39 orbital diagram of f-
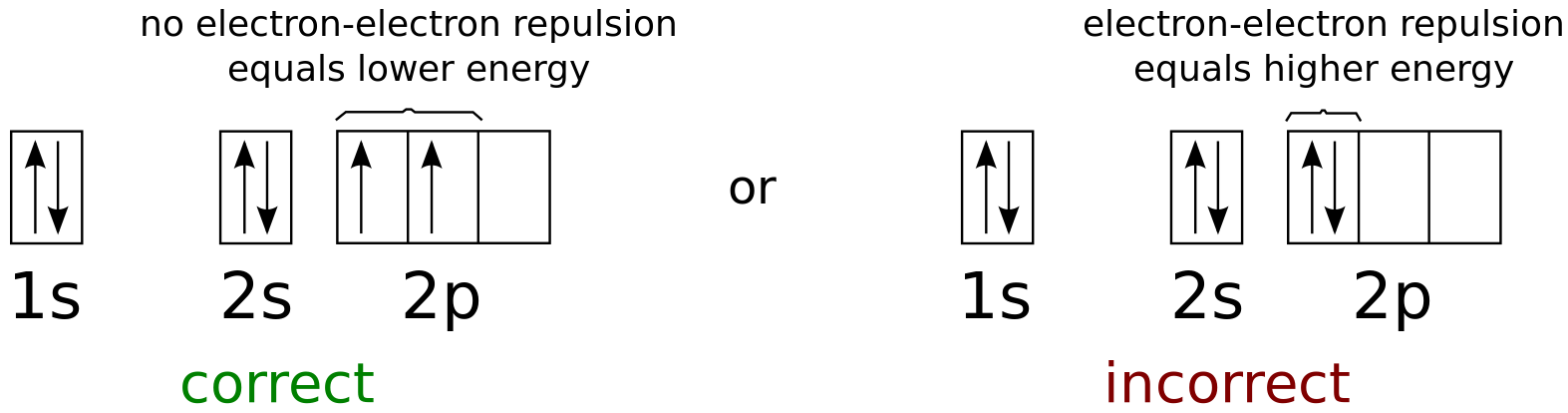
The energy difference between 2s and 2p orbitals in O, F, and Ne is greater than that in Li, Be, B, C, and N. What is a orbital diagram? Orbital diagrams are pictorial descriptions of the electrons in an atom. Three rules are useful in forming orbital diagrams. According to the Auf Bau Principle, each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital. F: 1s22s22p5 Now, the F− anion is formed when 1 electron is added to a neutral fluorine atom. Notice that the 2p-subshell of the neutral atom contains 5 electrons. Its maximum capacity is actually 6 electrons, two electrons for each p-orbital. This means that the extra electron will be added to one of the three 2p-orbitals, let's say to 2py.
Orbital diagrams are a visual way to show where the electrons are located within an atom. Orbital diagrams must follow 3 rules: The Aufbau principle, the Pau...

Orbital diagram of f-
Apr 10, 2021 · Orbital diagram of Lithium (Li) 4: Orbital diagram of Beryllium (Be) 5: Orbital diagram of Boron (B) 6: Orbital diagram of Carbon (C) 7: Orbital diagram of Nitrogen (N) 8: Orbital diagram of Oxygen (O) 9: Orbital diagram of Fluorine (F) 10: Orbital diagram of Neon (Ne) 11: Orbital diagram of Sodium (Na) 12: Orbital diagram of Magnesium (Mg) 13 ... General Notes on Molecular Orbital Diagrams. The Y-axis of a MO diagram represents the total energy (not potential nor Gibbs Energy) of the orbitals. Individual atomic orbitals (AO) are arranged on the far left and far right of the diagram. Overlapping atomic orbitals produce molecular orbitals located in the middle of the diagram. s, p, d, and f Orbitals . The shapes corresponding to each orbital are designated by a single letter. You must be able to draw the shape of an s and a p orbital. The first orbital we will examine is the most basic orbital shape. It is an s orbital. This orbital is spherical in shape, as seen in Figure 1, and can contain a maximum of two electrons.
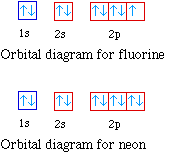
Orbital diagram of f-. An orbital diagram, or orbital box diagram, is a way of representing the electron configuration of an atom. A box, line, or circle, is drawn to represent each orbital in the electron configuration (using the Aufau Principle to order the orbitals and hence the boxes, lines or circles, as shown below) F Orbital. The sequence for the f block is unique. Beginning with lanthanum (Z=57) it starts a block that contains 15 elements. The 5 th level of a tetrahedron has 15 units. There are 15 elements for the f block (Z=57 to 71), although an odd number affects the number of orbitals (14 / 2 = 7). It converts a proton to neutron in the next d block to compensate, beginning with the 5d block. Orbital diagram shows how electrons are distributed in various kinds of shells in the increasing order for a particular ion or element. The filling of electrons is studied and done by the help of ... Electron configuration of fluorine (F) atom through orbital diagram Atomic energy levels are subdivided into sub-energy levels. These sub-energy levels are called orbital. The sub energy levels are expressed by 'l'. The value of 'l' is from 0 to (n - 1). The sub-energy levels are known as s, p, d, f.
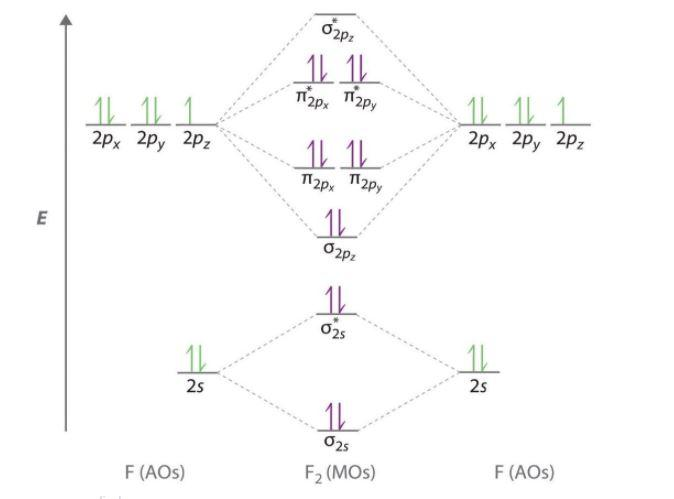
Each such orbital can be occupied by a maximum of two electrons, each with its own projection of spin. The simple names s orbital, p orbital, d orbital, and f orbital refer to orbitals with angular momentum quantum number ℓ = 0, 1, 2, and 3 respectively. The Fluoride ion formed by addition of electron to its neutral state. F + e^- rightarrow F^- Thus, F^- ion has 10 electrons. The electronic configuration of Fluoride ion is 1s^2 3s^2 2p^6. As the energy of the atomic orbital is 1s^2 < 2p^6 (2p^2_x = 2p^2_y = 2p^2_z), the orbital energy diagram is represented as shown below: Hottest videos. Widget. 8 - Drawing Molecular Orbital Diagrams. Abstract (TL;DR) Molecular orbital diagrams are a fantastic way of visualizing how molecular orbitals form using what we already understand about sigma and pi bonds. Depending on if it is a homonuclear case, where the bonding atoms are the same, or a heteronuclear case, where the bonding atoms are ... The qualitative approach of MO analysis uses a molecular orbital diagram to visualize bonding interactions in a molecule. In this type of diagram, the molecular orbitals are represented by horizontal lines; the higher a line the higher the energy of the orbital, and degenerate orbitals are placed on the same level with a space between them.
The first number is the principal quantum number (n) and the letter represents the value of l (angular momentum quantum number; 1 = s, 2 = p, 3 = d and 4 = f) for the orbital, and the superscript number tells you how many electrons are in that orbital. Orbital diagrams use the same basic format, but instead of numbers for the electrons, they ... Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories: Valence Bond Theory and Molecular… Draw molecular orbital diagram for F 2 molecule. Also, gives its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. Hint: The Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT) explains the formation of the molecule in a better way than Valence Bond Theory (VBT). The bond order calculations are feasible using MOT and so is the description of electronic ... E f = −2.357 × 10 10 J. E f = −23.57 GJ (geostationary orbit) To satisfy the minimum energy requirements of this problem the satellite should be launched from someplace on the equator where the speed of rotation (and thus the kinetic energy) is a maximum.
Orbitals Chemistry (s, p, d, and f Orbital) - Atomic Orbitals are of four different kinds, denoted s, p, d, and f, each with a different shape. Of the four, we'll be concerned primarily with s and p orbitals because these are the most common in organic chemistry. Learn more about atomic orbital at Byjus
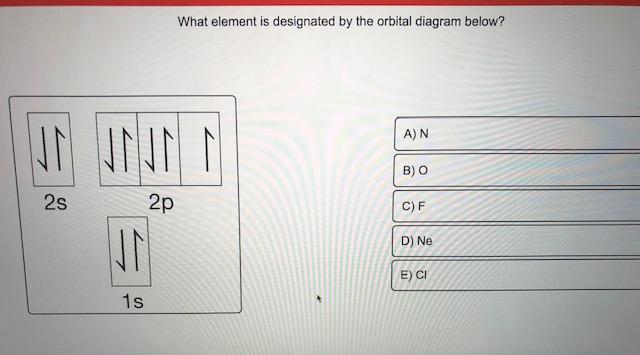
Orbital diagram for chlorine(Cl) Chlorine(Cl) excited state electron configuration. Atoms can jump from one orbital to another orbital by excited state. This is called quantum jump. Ground state electron configuration of chlorine is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 5. The valency of the element is determined by electron configuration in the excited state.
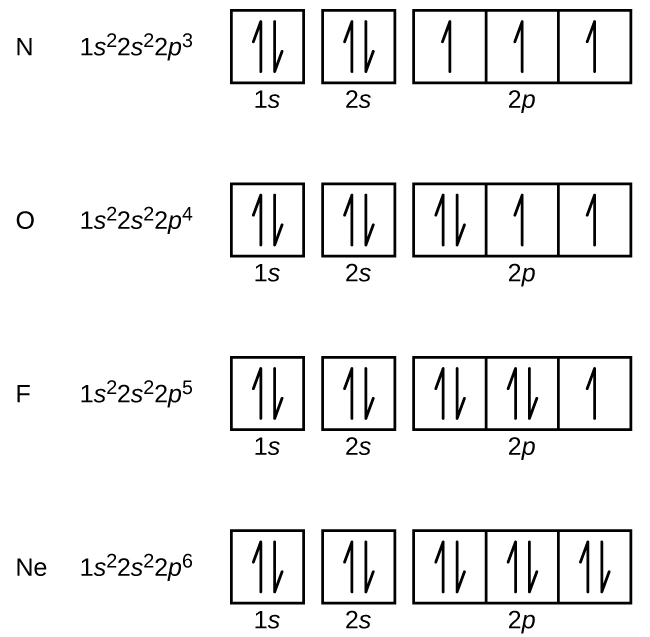
In writing the electron configuration for fluorine the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for F go in the 2s orbital. The remaining five electrons will go in the 2p orbital. Therefore the F electron configuration will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 5.
Construct the orbital diagram of the F- ion. If you can't find your institution, please check your spelling and do not use abbreviations. If your institution is not listed, please visit our Digital Product Support Community .
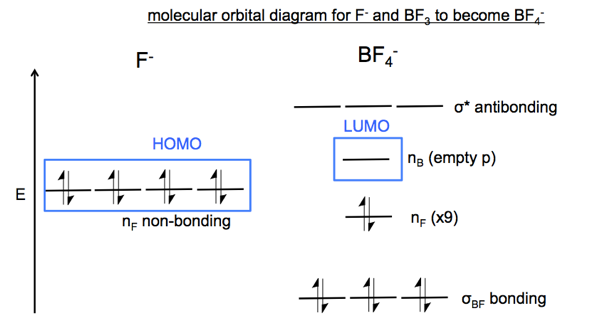
The molecular orbital diagram of HF looks different than most other diatomic species because the electronegativity difference between H and F is so large. The Is atomic orbital of H interacts with just one of the 2p atomic orbitals of F to form a bonding sigma molecular orbital and an antibonding sigma* molecular orbital.
This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into orbital diagrams and electron configuration. It explains how to write the orbital diagram n...
The orbital wave function or Φ Φ is a mathematical function that is used to denote the coordinates of an electron. The square of Φ Φ indicates the probability of finding an electron in the orbital. Φ Φ helps in drawing out the boundary surface diagrams.
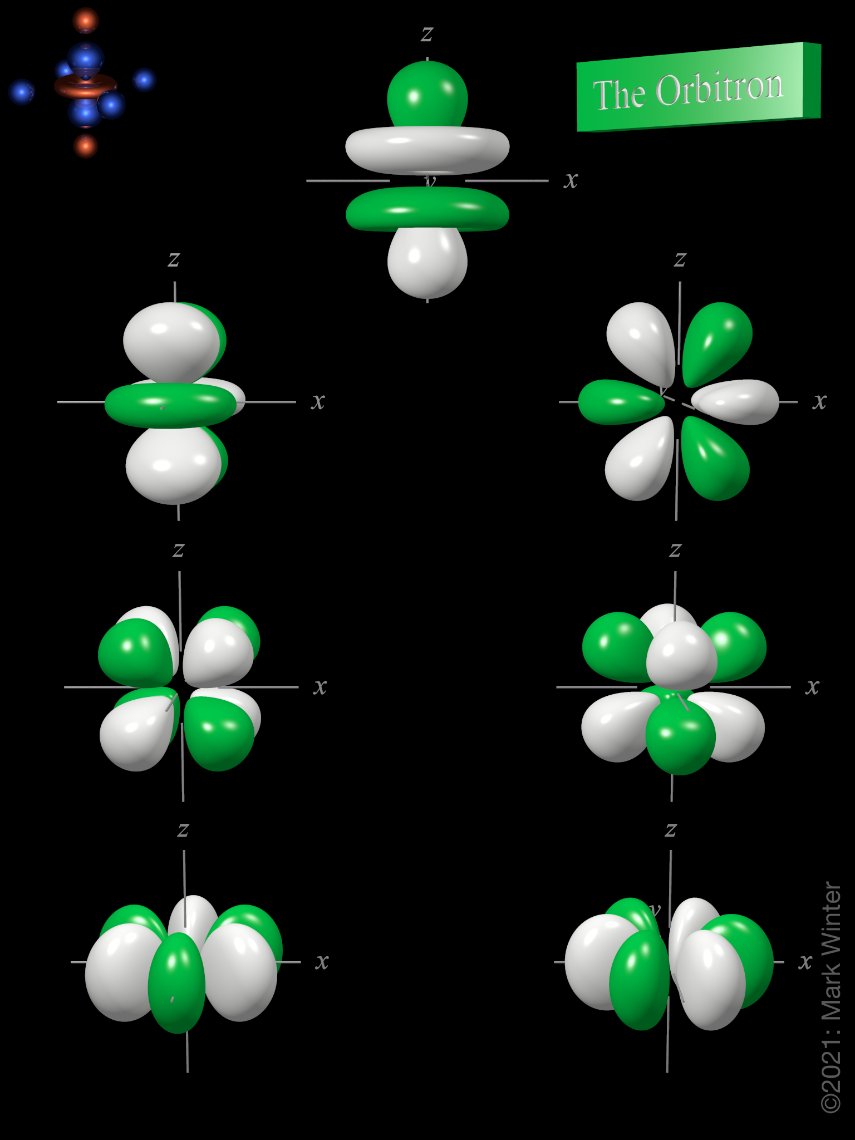
These are s, p, d and f. The shapes of these orbitals are discussed below: s-orbitals. The s-orbitals are solid spherical shape around the nucleus. When principal quantum number n = 1 and azimuthal quantum number l = 0, that is 1s orbital which is closest to the nucleus. When n = 2 and l = 0 , i.e 2s orbital which contains one node.
f ORBITALS At the fourth and higher levels, there are seven f orbitals in addition to the 4s, 4p, and 4d orbitals. Counting the 4s, 4p, and 4d orbitals, this makes a total of 16 orbitals in the fourth level. They have even more complicated shapes. s, p, d, and f orbitals are available at all higher energy levels as well.
Molecular Orbital Diagrams of more complicated molecules XH 2 (D ∞ h) H--X--H molecular orbitals general MO diagram layout linear central atom's (X 's) atomic orbitals atomic orbitals of terminal atoms H 1 + H 2 a linear combination of symmetry adapted atomic orbitals (LGO's)
Sodium(Na) is the 11th element in the periodic table and its symbol is ‘Na’. This article gives an idea about the electron configuration of sodium and orbital diagram, period and groups, valency and valence electrons of sodium, bond formation, compound formation, application of different principles.
Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule, O 2. From this diagram, calculate the bond order for O 2. How does this diagram account for the paramagnetism of O 2? Solution We draw a molecular orbital energy diagram similar to that shown in . Each oxygen atom contributes six electrons, so the diagram appears as shown in .
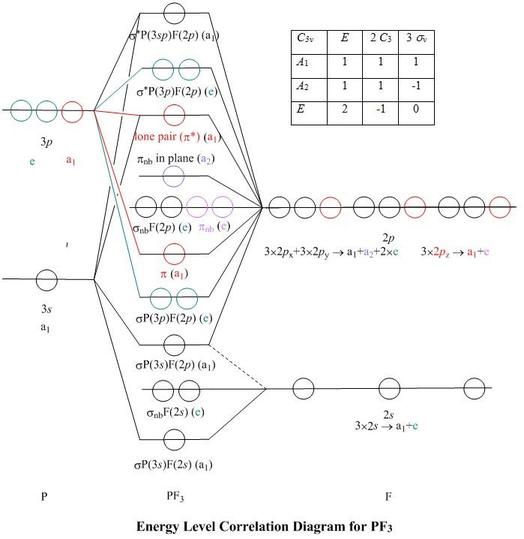
In picture 1 we show the molecular orbital structure of F2. In picture 2 we show the overlapping p orbitals, which form the bond between the two fl uorine atoms, in red and green gradients. The dashed lines show the remaining p orbitals which do not take part in the bonding. σ z y x σ* x y z Construct the molecular orbital diagram for ...
Instructions: (Part 2) Complete the F 2 orbital interaction diagram below. The 8 MOs should be labeled and ordered correctly relative to one another. Absolute position however is not expected. Draw dashed lines to show which atomic orbitals interact to form the MOs.
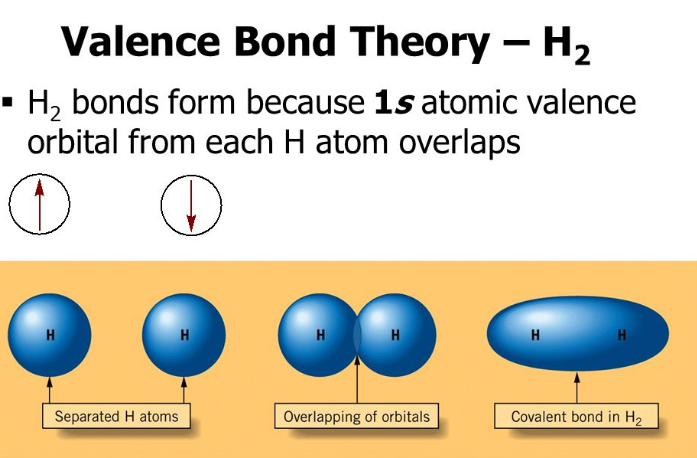
1) An orbital is a three dimensional description of the most likely location of an electron around an atom. Below is a diagram that shows the probability of finding an electron around the nucleus of a hydrogen atom. Notice that the 1s orbital has the highest probability. This is why the hydrogen atom has an electron configuration of 1s 1 .
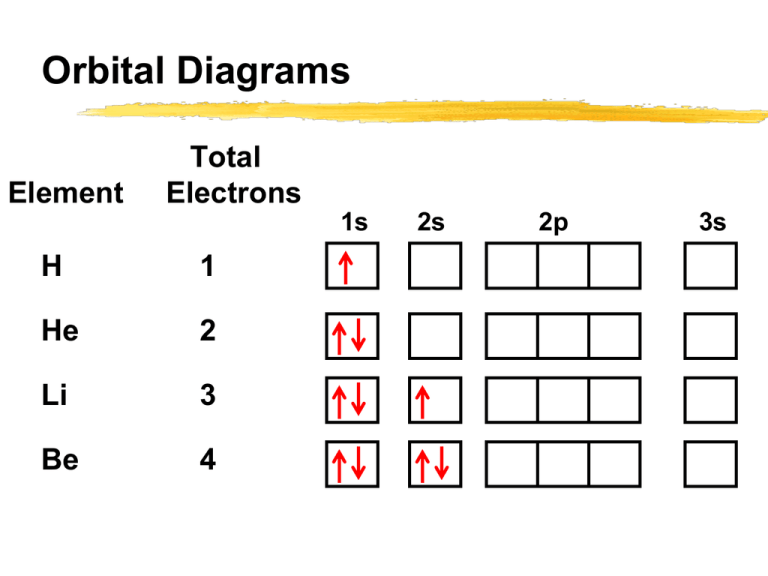
Orbital Filling Diagrams. An orbital filling diagram is the more visual way to represent the arrangement of all the electrons in a particular atom. In an orbital filling diagram, the individual orbitals are shown as circles (or squares) and orbitals within a sublevel are drawn next to each other horizontally.
s, p, d, and f Orbitals . The shapes corresponding to each orbital are designated by a single letter. You must be able to draw the shape of an s and a p orbital. The first orbital we will examine is the most basic orbital shape. It is an s orbital. This orbital is spherical in shape, as seen in Figure 1, and can contain a maximum of two electrons.
General Notes on Molecular Orbital Diagrams. The Y-axis of a MO diagram represents the total energy (not potential nor Gibbs Energy) of the orbitals. Individual atomic orbitals (AO) are arranged on the far left and far right of the diagram. Overlapping atomic orbitals produce molecular orbitals located in the middle of the diagram.
Apr 10, 2021 · Orbital diagram of Lithium (Li) 4: Orbital diagram of Beryllium (Be) 5: Orbital diagram of Boron (B) 6: Orbital diagram of Carbon (C) 7: Orbital diagram of Nitrogen (N) 8: Orbital diagram of Oxygen (O) 9: Orbital diagram of Fluorine (F) 10: Orbital diagram of Neon (Ne) 11: Orbital diagram of Sodium (Na) 12: Orbital diagram of Magnesium (Mg) 13 ...














![Expert Answer] Draw the molecular orbital diagram for F2 and ...](https://hi-static.z-dn.net/files/d7a/d377148aa5469a29270f608aa4d77ef6.png)
![Honors Chem] Electron Configurations and Orbital Diagrams ...](https://o.quizlet.com/kx6BU-Vwh490OnlBu2GY6w.png)








0 Response to "39 orbital diagram of f-"
Post a Comment