42 molecular orbital diagram for be2
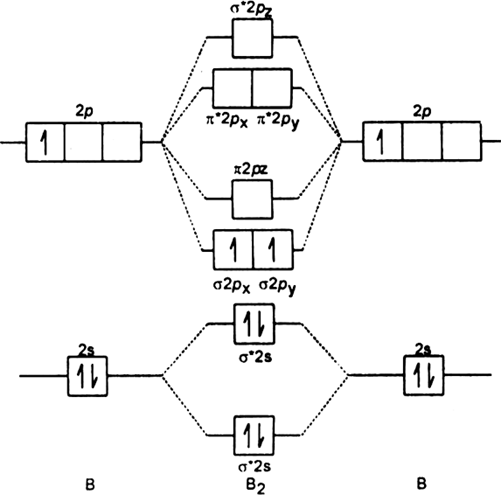
Nov 11, · As discussed in class the MO diagram for B 2 shows that it has two unpaired electrons (which makes it paramagnetic) and these electrons are in bonding molecular orbitals resulting in the equivalent bond strength of one bond. As discussed in class it is not a bond. Which of the following is paramagnetic? (use the molecular orbital diagram) a) Li 2. b) Be 2. c) B 2. d) C 2. e) N 2. Learn this topic by watching MO Theory: Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules Concept Videos.
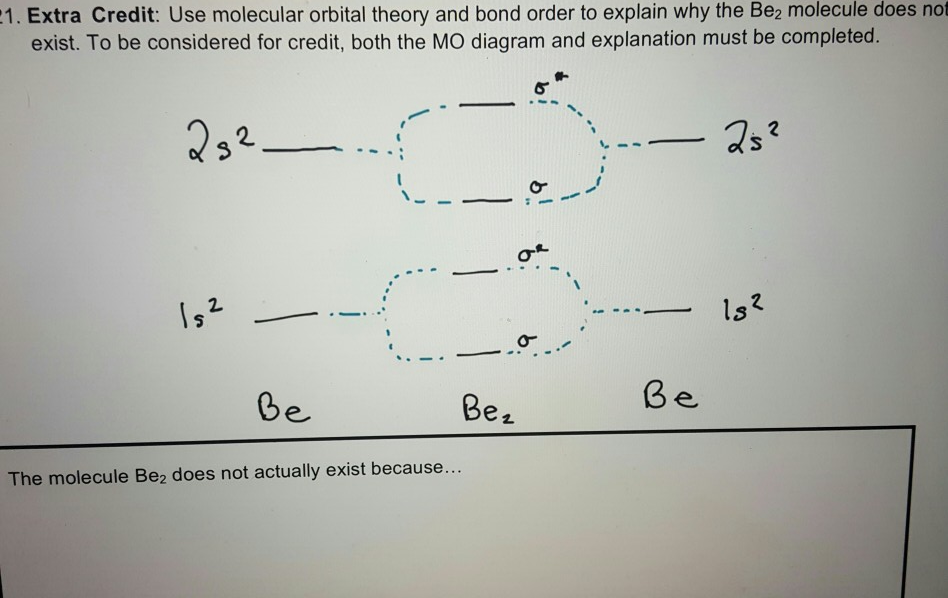
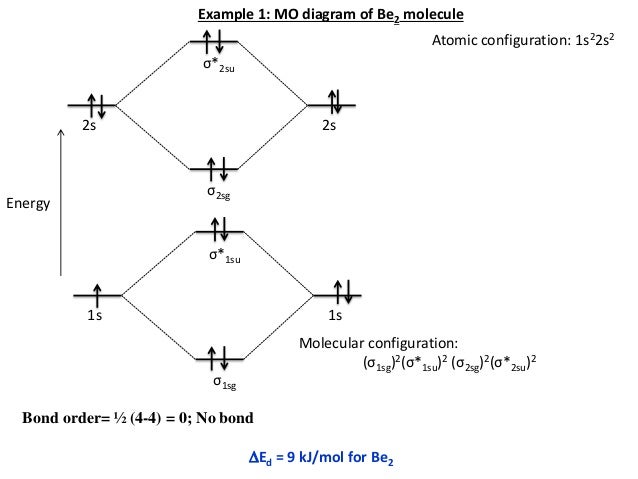
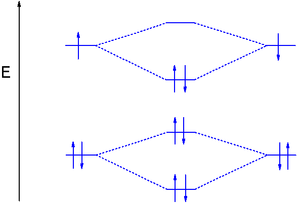
Molecular Orbital Diagram Be2 Even rather simple molecular orbital (MO) theory can be used to predict which we start reading from the bottom of the diagram because this is how MO diagrams are constructed, Diberyllium, Be2, has a bond order of zero and is unknown.

Molecular orbital diagram for be2
Re: M.O. Diagram for B2 Post by Chem_Mod » Tue Nov 11, 2014 11:21 pm As discussed in class the MO diagram for B 2 shows that it has two unpaired electrons (which makes it paramagnetic) and these electrons are in bonding molecular orbitals resulting in the equivalent bond strength of one bond. 1. Draw the molecular orbital energy level diagram for each of the following species Be2+, Be2, and Be2-. Indicate theirnumbers of unpaired electron and mention their magnetic properties.Calculate their bond orders, and state which species is moststable. Question: 1. Draw the molecular orbital energy level diagram for each of the following ... Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals. Then we rank them in order of increasing energy. We can ignore the 1s orbitals, because they do not contain the valence electrons. Each boron atom has one 2s and three 2p valence orbitals.
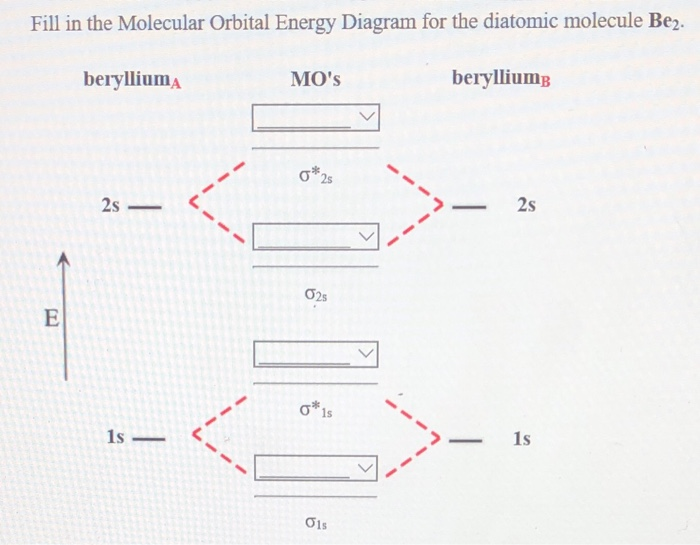
Molecular orbital diagram for be2. The valence molecular orbital diagram for Be2+ is shown, which of the following statements correctly interpret the diagram? *Be2+ is more likley to exist than Be2-be2+ has a weaker bond than H2-Mo bond order for Be2+ is 1/2. This problem has been solved! See the answer. See the answer See the answer done loading. draw the molecular orbital (MO) electron diagram for the Be2^2- molecular ion. be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in the ion, including any core electrons. Show transcribed image text. Problem 43 Hard Difficulty. Draw an MO energy diagram and predict the bond order of Be2+ and Be2-. Do you expect these molecules to exist in the gas phase?Jul 12, 2021 Construct the molecular orbital diagram for Be2- while applying the necessary rules in filling up the orbitals. Step 1: Calculate the total number of valence electrons present. Step 2: Draw the molecular orbital diagram. Recall that the bonding MOs are those without an asterisk (e.g., σ1s), while the antibonding MOs are those with an asterisk ...
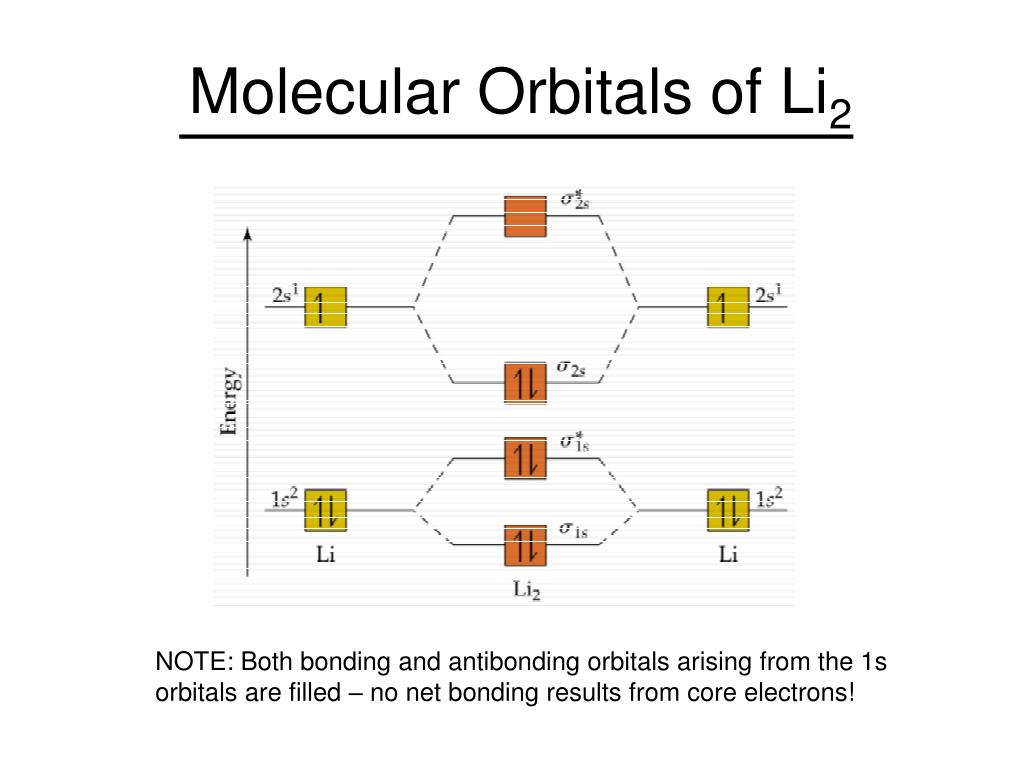
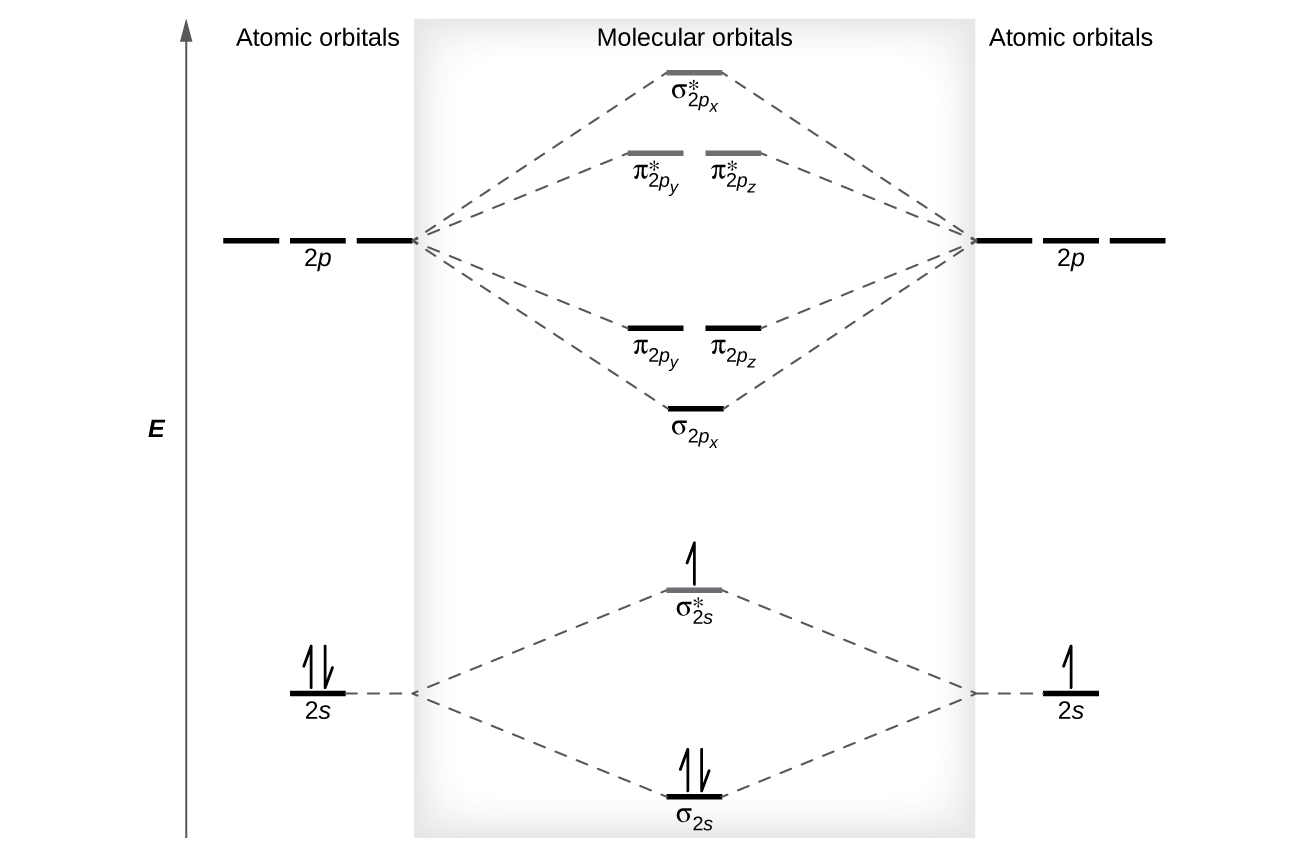
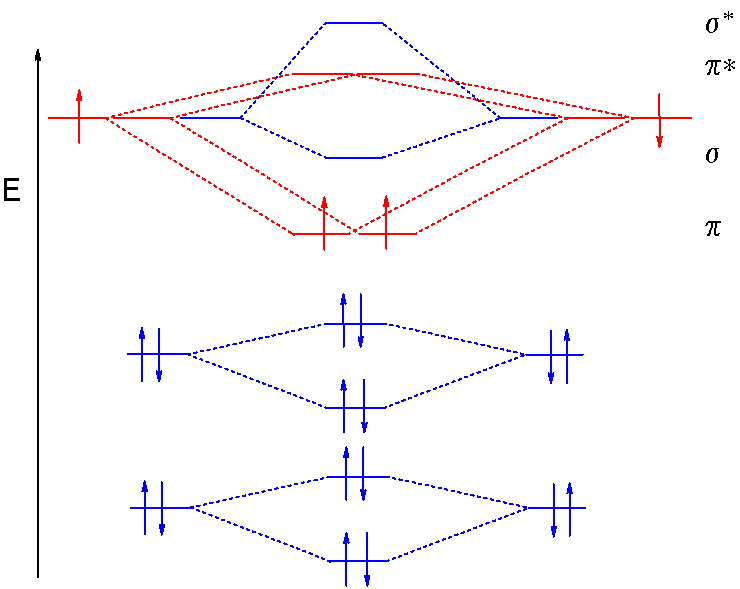
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ... Answer (1 of 8): Well, as the first point it is to be noted that an atom forms a molecule in order to get stabilised. In other word we can say that in order to form a molecule the energies of the atomic orbitals should be lowered in the molecule. Now, we know that in a molecule the atomic orbita... For the ion Be2+:a) Draw the molecular orbital diagram.b) Calculate the bond order.c) Would this ion exist?d) Write the electron configuration of the ion————... Molecular Orbital Diagrams, Bond Order, and Number of Unpaired Electrons Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule, O 2. From this diagram, calculate the bond order for O 2. How does this diagram account for the paramagnetism of O 2? Solution We draw a molecular orbital energy diagram similar to that shown in Figure 8.37.
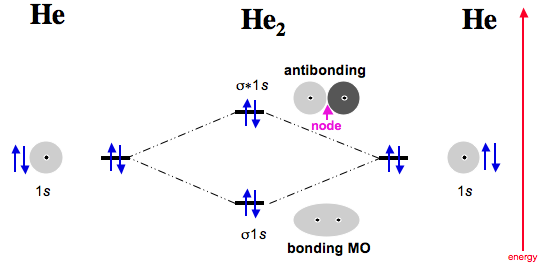
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory ... Use molecular orbital theory to explain why the Be2 molecule does not exist. ... Without the half- filled orbital, the overlapping is not possible, therefore Be2 molecule does not exist. Previous Question Next Question. Popular Questions of Class 11 Chemistry. Q:-The mass of an electron is 9.1 × 10 -31 kg. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories: Valence Bond Theory and Molecular… Electronic configuration according to molecular orbital theory: σ1s2,σ∗1s2,σ2s2,σ∗2s2. Solve any question of Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure with ...1 answer · Top answer: Total no. of electrons in Be2 = 8 .Electronic configuration according to molecular orbital theory: σ1s^2 , σ^*1s^2 , σ2s^2 , σ^*2s^2
+ and Be2.A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. 1.
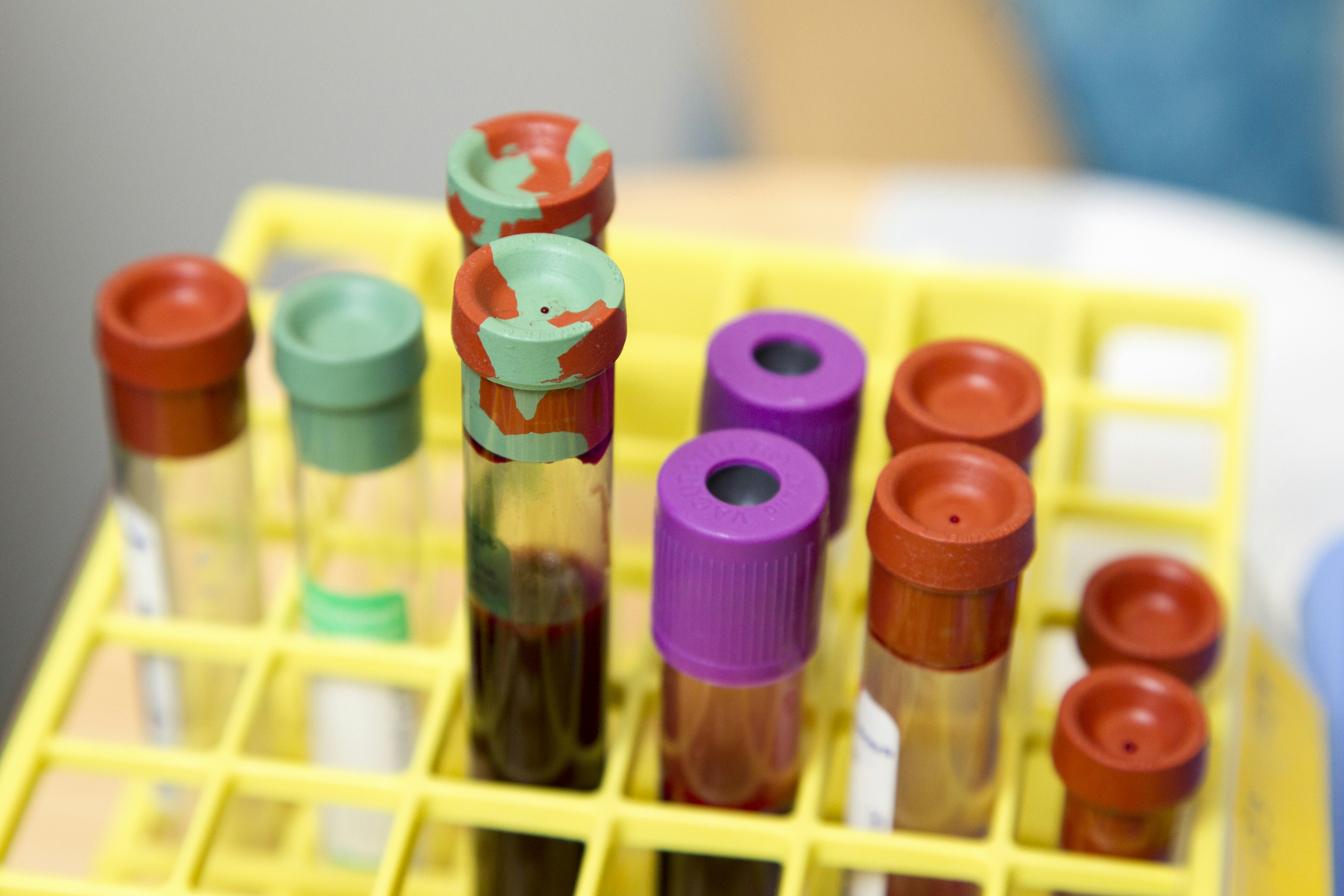
Vials of Blood. Vials of blood taken in the course of patient care at the National Institutes of Health Clinical Center in Bethesda, Maryland. Test tubes. Blood test. Creator: Daniel Sone
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
Aug 11, 2018 · Molecular Orbital Diagram Be2. Even rather simple molecular orbital (MO) theory can be used to predict which we start reading from the bottom of the diagram because this is how MO diagrams are constructed, Diberyllium, Be2, has a bond order of zero and is unknown.
So the bond order of B2 is equal to 1, which you can get by drawing the molecular orbital diagram and performing the equation Bond Order = . 5 * (# of bonding electrons - # of antibonding electrons). However, when you draw the Lewis structure of B2, you get a triple bond . Is B2 molecule is paramagnetic or diamagnetic explain?
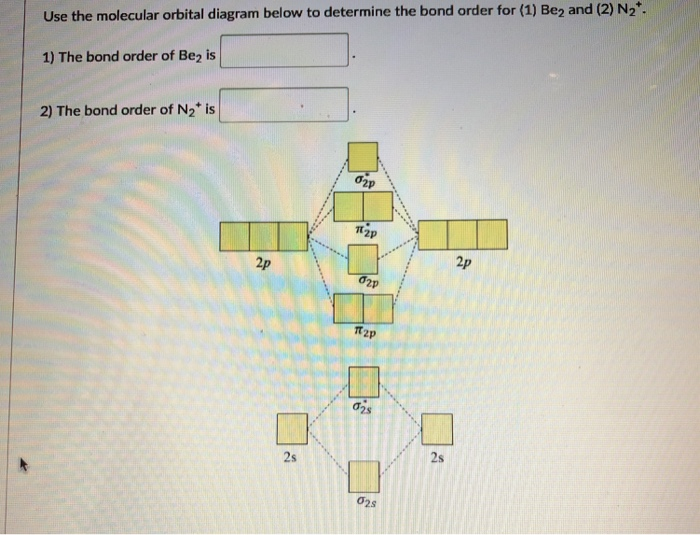
Hint: According to the molecular orbital theory, the bond order is defined as the number of covalent bonds in a molecule. Bond order is equal to half of the ...

A technician viewing a blot on a fluorescence microscope while another technician is using a pipette at the Advanced Technology Research Facility (ATRF), Frederick National Laboratory for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute.
from the above mo diagram we can see that number of elctrons in the bonding and antibonding orbital is same and hence be does not form be2 molecule (for.may 04, · turning to [be2]^- we have [be2]^- 5 valence e⁻s: σ1 (2e⁻) σ2 (2e⁻) π1 (1e⁻) σ3 (0e⁻) π2* (0e⁻) σ4* (e⁻) bond order = ½ [σ (bonding e⁻) - σ (antibonding e⁻)] so if we take the bonding …
(i) Be2 molecule: The electronic configuration of Be(Z = 4) is: 4 Be 1s 2 2s 1 Be 2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both beryllium atoms. Number of valence electrons in Be atom = 2 Thus in the formation of Be 2 molecule, two outer electrons of each Be atom i.e. 4 in all, have to be accommodated in various molecular orbitals in the increasing order of their energies.
This video discusses how to draw the molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the Be2+ ion. The bond order of Be2+ is also calculated and the meaning of this numbe...
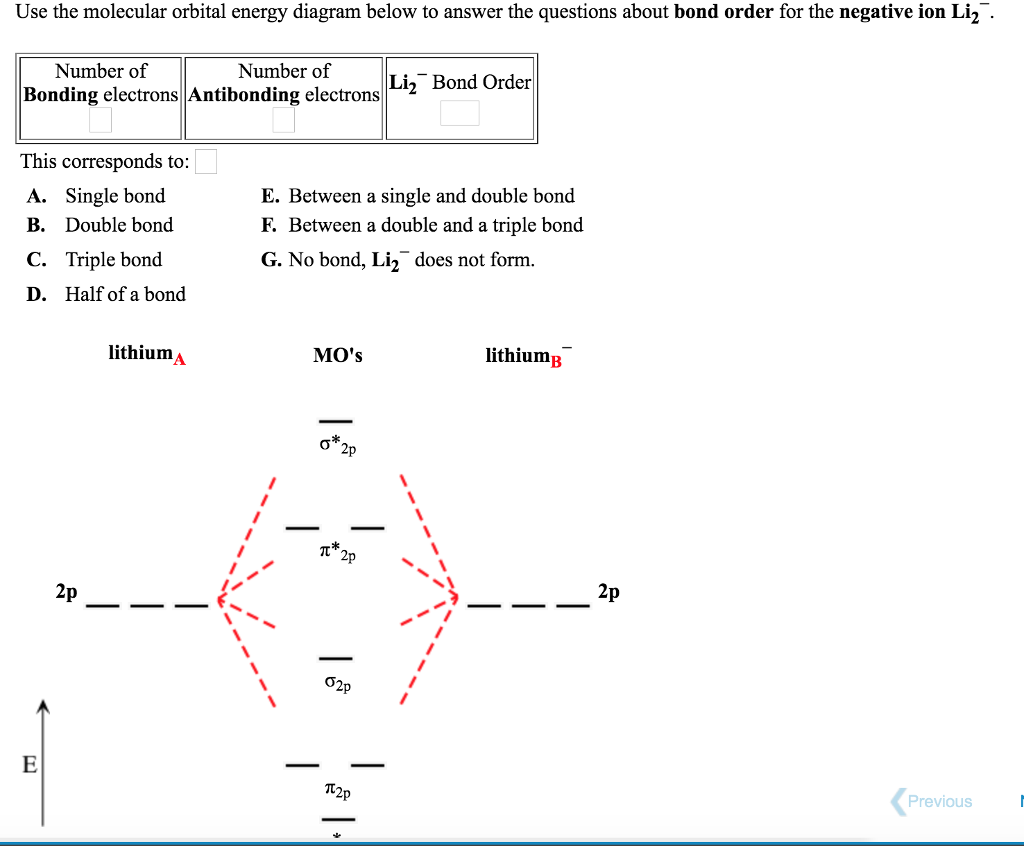
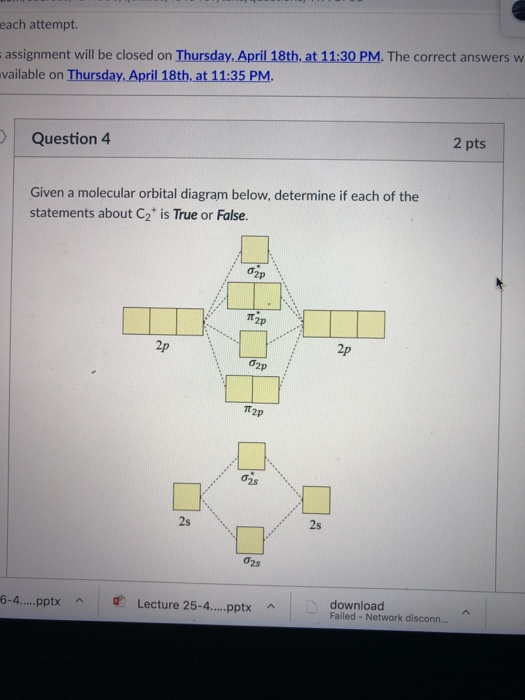
The lowest energy unoccupied molecular orbital is 2pσ, so that is where the extra electron will be added. The electron configuration of the neutral C2 molecule is -- I'll use the notation given to you in the diagram. C2:(1sσ)2(1s* σ)2(2sσ)2(2s* σ)2(2pπ)4. The electron configuration of the C− 2 ion will be.
Watch the video solution for the question: What is the bond order of Be2 −? ... And yes, we do need to draw our molecular orbital diagram in order for us ...Sep 18, 20201 answer · Top answer: 0.5
Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals. Then we rank them in order of increasing energy. We can ignore the 1s orbitals, because they do not contain the valence electrons. Each boron atom has one 2s and three 2p valence orbitals.
1. Draw the molecular orbital energy level diagram for each of the following species Be2+, Be2, and Be2-. Indicate theirnumbers of unpaired electron and mention their magnetic properties.Calculate their bond orders, and state which species is moststable. Question: 1. Draw the molecular orbital energy level diagram for each of the following ...
Re: M.O. Diagram for B2 Post by Chem_Mod » Tue Nov 11, 2014 11:21 pm As discussed in class the MO diagram for B 2 shows that it has two unpaired electrons (which makes it paramagnetic) and these electrons are in bonding molecular orbitals resulting in the equivalent bond strength of one bond.
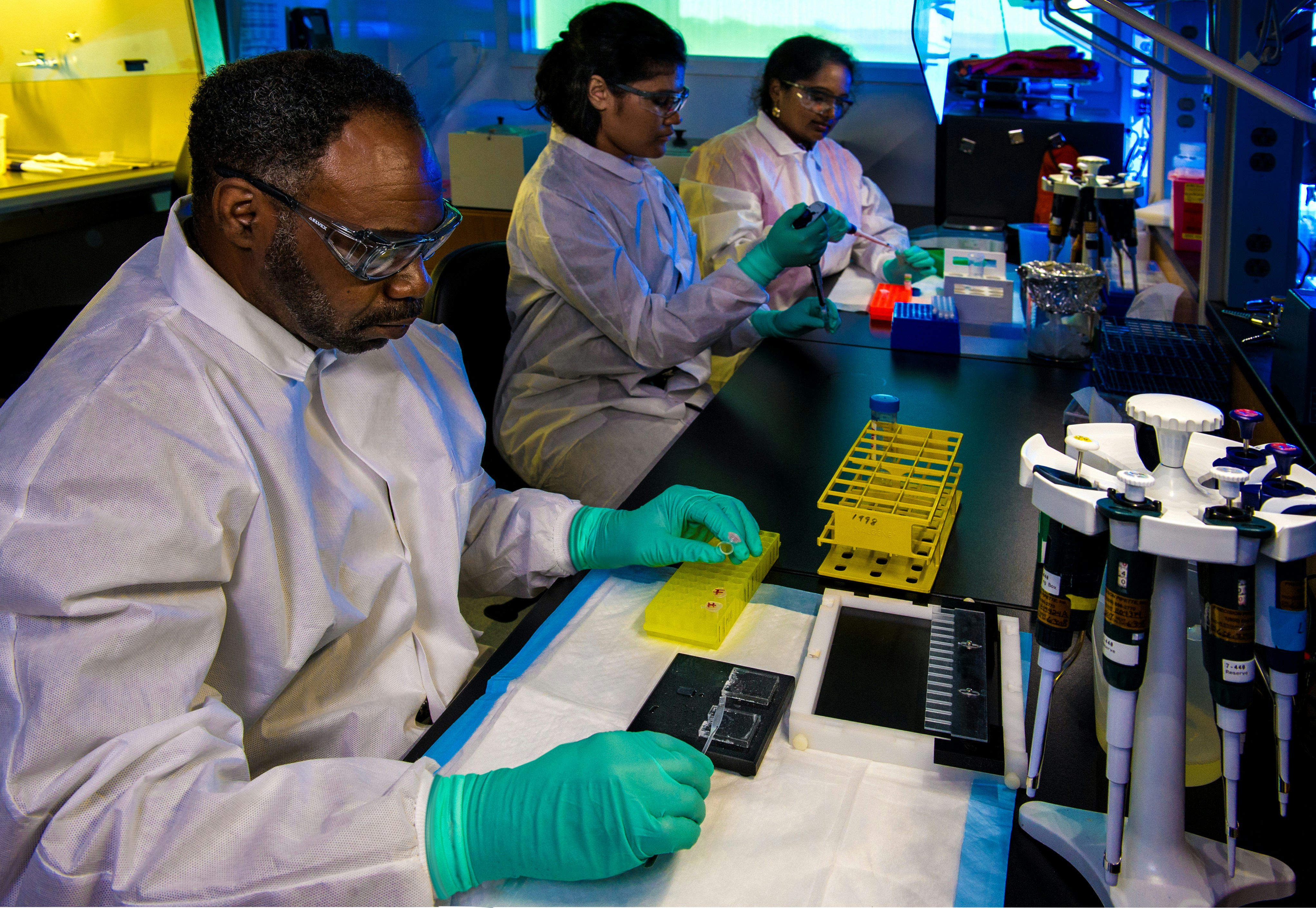

This photograph depicted Enteric Diseases Laboratory Branch (EDLB), Public Health scientists, as they were preparing enteric bacteria samples for “DNA fingerprinting�, using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE).
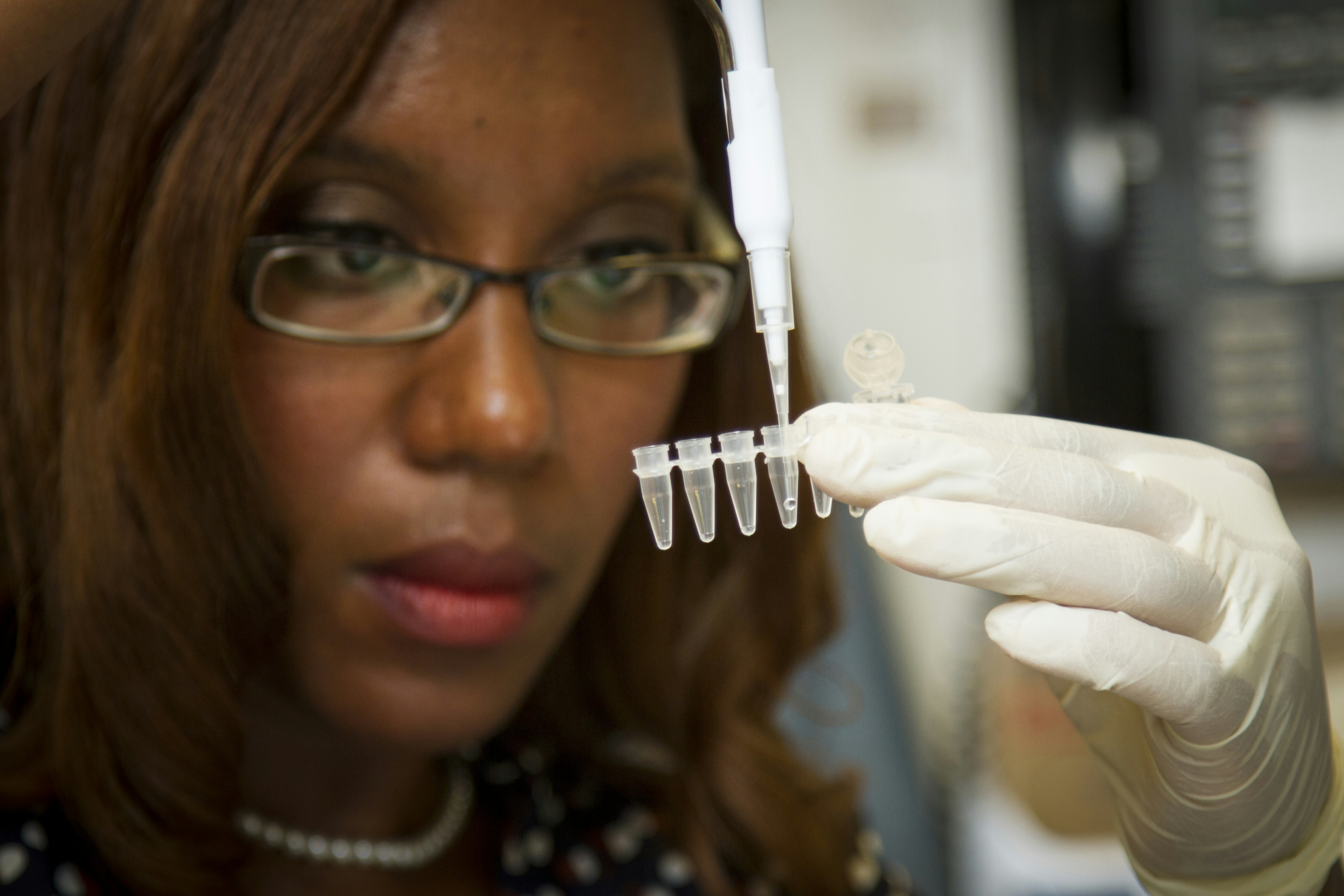
Chanelle Case Borden, Ph.D., a postdoctoral fellow in the National Cancer Institute's Experimental Immunology Branch, pipetting DNA samples into a tube for polymerase chain reaction, or PCR, a laboratory technique used to make multiple copies of a segment of DNA.











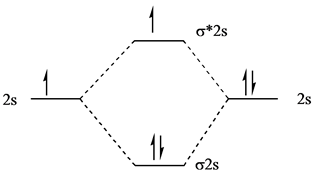






0 Response to "42 molecular orbital diagram for be2"
Post a Comment