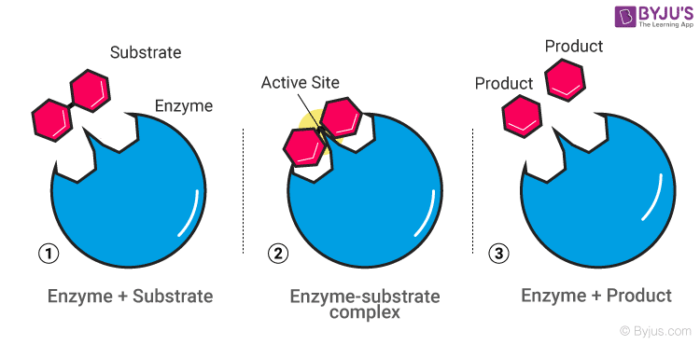
39 below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction
HW.docx - HW6 1. Which of the following is an assumption ... 1 . A chemical group within the enzyme that has a p Ka of around 7 is likely involved in the catalytic mechanism .b. For an uncatalyzed reaction in which Substrate is converted to Product , S < --> P , there is a forward rate constant , k F , of 10 - 5 / s , and a reverse rate Solved Below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general ... Question: Below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Put the labels in the correct locations. The abbreviations E, P, and S indicate the enzyme, product, and substrate, respectively. This problem has been solved! See the answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer 100% (159 ratings) The ab …
12.7 Catalysis - Chemistry - opentextbc.ca Gas and liquid phase reactions catalyzed by heterogeneous catalysts occur on the surface of the catalyst rather than within the gas or liquid phase. Heterogeneous catalysis has at least four steps: Adsorption of the reactant onto the surface of the catalyst Activation of the adsorbed reactant Reaction of the adsorbed reactant

Below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction
Answered: Complete the diagram of the mechanism… | bartleby Complete the diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. The abbreviations E, P, and S indicate the enzyme, product, and substrate, respectively. 1L Answer Bank E + P SP E + S ES Question 31 Transcribed Image Text:Complete the diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Chapter 7 Enzyme RQ + HW Flashcards | Quizlet The lock-and-key model of enzyme catalysis involves a rigid fit between the substrate and the enzyme. The following are critical for enzyme structure and function, EXCEPT covalent modification affecting the bioavailability of an enzyme. The ∆G‡ for a catalyzed reaction is indicated by which letter in the figure below? C (middle energy) Answered: The diagram shows the mechanism of a… | bartleby The diagram shows the mechanism of a general enzyme‑catalyzed reaction. Put the labels in the correct locations. The abbreviations E, P and S indicate the enzyme, product, and substrate, respectively. Transcribed Image Text: The diagram shows the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Put the labels in the correct locations.
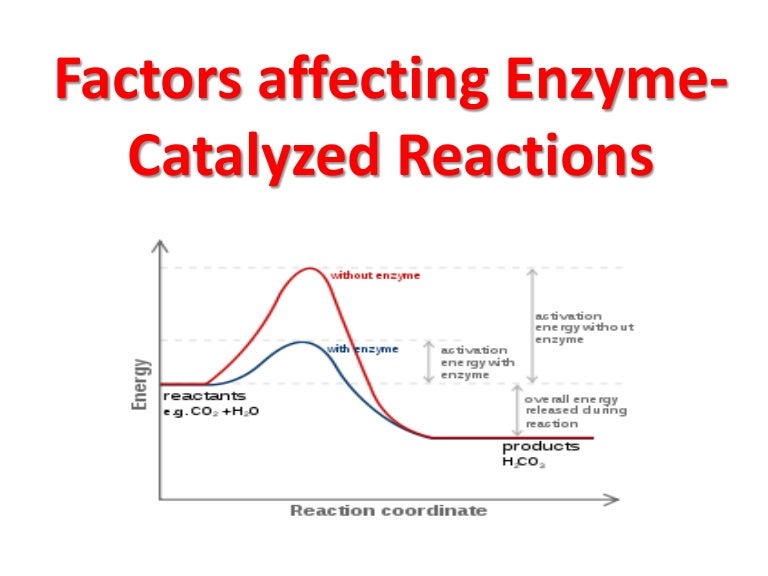
Below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. 12.7: Catalysis - Chemistry LibreTexts 1. Figure 12.7. 1: This graph compares the reaction coordinates for catalyzed and uncatalyzed alkene hydrogenation. Catalysts function by providing an alternate reaction mechanism that has a lower activation energy than would be found in the absence of the catalyst. In some cases, the catalyzed mechanism may include additional steps, as ... SOLVED:Q2 The free energy diagram of an enzyme- catalyzed ... Q2 The free energy diagram of an enzyme- catalyzed reaction is shown below. Please answer the following questions about this reaction making sure to provide a brief justification for your answer using appropriate biochemical terminology: 5 2 J ES E+P progress of reaction How many steps are involved in the mechanism of this reaction? b. Chapter 7: Catalytic Mechanisms of Enzymes - Chemistry An oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction is a type of chemical reaction that involves a transfer of electrons between two atoms or compounds. The substance that loses the electrons is said to be oxidized, while the substance that gains the electrons is said to be reduced. Redox reactions always have to occur together. Difference between catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions ... Catalyzed reaction has a lower activation energy because there is an enzyme present in the reaction. Uncatalyzed reaction has a higher activation energy because there is no enzyme present in the ...
Biochem Exam 2 Flashcards | Quizlet Consider the reaction above to answer the two questions below based on the following information. For the uncatalyzed reaction, kF (uncatalyzed) = 5 X 10-4 s-1 and Keq is 2.5 X 102. For the same reaction in the presence of an enzyme, kF (catalyzed) is 5 X 105 s-1. Remember that Keq = kF/kR = k1/k-1. A.) Solved Below is a | Chegg.com This problem has been solved! Below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Put the labels in the correct locations. The abbreviations E, P, and S indicate the enzyme, product, andsubstrate, respectively. 3.2: The Equations of Enzyme Kinetics - Chemistry LibreTexts Many enzyme-substrate reactions follow a simple mechanism that consists of the initial formation of an enzyme-substrate complex, \(ES\), which subsequently decomposes to form product, releasing the enzyme to react again. Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): An enzyme catalyzes the reaction of two substrates and to form one product. from Wikipedia. biochemistry chapter #6 Flashcards - Quizlet A mechanism 2) Which mode (s) of catalysis is/are classified as chemical effects? 1. Transition state stabilization 2. Acid-base catalysis 3. Covalent catalysis 4. Proximity effect A) 3 only. B) 1, 2 and 3. C) 2 and 3. D) All of them. C acid-base catalysis AND covalent catalysis : Section 6-1 3) How is the half-reaction Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu classified?
Catalysis | Chemistry for Majors - Lumen Learning Reaction diagrams for a chemical process with and without a catalyst are shown below. Both reactions involve a two-step mechanism with a rate-determining first step. Compute activation energies for the first step of each mechanism, and identify which corresponds to the catalyzed reaction. Reactions and Mechanism of Enzyme Catalysis - VEDANTU Enzyme Catalysis - An enzyme is a substance which fastens a chemical reaction. A substrate is attracted towards the active site of the enzyme which leads to the catalysis of a chemical reaction and formation of products. Read more about the Reactions and mechanism of enyme catalysis at vedantu.com. Biochem Chapter 7: Enzyme Mechanisms Flashcards | Quizlet Reaction coordinate diagrams clearly show that the energy of an enzyme bound to a transition state is higher than the energies of the E + S, E + P, and ES that occur along the same reaction coordinate. The energy of an enzyme bound to a transition state analog would lie _____ in the diagram. Energy diagrams for enzyme‐catalyzed reactions: Concepts ... Most modern Biochemistry textbooks, resting on the energetic profile of enzymic reaction, try to bridge the gap between the thermodynamic and the mechanistic description of enzyme action. In this sense, the energy diagram for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is an invaluable teaching and learning tool.
Energy Diagram Catalyzed Vs Uncatalyzed Reaction This effect can be illustrated with an energy profile diagram.Catalyzed reaction has a lower activation energy because there is an enzyme present in the reaction. Uncatalyzed reaction has a higher activation energy because there is no enzyme present in the reaction. Energy Diagrams for Catalyzed and Uncatalyzed Reactions.
Mechanism of Enzyme Reaction (With Equations) In an enzyme-catalysed biochemical reaction, the enzyme molecule binds specifically and reversibly to the substrate molecule resulting in formation and breaking of chemical bonds to produce the product. Thus, there is formation of an unstable enzyme-substrate complex which immediately breaks into the product.
Activation diagrams in enzyme catalysis - ScienceDirect Subscript n.e. refers to non-enzyme catalyzed reaction. 'Energy' not defined precisely (G, G~, etc.). At 2 = 0 and 2 = 1, activation diagrams for catalyzed and non-catalyzed reactions are congruent. If by 'energy' is meant G, then: (a) AG between substrate bound and non-bound is zero; and the concentrations must be adjusted for this.
of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Put the labels in ... of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Put the labels in t… Show more Below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Put the labels in the correct locations. The abbreviations E, P, and S indicate the enzyme, product, andsubstrate, respectively ______ <------> ______ <-------> _______ Labels: E+S SP E+P ES • Show less
12.7 Catalysis - Chemistry 2e - OpenStax For the first step, Ea = 80 kJ for (a) and 70 kJ for (b), so diagram (b) depicts the catalyzed reaction. Activation energies for the second steps of both mechanisms are the same, 20 kJ. Homogeneous Catalysts A homogeneous catalyst is present in the same phase as the reactants.
QUIZ 2 mega quizlet Flashcards | Quizlet The oxygen dissociation curve is sigmoidal in shape ("S"‑shaped). As oxygen binds to this molecule the shape of the molecule changes, enhancing further oxygen binding. The binding pattern for this molecule is considered cooperative. This molecule delivers oxygen more efficiently to tissues. Myoglobin
PDF Diagram Of An Enzyme Substrate Reaction labeled 1 enzymes and the, below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme catalyzed reaction put the labels in the correct locations put the labels in the correct locations the abbreviations e p and s indicate the enzyme product and substrate respectively, enzymes are proteins that have the ability to bind ...
Enzyme Mechanism - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Enzyme-catalyzed reactions are time-dependent. ... or enzyme displacement, mechanism where one product is released prior to the binding of the second substrate. This third major type of bimolecular reaction is depicted in the following diagram where E' indicates that the enzyme exists in a chemically modified form.
Answered: The diagram shows the mechanism of a… | bartleby The diagram shows the mechanism of a general enzyme‑catalyzed reaction. Put the labels in the correct locations. The abbreviations E, P and S indicate the enzyme, product, and substrate, respectively. Transcribed Image Text: The diagram shows the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Put the labels in the correct locations.
Chapter 7 Enzyme RQ + HW Flashcards | Quizlet The lock-and-key model of enzyme catalysis involves a rigid fit between the substrate and the enzyme. The following are critical for enzyme structure and function, EXCEPT covalent modification affecting the bioavailability of an enzyme. The ∆G‡ for a catalyzed reaction is indicated by which letter in the figure below? C (middle energy)
Answered: Complete the diagram of the mechanism… | bartleby Complete the diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. The abbreviations E, P, and S indicate the enzyme, product, and substrate, respectively. 1L Answer Bank E + P SP E + S ES Question 31 Transcribed Image Text:Complete the diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction.
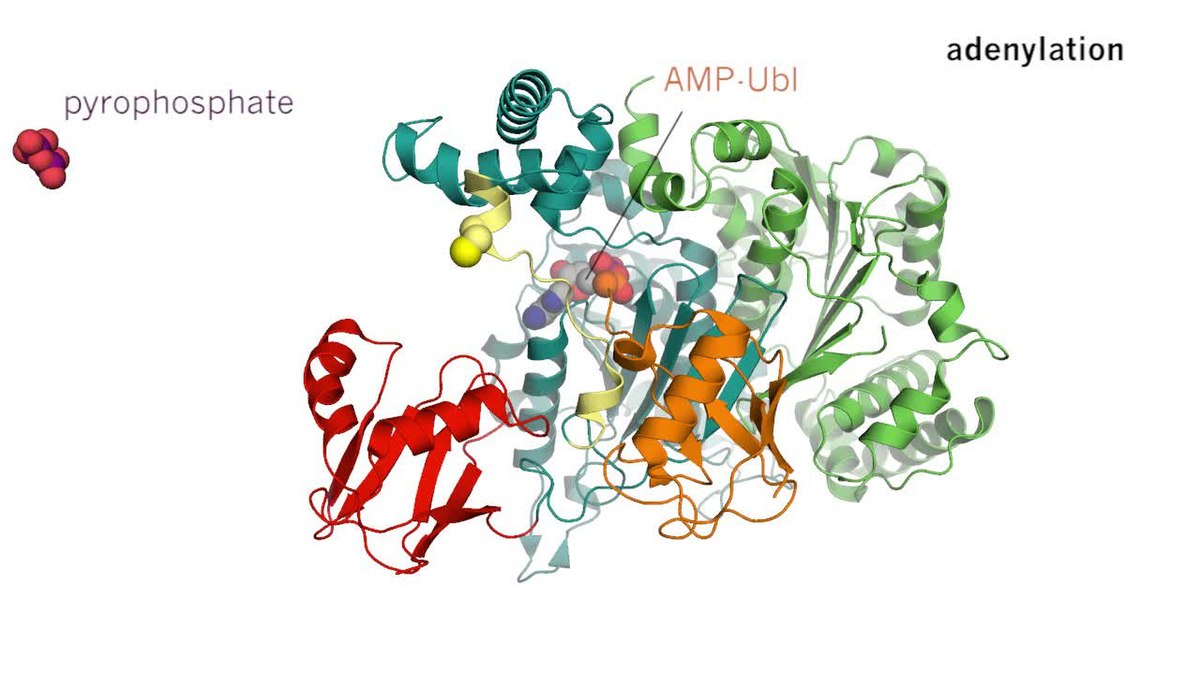





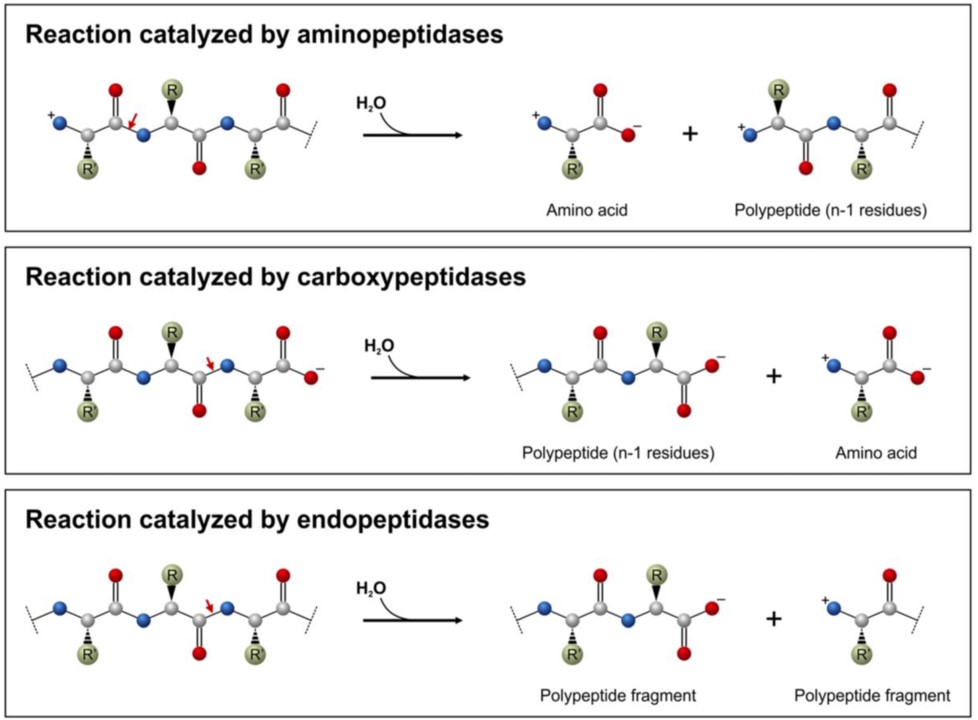




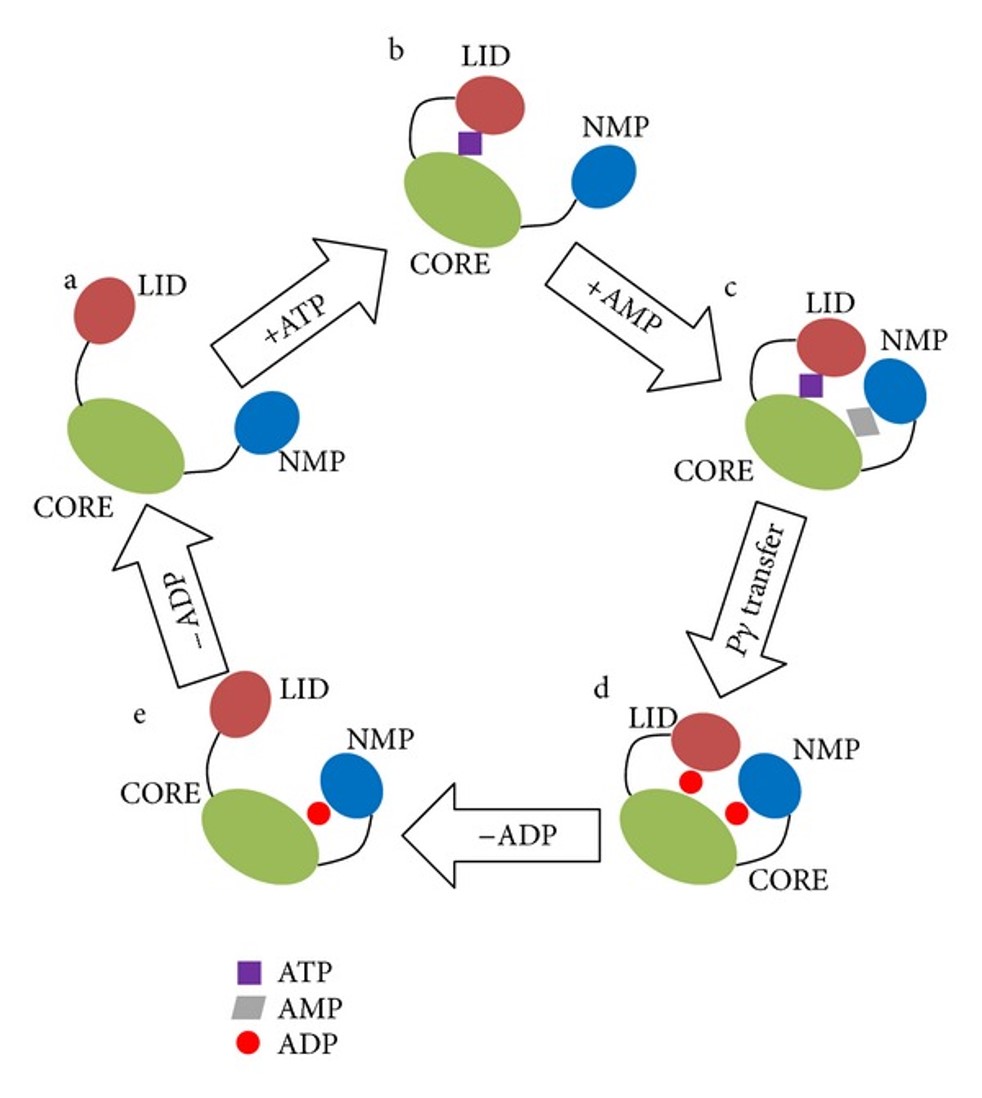
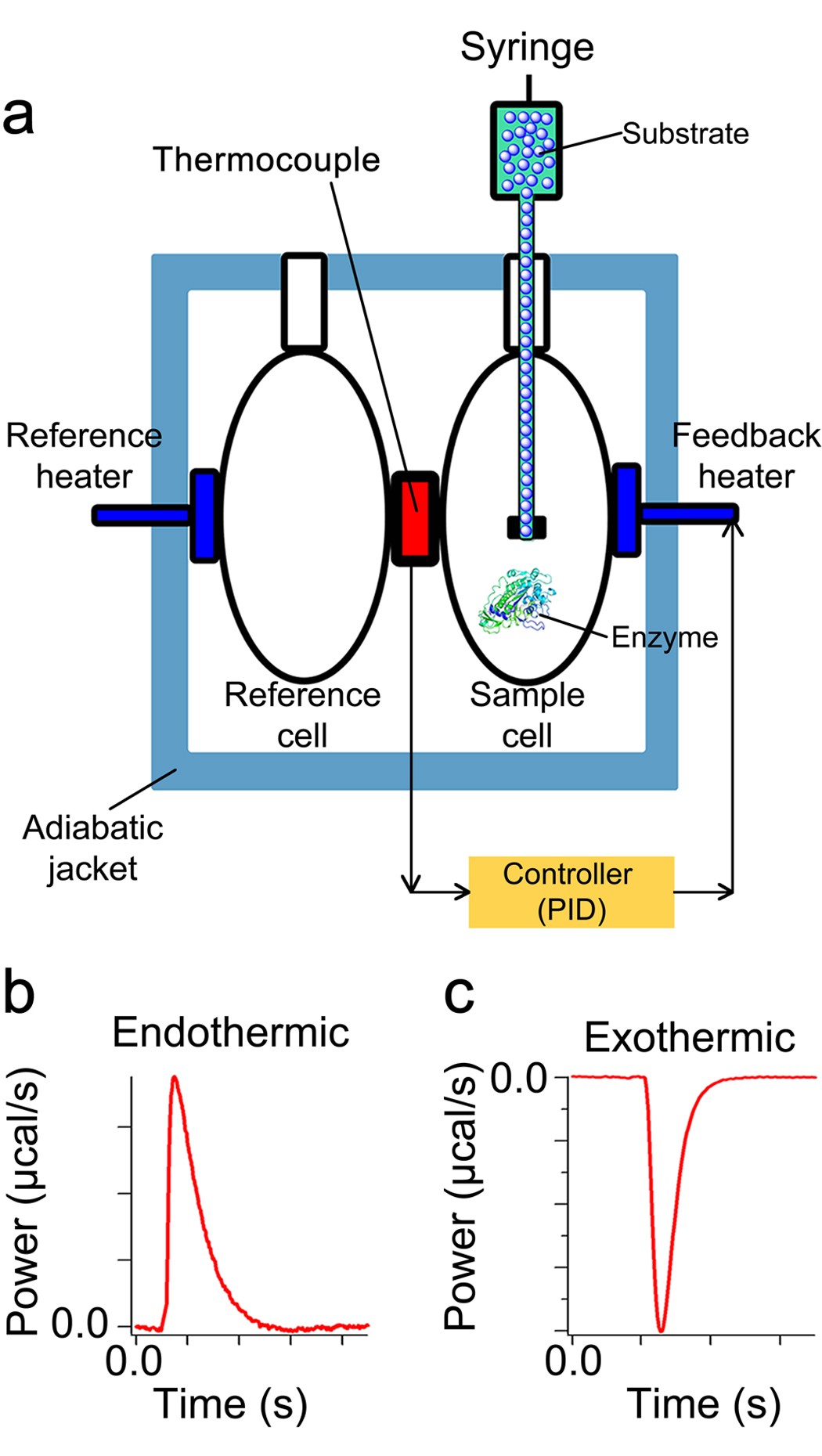
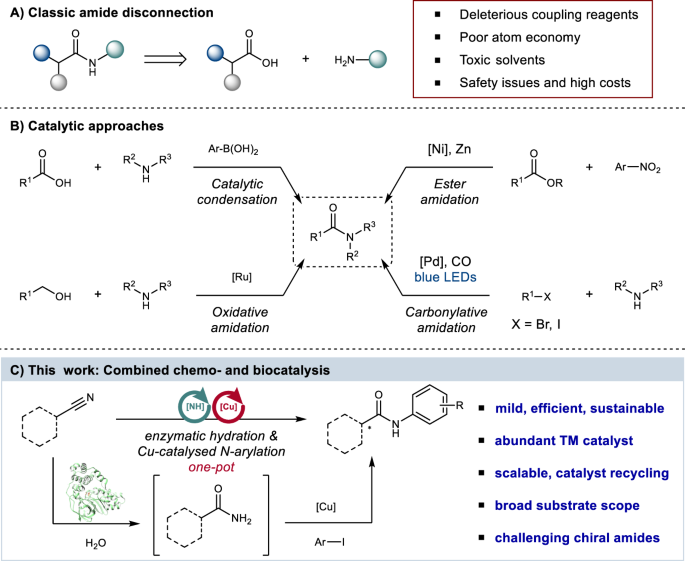
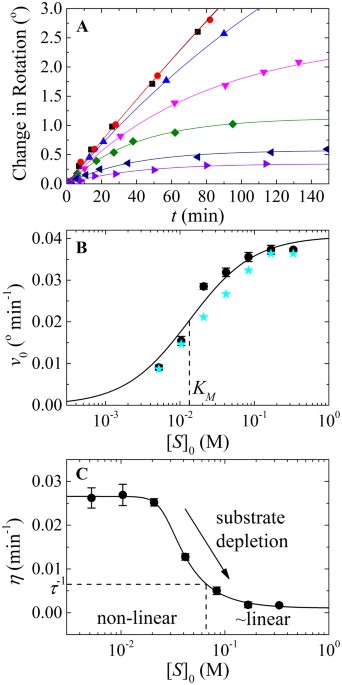


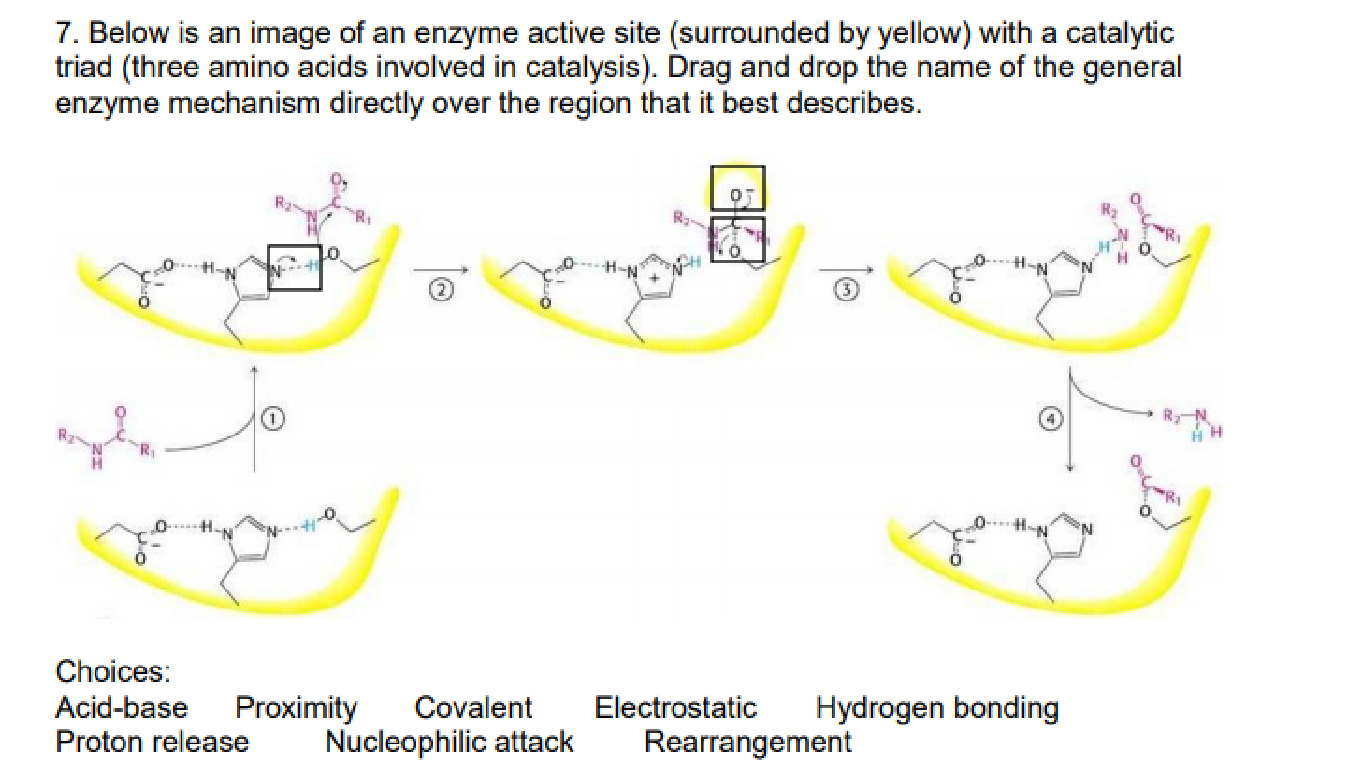
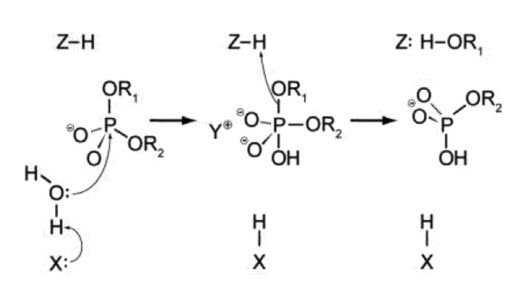
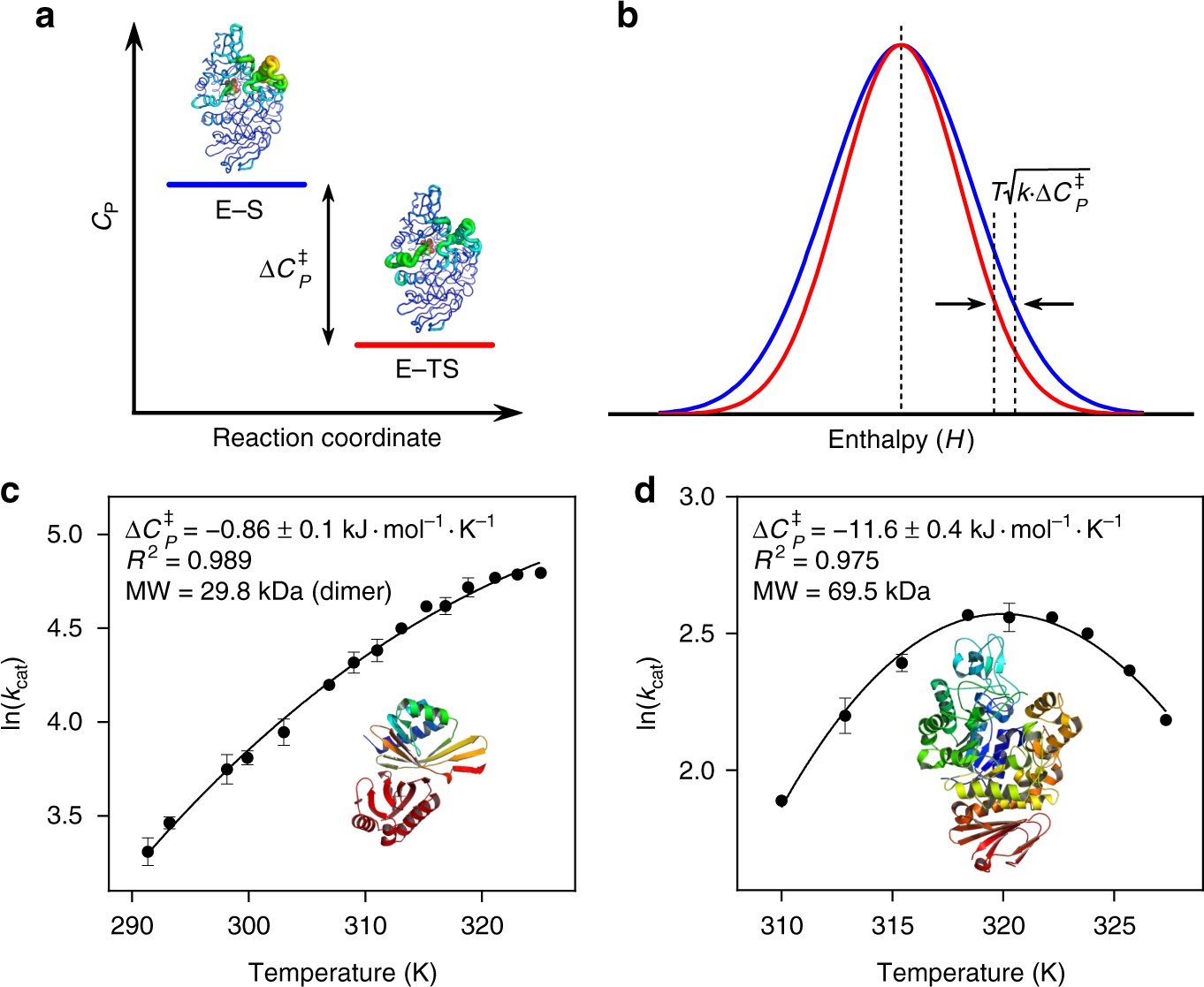


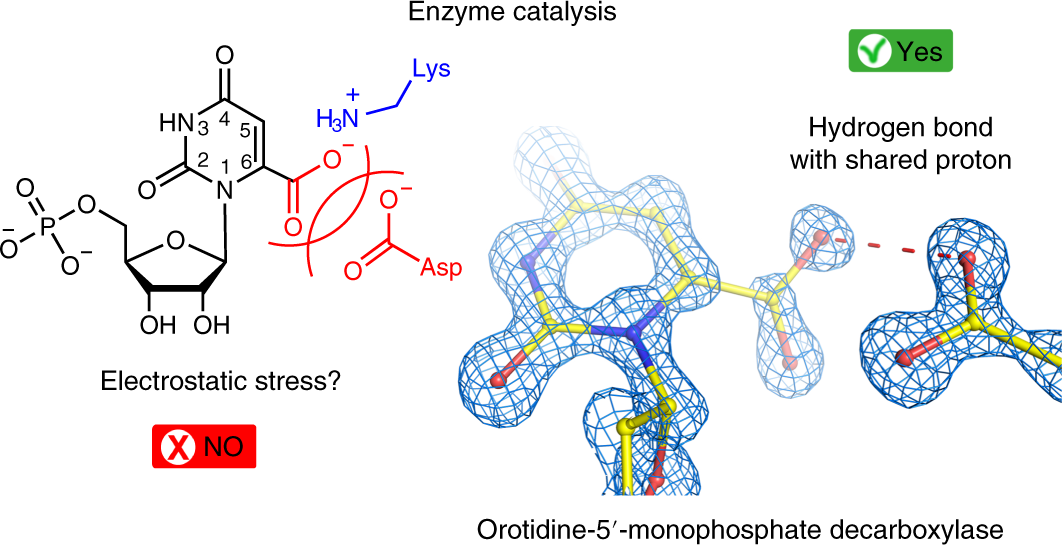







0 Response to "39 below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction"
Post a Comment