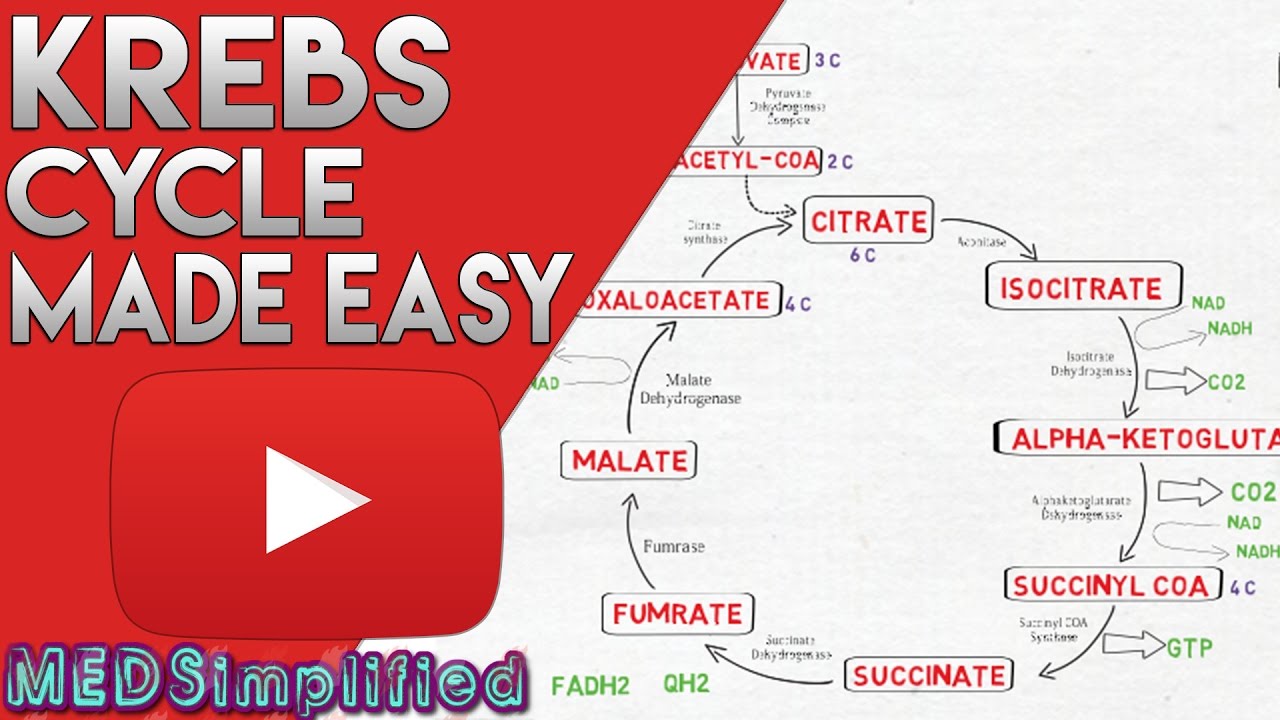
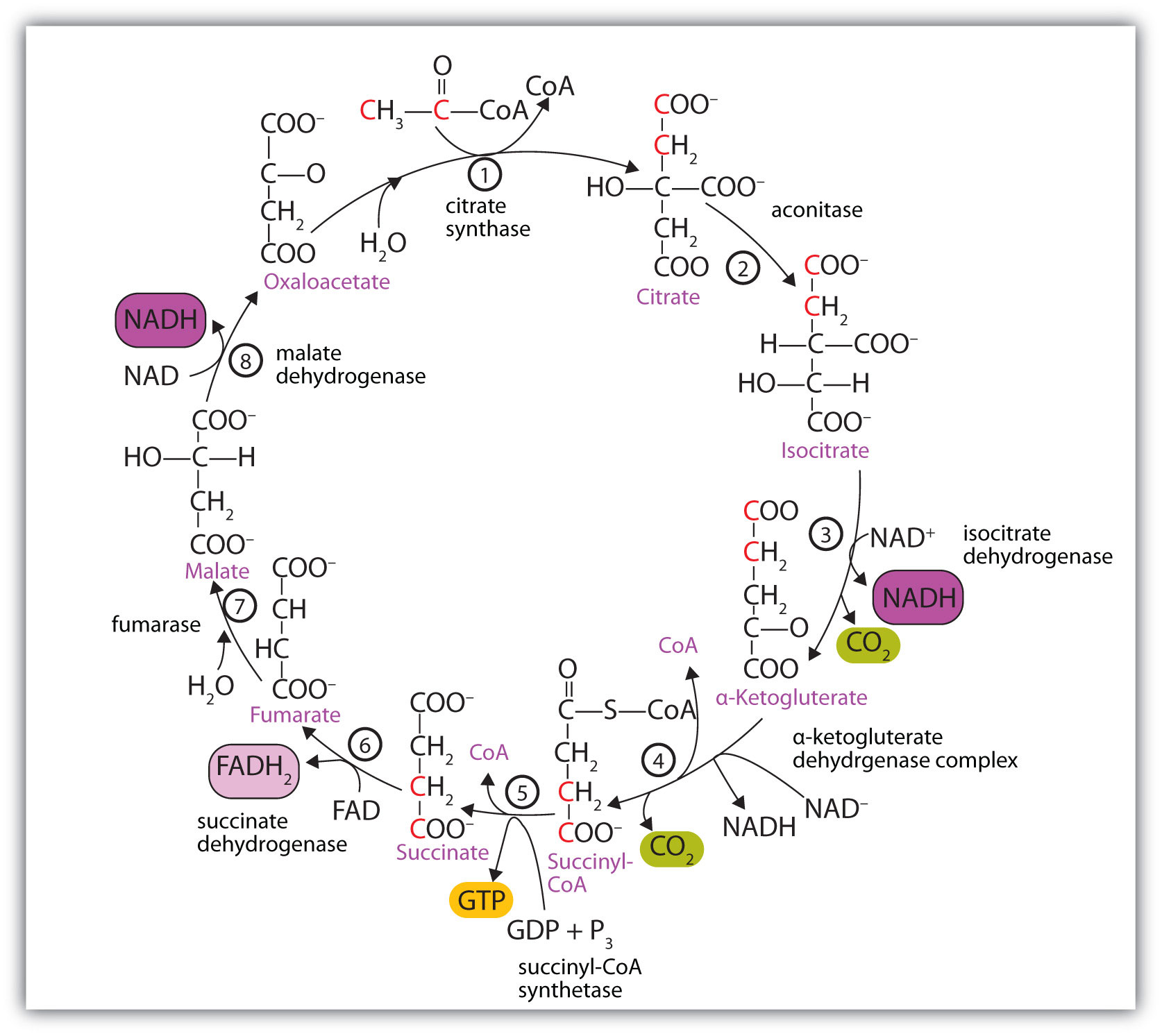
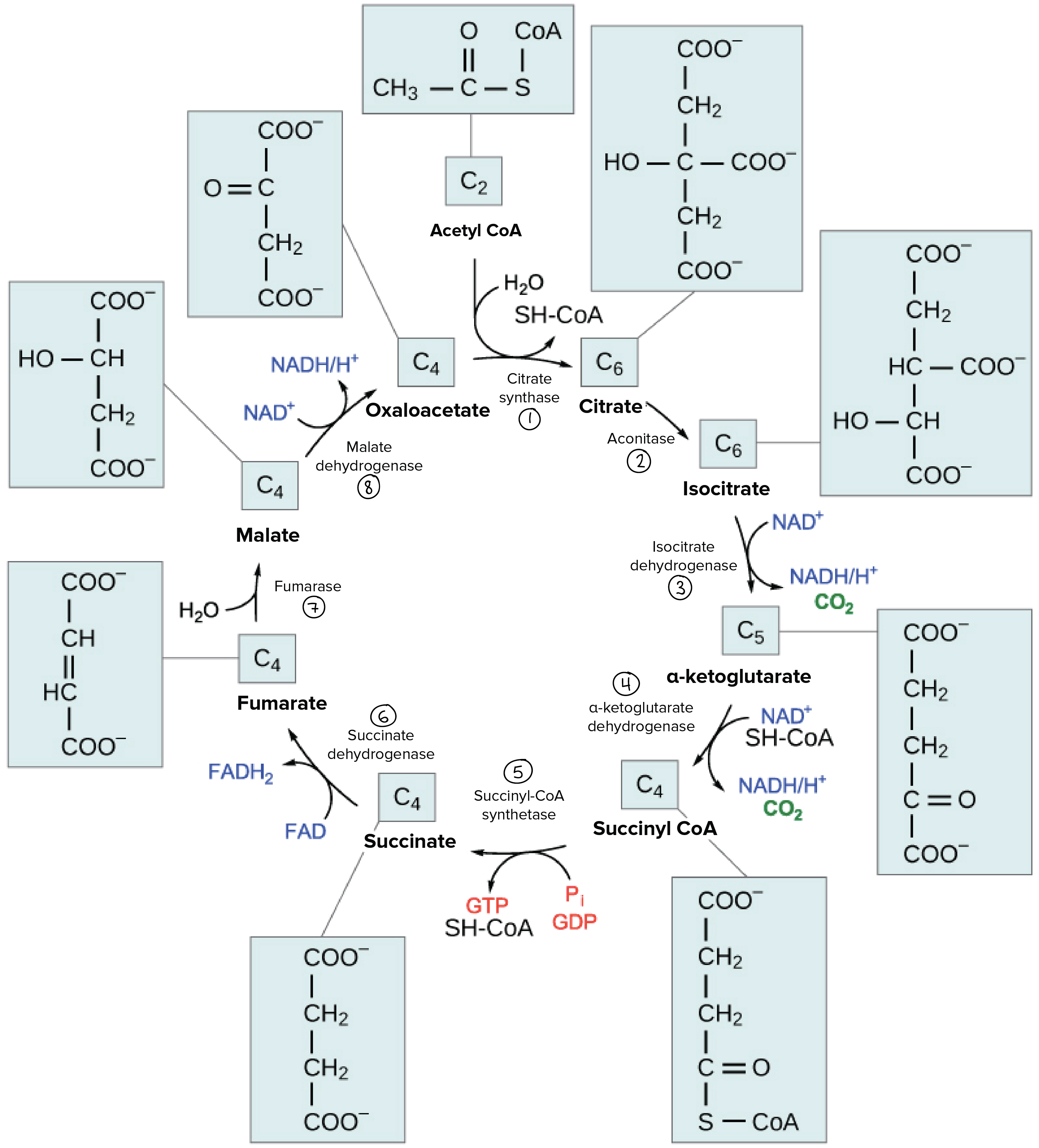
40 the image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. label the enzymes on the diagram.
Figure of the 4 step citric acid cycle. Step 1: Glycolysis. A 6-carbon glucose molecule is split into two 3-carbon molecules called pyruvates. Pyruvate is needed in order to create acetyl CoA. Step 2: The transformation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA. This is a very short step in between glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. Home › 41 drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the steps in a reaction both with and without enzymes. 41 drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the steps in a reaction both with and without enzymes. Written By Eric Y. Gallegos Wednesday, November 17, 2021 Add Comment Edit. The answer depends on the enzyme.
The electron transport chain is a series of four protein complexes that couple redox reactions, creating an electrochemical gradient that leads to the creation of ATP in a complete system named oxidative phosphorylation. It occurs in mitochondria in both cellular respiration and photosynthesis. In the former, the electrons come from breaking down organic molecules, and energy is released.
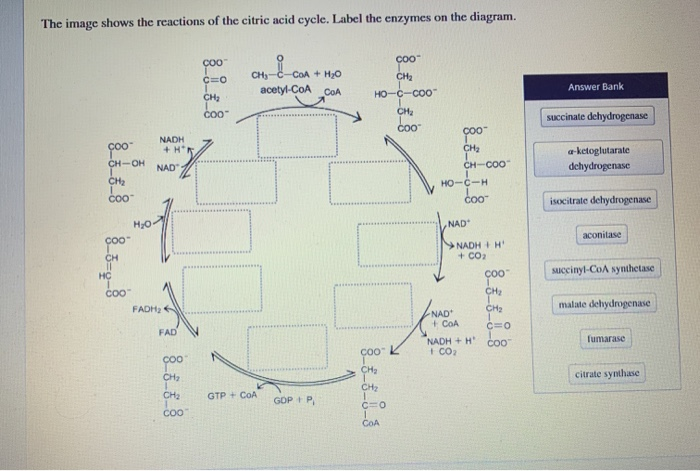
The image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. label the enzymes on the diagram.
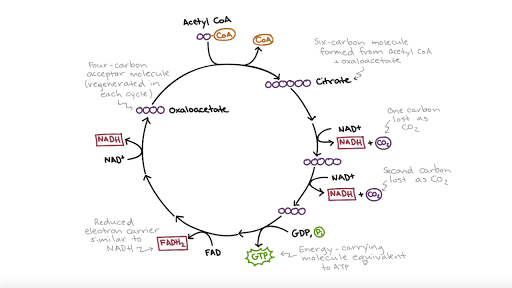
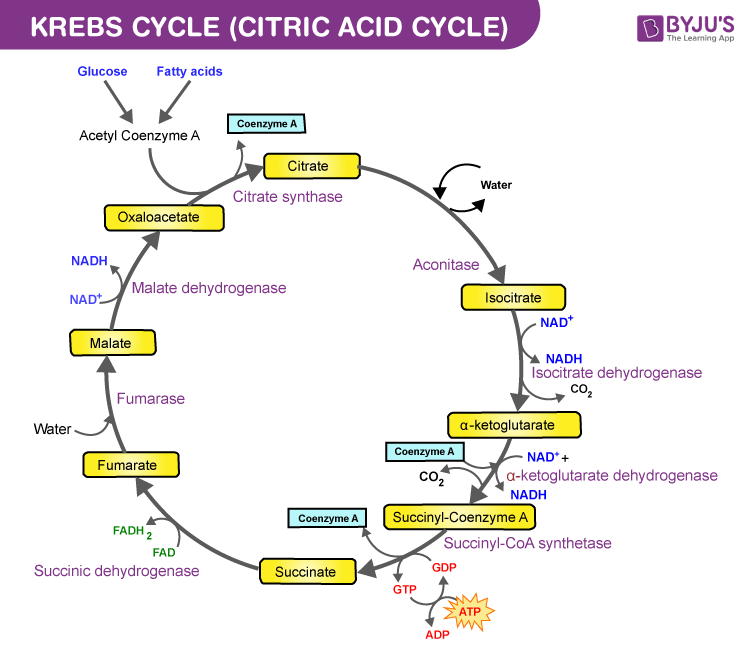
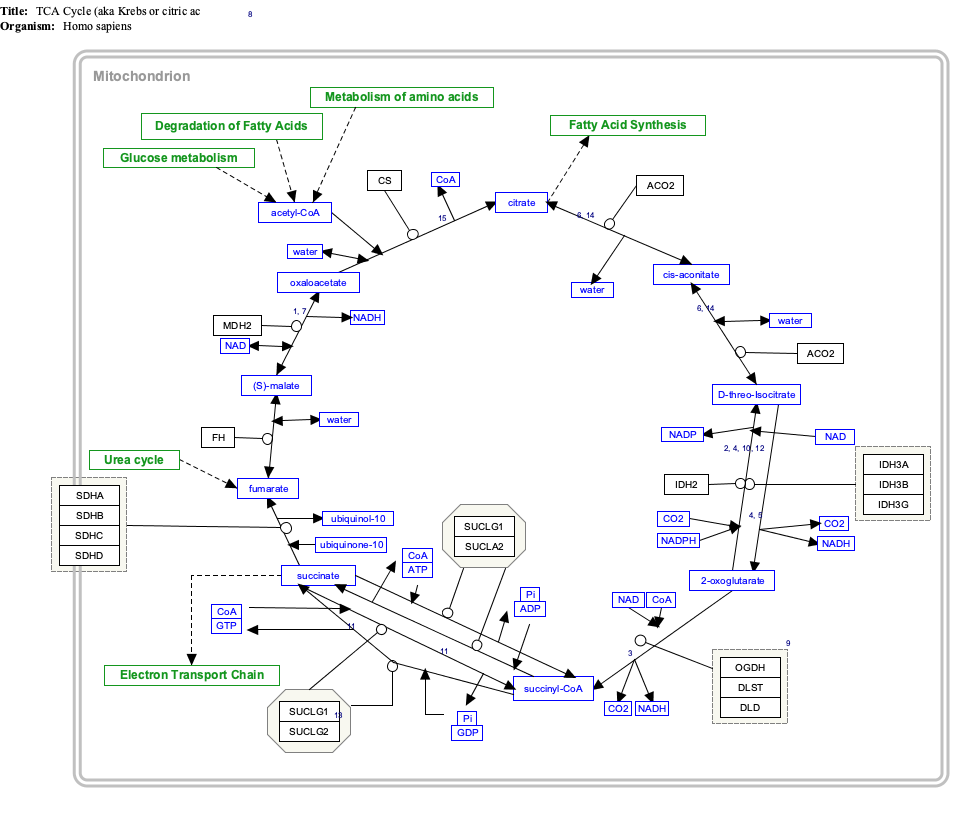
The matrix enzymes include those that metabolize pyruvate and fatty acids to produce acetyl CoA and those that oxidize acetyl CoA in the citric acid cycle. The principal end-products of this oxidation are CO 2 , which is released from the cell as waste, and NADH, which is the main source of electrons for transport along the respiratory chain ... After a quick rearrangement, this six-carbon molecule releases two of its carbons as carbon dioxide molecules in a pair of similar reactions, producing a ... The Krebs cycle has 9 main reactions, which happen quickly in succession. The image below shows these reactions. Note that citrate is the first molecule created after acetyl CoA is added. This is why the Krebs cycle is also known as the citric acid cycle. The products of the cycle are in the image above.
The image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. label the enzymes on the diagram.. Carbs, Proteins, and Fats . The Citric Acid Cycle, also known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle or the Krebs Cycle, begins after the two molecules of the three carbon sugar produced in glycolysis are converted to a slightly different compound (acetyl CoA).It is the process that allows us to use the energy found in carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. ... the image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. Label the enzymes on the diagram. Question: the image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. Label the enzymes on the diagram. the image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. Label the enzymes on the diagram. The image below shows she reactions of the cltric acid cycle. Label the enzymes on the diagram dehydragars coo Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
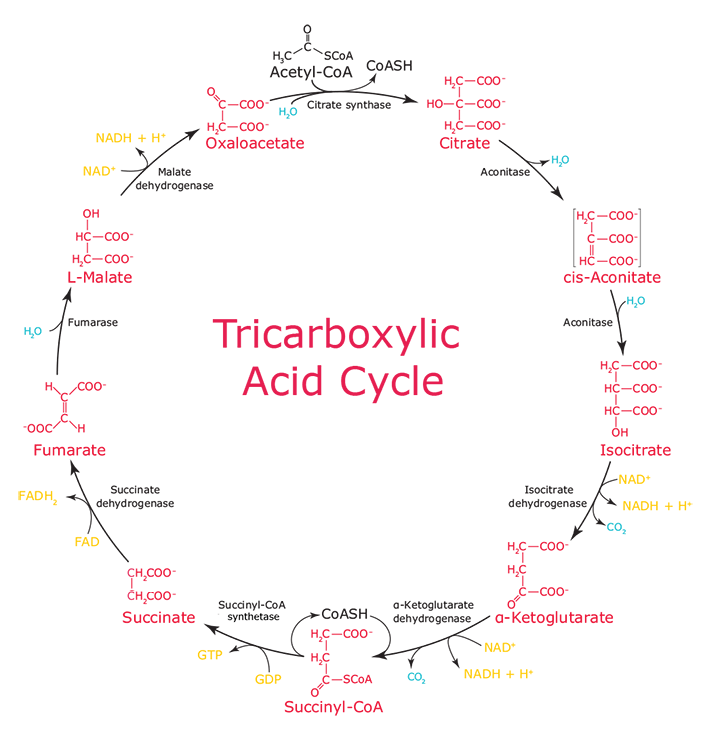
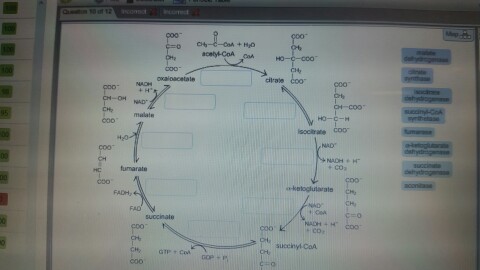
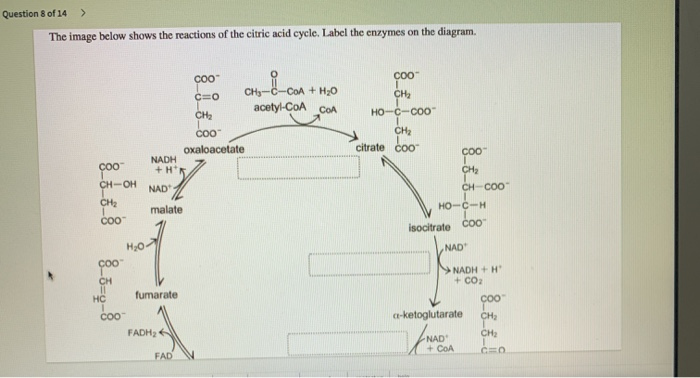
Transcribed image text: Question 8 of 14 > The image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. Label the enzymes on the diagram. -Electrons generated by the citric acid cycle in the mitochondrial matrix enter the ETC-Electron transfer in the ETC is coupled to proton transfer from the matrix to the intermembrane space-The reactions of the ETC take place in the inner membrane of mitochondria Transcribed image text: The image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. Label the reaction types on the diagram. Mapo 0 coo CHs-C-CoA + H20 ... The image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. Label the enzymes on the diagram Map Coo o CH3-C-CoA+ H20 acetyl-CoA CoA CH2 succinyl-CoA synthetase HO-C-COO CH2 CH2 COO succinate dehydrogenase oxaloacetate citrate COO NADH COO fumarase CH2 CH-OH malate NAD CH COO dehydrogenase CH2 malate citrate synthase COO isocitrate COO H20 ...
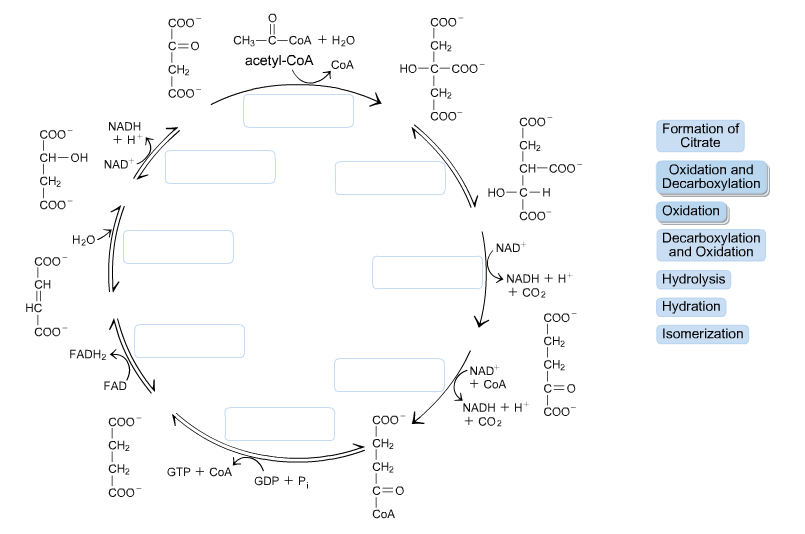
In aerobic glucose metabolism, the oxidation of citric acid uses ADP and Mg²+, which will increase the speed of reaction: Iso-citric acid + NADP (NAD) — isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) = alpha-ketoglutaric acid. In the Krebs cycle (the citric cycle), IDH1 and IDH2 are NADP+-dependent enzymes that normally catalyze the inter-conversion of D ... The image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. ... the answer choice with the labels correctly corresponding to the enzymes on the diagram. The image below shows the reaction of the citric acid cycle. Label the reaction types on the diagram. COO COO CH2 HO-C-COO CH2 COO acetyl-CoA CoA CH2 COO COO CH2 CH-COO NADH Formation of cOO CH-OH CH2 COO Citrate NAD Oxidation and Decarboxylation Oxidation Decarboxylation HO-C-H Coo H20 NAD+ and... The image below shoshone the reactions of the citric acid cycle. Label the enzymes on the diagram. CH-OH WAD + Cos Hc fumarate CHi succinale co. Show ...
The reaction of the citric acid cycle that produces an ATP equivalent (in the form of GTP) by substrate level phosphorylation is the conversion of: succinyl-CoA to succinate. Citrate synthase and the NAD+-specific isocitrate dehydrogenase are two key regulatory enzymes of the citric acid cycle.
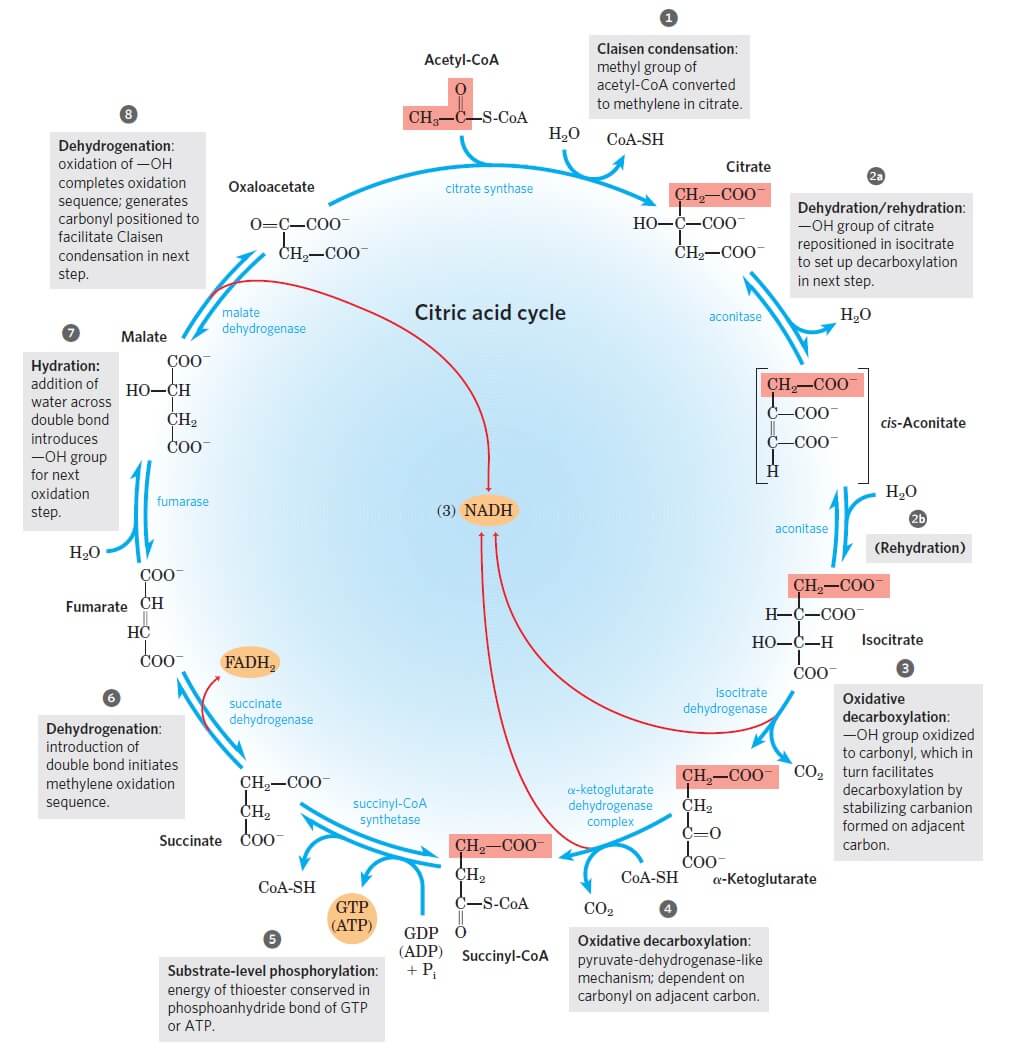
Show the structures of the reactants and products for two of the four redox reactions in the citric acid cycle. Indicate where any cofactors participate, and label the reactants, products, and cofactors as oxidants or reductants in the reaction.
The reactions of the citric acid cycle are shown in the image. As labeled in the diagram, reactions 1, 3, and 4 are regulation points in the citric acid cycle. ... Label the enzymes on the diagram. ... The image shows the tertiary structure of a protein segment. Tertiary structure results from different interactions, or forces, between groups.
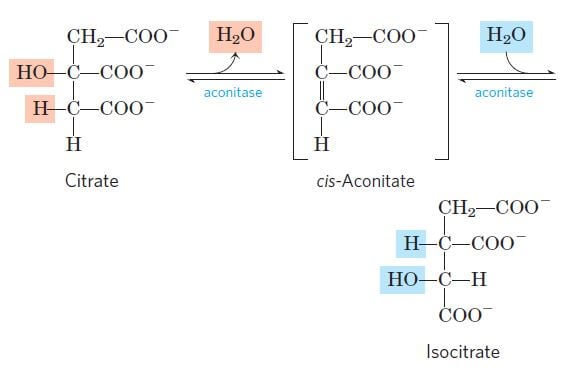
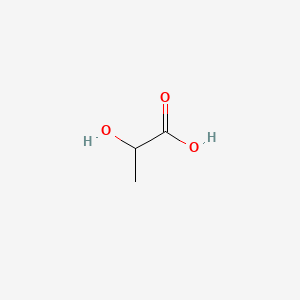
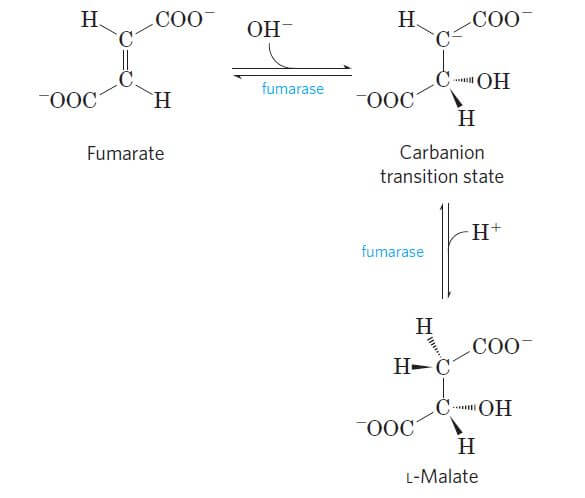
Reaction 2: Formation of Isocitrate. The citrate is rearranged to form an isomeric form, isocitrate by an enzyme acontinase.. In this reaction, a water molecule is removed from the citric acid and then put back on in another location. The overall effect of this conversion is that the -OH group is moved from the 3′ to the 4′ position on the molecule.
Reaction 2: Acontinase. The next reaction of the citric acid cycle is catalyzed by the enzyme acontinase. In this reaction, a water molecule is removed from the citric acid and then put back on in another location. The overall effect of this conversion is that the –OH group is moved from the 3' to the 4' position on the molecule.
Label the diagram of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex reactions with the names of the enzymes and cofactors. ... The reactions of the citric acid cycle are shown in the figure. Reactions 1, 3, and 4 are regulation points in the citric acid cycle. ... The image shows the reactions of the β oxidation pathway. Identify the reaction types on the ...
Transcribed image text: The image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. Label the enzymes on the diagram, Coo CHECCO HO acetyl-CoA COA coo CH Hoo-coo CH citrate oxaloacetate citrate coo NADH CHOHAD coo CHA CH-coo HOOH fumarase malate COO socitrate coo malate dehydrogenase NAD socitrate hydrogenas NAOH CO fumarate соо -ketoglutarate CH SUCC dehydrogenase FADH NAD kelogiar tu ...
The Krebs cycle has 9 main reactions, which happen quickly in succession. The image below shows these reactions. Note that citrate is the first molecule created after acetyl CoA is added. This is why the Krebs cycle is also known as the citric acid cycle. The products of the cycle are in the image above.
After a quick rearrangement, this six-carbon molecule releases two of its carbons as carbon dioxide molecules in a pair of similar reactions, producing a ...
The matrix enzymes include those that metabolize pyruvate and fatty acids to produce acetyl CoA and those that oxidize acetyl CoA in the citric acid cycle. The principal end-products of this oxidation are CO 2 , which is released from the cell as waste, and NADH, which is the main source of electrons for transport along the respiratory chain ...












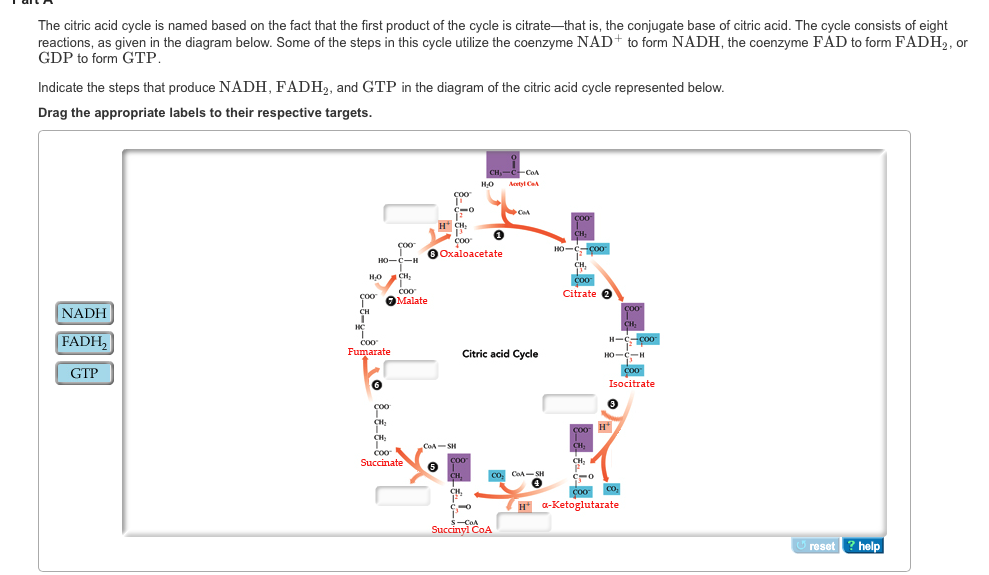




0 Response to "40 the image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. label the enzymes on the diagram."
Post a Comment