37 ray diagram for concave lens
Ray diagram for an object viewed through a concave lens. For an object viewed through a concave. lens, light rays from the top of the object will be refracted. and will diverge. on the other side ... The example "Ray tracing diagram for concave lens" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Physics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park. Ray tracing diagram. Used Solutions.
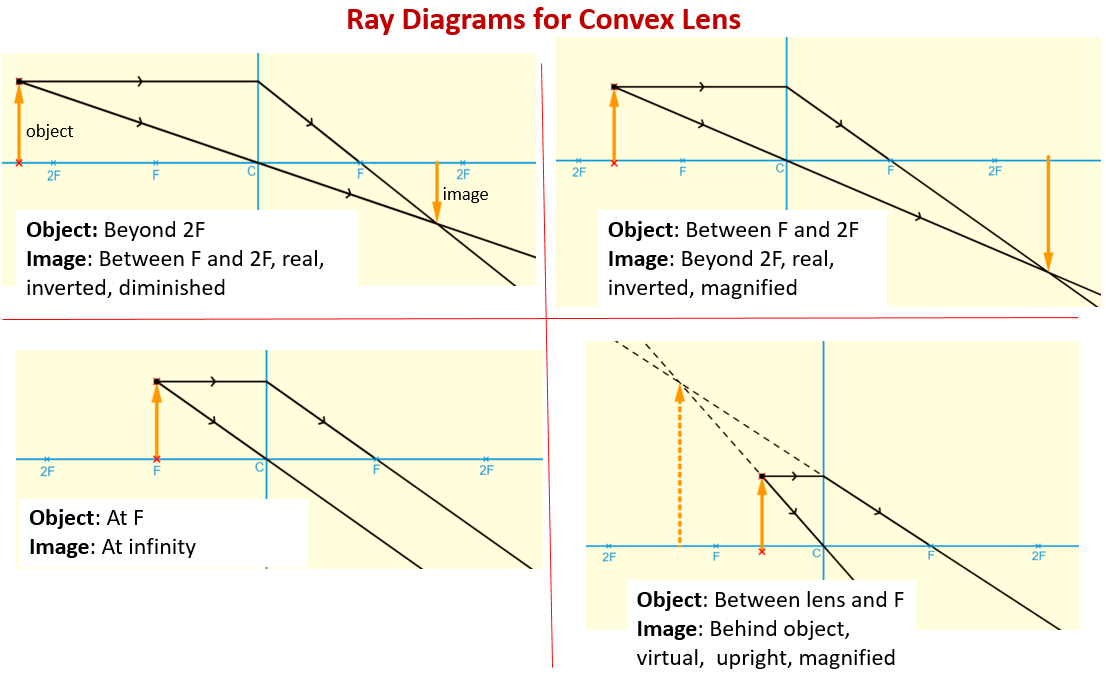
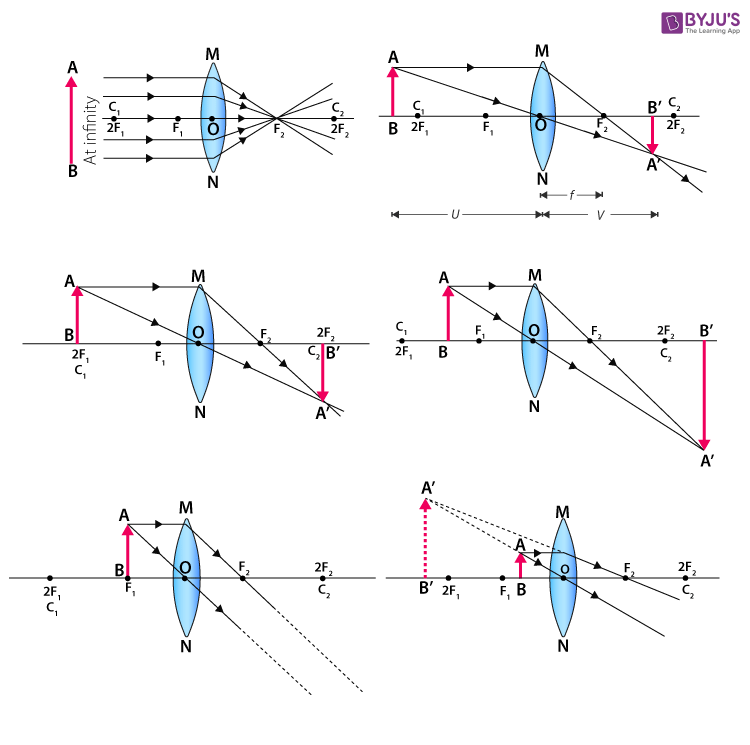
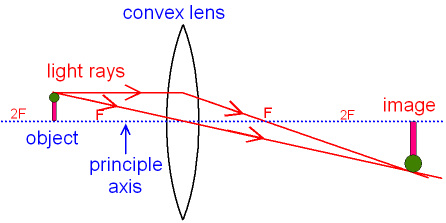
When a ray, passing through focus strikes concave or convex lenses, the reflected ray will pass parallel to the principal axis. Image Formation by Concave and Convex Lenses: Convex Lenses. When an object is placed at infinity, the real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller than that of the object.

Ray diagram for concave lens
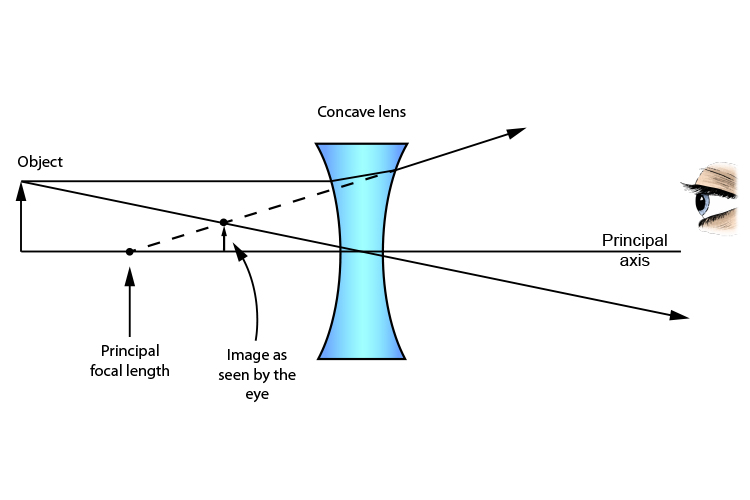
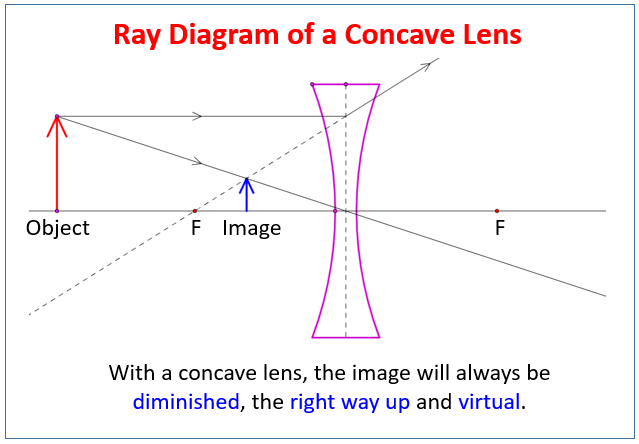
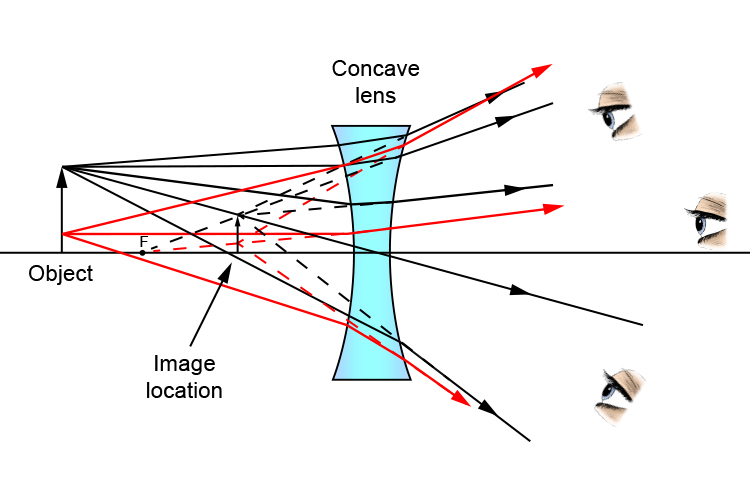
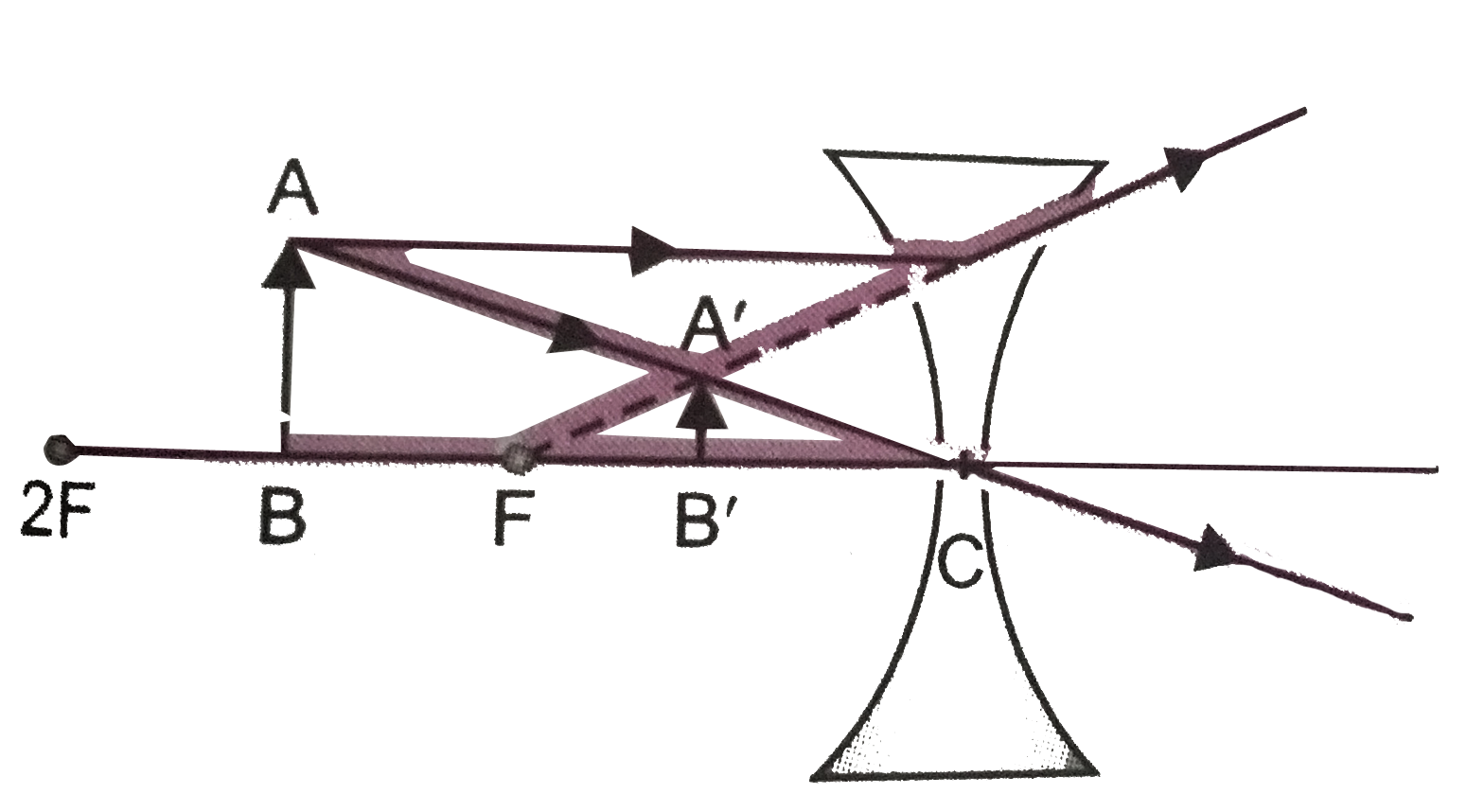
Ray diagrams for diverging (concave) lens. If an object is on one side of the concave lens, the concave lens can form the image of the object. If the position of the object on one side of the concave lens is known, how to draw the image formation of the object? Suppose an object is on the left side of the concave lens as shown in the figure below. A concave lens ray diagram is a simple way of visualising the path that light rays take when passing through a concave lens. To draw a ray diagram you only need to draw two ray lines. This is sometimes referred to as "the two rules of refraction for diverging lenses". With a concave lens, the image will always be diminished, the right way up and virtual. Draw a ray diagram to show how an image is formed by a concave lens. Describe the properties of an image produced by a concave lens. Draw different ray diagrams with the object at different places in relation to the focus and find out where the image appears.
Ray diagram for concave lens. Draw ray diagrams for a concave lens for the situation illustrated. Concave lens: Ray diagrams de > 1 de < </ 6. An object 5cm high (he - Scm) is placed 10cm in front of a converging lens whose focal length is 20cm (a) Find the position and the size of the image. (b) Find the magnification M. c) Find the refractive power of the lens. 7. Ray tracing diagram for concave lens. "In physics, ray tracing is a method for calculating the path of waves or particles through a system with regions of varying propagation velocity, absorption characteristics, and reflecting surfaces. Under these circumstances, wavefronts may bend, change direction, or reflect off surfaces, complicating ... A convex lens is thicker in the middle than it is at the edges. Parallel light rays that enter the lens converge. They come together at a point called the principal focus. In a ray diagram, a ... Concave Mirror Ray Diagram. Concave Mirror Ray Diagram lets us understand that, when an object is placed at infinity, a real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller compared to that of the object. When an object is placed behind the center of curvature, a real image is formed between the center of curvature and focus.
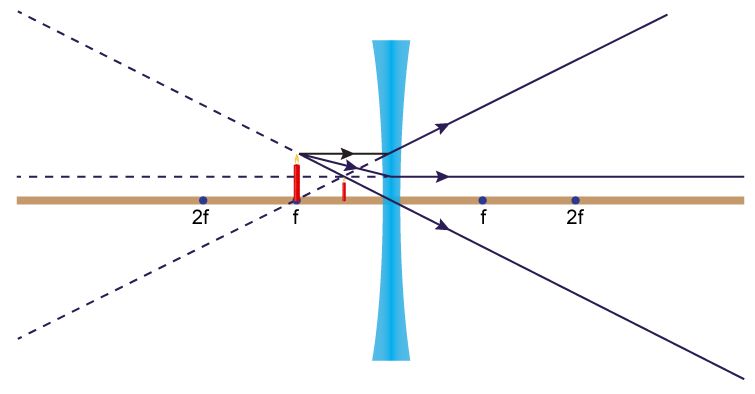
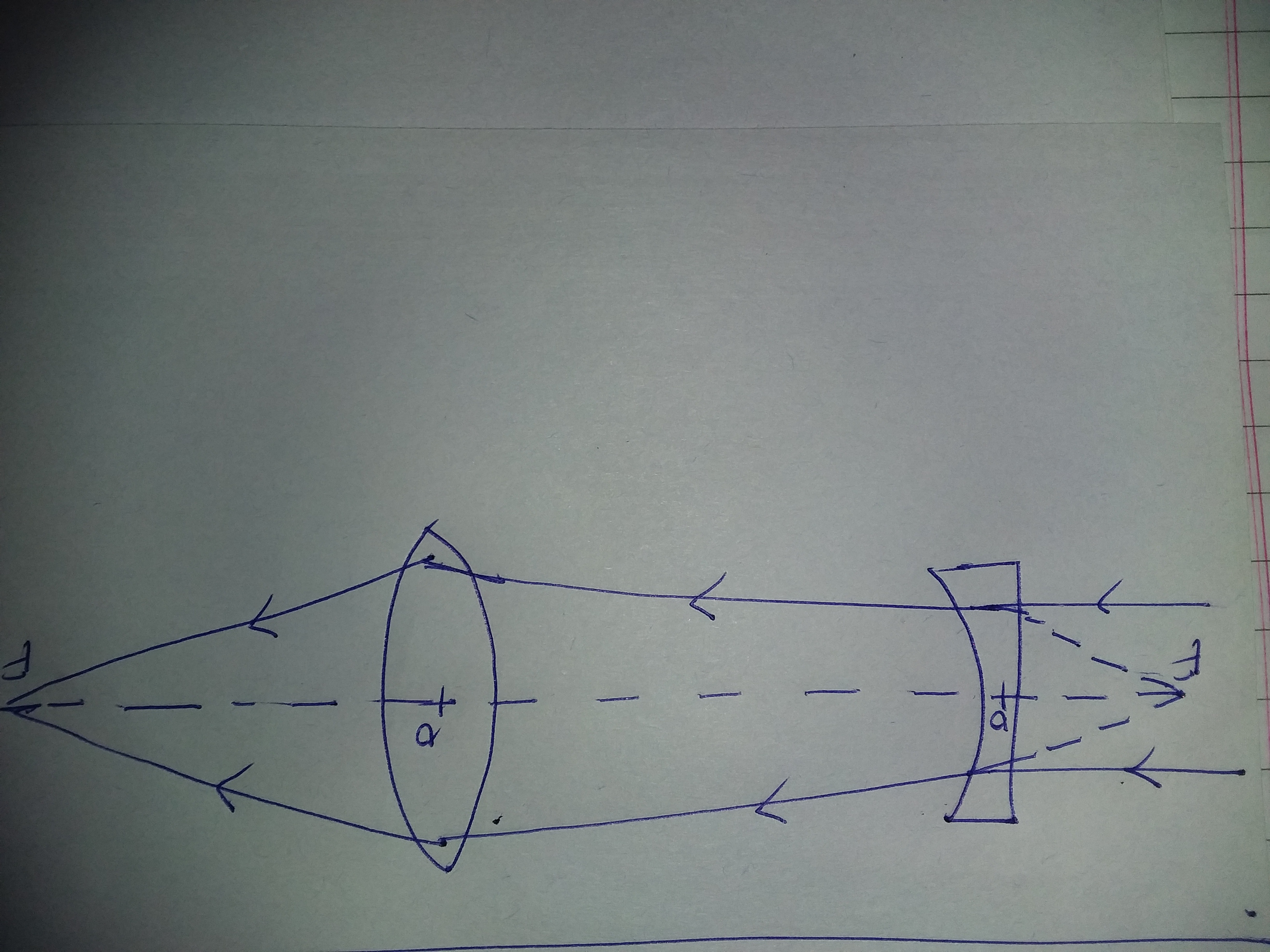
The method is applied to the task of drawing a ray diagram for an object located beyond the center of curvature (C) of a concave mirror. Yet the same method works for drawing a ray diagram for any object location. 1. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw two incident rays traveling towards the mirror. A concave lens is thinner in the middle than it is at the edges. This causes parallel rays to diverge. A concave lens separates but appears to come from a principal focus on the other side of the lens. In the concave lens ray diagram, a concave lens is drawn as a vertical line with inward-facing arrows to indicate the shape of the lens. To create the diagram, a student should pick a point on ... Mirror Ray Tracing. Mirror ray tracing is similar to lens ray tracing in that rays parallel to the optic axis and through the focal point are used. A third useful ray is that through the center of curvature since it is normal to the mirror and retraces its path backward. The ray diagram shown in Fig3. for diverging lenses was created using the rules given in Table. The first ray, parallel to the axis, appears to come from the focal point on the same side of the lens as the object. This ray is indicated by the oblique dashed line. The second ray passes through the center of the lens and is not refracted.
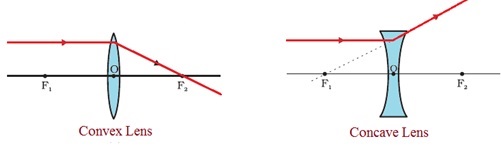
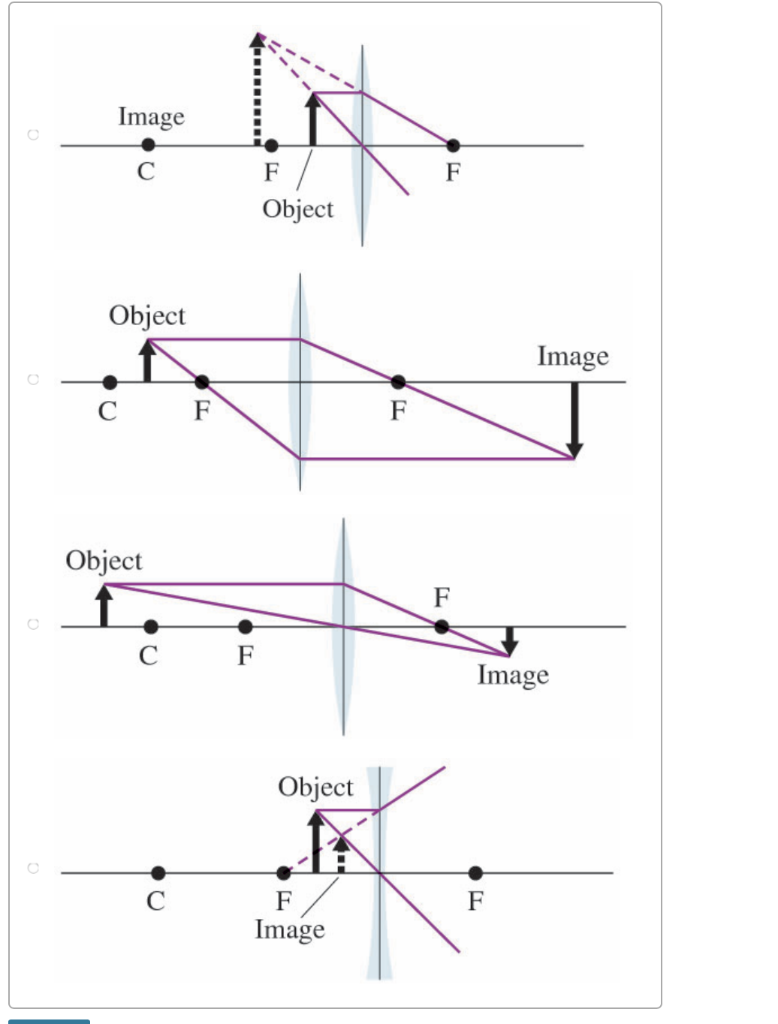
Concave Lens - Ray diagram Uses of Concave and Convex Lens Sign convention for Convex and Concave Lens Lens Formula Power of a lens NCERT Questions → Class 10. Chapter 10 Class 10 - Light - Reflection and Refraction (Term 1) Concepts NCERT Questions ... The ray diagram above illustrates that the image of an object in front of a double concave lens will be located at a position behind the double concave lens. Furthermore, the image will be upright, reduced in size (smaller than the object), and virtual. This is the type of information that we wish to obtain from a ray diagram. Arial Calibri Default Design Lenses What phenomenon is evident in lenses? Basic Types of Lenses Convex Lens Concave Lens Type of Image Convex Lens Ray Diagram for Convex Lens Rules for Ray Diagrams for Convex Lens PowerPoint Presentation Summary for Convex Lens Sign Convention Magnification Lens Equation Concave Lens Summary for Concave Lens ... The students can use a convex lens diagram to understand the ray's path after passing through a convex lens. The students may create a convex ray diagram by hand, but the process is lengthy, and at the same time, complicated. If the students fail to place the paths of the light properly, they may end up with a faulty convex lens ray diagram.
Lens and Mirror Lab. Category. Optics, Physics. Change the location of the object and use the ray diagrams to determine the location of the image. The following lab was created by Nick Donovan. Thanks Nick!
Shows how to draw ray diagrams to locate the image formed by a convex lens. You can see a listing of all my videos at my website, http://www.stepbystepscienc...
Voronoi Diagrams with Cones; Juggling 13 Balls; Concave and Convex Lenses. Description Simulation of image formation in concave and convex lenses. Move the tip of the "Object" arrow to move the object. Move the point named " Focus' " to change the focal length. Move the point named " Focus' " to the right side of the lens to change to a concave ...
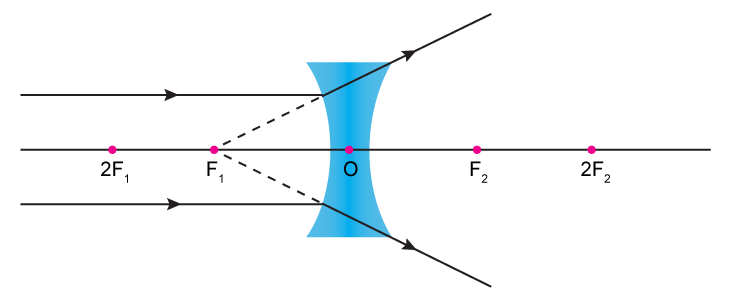
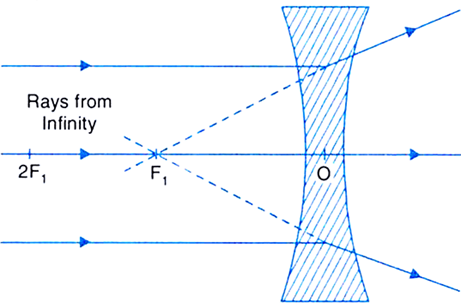
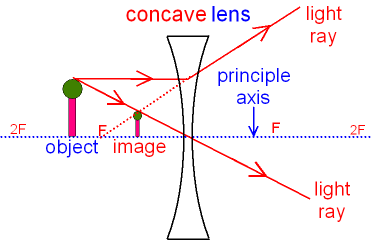
The image formation by concave lenses using ray diagram depiction can be briefly explained as follows, When the object is placed at infinity: When the object is placed at infinity, the image formed by the concave lens will be at the first focus, F1. The nature of the image obtained will be a virtual image and it will be in erect form.
Oct 25, 2021 · Worksheets are Mirror ray diagram work answers, Work 6 curved mirror problems quantitative, Convex mirror ray diagrams answer key, Lens ray diagram answer, 1 1 1 h d i i in every problem draw a ray i o f h d o o, Ray diagrams for concave mirrors, Activity 5 curved mirrorsWhere will an image form if an object is placed. 1 Name ...
The ray passing through the focal point becomes parallel to the principal axis after refraction by the lens. Ray diagram for concave lens. Image formation in convex lens Case 1:When object beyond 2F: In this case image will form between F and 2F, image will be real, inverted, smaller than the object. ...
Draw one ray diagram each for the distant object method and the lens equation method used to determine the focal lengths of the lenses. s o i 2. A concave lens made out of air is immersed in water (two watch glasses glued to a piece of pipe so that air is inside).
Lens Ray Diagrams Worksheet Answers In conducting this project the student is obtaining basic information on what happens to light rays as they pass through convex and concave lenses. Using a hand lens ... a final report with ... The Eyes Have It! The lens sits behind the iris and is clear and colorless. The lens' job is to focus light rays on ...
For a Concave lens,There are only 2 casesThey areObject is Placed at InfinityObject is Placed between Infinity and Optical CenterCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray pa
Ray Diagrams for Concave Lenses. The ray diagrams for concave lenses inside and outside the focal point give similar results: an erect virtual image smaller than the object. The image is always formed inside the focal length of the lens.
Shows how to draw the ray diagrams for locating the image produced by a concave lens and a convex mirror. You can see a listing of all my videos at my websit...
With a concave lens, the image will always be diminished, the right way up and virtual. Draw a ray diagram to show how an image is formed by a concave lens. Describe the properties of an image produced by a concave lens. Draw different ray diagrams with the object at different places in relation to the focus and find out where the image appears.
A concave lens ray diagram is a simple way of visualising the path that light rays take when passing through a concave lens. To draw a ray diagram you only need to draw two ray lines. This is sometimes referred to as "the two rules of refraction for diverging lenses".
Ray diagrams for diverging (concave) lens. If an object is on one side of the concave lens, the concave lens can form the image of the object. If the position of the object on one side of the concave lens is known, how to draw the image formation of the object? Suppose an object is on the left side of the concave lens as shown in the figure below.
















0 Response to "37 ray diagram for concave lens"
Post a Comment