38 virtual image lens diagram
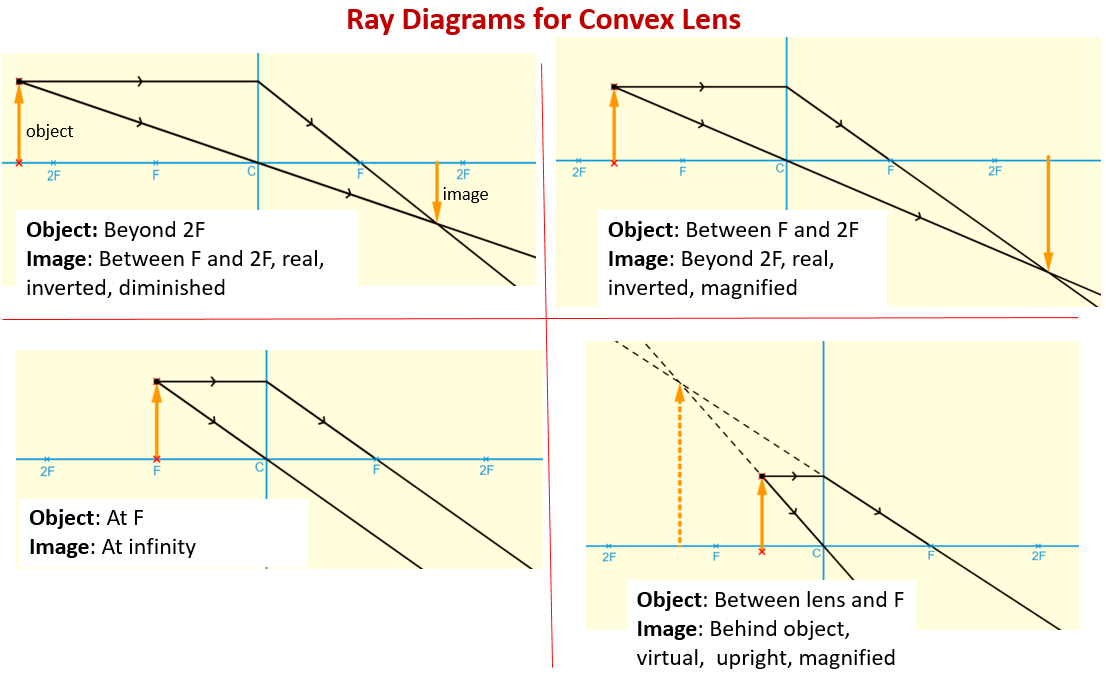
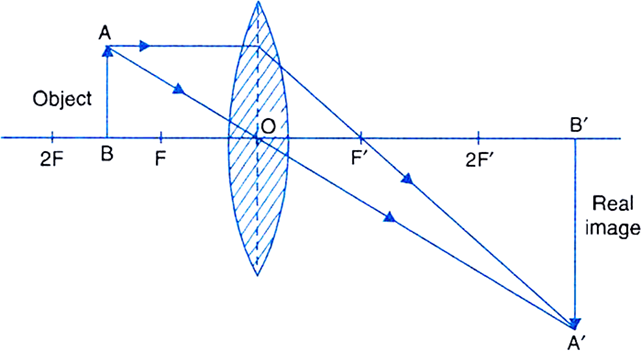
hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu › hbase › geooptRay Diagrams for Lenses - Georgia State University The ray diagrams for concave lenses inside and outside the focal point give similar results: an erect virtual imagesmaller than the object. The image is always formed inside the focal length of the lens. Ray diagrams for lenses Index Lens concepts HyperPhysics*****Light and Vision R Nave Go Back Ray Diagram for Two Lenses Ray diagrams for lenses Convex Lens - Ray diagram, Image Formation, Table - teachoo Hence, we extend both rays behind the lens We see that the rays form an image behind the lens (on the left side). So, the image is virtual And image formed would be larger than the object We can say that Image is virtual (behind the lens) Image is erect Image is larger than the object (Magnified) To summarise
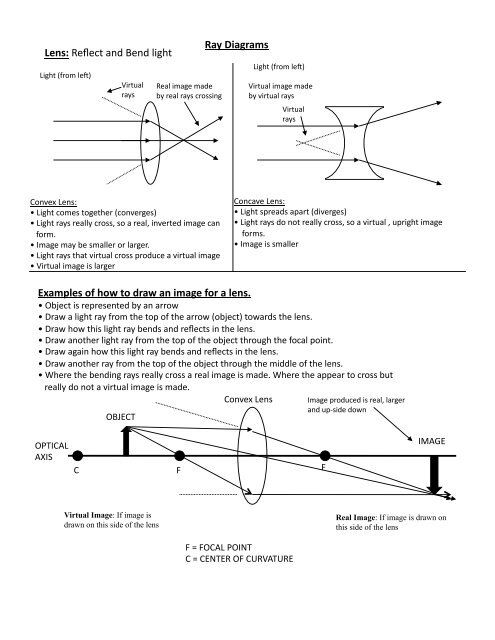
Virtual image - Wikipedia In other words, a virtual image is found by tracing real rays that emerge from an optical device ( lens, mirror, or some combination) backward to perceived or apparent origins of ray divergences. In diagrams of optical systems, virtual rays are conventionally represented by dotted lines.

Virtual image lens diagram
› what-is › another-word-forWhat is another word for image? | Image Synonyms - WordHippo Synonyms for image include picture, photo, photograph, snapshot, reproduction, facsimile, portrait, shot, snap and avatar. Find more similar words at wordhippo.com! en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Virtual_retinal_displayVirtual retinal display - Wikipedia A diagram showing the workings of the virtual retinal display A virtual retinal display ( VRD ), also known as a retinal scan display ( RSD ) or retinal projector ( RP ), is a display technology that draws a raster display (like a television ) directly onto the retina of the eye. Image Formation by Lenses | Physics - Lumen Learning Virtual images are always upright and cannot be projected. Virtual images are larger than the object only in case 2, where a convex lens is used. The virtual image produced by a concave lens is always smaller than the object—a case 3 image. We can see and photograph virtual images only by using an additional lens to form a real image.
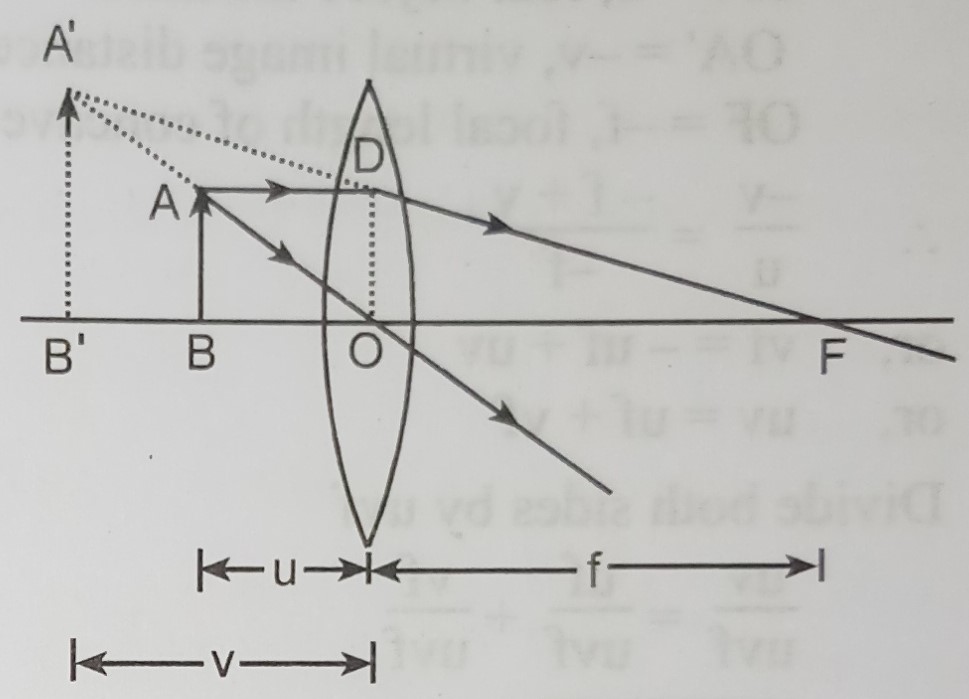
Virtual image lens diagram. Difference Between Real Image and Virtual Image - VEDANTU A virtual image is formed by tracing real rays that arise from an optical device like a mirror or lens, backward to apparent origins of ray divergences. In the diagram of the optical system, the dotted lines represent the conventional virtual ray. Concave and Convex Lenses - Image Formation | Curvature ... The size of the image is larger than that of the object. Concave Lenses. When an object is placed at infinity, a virtual image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller than that of the object. When an object is placed at a finite distance from the lens, a virtual image is formed between the pole and the focus of the convex ... Rules for identifying sign in Convex and Concave Lens ... 15.05.2020 · If a virtual image is formed, image is formed on left side, so image distance is negative Since object is always above the principal axis, object height will be positive If image is above the principal axis, image height will be positive. It means that image is erect If image is below the principal axis, image height will be negative. It means that image is inverted Next: … (a) Explain what is meant by a virtual, magnified image.(b ... (b) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of a virtual magnified image of an object by a convex lens. In your diagram , the position of object and image with respect to the principal focus should be shown clearly. (c) Three convex lenses are available having focal lengths of 4cm,40cmand 4mrespectively .
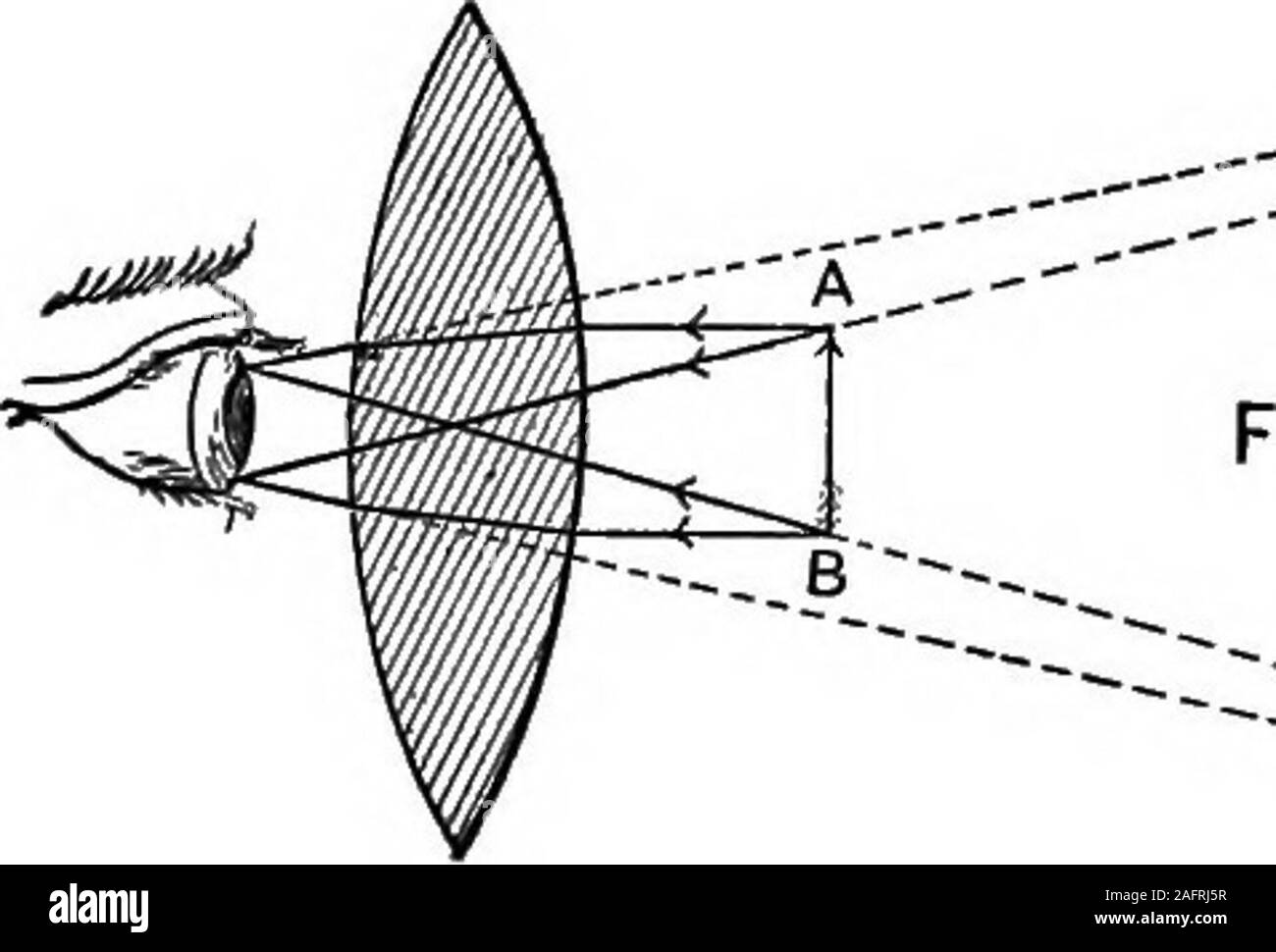
A lens forms an erect, magnified and virtual image of an ... A lens forms an erect, magnified and virtual image of an object. Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the image formation Medium Solution Verified by Toppr For getting an erect, magnified and virtual image of an object, we have to keep the object between F 1 and the optical centre of a convex lens. The image is formed in the same side of the lens. L6-05. Optical Board - Ray Diagram - Virtual Image Pos Lens Optical Board - Ray Diagram - Virtual Image Pos Lens Purpose To use principal rays to locate a virtual image produced by a convex lens. Equipment Optical board with double mirror "object" and hyperbolic lens, spherical lens to keep ray narrow. Images Description Real and virtual images - Lenses and ray diagrams - OCR ... virtual (cannot be produced on a screen) Ray diagram for an object placed less than one focal length from a convex lens Only the person using the magnifying glass can see the image. The image... PDF 7.1 INTRODUCTION 7.2 VIRTUAL IMAGES - Pomona Figure 7.3: Using a ray diagram to locate the virtual image formed by a diverging lens. The dotted lines show the trajectories that the photons appear to follow, according to the observer. The gray lines indicate the relationships between the second and third principal rays and the focal points of the diverging lens. object image eye second ...
L6-22. Optical Board - Ray Diagram - Virtual Image Neg Lens Optical Board - Ray Diagram - Virtual Image Neg Lens Purpose To use the three principal rays to locate the virtual image of a diverging lens. Equipment Optical board with diverging lens, mirror assembly and convex lens for light ray collimation. Images Description The central ray passing through the half-silvered mirror serves as the optic axis. The image formed by a lens is always virtual, erect and ... A lens forms an erect, magnified and virtual image of an object. (a) Name the type of lens. (b) Where is the object placed in relation to the lens? (c) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image. (d) Name the device which uses this principle. Images, real and virtual - Michigan State University Virtual images are formed by diverging lenses or by placing an object inside the focal length of a converging lens. The ray-tracing exercise is repeated for the case of a virtual image. In this case the virtual image is upright and shrunken. The same formula for the image and object distances used above applies again here. Convex Lens Ray Diagram - Virtual Image - YouTube Convex Lens Ray Diagram with Virtual Image. Convex Lens Ray Diagram with Virtual Image.
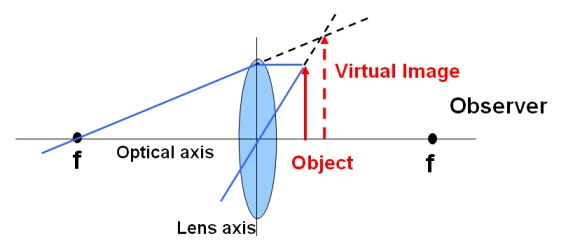
Physics Tutorial: Refraction and the Ray Model of Light A virtual image is formed if the object is located less than one focal length from the converging lens. To see why this is so, a ray diagram can be used. A ray diagram for the case in which the object is located in front of the focal point is shown in the diagram at the right. Observe that in this case the light rays diverge after refracting ...
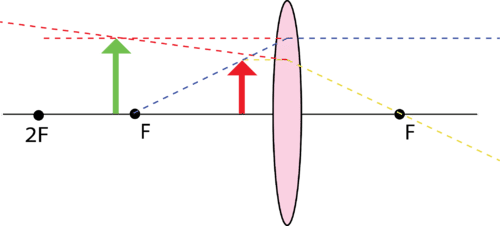
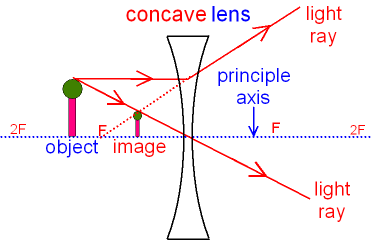
PDF 3.1.Image formation by Mirrors and Lenses Virtual image Upright Parallel light though a diverging lens appears to go through the focal point. A virtual image is formed. Image formed by a Diverging lens Virtual Upright Reduced A Diverging lens always forms a virtual image Question How will the image of an object formed by a diverging lens change as the lens is brought closer to the object?
Convex & Concave Lens Ray Diagrams | How to Draw Ray ... Images formed by a convex lens are always smaller, upright, and virtual, regardless of the position of the object from the lens. Convex lenses are used in some telescopes and other optical devices ...
📐Which of the following diagrams involves a virtual image ... The Diagram that involves a virtual image is the third diagram ( C ) The third diagram involves a virtual image because it has its Image on the same side as the object as seen from the description :. The convex lens is centered at 7cm and the object is located at 6cm while the Focal points are 5.5 and 8.5 cm
Converging lens - interactive simulations - eduMedia Here you have the ray diagrams used to find the image position for a converging lens. You can also illustrate the magnification of a lens and the difference between real and virtual images. Ray diagrams are constructed by taking the path of two distinct rays from a single point on the object. A light ray that enters the lens is an incident ray.
Virtual Image | COSMOS - Swinburne Virtual Image A virtual image (as opposed to a real image) is produced by an optical system (a combination of lenses and/or mirrors) when light rays from a source do not cross to form an image. Instead they can be 'traced back' to a point behind the lens or mirror. Virtual images can be seen directly without using a screen for projection.
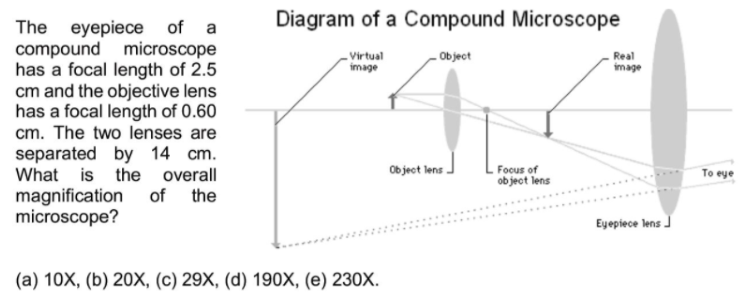
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › EyepieceEyepiece - Wikipedia A simple convex lens placed after the focus of the objective lens presents the viewer with a magnified inverted image. This configuration may have been used in the first refracting telescopes from the Netherlands and was proposed as a way to have a much wider field of view and higher magnification in telescopes in Johannes Kepler 's 1611 book ...
Ray diagram for diverging lens with both object and image ... The top diagram shows the formation of the virtual object where converging rays are prevented from meeting by the diverging lens. Then those converging rays are made to diverge by the lens and so a virtual image is formed. Update as a result of a comment from @Floris.
› NewGroupPage9Lens Tutorial - Thorlabs Sep 16, 2019 · The performance of this lens shape is best for an infinite conjugate ratio (focusing collimated light or collimating a point source). Bi-convex lenses perform best when one conjugate distance is between 0.2 and 5 times the other conjugate distance. The performance of this lens shape is best when the object and image distances are the same.
Difference Between Real Image and Virtual Image with ... A virtual image is an upright image that is achieved where the rays seem to diverge. A virtual image is produced with the help of a diverging lens or a convex mirror. A virtual image is found by tracing real rays that emerge from an optical device backward to perceived or apparent origins of ray divergences.
Thin Lenses Calculator - herramientasingenieria.com Real images occur when objects are placed outside the focal length of a converging lens (s>f). If the lens is converging but the distance from the object to the lens is smaller than the focal length, the image will be virtual. Diverging lenses always produce virtual images. This calculator shows a ray diagram when the image is real. Magnification
Ray Diagrams for Lenses - Wolfram Demonstrations Project This Demonstration lets you visualize the ray diagrams for converging and diverging lenses. By manipulating the object and lens locations, you can create real or virtual images. The rays parallel to the principal axis and the ray through the center of the lens are drawn.Locators allow you to drag both the object and the lens. You can change the focal length using a slider.
To find the focal length of a concave lens ... - Learn CBSE 01.12.2016 · As a concave lens always forms a virtual image, its focal length can not be found directly as for a convex lens. For this purpose, indirect method is used, as described below. An object needle O is placed on one side of a convex lens L 1 and its real inverted image I is located (by image needle) on the other side as shown in ray diagram. The concave lens L 2 is placed …
Real and virtual images - Lenses - AQA - GCSE Physics ... A virtual image appears to come from behind the lens. To draw a ray diagram: Draw a ray from the object to the lens that is parallel to the principal axis. Once through the lens, the ray should...
Concave Lens - Ray diagram, Images Formed - with Steps ... 26.04.2020 · Image is virtual (left side of the lens) Image is Erect Image is Smaller than the Object (Highly Diminished) Case 2 - Object is between Infinity and Optical Center Here, Object AB kept anywhere on the principal axis - between Infinity and Optical Center (O) First, we draw a ray parallel to principal axis So, it appears to pass through focus after reflection We draw another …
Physics Tutorial: Refraction and the Ray Model of Light Previously in Lesson 5, ray diagrams were constructed in order to determine the location, size, orientation, and type of image formed by double concave lenses (i.e., diverging lenses). The ray diagram constructed earlier for a diverging lens revealed that the image of the object was virtual, upright, reduced in size and located on the same side of the lens as the object.
Lenses - StickMan Physics Use a ruler to follow the arrow tip lines back to the virtual side of the lens. Where the two lines cross the object appears. Draw the object top where the rays intersect. Draw the base of the image arrow (blue in the picture) to the principle line. Now analyze your image drawing compared the the original object:

Show by drawing a ray-diagram that the image of an object formed by a concave lens is virtual, erect and diminished.
Diverging lens - interactive simulations - eduMedia virtual image Summary Here you have the ray diagrams used to find the image position for a diverging lens. A diverging lens always form an upright virtual image. Ray diagrams are constructed by taking the path of two distinct rays from a single point on the object: A ray passing through the center of the lens will be undeflected.
Convex Lens: Virtual Images - CBakken Finally, we can actually photograph the virtual image, capturing it on film, and we use the virtual image formed in several important applications. BUILD UP: In the diagram below, we place a point light source at three different places along the axis of our convex lens.
exploratorium.edu › learning_studio › cow_eyeCow's Eye Dissection - step 1 - Exploratorium Learn how to dissect a cow's eye in your classroom. This resource includes: a step-by-step, hints and tips, a cow eye primer, and a glossary of terms.
Image Formation by Lenses | Physics - Lumen Learning Virtual images are always upright and cannot be projected. Virtual images are larger than the object only in case 2, where a convex lens is used. The virtual image produced by a concave lens is always smaller than the object—a case 3 image. We can see and photograph virtual images only by using an additional lens to form a real image.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Virtual_retinal_displayVirtual retinal display - Wikipedia A diagram showing the workings of the virtual retinal display A virtual retinal display ( VRD ), also known as a retinal scan display ( RSD ) or retinal projector ( RP ), is a display technology that draws a raster display (like a television ) directly onto the retina of the eye.
› what-is › another-word-forWhat is another word for image? | Image Synonyms - WordHippo Synonyms for image include picture, photo, photograph, snapshot, reproduction, facsimile, portrait, shot, snap and avatar. Find more similar words at wordhippo.com!



















0 Response to "38 virtual image lens diagram"
Post a Comment