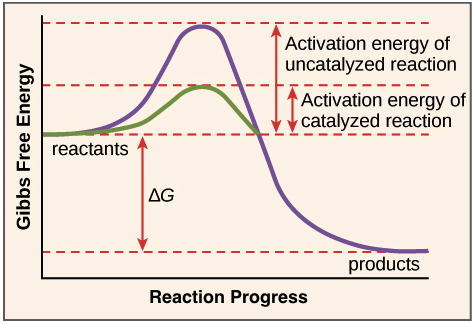
A reaction coordinate diagram is a graph that plots energy versus reaction progress. The amount of energy that needs to be added is called the activation energy, which is the point where the line ...
Enzymes work by binding to reactant molecules and holding them in such a way that the chemical bond-breaking and bond-forming processes take place more readily. Reaction coordinate diagram showing the course of a reaction with and without a catalyst. With the catalyst, the activation energy is lower than without.
August 11, 2020 - Catalysts affect the rate of a chemical reaction by altering its mechanism to provide a lower activation energy. Catalysts can be homogenous (in the same phase as the reactants) or heterogeneous (a …
Biochem1 Lecture #8 Ch5 2014.ppt Biochem 1 2014 Study Guide Chapter5ch 13 and 14 Study Guide Protein Sorting Biochem 1 2014 Continue reading Chapter 5 · How is the JAK-STAT pathway unique? Continue reading Chapter 12 question
... a simple enzyme-catalyzed reaction scheme (Figure 4), the reaction coordinate diagram shows that in order for the enzyme to catalyze the reaction, DG ETS ...
Export articles to Mendeley · Get article recommendations from ACS based on references in your Mendeley library
Reaction Coordinate Diagram We've already seen that the rate of a chemical reaction depends on the height of the activation barrier in the reaction coordinate diagram.Consider the reaction below where reactants A and B combine to form the product C.
Introduction - Enzyme Characteristics: The basic mechanism by which enzymes catalyze chemical reactions begins with the binding of the substrate (or substrates) to the active site on the enzyme. The active site is the specific region of the enzyme which combines with the substrate. The binding of the substrate to the enzyme causes changes in the distribution of electrons in the chemical bonds ...
There are over 2000 known enzymes, each of which is involved with one specific chemical reaction. Enzymes are substrate specific. The enzyme peptidase (which breaks peptide bonds in proteins) will not work on starch (which is broken down by human-produced amylase in the mouth). Enzymes are proteins.
Figure 1 Gibbs free energy reaction coordinate profile for an enzyme catalysed reaction ( AG~) compared to an uncatalysed reaction ( AG~,c) depicted in some textbooks enzyme action, as well as in the thermodynamic param- eters of enzyme-substrate complex formation, and the chemical steps of the enzyme catalysed reactions are completely ignored.
Volume 24 February 15, 2013 Reaction coordinate diagrams | 435 chain. Thus the reaction coordinate diagram (Figure 3C) reflects a pathway that proceeds via four transition states, two tetrahedral in-termediates and a covalently bonded acyl enzyme intermediate. In this reaction, the overall ΔG is negative and the formation of the first
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website · If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked
July 24, 2007 - The transition path sampling method previously applied in our group to the reaction catalyzed by lactate dehydrogenase was used to generate a transition path ensemble for this reaction. Based on analysis of the reactive trajectories generated, important residues behind the active site were ...
Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for this reaction as above but add the activation energy, E a, for the catalyzed reaction on the appropriate curve in this diagram and label it. This is a bit more subtle since .Types of catalysts (article) | Kinetics | Khan AcademySection The Rate of a Reaction
And looking at a reaction coordinate diagram you notice that enzymes do this by lowering the reaction's activation energy. Also, before we talk about covalently modified enzymes, I want to remind you that not all enzymes are proteins. And often, when we think of enzymes we think of proteins, which are amino acid polymers with primary, secondary ...
4 Enzyme Kinetics 75 G Reaction coordinate Transition state ΔG 1 ‡ ΔG 1 ‡' ΔG –1 ‡' ΔG –1 ‡ ΔG° G A G P Initial state Final state Fig. 4.2 A free energy (G) diagram for a simple reversible exothermic reaction A↔P(solid and broken lines).
When the S P reaction is catalyzed by an enzyme, the ES and EP complexes are intermediates (Eqn 8-1); they occupy valleys in the reaction coordinate diagram (.Fig. 8-4). When several steps occur in a reaction, the overall rate is determined by the step (or steps) with the highest activation energy; this is called the rate-limiting step.
February 15, 2013 - To provide a familiar biochemical context for discussing these subcellular force generators, I first review the application of reaction coordinate diagrams to the mechanisms of simple chemical and enzyme-catalyzed reactions. My description of reaction coordinate diagrams of motors and polymer ...
In chemistry, a reaction coordinate is an abstract one-dimensional coordinate which represents progress along a reaction pathway. It is usually a geometric parameter that changes during the conversion of one or more molecular entities. In molecular dynamics simulations, a reaction coordinate ...
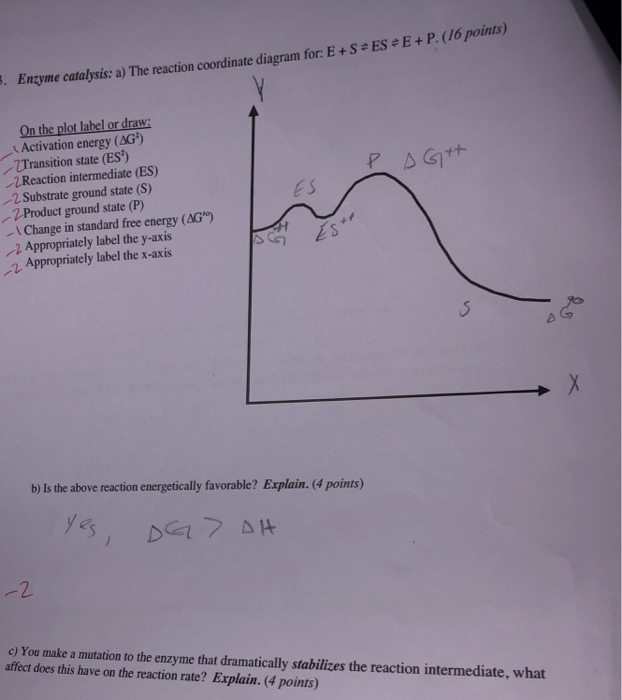
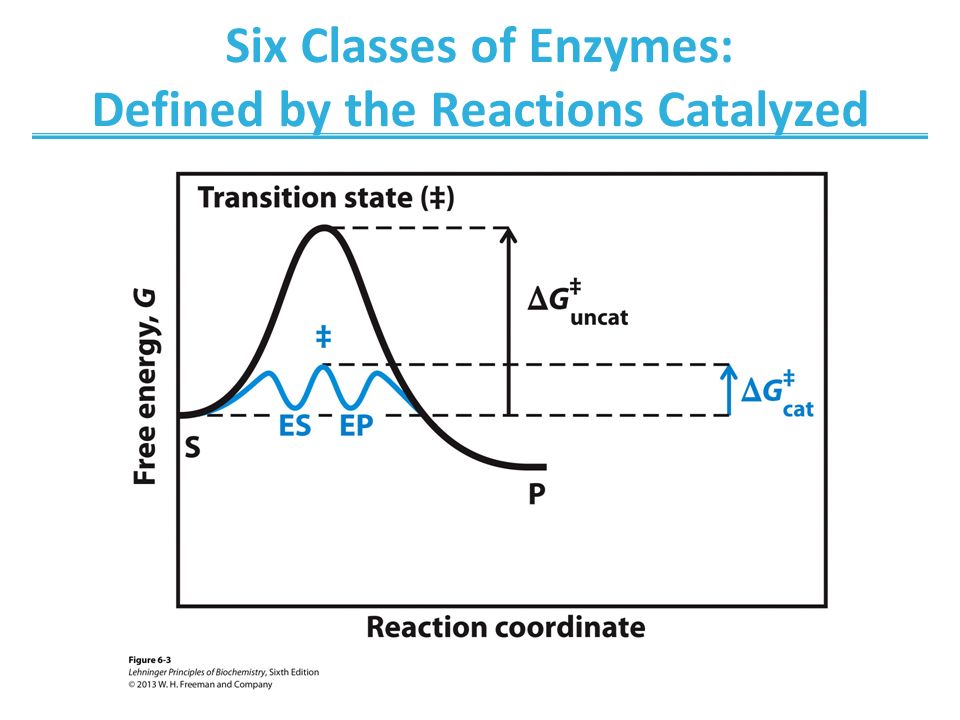


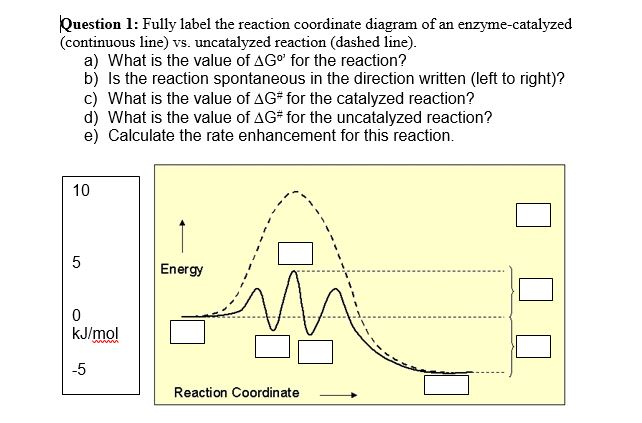

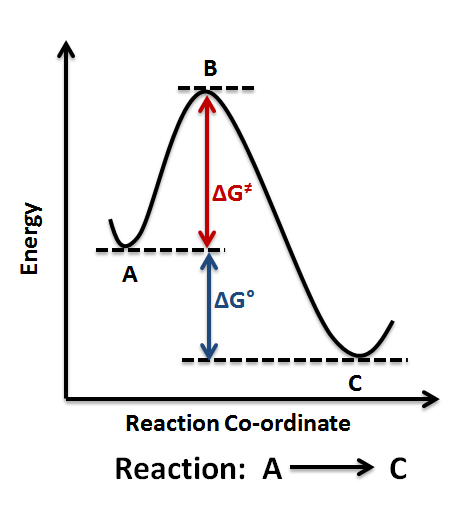












0 Response to "36 enzyme reaction coordinate diagram"
Post a Comment