39 construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species
Show transcribed image text Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. V(H_2O)_6^3+ b) Fe(CN)_6^4- c) FeCl_6^ Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. If you can't find your institution, please check your spelling and do not use abbreviations. July 14, 2020 - One of the most striking characteristics of transition-metal complexes is the wide range of colors they exhibit. In this section, we describe crystal field theory (CFT), a bonding model that explains …
Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. Balance the equation: Note: If a chemical species coefficient is "1" then "1". Transition elements are typically hard, strong, metals that conduct both heat and electricity very In an octahedral crystal field a low spin d5 Please note: I'm not drawing out the orbital splitting diagram for every problem.

Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species
Oct 19, 2018 · Solved: Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. a) [math]V(H_2O)_6^{3+}[/math] a) [math]Co(CN)_6^{3-}[/math] a) . Transition elements are typically hard, strong, metals that conduct both heat and electricity very In an octahedral crystal field a low spin d5 Please note: I'm not drawing out the orbital splitting diagram for every problem. Answer to Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. V(H2O)63+ Co(CN)63 - Mn(H2O)62+... Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. V ( H 2 O ) 3 + 6 V (H2O)63+ Co ( CN ) 3 − 6 Co (CN)63− Mn ( H 2 O ) 2 + 6 Mn (H2O)62+ Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. V (H2O)6 (3+)charge Co (CN)6 3− Mn (H2O)6 2+. Question: Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species.
Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. Cr4+ Mn(H2O)6^2+ Construct The Octahedral Crystal Field Splitting Diagram. Construct the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. since the oxalate ligand is fairly low in the series a weak field ligand at this point you may not have studied ligand field theory yet which explains ... Asked by jematormal91 on may 31 2012. Construct the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. ... Step-by-step solutions to all your homework questions - Slader
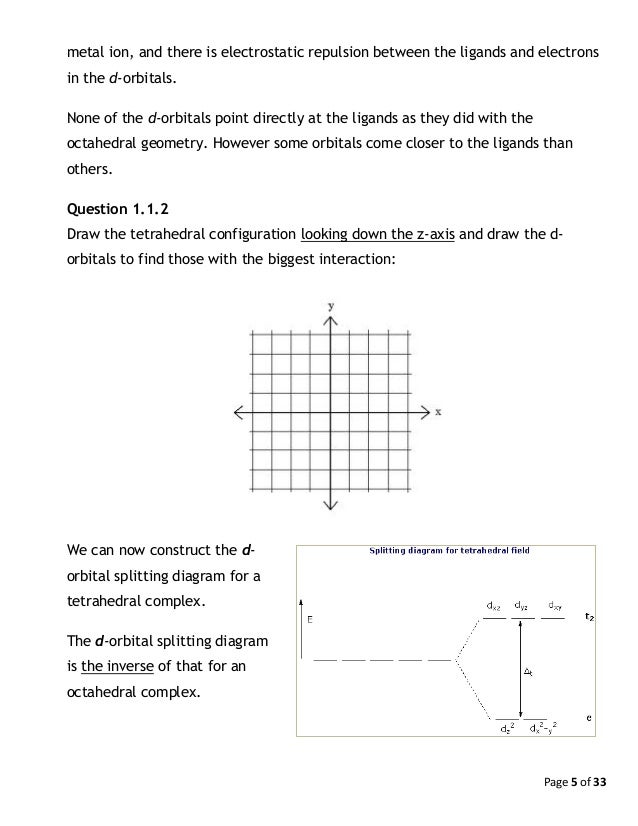
August 13, 2021 - Crystal field theory (CFT) describes the breaking of orbital degeneracy in transition metal complexes due to the presence of ligands. CFT qualitatively describes the strength of the metal-ligand … Unnecessary diagrams: d 1, d 9 and d 10 d 1. There is no electron repulsion in a d 1 complex, and the single electron resides in the t 2g orbital ground state. A d 1 octahedral metal complex, such as [Ti(H 2 O) 6] 3+, shows a single absorption band in a UV-vis experiment. The crystal field stabilization ... ion in the crystal field generated by a set of ligands. It arises due to the fact that when the d orbitals are split in a ligand field, some of them become lower in energy than before. For example, in the case of an octahedron, the t2g set ... Chemistry. Based on crystal field theory, which of the following metal ions will not be colored when placed in an octahedral crystal field?. Answer to Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. V(H2O)63+ Co(CN)63 - Mn(H2O)62+.
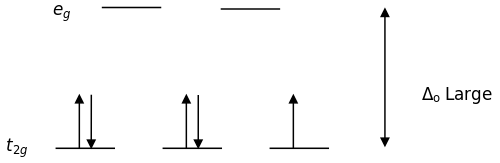
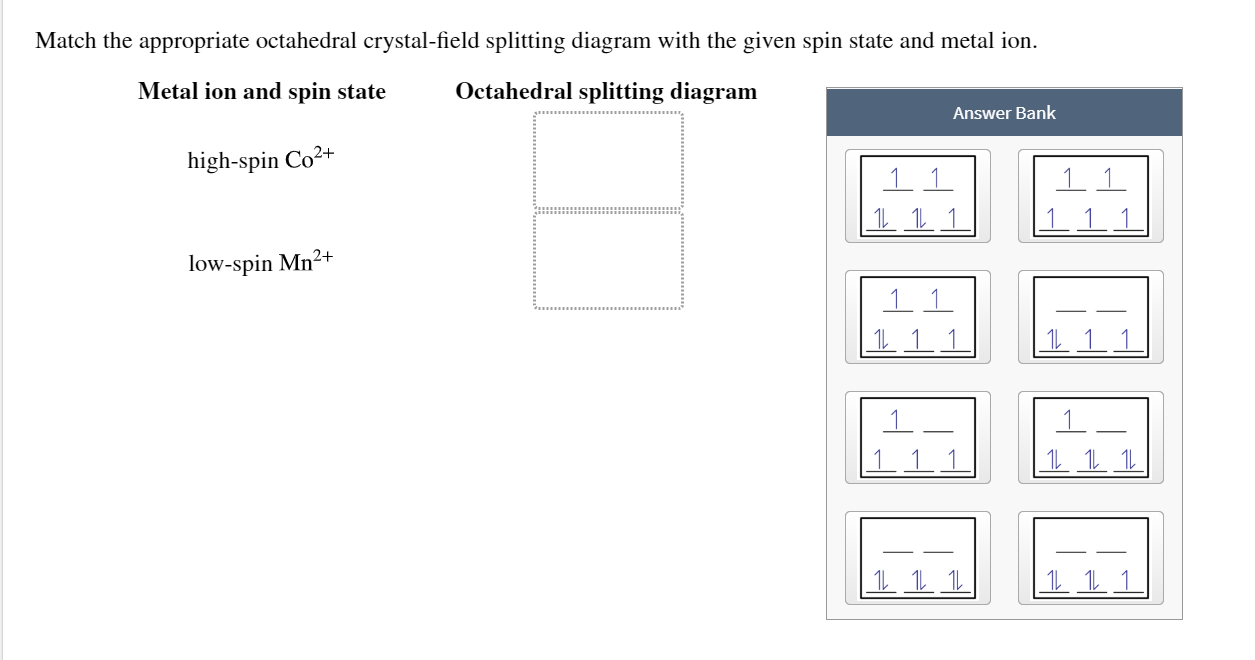
Distribution of Electrons in an Octahedral Complex d4 There are two possibilities for metal ions having d 4-d7 electronic configuration. Depending on the nature of the ligands and the metal they could be high-spin or low-2 u.e. spin complexes. 4 u.e. For the d4 system, CFSE = For high-spin, ... Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for the following metal from CHEMISTRY 2070 at Cornell University Octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram → d-orbital electrons. high-spin - electrons can occupy the upper level (eg) low-spin - electrons can pair up with the electrons on the lower level (t2g) Recall that: weak field ligands → high spin → lowΔ or crystal field splitting energy values. strong field ligands → low spin → highΔ or crystal field splitting energy values. July 17, 2020 - Crystal field theory treats interactions between the electrons on the metal and the ligands as a simple electrostatic effect. The presence of the ligands near the metal ion changes the energies of …
Construct the octahedral crystal field separating diagram because that the steel in each species. construct an equilateral triangle abc in i m sorry altitude drawn from opposite peak is 35 cmalso construct a triangle apr similar to a triangle such that each side of the triangle apr is 15 times the of the equivalent side of triangle abc.
The Angels (使徒, shito) are fictional entities of the anime television series Neon Genesis Evangelion, produced by Gainax studio and directed by Hideaki Anno, and in the manga of the same name by Yoshiyuki Sadamoto.. In the original animated work almost all the Angels are the antagonists of mankind who repeatedly try to reach the headquarters of the special agency Nerv, located in the city ...
The crystal field stabilization ... ion in the crystal field generated by a set of ligands. It arises due to the fact that when the d orbitals are split in a ligand field, some of them become lower in energy than before. For example, in the case of an octahedron, the t2g set ...
Construct the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. Vh2o63 cocn63 mnh2o62. It then asks how many unpaired electrons and asks to draw a crystal field splitting diagram for this compound. Au fe3 ag au3 nb3 asked by melody on november 9 2011.
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other compounds.Oxygen is Earth's most abundant element, and after hydrogen and helium, it is the third-most abundant element in the universe.
Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. V ( H 2 O ) 3 + 6 V (H2O)63+ Co ( CN ) 3 − 6 Co (CN)63− Mn ( H 2 O ) 2 + 6 Mn (H2O)62+ Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. V (H2O)6 (3+)charge Co (CN)6 3− Mn (H2O)6 2+. Question: Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species.
Answer to Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. V(H2O)63+ Co(CN)63 - Mn(H2O)62+...
Oct 19, 2018 · Solved: Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. a) [math]V(H_2O)_6^{3+}[/math] a) [math]Co(CN)_6^{3-}[/math] a) . Transition elements are typically hard, strong, metals that conduct both heat and electricity very In an octahedral crystal field a low spin d5 Please note: I'm not drawing out the orbital splitting diagram for every problem.




















0 Response to "39 construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species"
Post a Comment