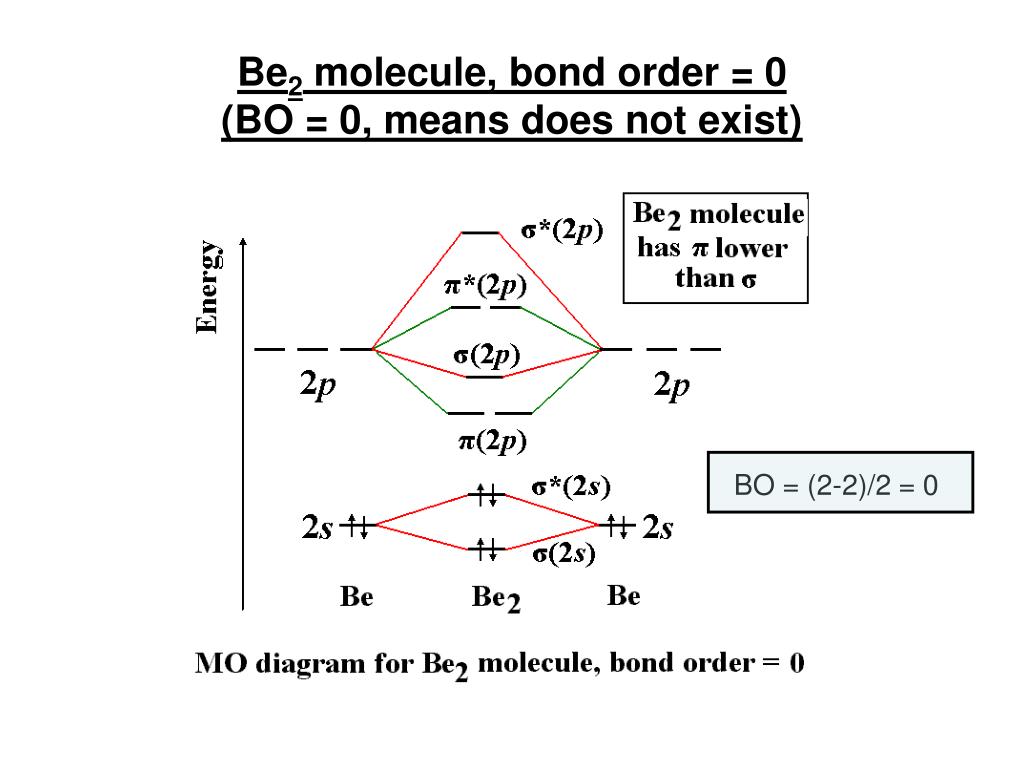
42 be2 molecular orbital diagram
1. Use Molecular orbital theory to predict if the ion Be2 2+ should exist in a relatively stable form. Include a molecular orbital diagram and a calculation of bond order. How would I go about solving this? The molecular orbital theory is confusing to me. What can you guys tell me to better understand it? Molecular Orbital Diagram for Beryllium Dimer (Be2)Fill from the bottom up, with 4 electrons total.Bonding Order is 0, meaning it does not bond, and it is...
Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. Valence Bond Theory proposes that electrons are localized between two atoms. On the other hand, Molecular Orbital Theory visions the electrons of a covalent bond to be delocalized over the entire molecule.
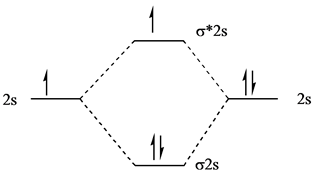
Be2 molecular orbital diagram
The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. Figure 9. The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that H2 will be a stable molecule with lower energy than the separated atoms. A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. The diagram is then completed by filling the energy levels with the correct number of electrons. The following molecules are currently available: Molecules of the First Row Molecular orbital diagram for hydrogen: For a diatomic molecule, an MO diagram effectively shows the energetics of the bond between the two atoms, whose AO unbonded energies are shown on the sides. The unbonded energy levels are higher than those of the bound molecule, which is the...
Be2 molecular orbital diagram. the valence molecular orbital diagram for the anion B2- is given. - the MO diagram shows the relative energy and number of electrons in each MO - The MO diagram can be used to calculate bond order and predict stability - the MO diagram typically includes valence-shell molecular orbitals only. Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals. The video below describes how to generate molecular orbital diagrams for B₂ and other diatomic molecules from Row 2 elements of the... The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is. To find the bond order, add the 15 electrons in the molecular orbitals (the blue-colored energy levels in the diagram) one at a time until you have used them up. Here's the Molecular Orbital diagram for the [math]Be_2 [/math]molecule. The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. Figure 8.35 The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that H2 will be a stable molecule with lower energy than the separated atoms.
Molecular orbital theory in overall involves a lot of complicated mathematics. However, the fundamental ideas behind the theory are very easy to The molecular orbital theory involves sophisticated hybridization models, according to which the orbital can be modified by the interaction... A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. Register alias and password only available to students enrolled in dr. A draw the molecular orbital diagram. Molecular Orbi... Pi star (π*): antibonding molecular orbital - Normally this orbital is empty, but if it should be occupied, the wave nature of hybrid orbitals. The 2p orbital extends along the entire axis with opposite phase in each lobe. This one is a lot easier and faster to draw. Lecture 2. Molecular Orbital Diagrams.
The second-lowest-energy molecular orbital in butadiene will have 1 node. The trick is knowing where to put it. As we saw with the allyl system, the node cannot just be placed anywhere; the A molecular orbital diagram without electrons is like an apartment building without people. Molecular Orbital Diagrams. 1. Electrons preferentially occupy molecular orbitals that are lower in energy. 2. Molecular orbitals may be empty, or contain one or two electrons. Group theory is usually used to develop molecular orbital diagrams and drawings of more complicated molecules. Valence bond (VB) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons. No. 1 Molecular Orbital Theory. Electrons may be considered either of particle or of wave nature. Therefore, an electron in an atom may be described as occupying an atomic orbital, or by a wave function Ψ The molecular orbital diagram representing this order of energy levels is shown in fig.
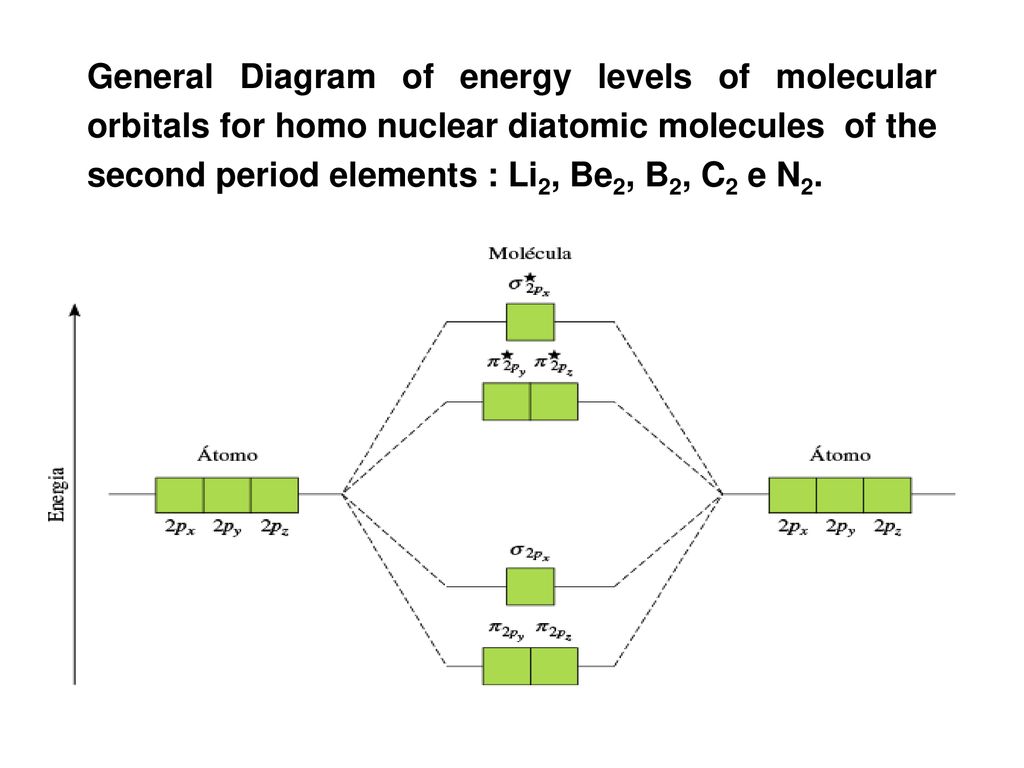
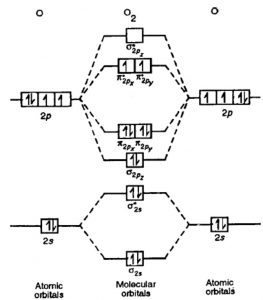
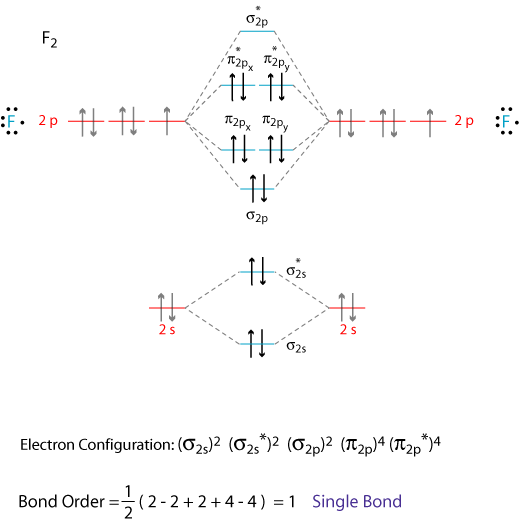
Figure 4.10.1: Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagrams for Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules.(a) For F2, with 14 valence electrons (7 from each F atom), all of It so happens that the molecular orbital description of this molecule provided an explanation for a long-standing puzzle that could not be...
Molecular orbital theory uses group theory to describe the bonding in molecules; it comple-ments and extends the introductory bonding models in Chapter 3 . In molecular orbital theory the Second, the atomic orbital energies must be similar. When the energies differ greatly, the change in the energy of...
This second orbital is therefore called an antibonding orbital. Construct a "molecular orbital diagram" of the kind shown in this lesson for a simple diatomic molecule, and indicate whether the molecule or its positive and negative ions should be stable.
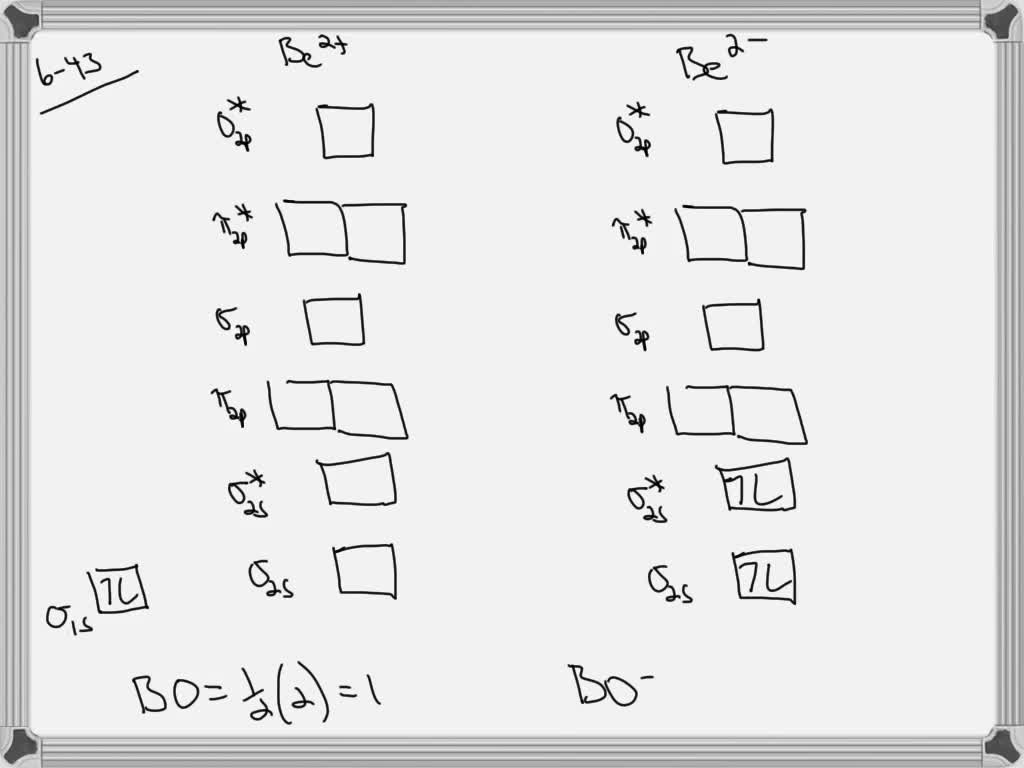
Combining two beryllium atoms would result in a total of four orbitals and eight electrons. B calculate the bond order.
Figure 9-2 Molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the combination of the 1s atomic orbitals on two To obtain the molecular orbital description of the bonding in a molecule or ion, follow these steps But the two electrons in the anti-bonding orbital would be less stable than in the separate atoms.
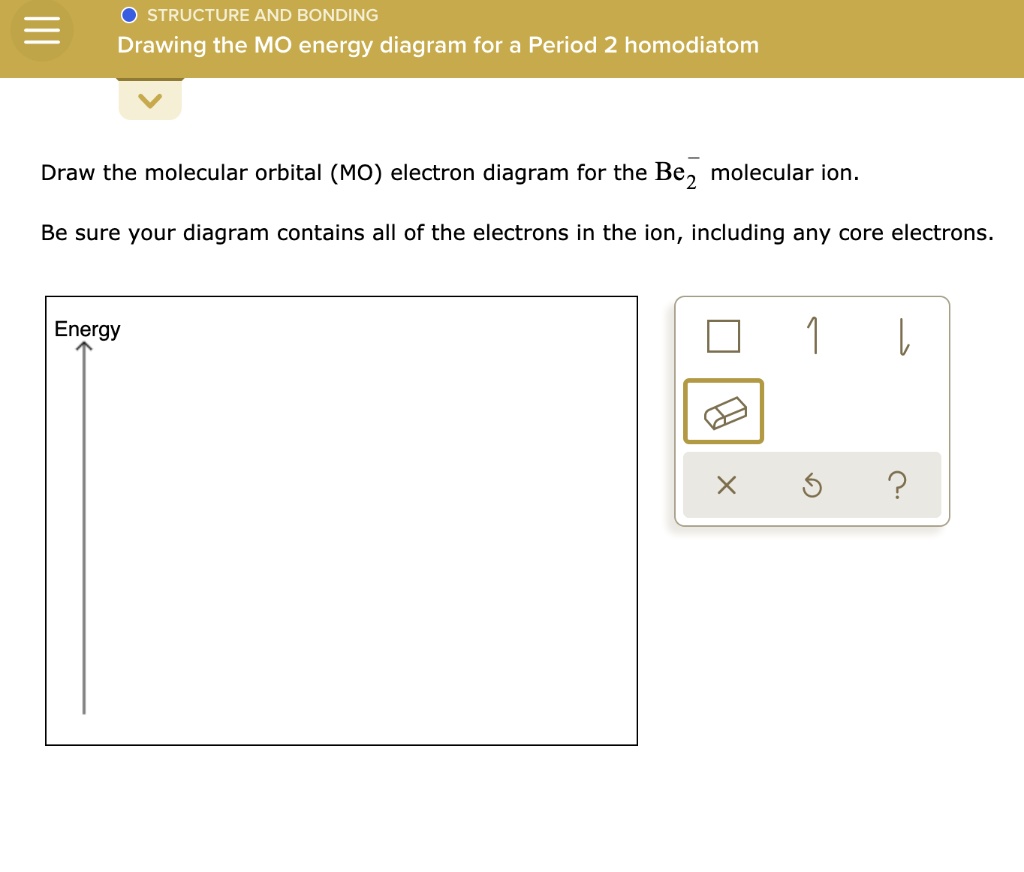
Shouldn’t you count the valence electrons for Be (which is 2) and subtract 1 because of the + sign? For O2, N2, NO, F2, etc, you count the number of valence electrons instead of the atomic number. Why is it that for Be, though, you look at the atomic number instead of the number of valence electrons it has? I apologize if this is a stupid question, but I appreciate any clarification on this
CD contains interactive energy diagrams. Electron travelling around nucleus in circular orbits - must be a balance between attraction to nucleus and flying off (like a planets orbit). Each orbital wavefunction (φ ) is most easily described in two parts radial term - which changes as a function of...
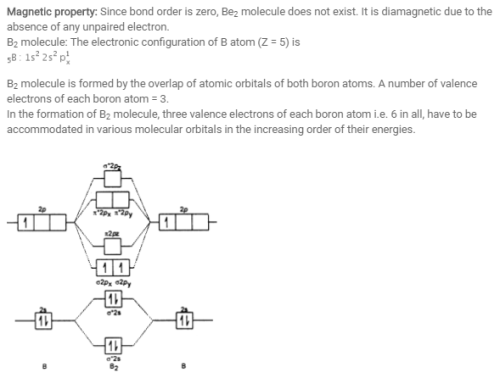
Molecular Orbital Theory: Detailed information on the molecular orbital theory class 11 and more in this article The molecular orbital energy level diagram for dioxygen molecule is shown below If all the molecular orbitals in a molecule occupy two electrons each, the substance is diamagnetic.
• For example, when two hydrogen atoms bond, a σ1s (bonding) molecular orbital is formed as well as a σ1s* (antibonding) molecular orbital. • The following slide illustrates the relative energies of the molecular orbitals compared to the original atomic orbitals. • Because the energy of the two electrons...
Molecular Orbital Theory. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Outline the basic quantum-mechanical approach to deriving molecular orbitals Molecular Orbital Theory. considers bonds as localized between one pair of atoms. considers electrons delocalized throughout the entire molecule.
This molecular orbital model can be used to explain why He2 molecules don't exist. The molecular orbital diagram for an O2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions between the 2s and 2p valence orbitals.
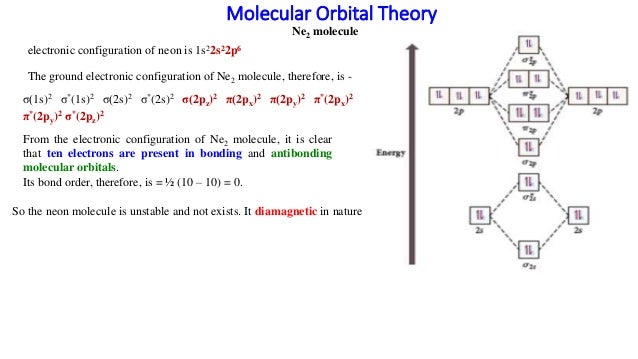
Molecular orbital : A molecule in which all the electrons are paired, is called diamagnetic. | Online Chemistry tutorial IIT, CBSE Chemistry, ICSE Chemistry, engineering and medical chemistry entrance exams Molecular orbital diagram of C2 molecule : Number of electrons in C2 molecule = 12.
Molecular orbital diagram for hydrogen: For a diatomic molecule, an MO diagram effectively shows the energetics of the bond between the two atoms, whose AO unbonded energies are shown on the sides. The unbonded energy levels are higher than those of the bound molecule, which is the...
A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. The diagram is then completed by filling the energy levels with the correct number of electrons. The following molecules are currently available: Molecules of the First Row
The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. Figure 9. The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that H2 will be a stable molecule with lower energy than the separated atoms.





















0 Response to "42 be2 molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment