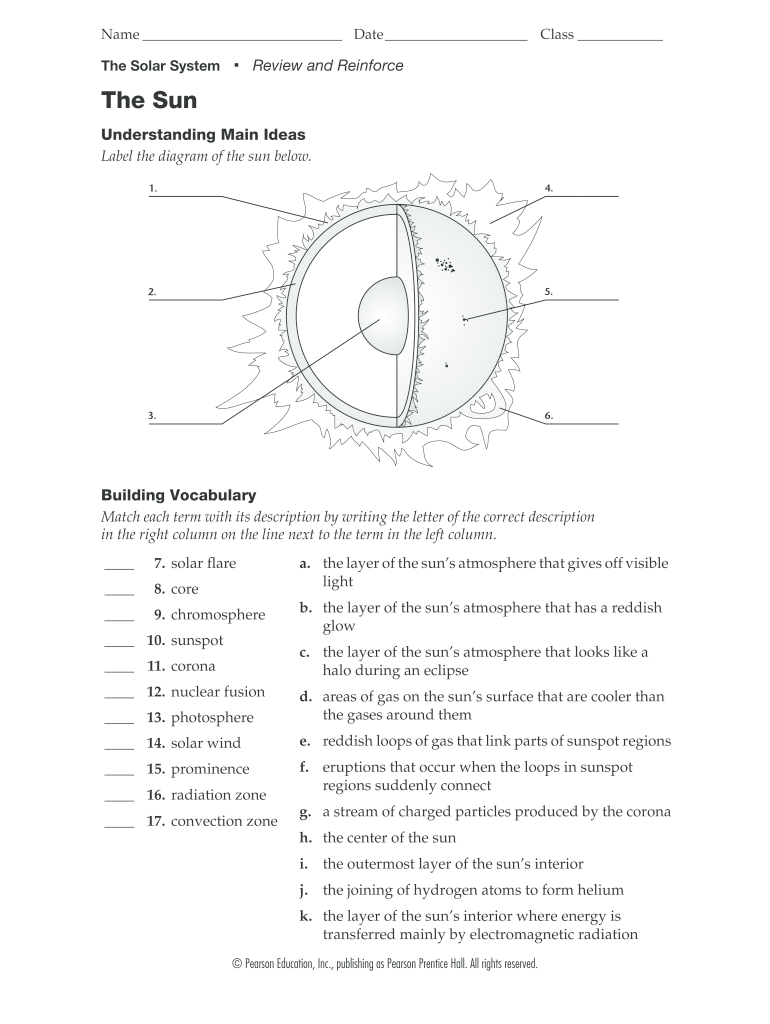
37 label the diagram of the sun below
Base your answers to questions 6 through 9 on the diagram below. The diagram is a model of the sky (celestial sphere) for an observer at 50° N latitude. The Sun's apparent path on June 21 is shown. 6. On the diagram mark with a dot the position of Polaris as viewed by the observer. Label this dot "Polaris." 7. The diagram below shows the position of the sun, moon, and Earth. The labels A, B, C, and D represent four coastlines on Earth. A D Earth B Moon Sun C As Earth rotates, coastline C moves to where coastline B is. Which statement is correct about coastline C in its new position? A.) It will experience a low tide because it experiences the least ...
The Layers of the Sun beneath the Visible Surface. Interior Structure of the Sun. In this cutaway illustration of the Sun, a triangular. Figure 3. Parts of ...
Label the diagram of the sun below
The sun's corona is normally visible only during a total solar eclipse when it is seen as an irregularly shaped pearly glow surrounding the darkened disk of the moon. Sunspots It is a spot or patch appearing from time to time on the sun's surface, appearing dark by contrast with its surroundings. A Diagram of the Earth-Sun Relationship Notice that the Earth's tilt is always directed towards one place in space (in this model, it is towards the left. But notice all you need to do is move your perspective to underneath or some other side, and saying the pole tilts towards "the left" becomes meaningless. Analyze the given diagram of the carbon cycle below. An image of carbon cycle is shown. The sun, a cloud, two trees, one towards left and the other towards right, an animal, lake, and a factory are included. Arrow A points from the sun to the left tree. Arrow B points from the air above the clouds to the left tree.
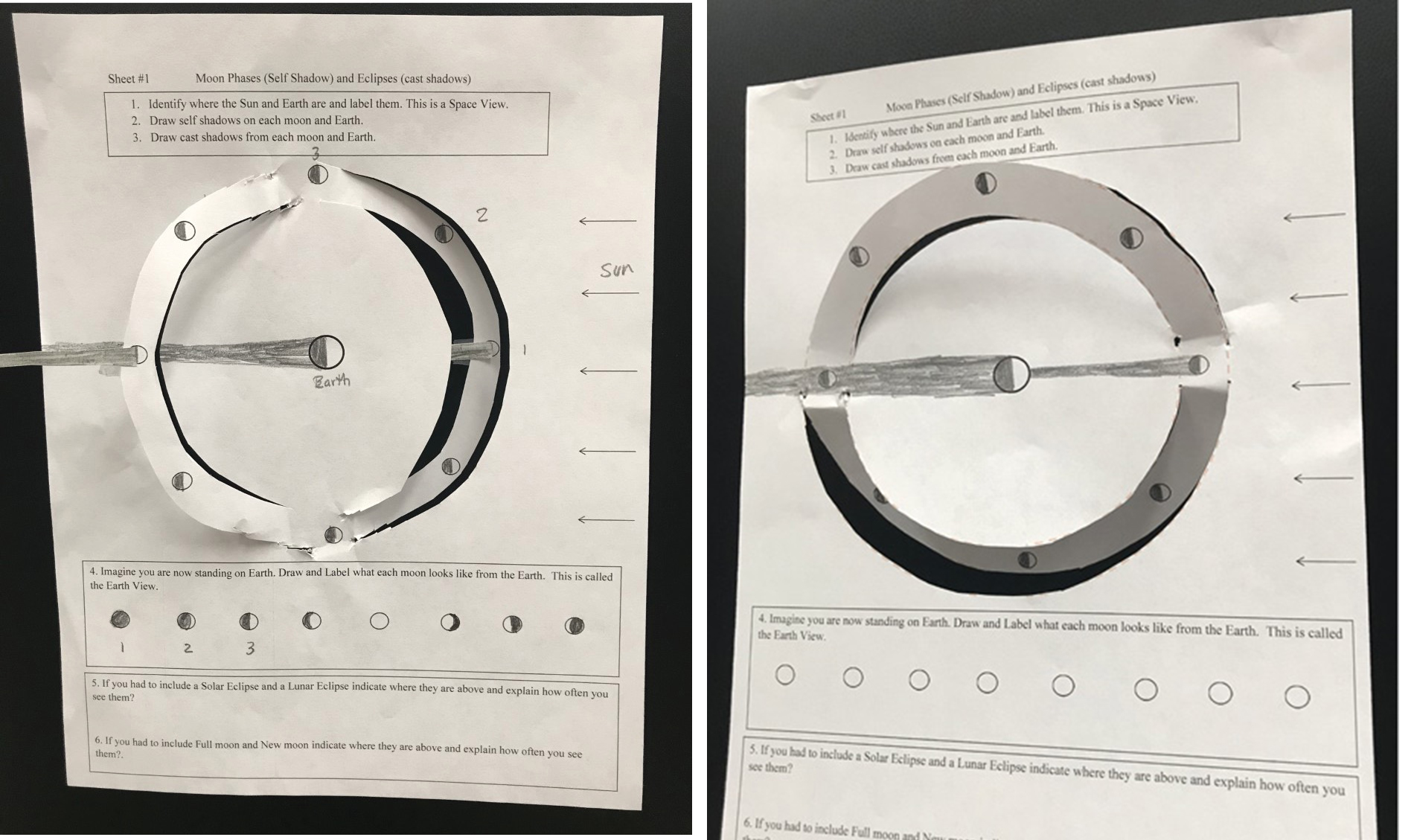
Label the diagram of the sun below. Use the word bank to label the diagram below Asthenosphere Lithosphere To scale Inner Core Outer Core Continental Crust Core Crust Oceanic Crust Liqtid Mantle Mesosphere 2.900 km ... the size of the Sun relative to the planets. c the planets are shown in the correct order d. the relative distance between the planets This diagram features pictures of the Sun, Earth and Moon, as well as circular lines denoting Earth and the Moon's orbits around the Sun and Earth respectively. To complete the activity, students must identify and label each of the three bodies and two orbits. This would be a good activity to give pupils at the start of a series of lessons on ... Sep 13, 2016 · Diagram: Below is a diagram of the Sun, originally developed by NASA for educational purposes. Visible, IR and UV radiation – The light that we see coming from the Sun is visible, but if you ... 1. Draw and label a diagram of the Earth-sun-moon system that you modeled. Include the revolution and rotation of the moon. 2. Use your model to explain the phenomena below. Why do people on Earth only see one side of the moon? What causes the moon to rise and set?
The Sun: A Diagram. Get to know Earth's star with with this diagram and vocabulary worksheet! Children will learn important solar terminology and trivia as they review a diagram of the Sun. They will then reinforce what they have learned through five reading comprehension questions. Read the definitions, then label the diagram below. Sun - The Sun is a star at the center of our Solar System. Mercury - Mercury is the planet closest to the Sun. Venus - Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is the hottest planet. Earth - Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the planet we live on. Label the diagram below of the GREENHOUSE EFFECT: 1. the Sun 2. incoming solar radiation 3. atmosphere 4. radiation reflected off the earth 5. outgoing solar radiation 6. solar radiation passes through atmosphere 7. earth 8. infrared radiation from the surface 9. some of the infrared radiation is absorbed and re-emitted by the greenhouse effect ... 7. solar flare a. the layer of the sun's atmosphere that gives off visible light 8. core 9. Question: The Solar System The Sun Understanding Main Ideas Label the diagram of the sun below. Building Vocabulary Match each term with its description by writing the letter of the correct description in the right column on the line next to the term in ...
an area on the Sun where magnetic fields are concentrated; sunspots, prominences, flares, and CMEs all tend to occur in active regions. apparent brightness. a measure of the amount of light received by Earth from a star or other object—that is, how bright an object appears in the sky, as contrasted with its luminosity. Label the diagram of the sun below. 1. 2. 3. Building Vocabulary Match eachterm with its description by writing the letter of the correct description in the right column on the line next to the term in the left column. 7. solar flare a. the layer of the sun's atmosphere that gives off visible light b. the layer of the sun's atmosphere that has ... Which statement below best describes the orbit of the Earth around the sun? A. The Earth orbits the sun with its axis always tilted away from the sun. ... This diagram is to represent what the Earth looks like for each of the four seasons. • Label the sun - "SUN" (1 point) • Use a line to represent the tilt on each of the four Earths ... See the diagram of the full moon below. Depending on earth's, moon's and sun's positions we see a different area of the moon being illuminated by the sun. The changing positions appear to us as different moon phases. When the earth, the moon and the sun are almost aligned, most of the surface of the moon (as seen from the earth) is illuminated ...
The Sun Understanding Main Ideas Label the diagram of the sun below. Building Vocabulary Match each term with its description by writing the letter of the correct description in the right column on the line next to the term in the left column. 1. 3. 2. 4. 5. 6. ____ 7. solar flare ____ 8. core ____ 9. chromosphere ____ 10. sunspot ____ 11. corona
File:Sun diagram.svg. Size of this PNG preview of this SVG file: 600 × 600 pixels. Other resolutions: 240 × 240 pixels | 480 × 480 pixels | 768 × 768 pixels | 1,024 × 1,024 pixels | 2,048 × 2,048 pixels | 1,800 × 1,800 pixels. This is a file from the Wikimedia Commons. Information from its description page there is shown below.
The sun worksheet answers.Displaying top 8 worksheets found for - The Sun Answers. Some of the worksheets for this concept are Solar energy the power of the sun Our amazing powerful sun work answer key The sun work Unit earth and space science planets stars Our moon Lesson 2 all about sunscreens teacher materials Chapter 25skill 1 earths seasons Main idea and details.
Lesson Summary Students draw and label the parts of the Sun that they are familiar with. ... The Sun's inverted image will appear on the paper below.
(a) Sketch a Hertzsprung−Russell diagram on the axes on the graph below. Label the position of the main sequence, white dwarf and giant stars. (3) (b) Label the minimum and maximum values on the scale of each axis. (2) (c) Some of the properties of three stars are shown in the table below.
The Sun’s rotation rate differs according to latitude: as seen from the Earth, the equatorial region rotates with a period of about 27 days, while the rotational period closer to the poles is about 32 days (Table 2–1). _____ * The Sun’s rotational period as observed from Earth is known as the synodic period . Because the Earth moves about
Label these parts of the Sun in the diagram below: PROMINENCE, PHOTOSPHERE, SUNSPOT, CORONA, CORE, RADIATIVE ZONE, CONVECTIVE ZONE, CHROMOSPHERE 2. Fill in the 5 answers in the table below: Name of part of Sun: Description of part of Sun: 1. Probably the largest part of the Sun: 2. Dark because they are cooler than the rest of the surface:
20.The graph below shows the varying amount of gravitational attraction between the Sun and an asteroid in our solar system. Letters A, B, C, and D indicate four positions in the asteroid's orbit. Which diagram best represents the positions of the asteroid in its orbit around the Sun? [Note: The diagrams are not drawn to scale.]
Label the neap and spring tides drawn below. spring neap Earth Sun Moon Why does the lineup of the Earth, sun, and moon impact the tides? The gravitation pull is increased when they are lined up together. Ho w can you tell/ remember the difference between a neap and a spring tide from a diagram? Neap Tides are perpendicular
Label the 6 layers 4 features of the sun. Outline the function of the stomach small intesti. ... Read the definitions below then label the digestive system anatomy diagram. The diagram of the digestive system that is provided in the article will give one a better understanding of this organ system as the food moves down from the mouth through ...
This diagram illustrates the path of the sun and the altitude of the noon sun on the celestial sphere for an observer in New York State (latitude 43N) at the beginning of each season. Label each month for the paths drawn in the diagram below Spring Summer Fall Winter NW SE NE 6/21 12/21 E 3/21 9/23 1.
Astronomy: Sun Diagram. The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. The Earth and other matter which by itself accounts for about 99.8of the Solar System's mass. Energy from the Sun, in the form of sunlight, supports almost all life on Earth via photosynthesis, and drives the Earth's climate and weather. Press play!
The Solar System The Sun Understanding Main Ideas Label the diagram of the sun below. Building Vocabulary Match each term with its description by writing ...
Read the definitions then label the diagram below. Rapid shutdown switch for solar pv system this label must be on the switch or no more than 1 meter 33 ft from the switch. An orrery is a model of the solar system that shows the positions of the planets along their orbits around the sun. Sun the sun is a star at the center of our solar system.
Teacher: mplete the worksheet. SECTION 2-2 REVIEW AND REINFORCE The Surn Understanding Main Ideas Label the diagram of the sun below. .sMocabulary ; Question: Teacher: mplete the worksheet. SECTION 2-2 REVIEW AND REINFORCE The Surn Understanding Main Ideas Label the diagram of the sun below. .sMocabulary
Analyze the given diagram of the carbon cycle below. An image of carbon cycle is shown. The sun, a cloud, two trees, one towards left and the other towards right, an animal, lake, and a factory are included. Arrow A points from the sun to the left tree. Arrow B points from the air above the clouds to the left tree.
A Diagram of the Earth-Sun Relationship Notice that the Earth's tilt is always directed towards one place in space (in this model, it is towards the left. But notice all you need to do is move your perspective to underneath or some other side, and saying the pole tilts towards "the left" becomes meaningless.
The sun's corona is normally visible only during a total solar eclipse when it is seen as an irregularly shaped pearly glow surrounding the darkened disk of the moon. Sunspots It is a spot or patch appearing from time to time on the sun's surface, appearing dark by contrast with its surroundings.
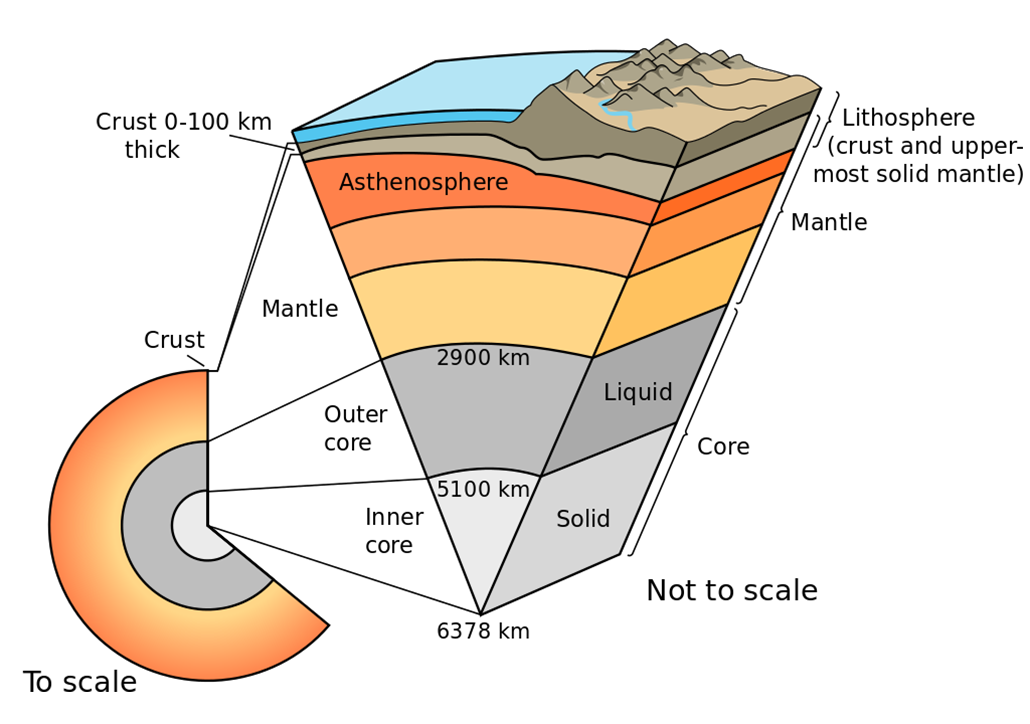

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/internal-structure-of-the-earthwith-english-labels--3d-illustration-523049135-5aa73e09ff1b780036f1c711-5bb78d5c46e0fb0026d10eef.jpg)










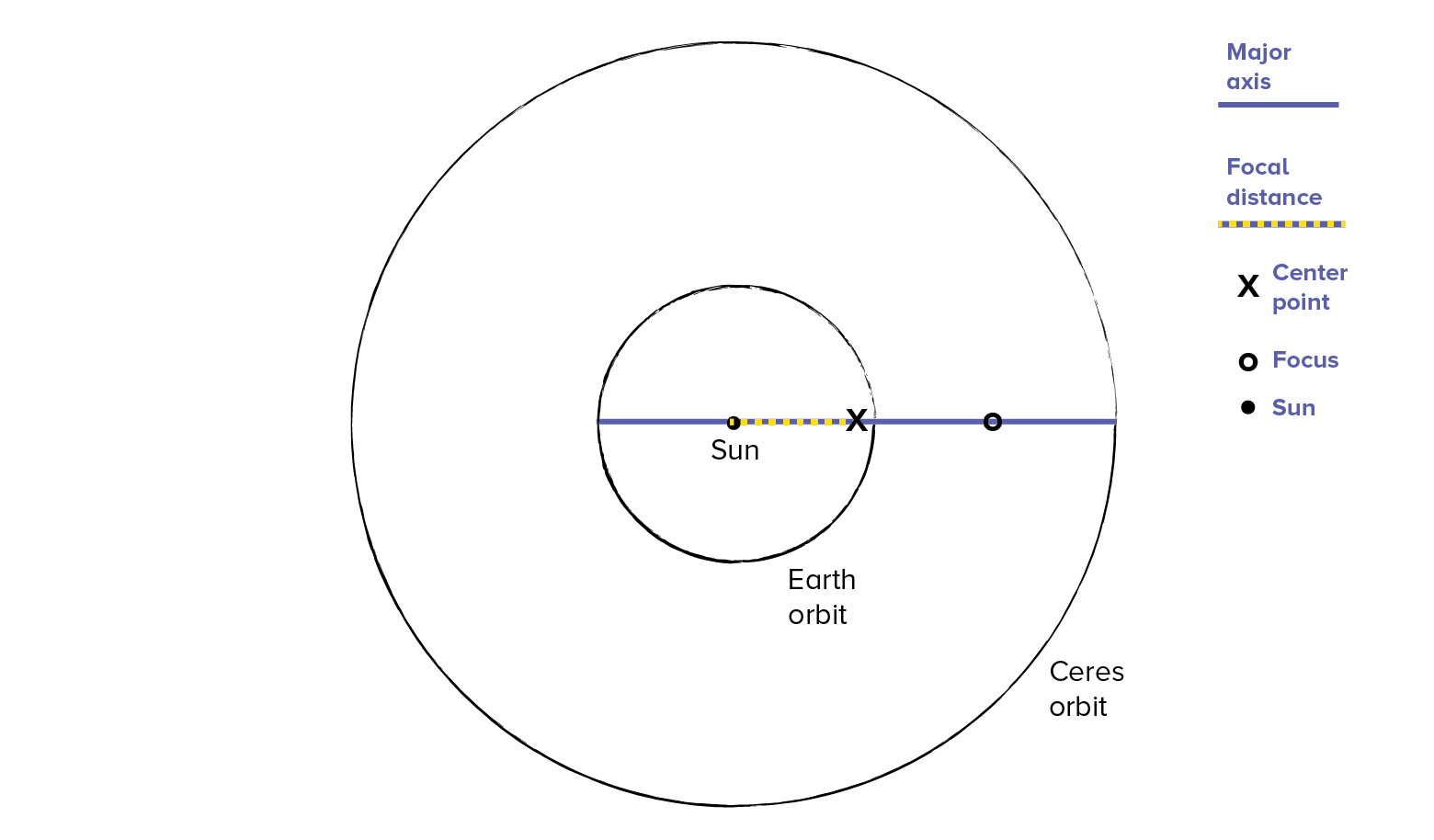




0 Response to "37 label the diagram of the sun below"
Post a Comment