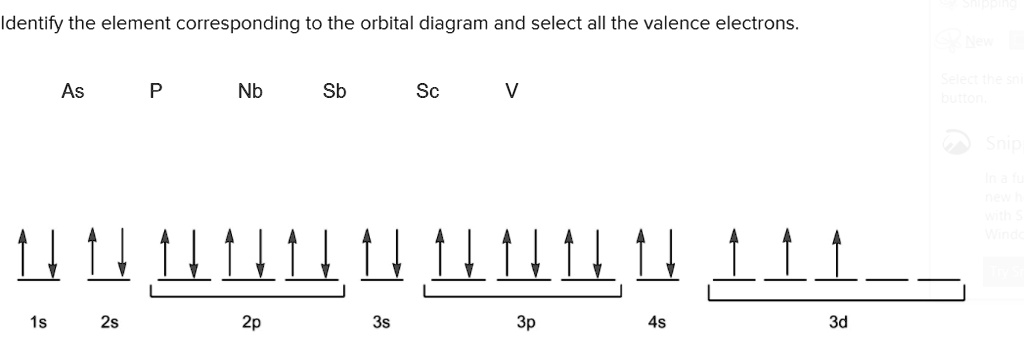
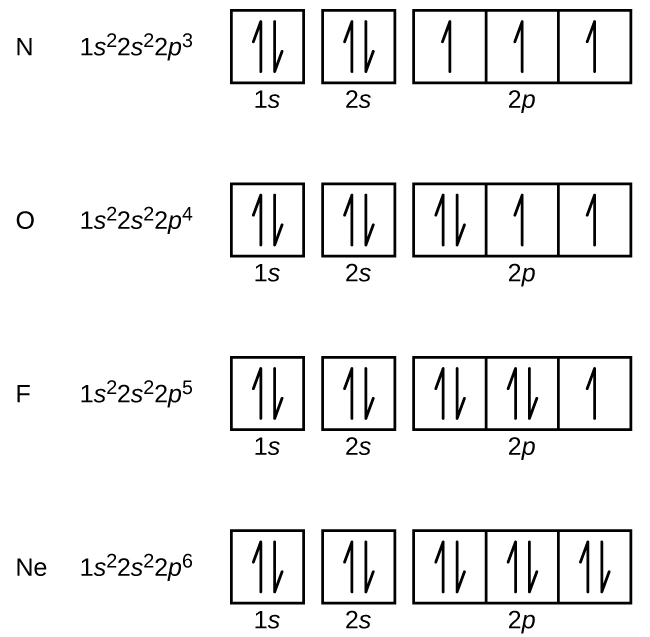
42 orbital diagram of elements
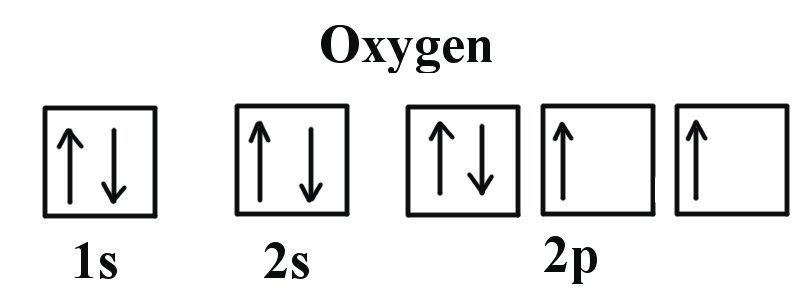
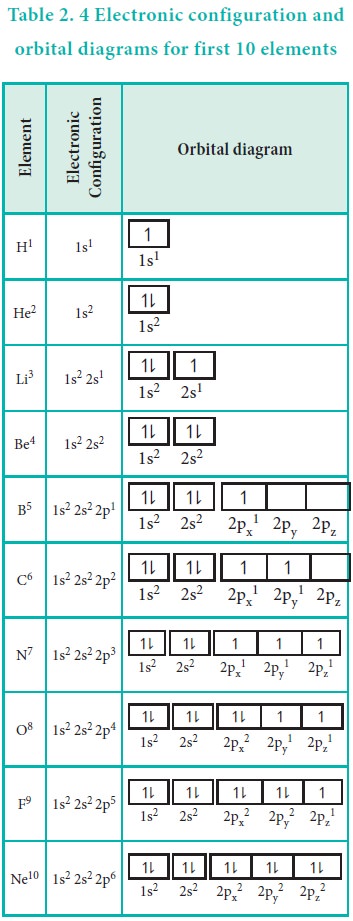
Carbon(C) electron configuration and orbital diagram The electron configuration of all the elements can be done through orbital diagram. Electron configuration of carbon(C) atom through orbital. Atomic energy levels are subdivided into sub-energy levels. These sub-energy levels are called orbital. The sub energy levels are expressed by ‘l’. The value of ‘l’ is from 0 to (n – 1). The sub-energy levels are known as s, p, d, f ... Molecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine …
Definition of Orbital Nodes - Chemistry Dictionary An example of this is orbital hybridization. Orbital Hybridization. Orbital hybridization is fundamental to understanding organic chemistry. When an s orbital and a p orbital hybridize, the orbital phases are crucial. This is summed up in the following diagram, where a positive phase 2s orbital and a 2p orbital interact to produce an sp hybrid ...

Orbital diagram of elements
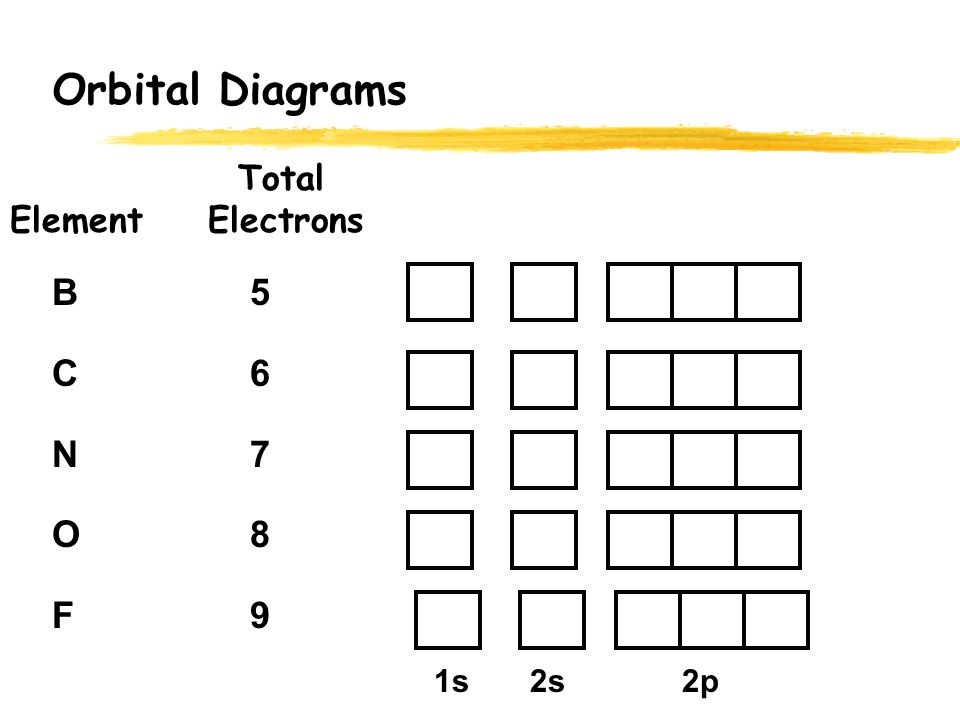
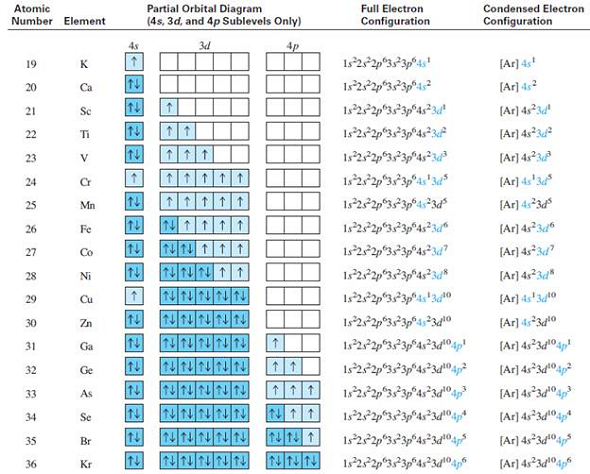
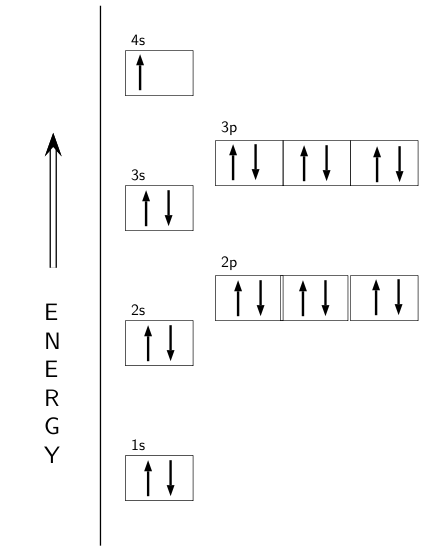
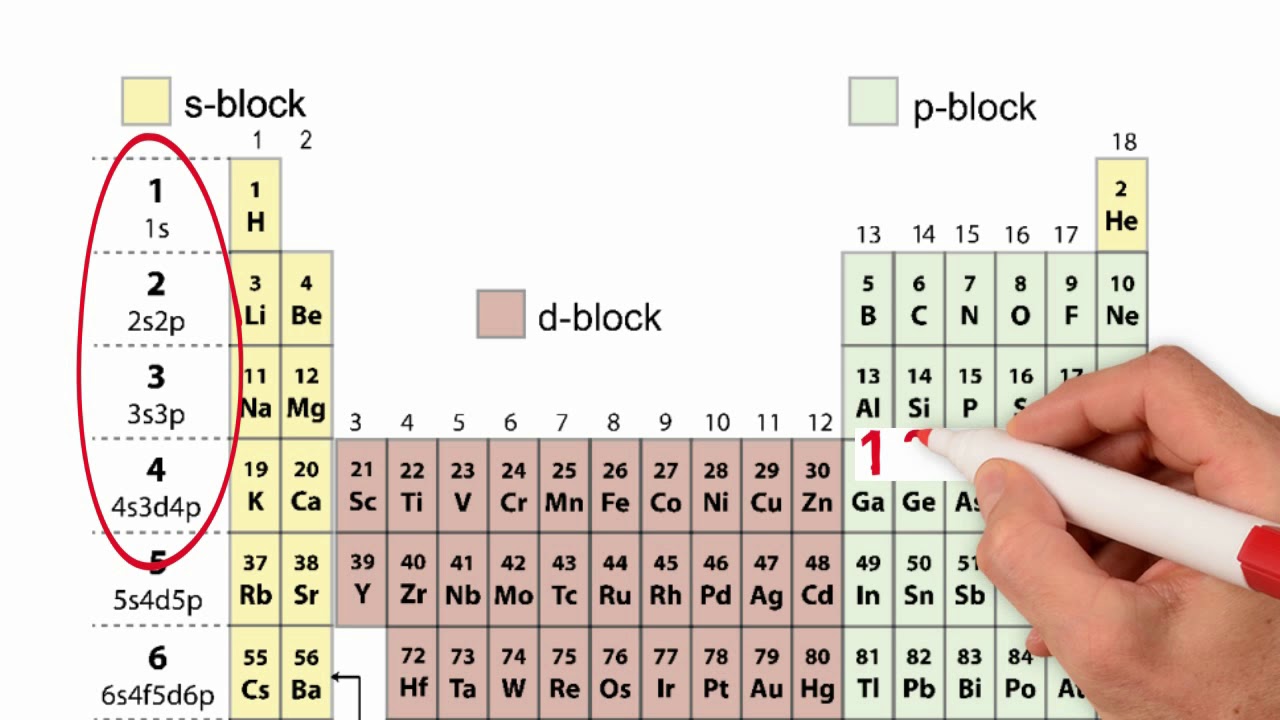
8.4 Molecular Orbital Theory – Chemistry Obtain the molecular orbital diagram for a homonuclear diatomic ion by adding or subtracting electrons from the diagram for the neutral molecule. Figure 11. This shows the MO diagrams for each homonuclear diatomic molecule in the second period. The orbital energies decrease across the period as the effective nuclear charge increases and atomic radius decreases. Between N … Orbital inclination - Wikipedia Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. ... The inclination is one of the six orbital elements describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit. It is the angle between the orbital plane and the plane of reference, normally stated in degrees. For a satellite orbiting a planet, the plane of reference is usually the plane containing the planet ... The Electron Configurations of Atoms - Chemistry at Illinois The order is summarized under the diagram. ... Four electrons fill both the 1s and 2s orbitals. The fifth electron is added to a 2p orbital, the sublevel next higher in energy (Figure 5.9). The electron configuration of boron is: B: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 1. Table 5.2 shows the electron configurations of the elements with atomic numbers 1 through 18. The electron configurations of elements with …
Orbital diagram of elements. Orbital Diagram For Nitrogen (N) | Nitrogen Electron ... 15.02.2021 · Orbital Diagram For Nitrogen (N) | Nitrogen Electron Configuration. February 15, 2021 by Sneha Leave a Comment. Nitrogen Electron Configuration: When we talk about school subjects, then one of the major subjects which are very important for knowledge perspective is science. For those who are new and are not aware of the divisions of the subject, so here we … The Electron Configurations of Atoms - Chemistry at Illinois The order is summarized under the diagram. ... Four electrons fill both the 1s and 2s orbitals. The fifth electron is added to a 2p orbital, the sublevel next higher in energy (Figure 5.9). The electron configuration of boron is: B: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 1. Table 5.2 shows the electron configurations of the elements with atomic numbers 1 through 18. The electron configurations of elements with … Orbital inclination - Wikipedia Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. ... The inclination is one of the six orbital elements describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit. It is the angle between the orbital plane and the plane of reference, normally stated in degrees. For a satellite orbiting a planet, the plane of reference is usually the plane containing the planet ... 8.4 Molecular Orbital Theory – Chemistry Obtain the molecular orbital diagram for a homonuclear diatomic ion by adding or subtracting electrons from the diagram for the neutral molecule. Figure 11. This shows the MO diagrams for each homonuclear diatomic molecule in the second period. The orbital energies decrease across the period as the effective nuclear charge increases and atomic radius decreases. Between N …








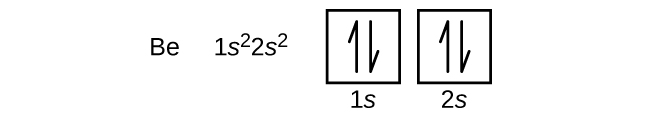

















0 Response to "42 orbital diagram of elements"
Post a Comment