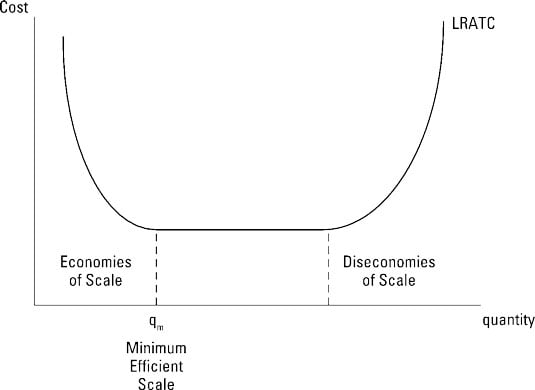
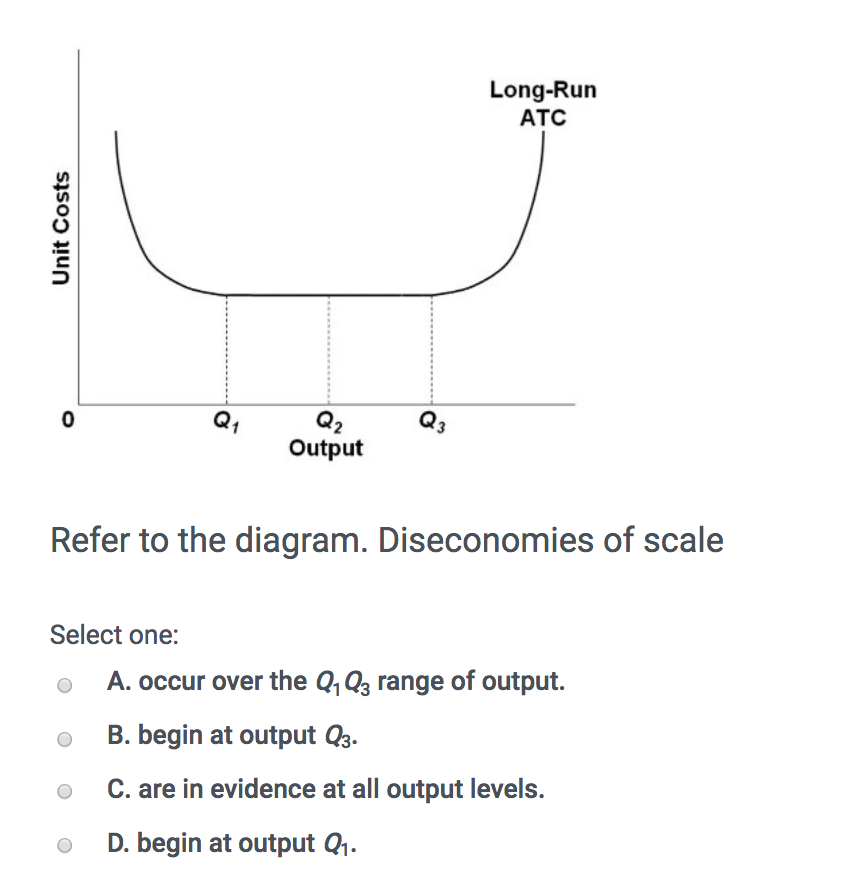
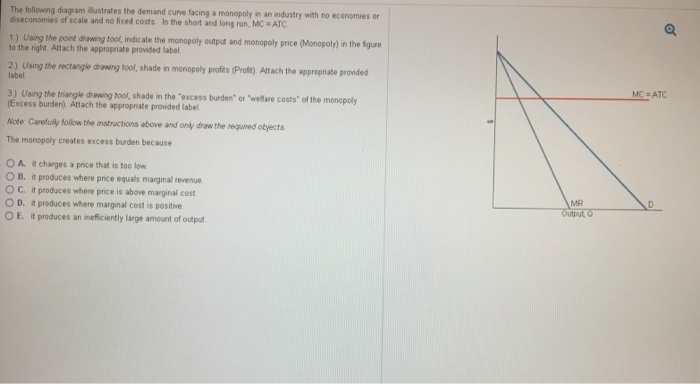
41 refer to the diagram. diseconomies of scale
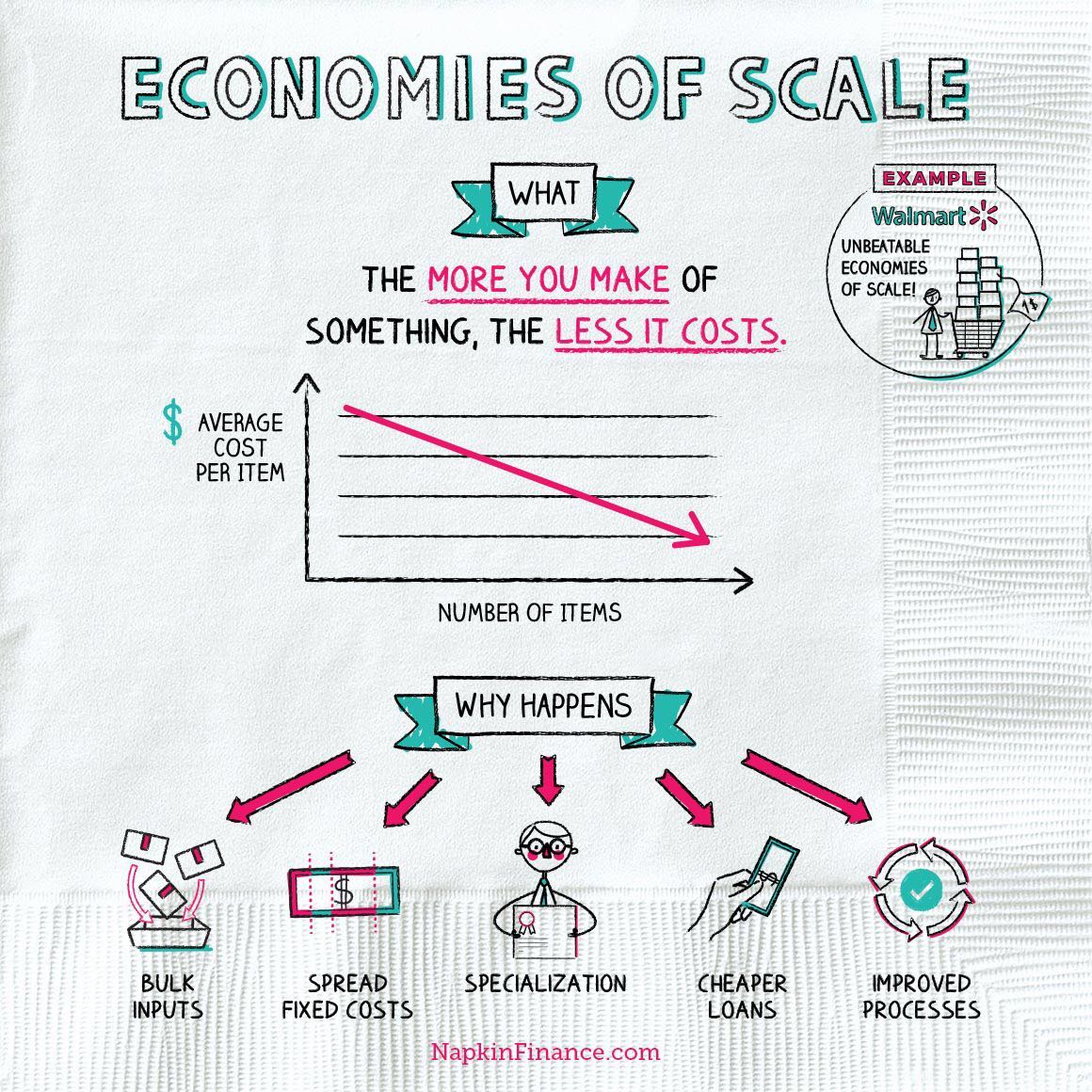
Economies of Scale vs Diseconomies of Scale . Economies of scale and diseconomies of scale are concepts that go hand in hand. They both refer to changes in the cost of output as a result of the changes in the levels of output. External diseconomies of scale: Refer to diseconomies that limit the expansion of an organization or industry. The factors that act as restraint to expansion include increased cost of production, scarcity of raw materials, and low supply of skilled laborer. There are a number of causes for diseconomies of scale. Some of the causes which lead to diseconomies of scale …
Refer to the above diagram. Which equation will help us determine whether we are realizing economies of scale, constant returns to scale or diseconomies of scale: A. TFC/Q = AFC. B. TVC/Q = AVC. C.TC/Q = ATC. D. TFC + TVC = TC. 22. Refer to the above diagram. Economies of scale: A. are evident over the entire range of output.

Refer to the diagram. diseconomies of scale
Refer to the above diagram. Economies of scale: A. are evident over the entire range of output. B. occur over the 0Q1 range of output. C. begin at output Q3. D. occur only over the Q1Q3 range of output. 1. Internal Economies of Scale. This refers to economies that are unique to a firm. For instance, a firm may hold a patent over a mass production machine, which allows it to lower its average cost of production more than other firms in the industry. 2. External Economies of Scale. These refer to economies of scale enjoyed by an entire industry. There are diseconomies of scale. In Figure 8.1, diagram "a" presents the cost curves that are relevant to a firm's production decision, and diagram "b" shows the market demand and supply curves for the market.
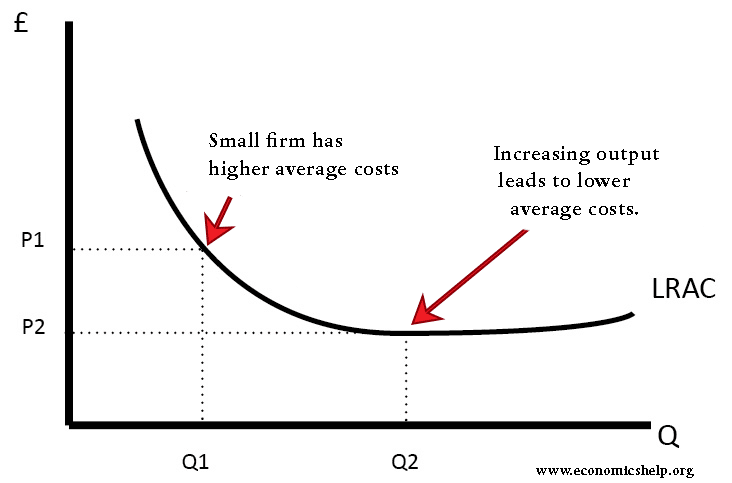
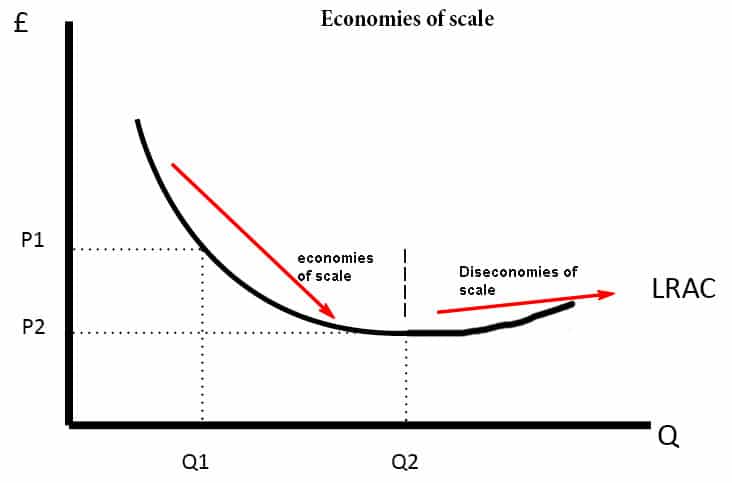
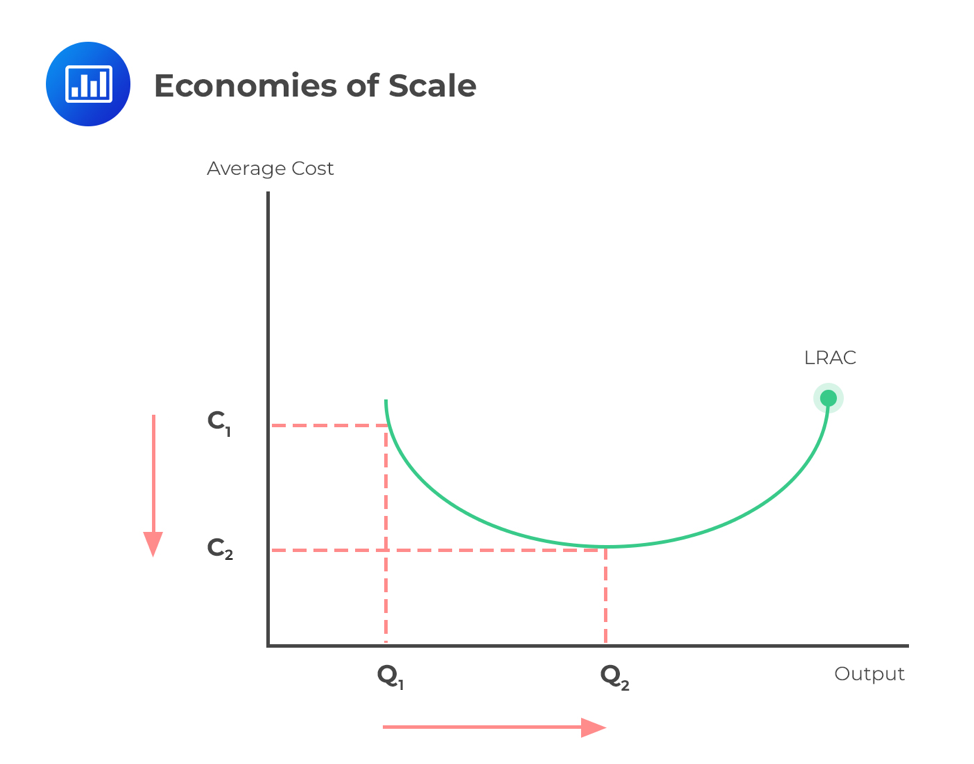
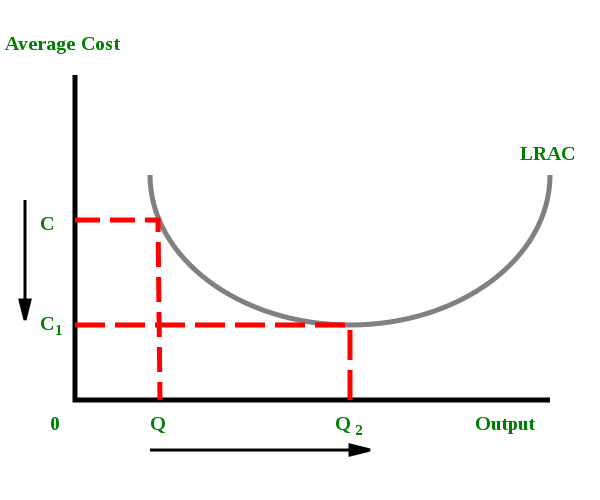
Refer to the diagram. diseconomies of scale. Diseconomies of scale occur when long-run average costs start to rise with increased output. Economies of scale occur up to Q1. After output Q1, long-run average costs start to rise. Reasons for dis-economies of scale. Poor communication in a large firm. It can be hard to communicate ideas and new working practices. Refer to the above diagram. Economies of scale: A. begin at output Q 3. B. occur only over the Q 1 Q 3 range of output. C. occur over the 0Q 1 range of output. D. are evident over the entire range of output. 2 points . QUESTION 28. A firm's long-run supply curve is the area of ATC curve that lies above the MC curve. True. False. 2 points . QUESTION 29. Refer to the above … Economies of scale refer to these reduced costs per unit arising due to an increase in the total output. Diseconomies of scale, on the other hand, occur when the output increases to such a great extent that the cost per unit starts increasing. In this article, we will look at the internal and external, diseconomies and economies of scale. The diagram below illustrates a diseconomy of scale. At point Q*, this firm is producing at the point of lowest average unit cost. If the firm produces more or less output, then the average cost...
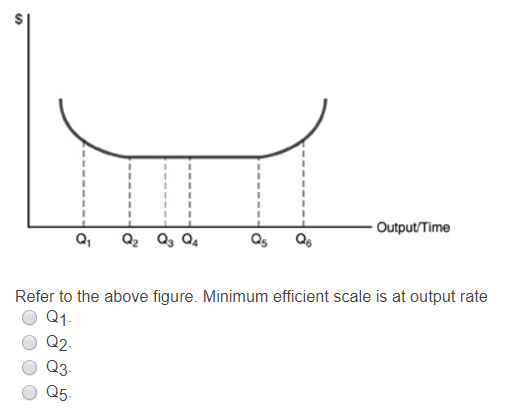
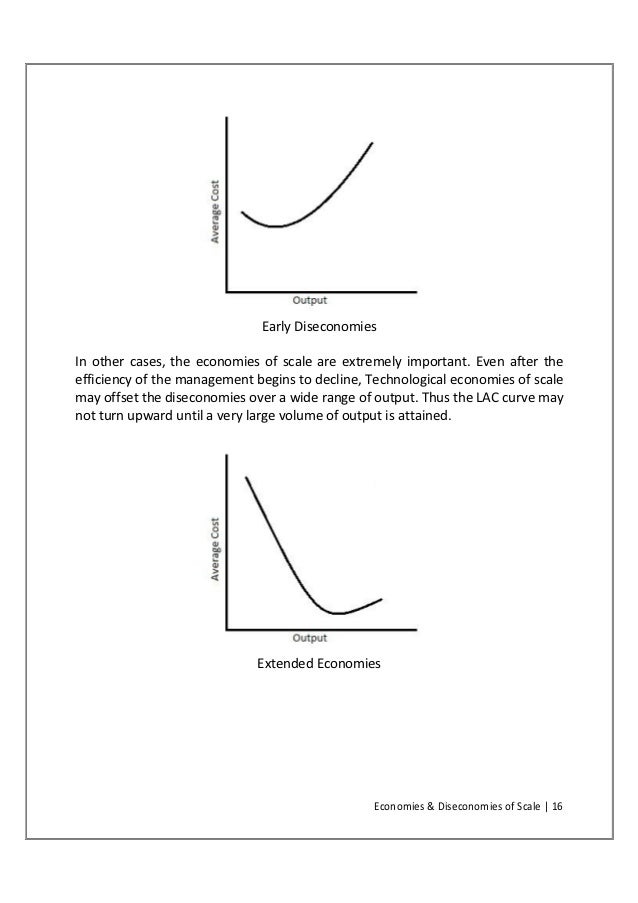
185. Refer to the above diagram. Diseconomies of scale: A) begin at output Q1. C) begin at output Q3. B) occur over the Q1Q3 range of output. D) are in evidence at all output levels. Answer: C. Type: G Topic: 6 E: 407 MI: 163 186. Refer to the above diagram. Minimum efficient scale: A) occurs at some output greater than Q3. C) is achieved at Q3 ... Economies of Scale. Economies of scale refer to the cost advantage brought about by an increase in the output of a product. Economies of scale arise due to the inverse relationship between the per-unit fixed cost and the quantity produced - the greater the production, the lower the fixed costs per unit. Transcribed image text: Refer to the below diagram. Diseconomies of scale: Long-run ATC Output O begin at output Q 1. O are in evidence at all output levels ... Refer to the diagram diseconomies of scale. Abegin at output q1. With this principle rather than experiencing continued decreasing costs and increasing output a firm sees an increase in marginal costs when output is increased. The law of diminishing returns is taking hold.
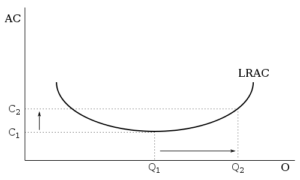
Refer to the above diagram Diseconomies of scale A begin at output Q 1 C begin from ECON 210 at University of South Dakota Diagram of diminishing returns . In this example, after three workers, diminishing returns sets in. After employing 4 workers or more - the marginal product (MP) of the worker declines and the marginal cost (MC) starts to rise. Difference between diminishing returns and dis-economies of scale This situation arises when after reaching a certain level of production, economies of scale are balanced by diseconomies of scale. This is known as homogeneous production function. Cobb-Douglas linear homogenous production function is a good example of this kind. This is shown in diagram 10. In figure 10, we see that increase in factors of production i.e. labour and capital … The concept of diseconomies of scale is the reverse of economies of scale. Considering the diagram illustrated above. After the quantity of production increase beyond the level of 10,000 (Q2) the average cost per item increases. Enterprises' experiences cost disadvantages due to an increase in organizational size or output.
Long-Run ATC 0 Output Refer to the diagram. Diseconomies of scale a) occur over the Q10s range of output. b) begin at output Q1- e) begin at output @s d) are in evidence at all output levels. 22. In answering the question, assume a graph in which dollars are measured on the vertical axis and output on the horizontal axis.
Refer to the above diagram. The vertical distance between ATC and AVC reflects: the average fixed cost at each level of output. Refer to the above data. In the long run the firm should use plant size "A" for: 10 to 30 units of output. Refer to the above information. The marginal cost of the third unit of output is. $15. Refer to the above data. The value for X is. 15. Refer to the above …
B. economies of scale. C. diseconomies of scale. D. constant costs. 148. The diagram shows the short-run average total cost curves for five different plant sizes of a firm. The position of these five curves in relation to one another reflects: A. economies and diseconomies of scale. B. the effect of fixed costs on ATC as output increases.
In the diagram above LRTC = long-run total costs. The firm is experiencing: A. economies of scale. B. diseconomies of scale. C. constant returns to scale. D. minimum efficient scale. 16. R-16 REF 22-139: Refer to the diagram minimum efficient scale. Refer to the above diagram for output level q per. C begin at output q3.
Economies of scale is related to and can easily be confused with the theoretical economic notion of returns to scale. Where economies of scale refer to a firm's costs, returns to scale describe the relationship between inputs and outputs in a long-run (all inputs variable) production function. A production function has constant returns to scale if increasing all inputs by some proportion ...
Diseconomies of scale occur when an additional production unit of output increases marginal costs , which results in reduced profitability . Instead of production costs declining as more units are produced (which is the case with economies of scale), the opposite happens, and costs increase with the production of each additional unit.
Economies of scale refers to the situation where, as the quantity of output goes up, the cost per unit goes down. This is the idea behind "warehouse stores" like Costco or Walmart. In everyday language: a larger factory can produce at a lower average cost than a smaller factory. Figure 1 illustrates the idea of economies of scale, showing ...
Refer to the above diagram. For output level Q, per unit costs of C are: O A. unobtainable and imply the inefficient use of resources. O B. unobtainable, given resource prices and the current state of technology. O C. obtainable, but imply the inefficient use of resources. O D. obtainable and imply that resources are being combined efficiently.
Refer to Figure 13-9. At output levels greater than N, the firm experiences. a. economies of scale. b. constant returns to scale. c. diseconomies of scale. d. minimum efficient scale. Figure 13-10. 53. Refer to Figure 13-10.
22.09.2021 · External economies and diseconomies of scale occur due to _____ (a) endogenous (b) exogenous (c) internal (d) both (b) and (c) 174. When a large firm takes up advertising and grants higher margin to retailers, it is called- (a) technical economies (b) managerial economies (c) marketing economies (d) financial economies. 175. When a firm’s …
Refer to the diagram diseconomies of scale. Achieving efficient flows of information in large businesses is expensive as is the cost of managing supply contracts with hundreds of suppliers at different points of an industrys supply chain. When diseconomies of scale occur. The greater the quantity of output produced the lower the per unit fixed ...
Diseconomies of scale refer to the inefficiency seen in firms when they become too large and start incurring greater costs as they expand. Big organisations move from economies of scale to diseconomies of scale after long-run average costs move past their lowest point. In the diagram above, the lowest point of the Long-run Average Cost Curve ...
A) diminishing returns. B) diseconomies of scale. C) economies of scale. D) declining fixed costs. Figure 11 -4 7) Refer to Figure 11 -4. What happens to the average fixed cost of production when the firm increases output from 150 to 200? 7) A) It could rise or fall depending on what happens to total cost. B) It falls. C) It remains constant. D ...
As the firm in the above diagram expands from plant size #3 to plant size #5, it experiences: A) increasing returns. B) economies of scale. C) diseconomies of scale. D) constant costs. Per unit costs are rising now in the LR and we call this diseconomies of scale due to excessive size of the business which creates lots of coordination problems etc
Refer to GST. Example: Sales connected with Australia. Alex runs an internet business selling mobile phone parts through his website. About half his sales are to Australian customers and half to overseas customers. He is not registered for GST. Recently Alex took on a new line of accessories and his sales have increased. His total sales for the past 12 months are now …
Refer to the above diagram diseconomies of scale a. Diseconomies of scale occur when the firms outgrow in the size which results in the increase in employee cost compliance cost administration cost etc. The long run average total cost curve falls. Are in evidence at all output levels. Marginal cost intersects average total cost.
Diseconomies of Scale Definition Diseconomies of Scale is an economic term that defines the trend for average costs to increase alongside output. At a specific point in production, the process starts to become less efficient. In other words, it starts to cost more to produce an additional unit of output.
External diseconomies of scale (DOS) refer to the increase in average cost when the industry rather than the scale of production expands. External diseconomies of scale are shown by an upward shift in the long-run average cost curve. There are several sources of external diseconomies of scale. When the industry expands, the demand for factor inputs will increase …
a. economies and diseconomies of scale. b. the effect of fixed costs on ATC as output increases. c. the law of constant costs. d. the law of diminishing returns. a. economies and diseconomies of scale. Refer to the diagram. Constant returns to scale: a. occur over the 0Q1 range of output b. occur over the Q1Q3 range of output c. begin at output Q3
D. fact that most monopolistically competitive firms encounter diseconomies of scale. A. amount by which actual production falls short of the minimum ATC output. 7. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. The profit-maximizing output for this firm will be: A. 100. B. 160. C. 180. D. 210. B. 160. 8. Refer to the above diagram for a ...
There are diseconomies of scale. In Figure 8.1, diagram "a" presents the cost curves that are relevant to a firm's production decision, and diagram "b" shows the market demand and supply curves for the market.
1. Internal Economies of Scale. This refers to economies that are unique to a firm. For instance, a firm may hold a patent over a mass production machine, which allows it to lower its average cost of production more than other firms in the industry. 2. External Economies of Scale. These refer to economies of scale enjoyed by an entire industry.
Refer to the above diagram. Economies of scale: A. are evident over the entire range of output. B. occur over the 0Q1 range of output. C. begin at output Q3. D. occur only over the Q1Q3 range of output.



/economies-of-scale-3305926-FINAL-5bc4bf7ac9e77c00528fcecf.png)
















0 Response to "41 refer to the diagram. diseconomies of scale"
Post a Comment