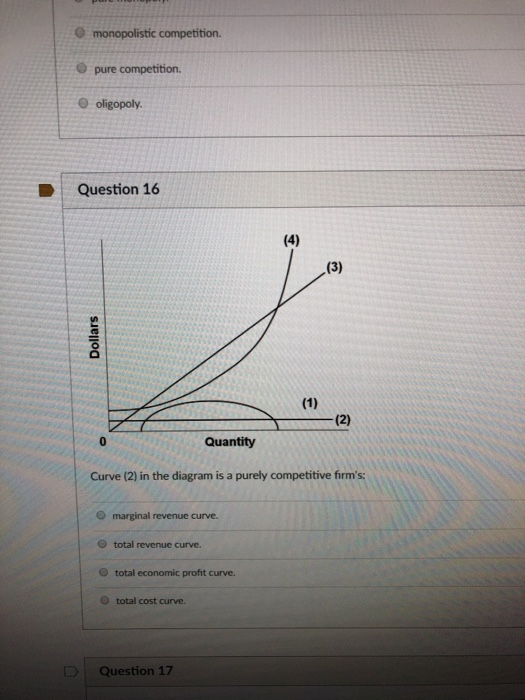
37 curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's
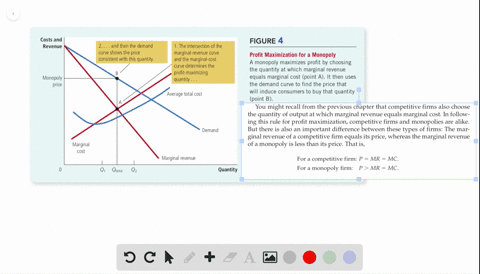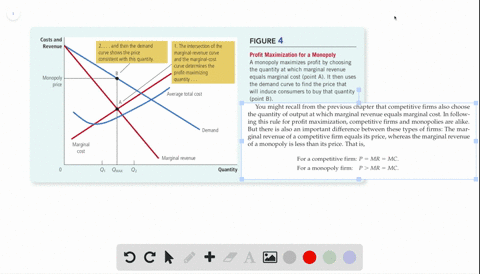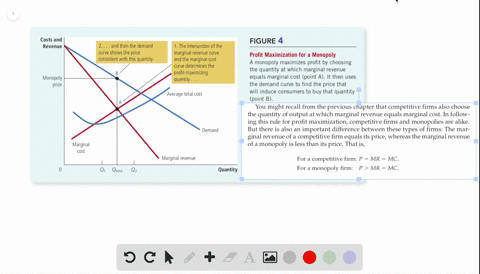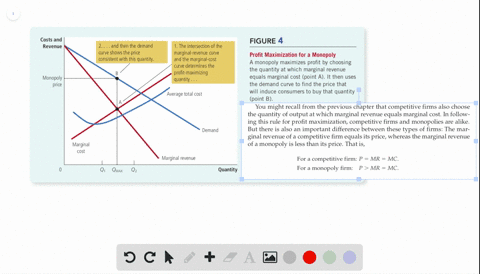
Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Marginal revenue will be zero at output: A. q 4. B. q 3. C. ... is less elastic than a purely competitive firm's demand curve. B. is perfectly elastic. C. ... In Figure 2 the firm's demand and marginal revenue curves are represented by: A. Business. Economics. Economics questions and answers. O pure competition. O oligopoly. Question 16 0 Quantity Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: O marginal revenue curve. O total revenue curve. O total economic profit curve. O total cost curve. Question 17.
Curve (1) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. total economic profit curve. Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. marginal revenue curve. Refer to the diagram. Other things equal, an increase of product price would be shown as ... Each purely competitive firm's demand curve is perfectly _____ at the equilibrium price.
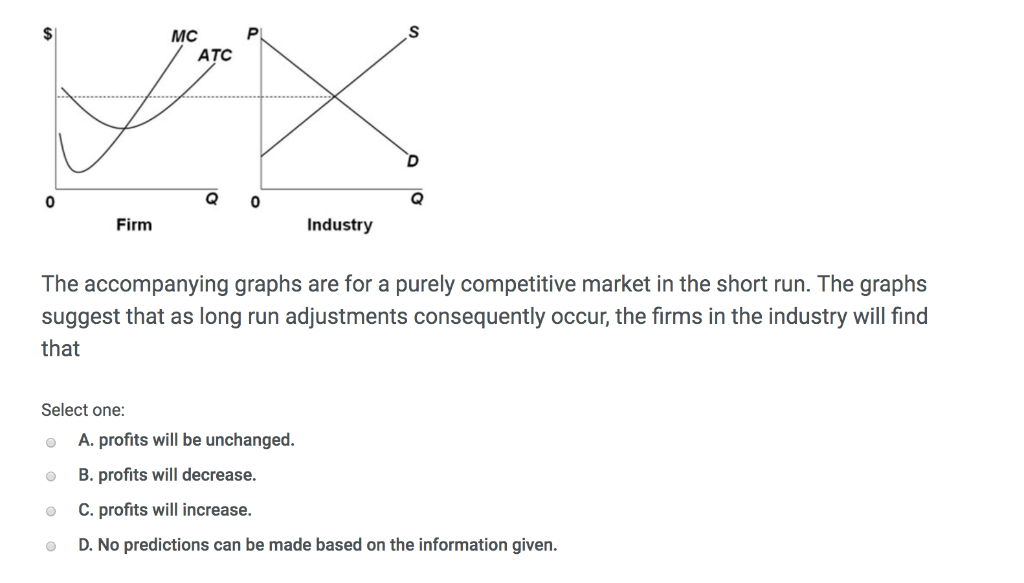
Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's
38. Curve (2) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve. B. total revenue curve. C. marginal revenue curve. D. total economic profit curve. Answer: C Topic: Profit maximization in the short run. Learning Objective: 11-03: Convey how purely competitive firms maximize profits or minimize losses in the short run. 73. Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. The firm's short-run supply curve is: A) the abcd segment of the MC curve. C) the cd segment of the MC curve. B) the bcd segment of the MC curve. D) not shown. Answer: B. Type: A Topic: 3 E: 424 MI: 180 74. The short-run supply curve of a purely competitive producer is based on ... Any level of output between 100 and 440 units will yield an economic profit. Curve (1) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. total economic profit curve. Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. marginal revenue curve. Curve (3) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. total revenue curve.
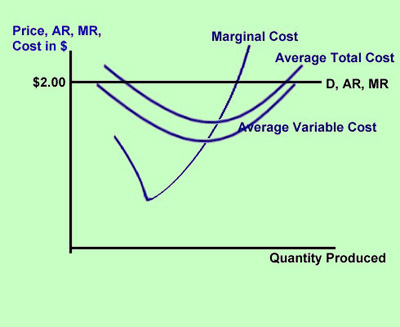
Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. Curve (2) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve.B. total revenue curve.C. marginal revenue curve.D. total economic profit curve. 15. Curve (3) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve.B. total revenue curve.C. marginal revenue curve.D. total economic profit curve. 27. In the short run a purely competitive firm will always make an economic profit if: D. P > ATC. 28. Suppose that at 500 units of output marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost. The firm is selling its output at $5 per unit and average total cost at 500 units of output is $6. On the basis of this information we: Marginal Cost and the Firm's Supply Curve. For a perfectly competitive firm, the marginal cost curve is identical to the firm's supply curve starting from the minimum point on the average variable cost curve. To understand why this perhaps surprising insight holds true, first think about what the supply curve means. Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's; Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: The demand schedule or curve confronted by the individual, purely competitive firm is; The demand schedule or curve confronted by the individual purely competitive firm is ...
43. Curve (1) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A) total cost curve. C) marginal revenue curve B) total revenue curve. D) total economic profit curve. Answer: D. Type: G Topic: 3 E: 416 MI: 172 44. Curve (2) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's A) total cost curve. C) marginal revenue curve B) total revenue ... The diagram shows the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's economic profit answer choices A) Both purely competitive and monopolistic firms are "price takers." B) Both purely competitive and monopolistic firms are "price makers." C) A purely competitive firm is a "price taker," while a monopolist is a "price maker." D) A purely competitive firm is a "price maker," while a monopolist is a "price taker." Technological advance improves productivity in a purely competitive industry. This change will result in a shift A. down of the individual firm's MC curve, causing the market supply curve to shift to the left. B. down of the individual firm's MC curve, causing the market supply curve to shift to the right.
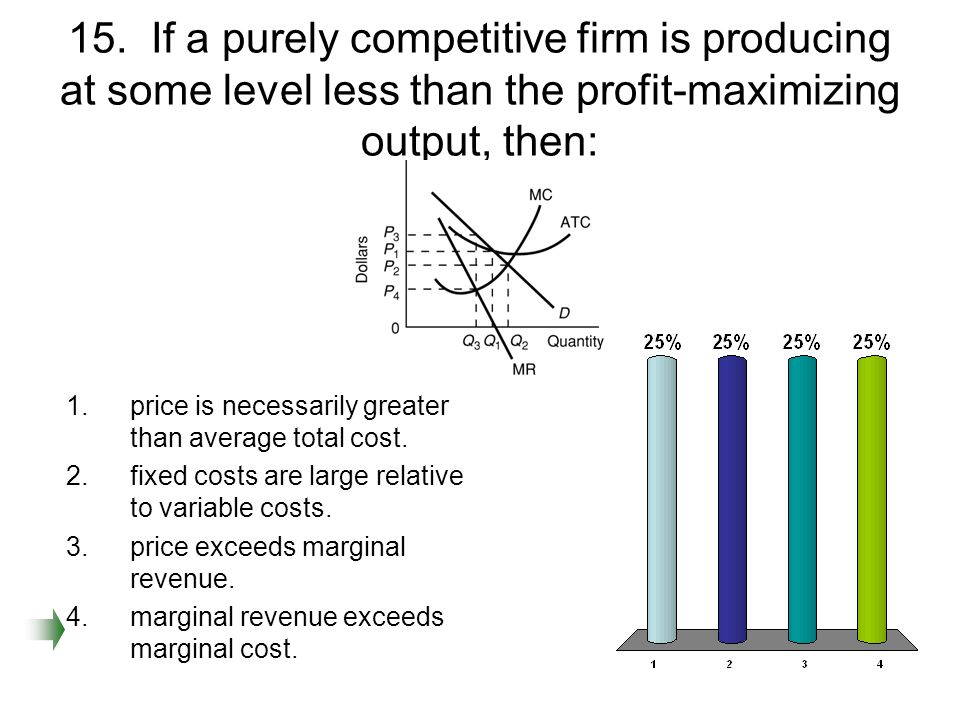
refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. The firm's short-run supply curve is a) the abcd segment and above on the MC curve b) the bcd segment and above on the MC curve c) the cd segment and above on the MC curve d) not shown 38. Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve. B. total revenue curve. C. marginal revenue curve. D. total economic profit curve. AACSB: Reflective Thinking Blooms: Apply Difficulty: 2 Medium Learning Objective: 10-04 Convey how purely competitive firms can use the total-revenue-total-cost approach to maximize profits or minimize losses in the short run. C. purely competitive market. D. oligopolistic market. 14. Refer to the above data. If the firm's minimum average variable cost is $10, the firm's profit-maximizing level of output would be: A. 2. B. 3. C. 4. D. 5. 15. Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. If product price is P3: A. the firm will maximize profit at point d. If firms enter a purely competitive industry, then in the long run this change will shift the industry: A. demand curve to the left, and the market price will decrease.
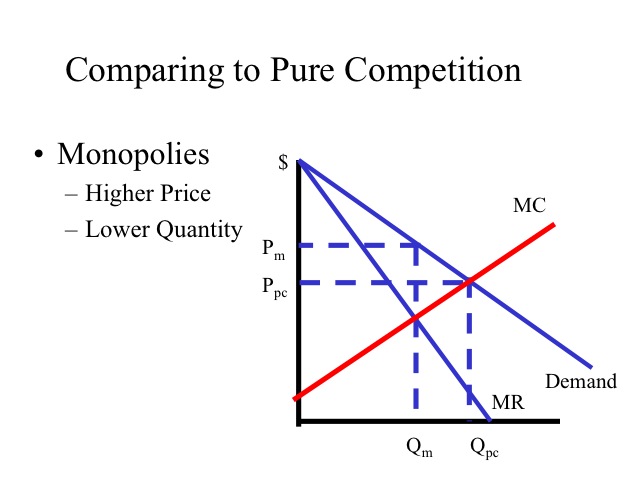
less elastic than that of either a pure monopolist or a purely competitive seller. B. less elastic than that of a pure monopolist, but more elastic than that of a purely competitive seller. ... This firm's profit-maximizing price will be: A. $10. B. $13. C. $16. D. $19. 5. ... production for the firm shown in the diagram above is: A.
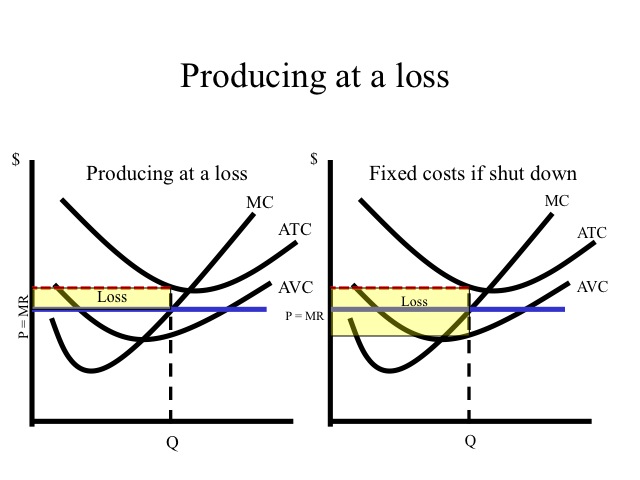
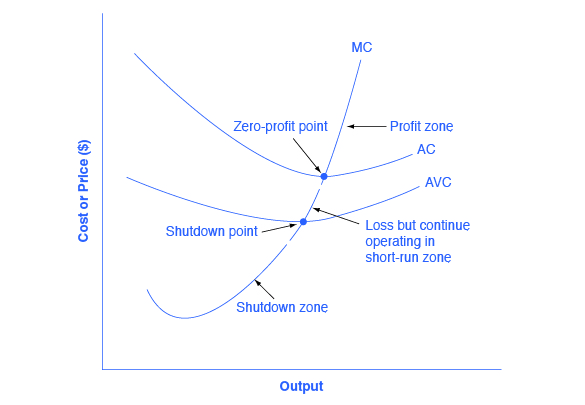
Refer to the above diagram showing the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. Suppose this firm is maximizing its total profit and the market price is $15. The firm's per unit profit is:
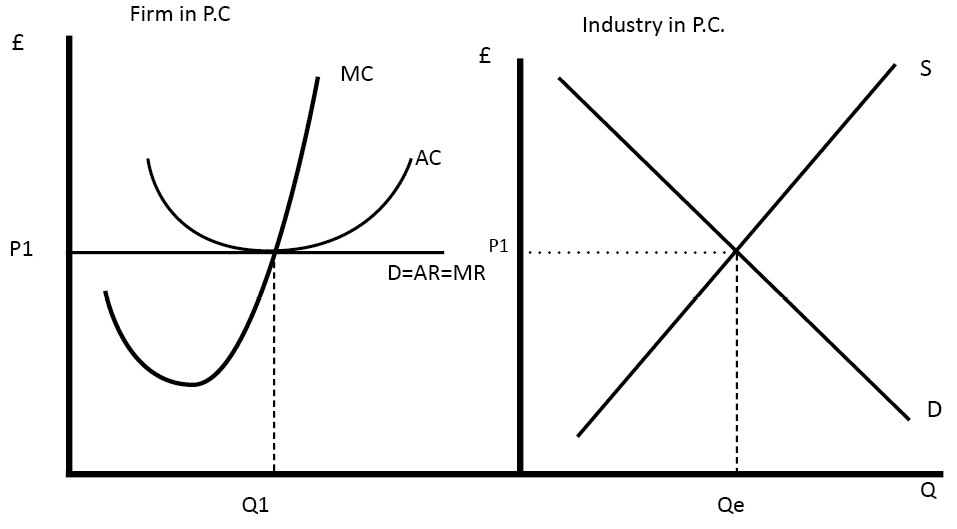
Note that the demand curve for the market, which includes all firms, is downward sloping, while the demand curve for the individual firm is flat or perfectly elastic, reflecting the fact that the individual takes the market price, P, as given.The difference in the slopes of the market demand curve and the individual firm's demand curve is due to the assumption that each firm is small in size.
The demand curve for a purely competitive firm is perfectly elastic, but the demand curve for a purely competitive industry is downsloping. Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: a. total cost curve b. total revenue curve c. marginal revenue curve d. total profit curve.
Curve (3) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's total cost curve. total revenue curve. marginal revenue curve. total economic profit curve. References Multiple Choice Difficulty: 02 Medium Learning Objective: 10-04 Convey how purely competitive firms can use the total-revenue-total-cost approach to maximize profits or minimize losses in the short run.
39. Curve (3) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve. B. total revenue curve. C. marginal revenue curve. D. total economic profit curve. AACSB: Reflective Thinking Bloom's: Level 3 Apply Difficulty: 2 Medium Learning Objective: 08-03 Convey how purely competitive firms maximize profits or minimize losses in the short run. ...
The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. If the market price for this firm's product is $87, it will produce Multiple Choice 8 units at an economic profit of $130.72. 6 units at a loss of $90. 9 units at an economic profit of zero. 9 units at an economic profit of $281.97.
Curve (1) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A) total cost curve. C) marginal revenue curve B) total revenue curve. D) total economic profit curve. Answer: D. McConnell/Brue: Economics, 16/e Page 695. Type: G Topic: 3 E: 416 MI: 172 44.
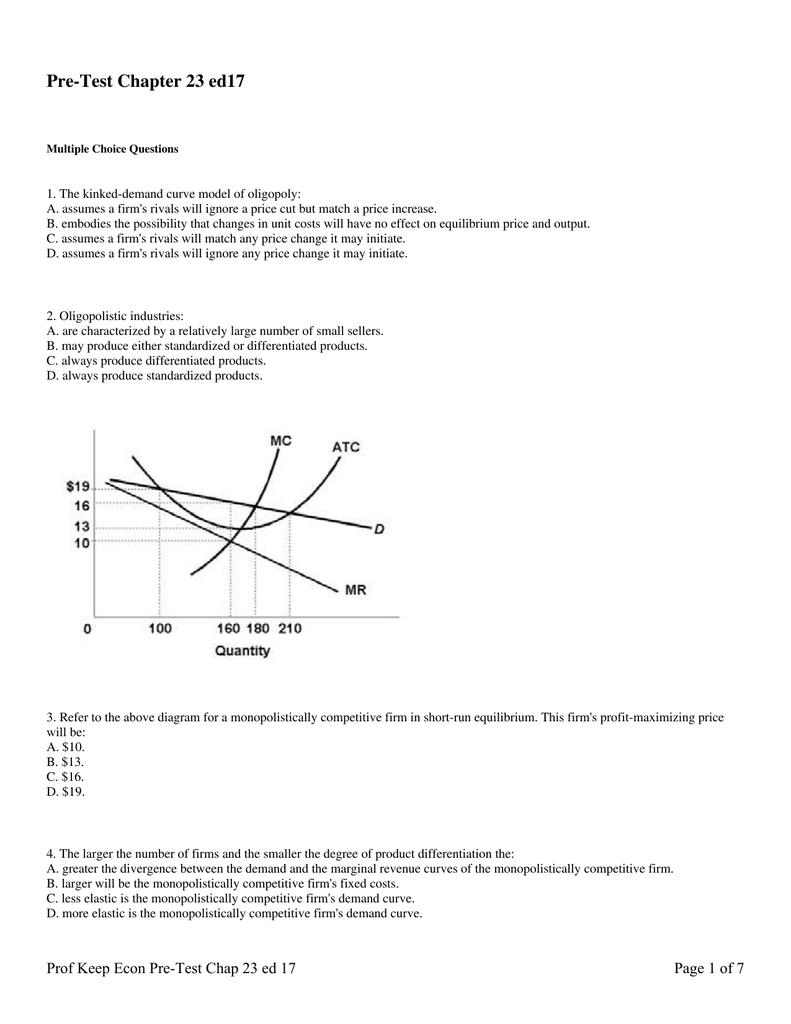
is the same as that of a purely competitive indiLstry is its average variable cost curve does not exist because prices are not "given" to a monopolist. Use the following to answer questions 15-16: $19 100 MC ATC MR 160 180 210 Quantity 15, Refer to the above diagram for 8 monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm's ...
Any level of output between 100 and 440 units will yield an economic profit. Curve (1) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. total economic profit curve. Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. marginal revenue curve. Curve (3) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. total revenue curve.
73. Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. The firm's short-run supply curve is: A) the abcd segment of the MC curve. C) the cd segment of the MC curve. B) the bcd segment of the MC curve. D) not shown. Answer: B. Type: A Topic: 3 E: 424 MI: 180 74. The short-run supply curve of a purely competitive producer is based on ...
38. Curve (2) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve. B. total revenue curve. C. marginal revenue curve. D. total economic profit curve. Answer: C Topic: Profit maximization in the short run. Learning Objective: 11-03: Convey how purely competitive firms maximize profits or minimize losses in the short run.
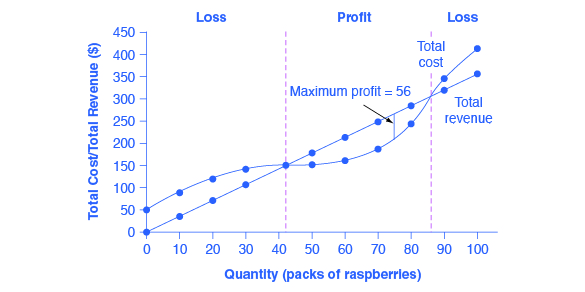



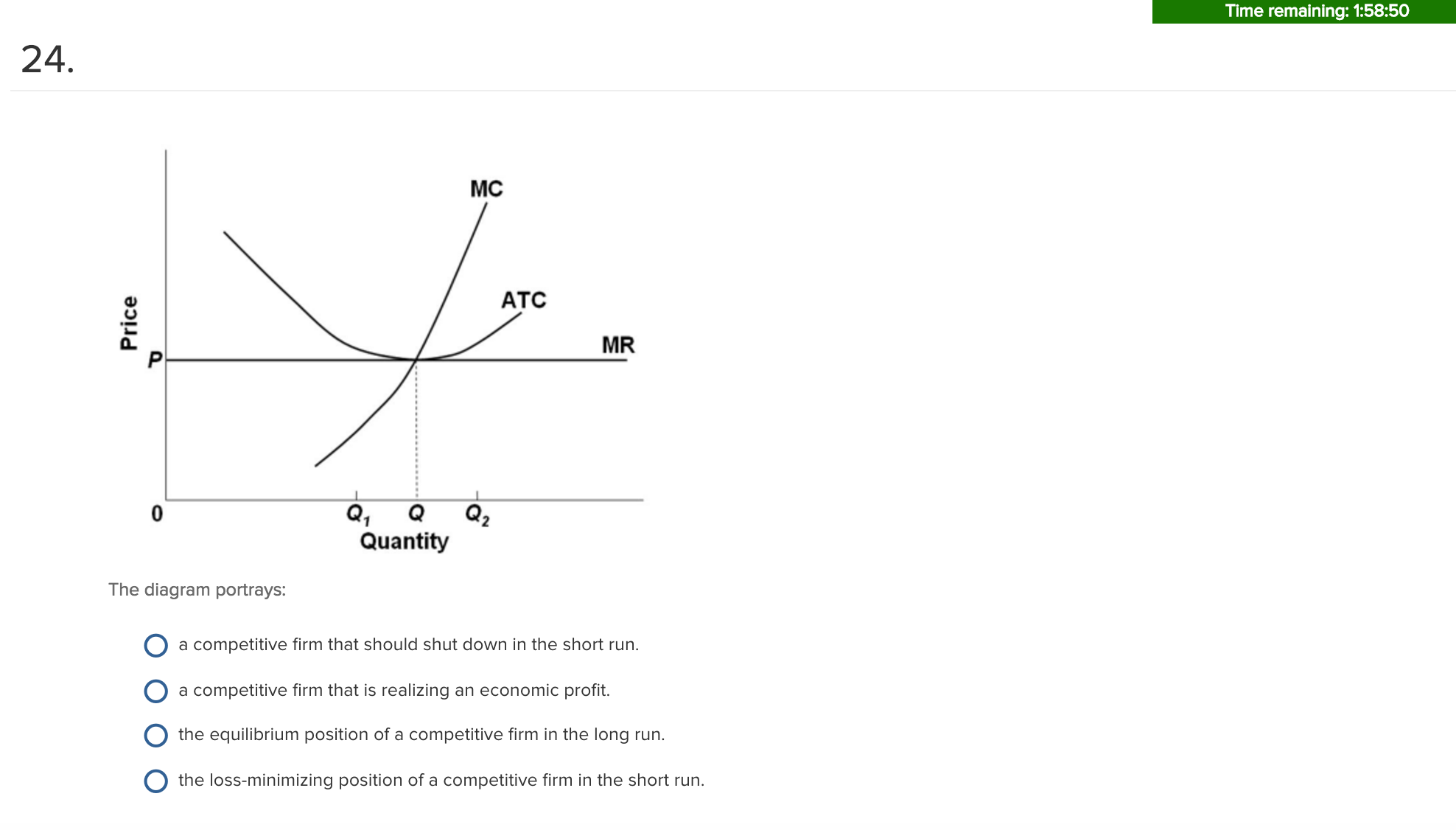

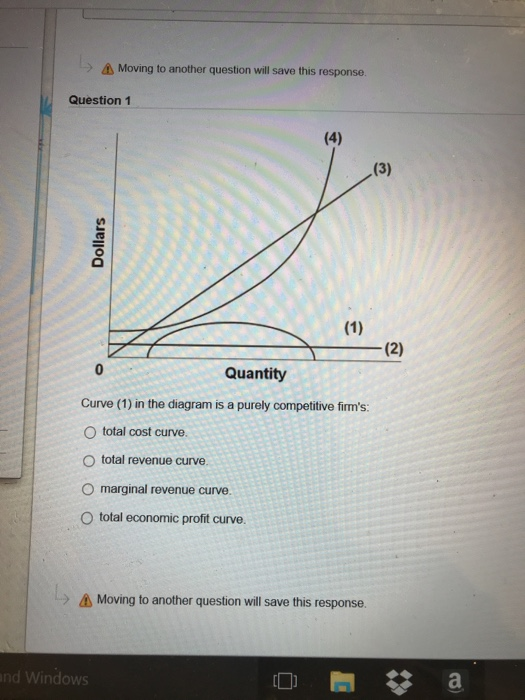









0 Response to "37 curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's"
Post a Comment