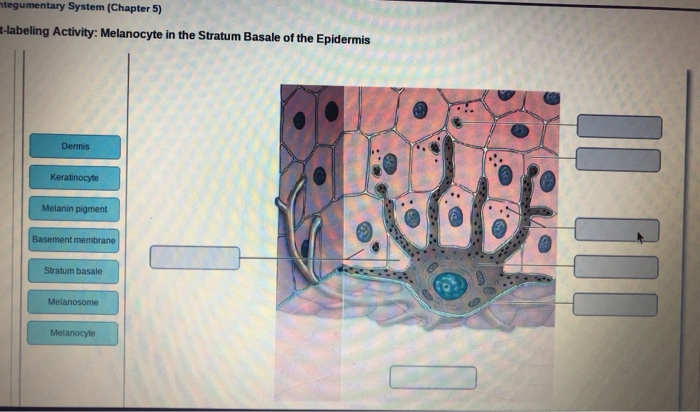
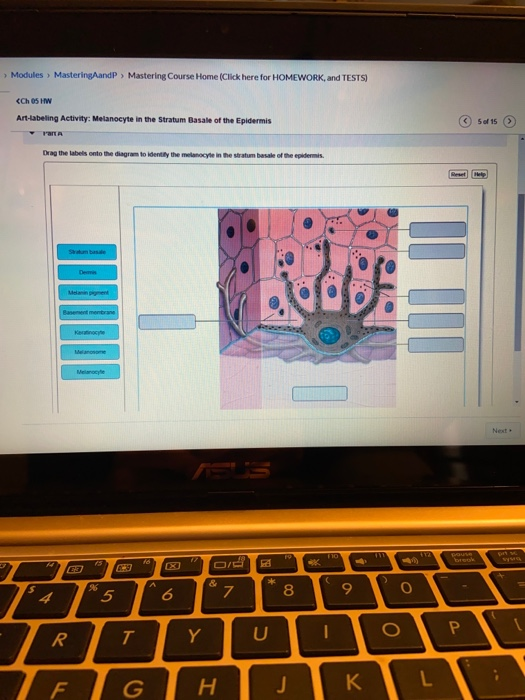
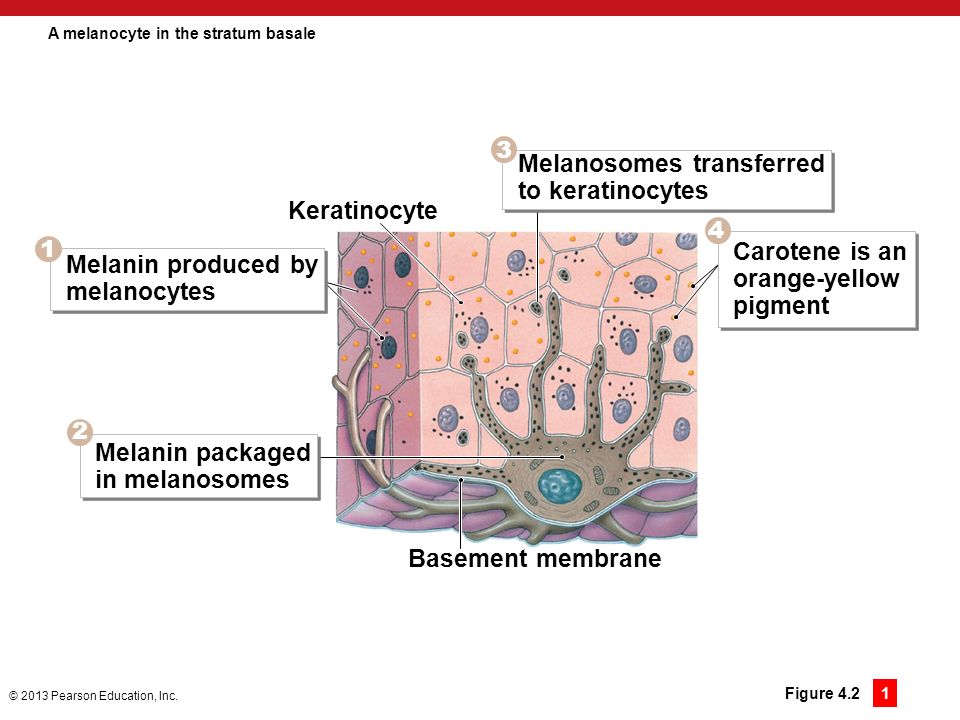
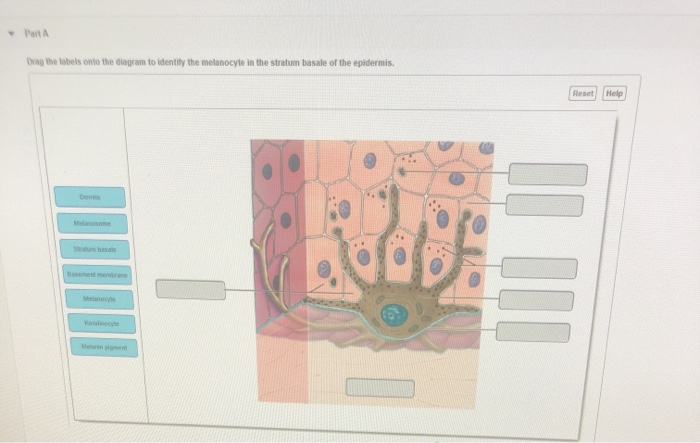
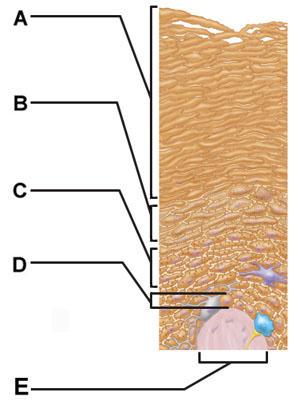
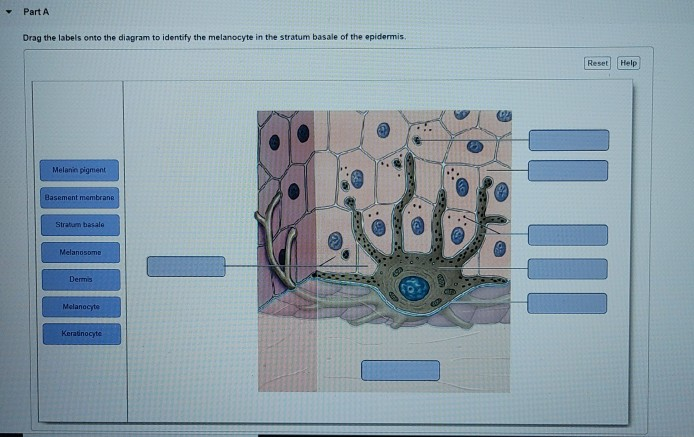
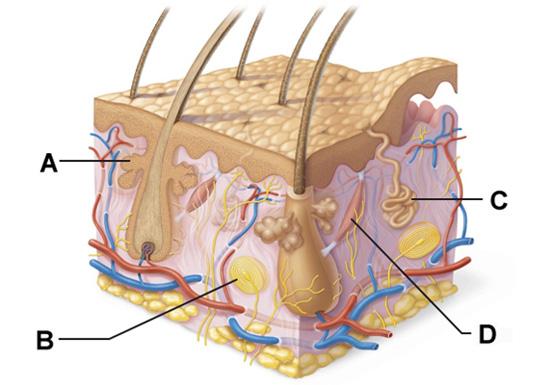
37 drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the melanocyte in the stratum basale of the epidermis.
Skin Diagram Labeling . 1. Label the diagram with the . letters. below according to the structure/area they describe. You may label with a line or put the label directly onto the area described. Be as precise as possible. If you are worried about the precision of your label add a word after to explain exactly where your label should be About ...
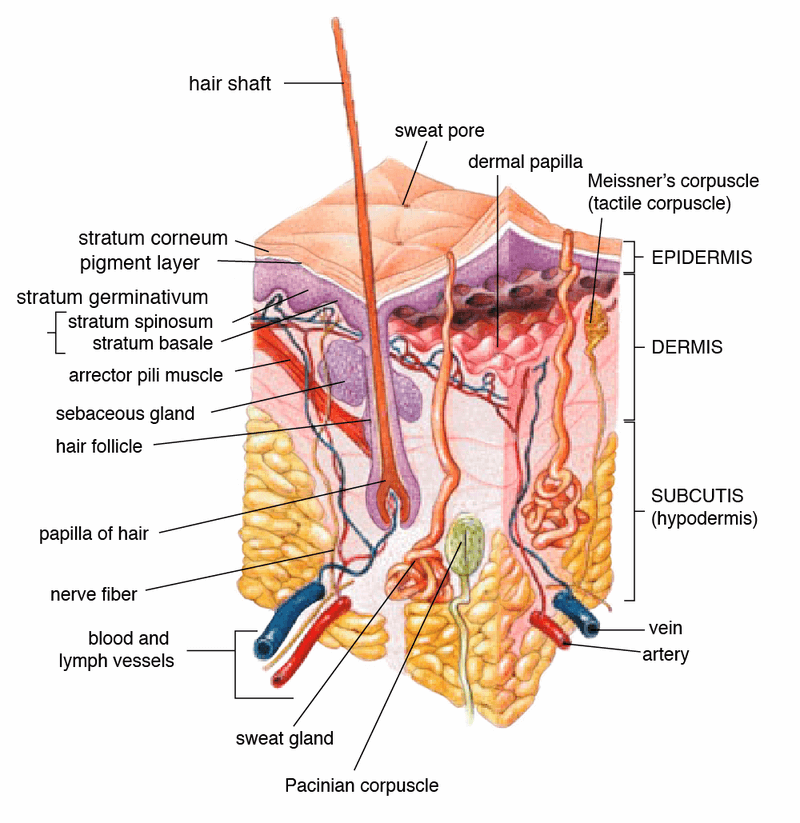
The 5 Layers of Your Skin. Your skin is the largest organ of your body. It is comprised of three main layers: the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis. The epidermis is the topmost layer of skin - the one you can see and feel on the surface. It contains four to five layers (depending on body location), each with an important role.
Module 5.2: The epidermis Epidermal layers overview Entire epidermis lacks blood vessels •Cells get oxygen and nutrients from capillaries in the dermis •Cells with highest metabolic demand are closest to the dermis •Takes about 7-10 days for cells to move from the deepest stratum to the most superficial layer

Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the melanocyte in the stratum basale of the epidermis.
A. Tactile cells anchor the skin to the body. B. Keratinocytes produce a fibrous protein to protect the epidermis. C. Melanin provides protection against ultraviolet (UV) radiation. D. Langerhans cells activate the immune system. A. Tactile cells anchor the skin to the body. The skin consists of two main regions.
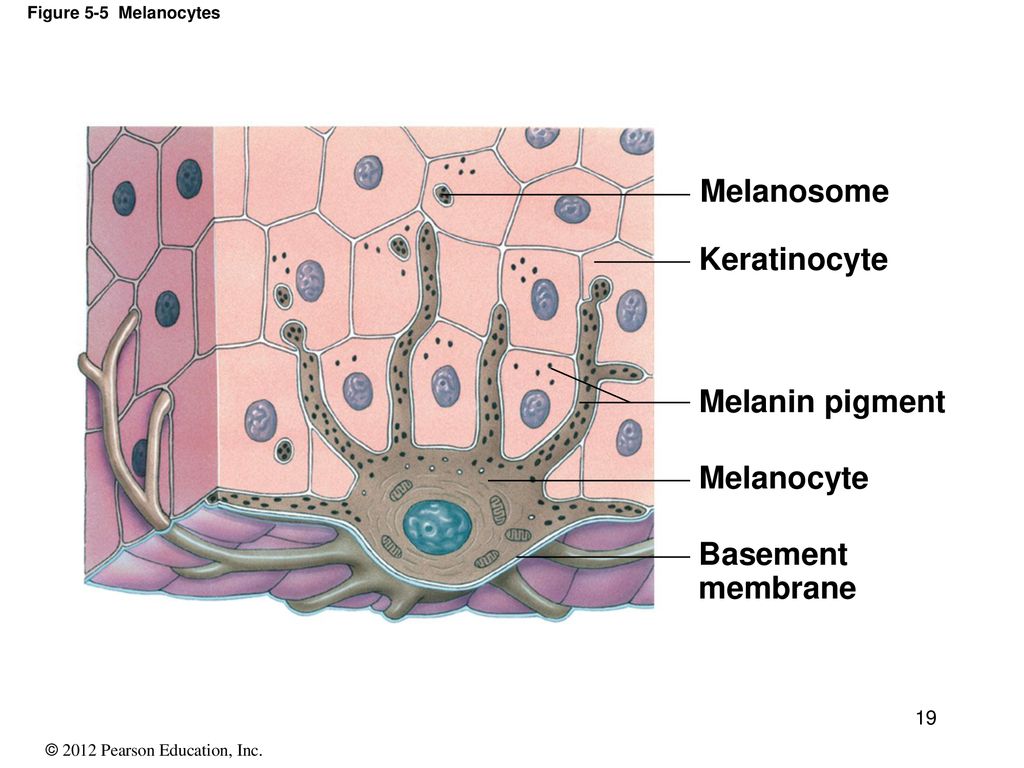
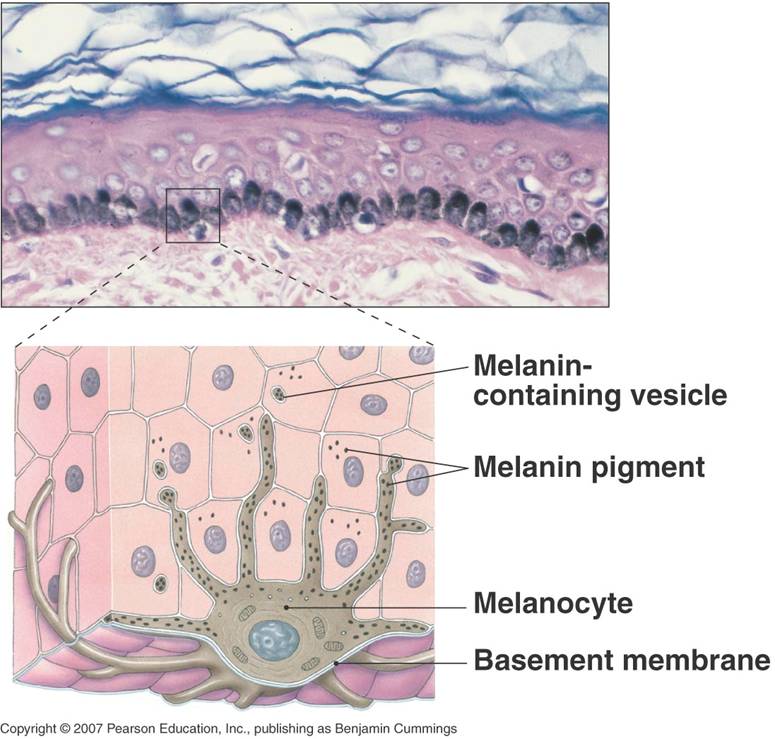
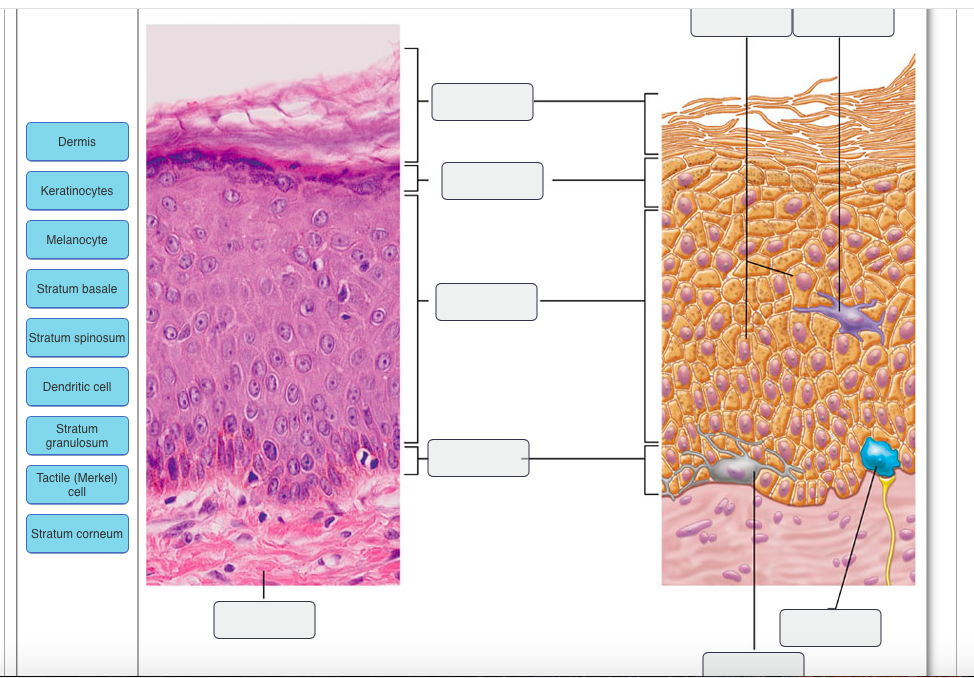
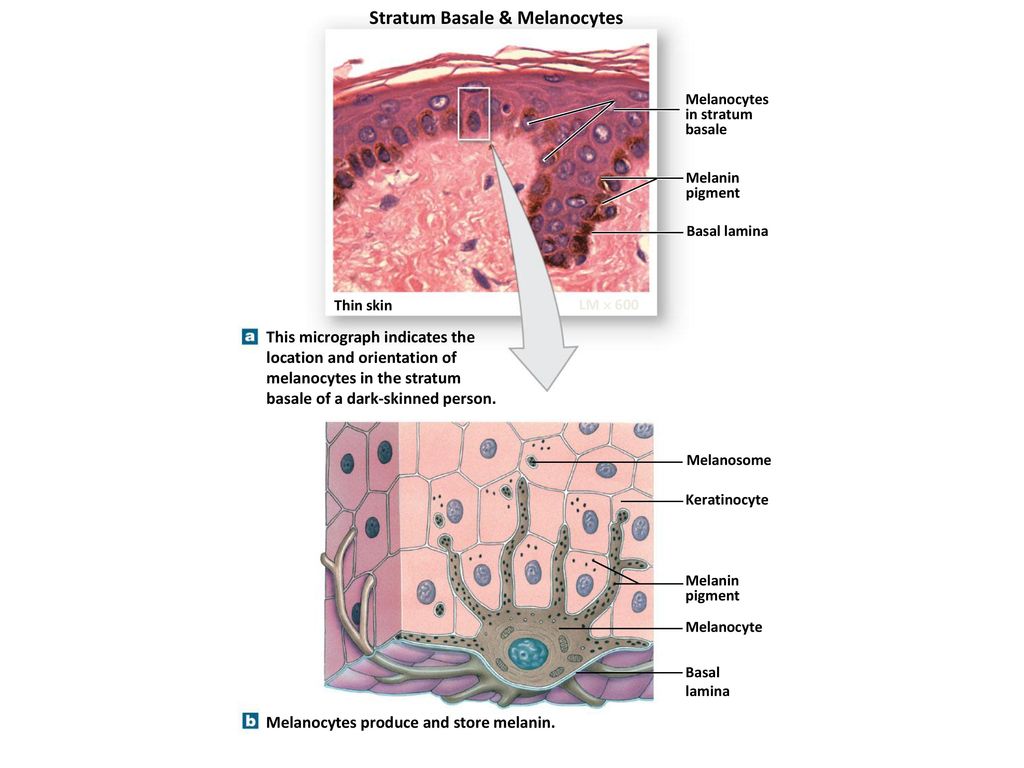
Stratum Basale. The stratum basale (also called the stratum germinativum) is the deepest epidermal layer and attaches the epidermis to the basal lamina, below which lie the layers of the dermis. The cells in the stratum basale bond to the dermis via intertwining collagen fibers, referred to as the basement membrane. A finger-like projection, or fold, known as the dermal papilla (plural ...
Stratum Basale. The stratum basale (also called the stratum germinativum) is the deepest epidermal layer and attaches the epidermis to the basal lamina, below which lie the layers of the dermis. The cells in the stratum basale bond to the dermis via intertwining collagen fibers, referred to as the basement membrane. A finger-like projection, or fold, known as the dermal papilla (plural ...
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the melanocyte in the stratum basale of the epidermis..
Start studying Art-labeling Activity: Melanocyte in the Stratum Basale of the Epidermis. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Keratinocytes reside in this layer of the skin, sandwiched between the stratum corneum and stratum basale. 5. The foundation of the epidermis that contains constantly dividing stem cells.
stratum basale d. stratum lucidum g. reticular layer b. stratum corneum e. stratum spinosum h. epidermis as a whole c. stratum granulosum f. papillary layer i. dermis as a whole d; stratum lucidum 1. layer of translucent cells in thick skin containing dead keratinocytes b, d; stratum corneum and lucidum 2. two layers containing dead cells
Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
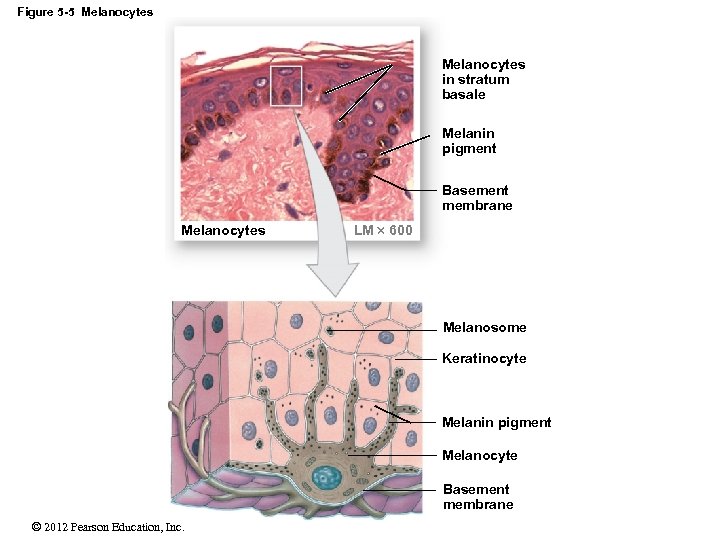
Label the components of the in tegumentary system. Part A Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the components of the in tegumentary system. ANSWER: Help Reset Stratum basale Dermis Basement membrane Melanocyte Melan in pigment Kerat in ocyte Melanosome Drag the labels to the table to describe the layers of the sk in. Drag the ...
Transcribed image text: Modules MasteringAandP Mastering Course Home (Click here for HOMEWORK, and TESTS) Ch 05 HW Art-labeling Activity: Melanocyte in the Stratum Basale of the Epidermis 5 of 15 rart A Drag the labels onto the diagram to identity the melanocyle in the stratum basale of the epidermis Reset Helo Statum basae Demis Melann pgment Basement mentrane Keratinocye Melanosome Melaocyle ...
Drag each label to the type of gland it describes. Drag each label to the type of gland it describes.. Label the structures of the hair follicle. Drag each label to the appropriate location on the diagram. Place the following events in the order they occur as a non steroid hormone activates its target cell. Expert answer 100 5 ratings.
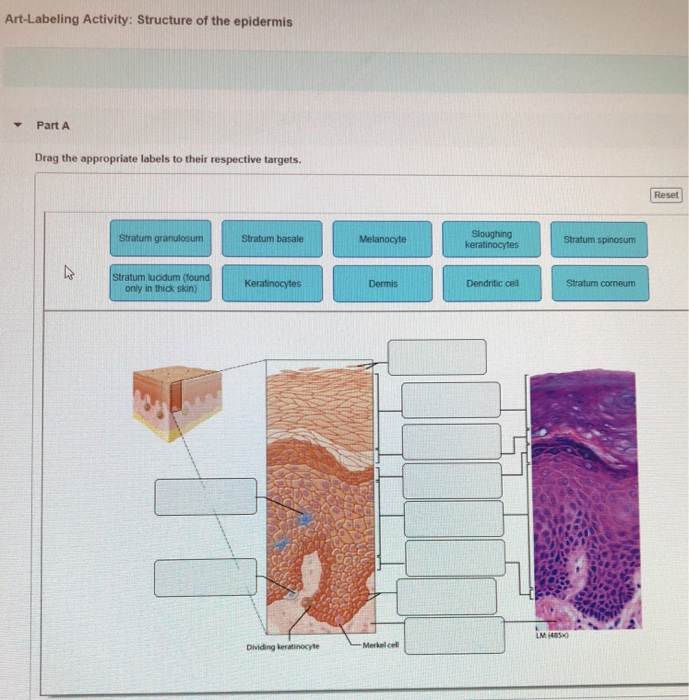
Question: Part A Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the layers of the epidermis. Reset stratum basale stratum granulosum stratum lucidum stratum corneum UM straturn spinosum . This problem has been solved! See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading.
Identify the epidermis, dermis and determine the type of tissue in each ... and label the dermal papilla and dermis •Name the Layers of skin and label the ... • SC: Stratum corneum SS: Stratum spinosum • SL: Stratum lucidum SB: Stratum basale • SG: Stratum granulosum SG. Identify the thick and thin skin. Can you name the layers ...
Anatomy of the Skin. The skin is a vital organ that covers the entire outside of the body, forming a protective barrier against pathogens and injuries from the environment. The skin is the body's largest organ; covering the entire outside of the body, it is about 2 mm thick and weighs approximately six pounds.
To learn the components of the integumentary system. Label the components of the integumentary system. Part A Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the components of the integumentary system. ANSWER: Help Reset Stratum basale Dermis Basement membrane Melanocyte Melanin pigment Keratinocyte Melanosome
Drag each label into the appropriate position to identify which chemical classification it describes. In meat we know it as gristle. Label the microscopic features of the pancreas. Drag each label to the cell type it describes. Place the following events in the order they occur as a non steroid hormone activates its target cell.
Figure 5.2 The main structural features of the skin epidermis. MelanocyteDesmosomes Melanin granule Tactile (Merkel) cell Sensory nerve ending Epidermal dendritic cell Dermis Dermis Keratinocytes (b) (a) Stratum corneum Stratum granulosum Stratum spinosum Stratum basale
Drag and drop onto image questions require students to drag and drop an image or text onto a background image to a preset location. You will define Drop zones which determine whe the r or not a student is correct. For example, a question might ask a student to drag and drop labels onto a diagram to illustrate a process.
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the basic structures of the epidermis-dermis junction. look at pic Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the melanocyte in the stratum basale of the epidermis.
Skin is the largest organ in the body and covers the body's entire external surface. It is made up of three layers, the epidermis, dermis, and the hypodermis, all three of which vary significantly in their anatomy and function. The skin's structure is made up of an intricate network which serves as the body's initial barrier against pathogens, UV light, and chemicals, and mechanical injury.
Label the melanocyte in the stratum basale of the epidermis. Part A Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the melanocyte in the stratum basale of the epidermis. ANSWER: HelpReset Blood vessels Papilla Connective tissue Keratinocytes 4-5 Distinct layers Water resistant Stratified squamous epithelium Merkel cellsDermis Epidermis
Epidermis. The epidermis is composed of keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium. It is made of four or five layers of epithelial cells, depending on its location in the body. It is avascular.. Thin skin has four layers of cells. From deep to superficial, these layers are the stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, and stratum corneum.Most of the skin can be classified as thin ...
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the tissues and structures. Reset Help bone ne Group 2 Group 2 Group 2 Group 2 Group 2 chondrocyte Group Group EL.UB. Best of Homework - Classification of Tissues Exercise 6 Review Sheet Art-labeling Activity 4 Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the tissues and structures.
Epidermis is a superficial layer of stratified epithelium which develops from ectoderm and acts as a physical and chemical barrier between the interior body and exterior environment. The multilayered structure which forms the dermoepidermal junction is called basement membrane. The epidermis is stratified squamous epithelium without any blood vessels.
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that make up the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water released from the body into the atmosphere through transepidermal water loss.. The epidermis is composed of multiple layers of flattened cells that overlie a ...
The stratum basale of the epidermis forms dermal ridges (also known as friction ridges) that extend into the dermis, increasing the area of contact between the two regions. Projections from the dermis toward the epidermis, called dermal papillae (singular, papilla), extend between adjacent ridges (Figure 1 and 2).
Label the parts of the neuromuscular junction. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the steps in a reaction both with and with out e... Ren in is an enzyme released by the juxtaglomerular cells of the kidneys in response to low blood pressure caus in g the transformation of angiotens in ogen Er cis golgi cisternae medial golgi cisternae.

















0 Response to "37 drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the melanocyte in the stratum basale of the epidermis."
Post a Comment