40 carbon molecular orbital diagram
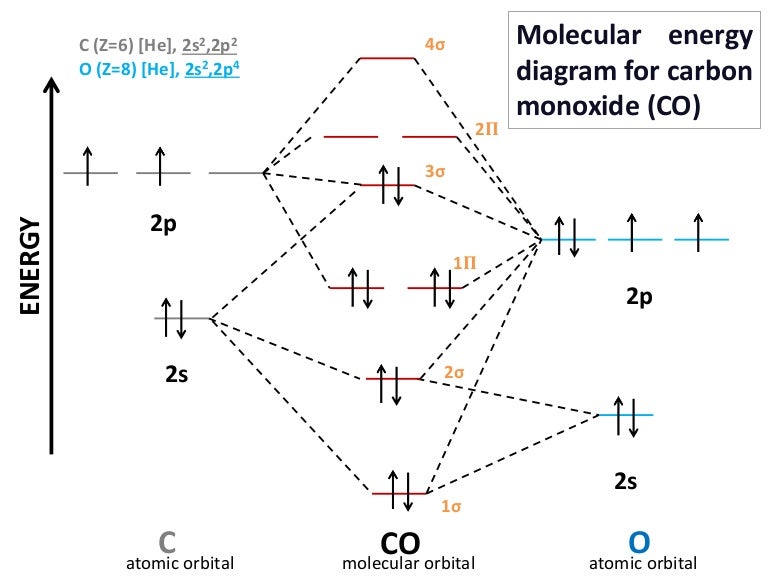
PDF Hybrid Molecular Orbitals - University of Illinois Urbana ... molecular orbital diagram as a non-bonding molecular orbital. 7. There are a total of 6 electrons to add to the molecular orbital diagram, 3 from boron and 1 from each hydrogen atom. sp Hybrid Orbitals in BeH2 1. The Lewis structure shows that the beryllium in BeH 2 makes 2 bonds and has no lone pairs. It is a linear molecule. Chemistry 104 ... Solved Draw the molecular orbital diagram for carbon ... Question: Draw the molecular orbital diagram for carbon monoxide. Label all molecular orbitals. Take into account that the high energy 2s orbital for carbon will mix with the low energy 2px orbital for oxygen. This problem has been solved!
PDF MO Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
Carbon molecular orbital diagram
Atomic and Molecular Orbitals - Michigan State University Atomic and Molecular Orbitals. A more detailed model of covalent bonding requires a consideration of valence shell atomic orbitals. For second period elements such as carbon, nitrogen and oxygen, these orbitals have been designated 2 s, 2p x, 2p y & 2p z. The spatial distribution of electrons occupying each of these orbitals is shown in the ... Molecular Orbital Diagram of Carbon Molecule - Nature of ... Molecular Orbital Diagram of Carbon Molecule Video Lecture from Chapter Nature of Chemical Bond of Subject Chemistry Class 11 for HSC, IIT JEE, CBSE & NEET.W... Explanation of the missing 1-s orbital electrons of carbon ... $\begingroup$ $99.9999...99$ % of the four atomic orbitals $1s$ of $\ce{H}$ are forming molecular orbitals with the $2s$ and $2p$ of the carbon atom. The rest, $0.000..01$ % is forming a dim molecular orbital with the $1s$ of the carbon. As a result, this molecular orbital is not different from the $1s$ of the carbon atom. $\endgroup$ -
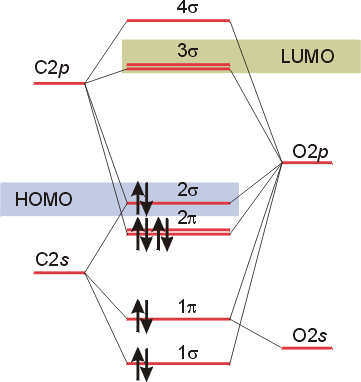
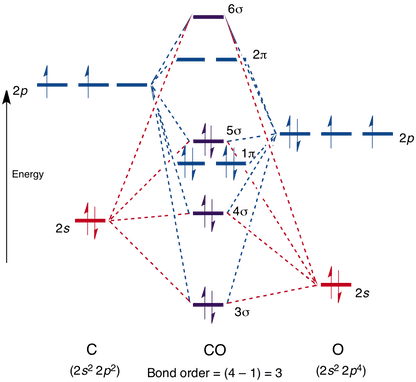
Carbon molecular orbital diagram. PDF Consider ethylene (also called ethene): C H . Draw a Lewis ... Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory (continued 1) • Filling of MOs with electrons is governed by the same rules as for atomic orbitals • Aufbau principle - Fill MOs beginning with the lowest energy unoccupied molecular orbital • Pauli exclusion principle - No more than two electrons can be accommodated in a MO, and their spins must be paired Carbon Monoxide Molecular Orbital Diagram Explanation There are 4 electrons in the outer shell of carbon and 6.A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. Molecular Orbital Theory | Boundless Chemistry Carbon monoxide, CO, has a total of 10 valence electrons. To satisfy the octet rule for the carbon, the two atoms form a triple bond with six shared electrons in three bonding molecular orbitals. Since four of the shared electrons come from the oxygen atom and only two from carbon, one of the bonding orbitals is occupied by two electrons from ... Molecular Orbital Diagram || Carbonyl M.o.t || Back ... in this video i have discussed about the molecular orbital diagram of co which is the most important ligand in organometalics and coordination chemistry.con...
Carbon Oxides - University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign Carbon dioxide is electron-poor at the central carbon and acts as an electrophile. The molecular orbital diagram of carbon monoxideis very similar to that of molecular nitrogen. Carbon, with 4 valence electrons, and oxygen with 6 valence electrons, together have the same number of electrons as dinitrogen. 13.3. Molecular orbitals for three-carbon systems ... Propene and higher alkenes. The pi-molecular orbitals in propene (CH 3-CH=CH 2) are essentially the same as those found in ethene, and so we need not examine them further.. Allene. However, when we look at allene (propa-1,2-diene), where we have two double bonds shared between three carbons, we find a new situation. The two outer carbons are still sp 2 hybridized, but the central carbon is now ... Carbon(C) electron configuration and orbital diagram Carbon (C) orbital diagram 1s is the closest and lowest energy orbital to the nucleus. Therefore, the electron will first enter the 1s orbital. According to Hund's principle, the first electron will enter in the clockwise direction and the next electron will enter the 1s orbital in the anti-clockwise direction. What is the orbital diagram for carbon? - MSI Carbon has 6 protons and electrons, so it has 2 in the 1S orbital, 2 in the 2S orbital, and 2 in the 1P orbital. This is often expressed as [HE]2S2 2Ps, because it has the same configuration as helium plus 4 additional electrons whose positions are shown after the bracketed element. How many protons and electrons does carbon have?
techiescientist.com › c2h4-lewis-structureC2H4 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, and ... Apr 04, 2022 · ( the antibonding orbital remains empty). The above diagram shows the Molecular Orbital(MO) diagram of ethene/ethylene. Polarity of C2H4. The C2H4 molecule is non-polar in nature as all the atoms are symmetrically arranged across the molecule and both carbon atoms have the same influence on the bonded electrons. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Non-bonding_orbitalNon-bonding orbital - Wikipedia An example of a non-similar one is the non-bonding orbital of the allyl anion, whose electron density is concentrated on the first and third carbon atoms. In fully delocalized canonical molecular orbital theory, it is often the case that none of the molecular orbitals of a molecular are strictly non-bonding in nature. 8 - Drawing Molecular Orbital Diagrams — Flux Science 8 - Drawing Molecular Orbital Diagrams. Abstract (TL;DR) Molecular orbital diagrams are a fantastic way of visualizing how molecular orbitals form using what we already understand about sigma and pi bonds. Depending on if it is a homonuclear case, where the bonding atoms are the same, or a heteronuclear case, where the bonding atoms are ... What is molecular orbital diagram of CO? - handlebar ... What is the molecular orbital configuration of CO? The suggested molecular orbital electronic configuration of Co is : KK (sigma_2s)^2 (sigma _ (2s))^2, (pi_ (2px))^2 (pi_ (2py))^2 (sigma_ (2pz))^2. Experimentally determined bond length in CO and CO^+ are 112.8 pm and 111.5 pm . What is an orbital energy diagram?
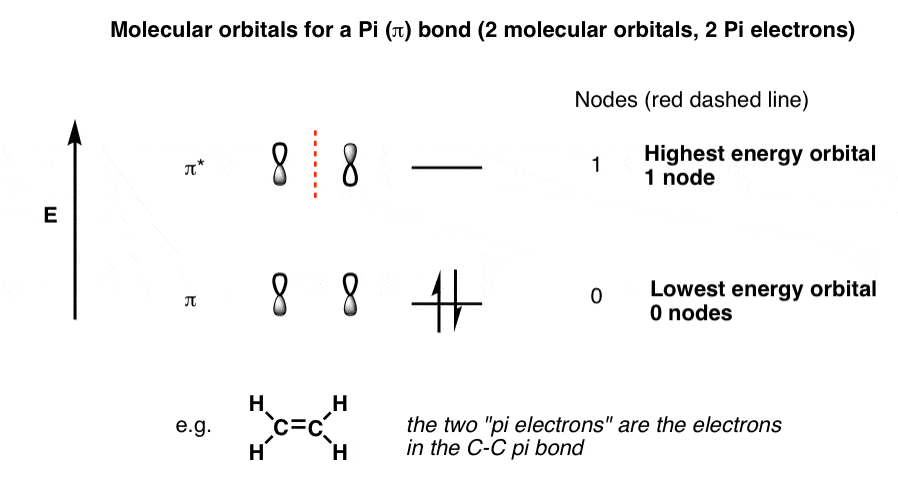
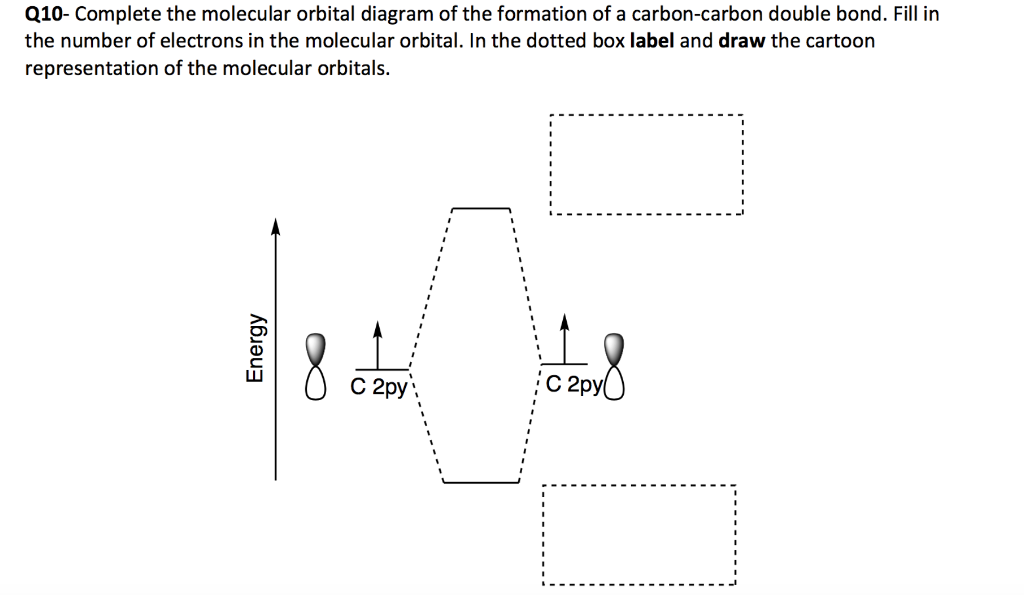
PDF 1 Lecture 2 Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds ... Each 2p orbital extends along its entire axis with opposite phase in each lobe. 2pz 2px Carbon has one electron available for each orbital to share with bonding partners. H C C H sp hybridized carbon carbon atom shape = linear bond angles about sp carbon = 180o number of sigma bonds = 2 number of pi bonds = 2 These terms all go together.
CN- lewis structure, molecular orbital diagram, and, bond ... Procedure to draw the molecular orbital diagram of CN 1. Find the valence electron of each atom in the CN molecule. Clearly, carbon has 4 valence electrons and nitrogen has 5. 2. Find if the molecule homo-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital or hetero-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital. Clearly, CN is hetero orbital. 3.
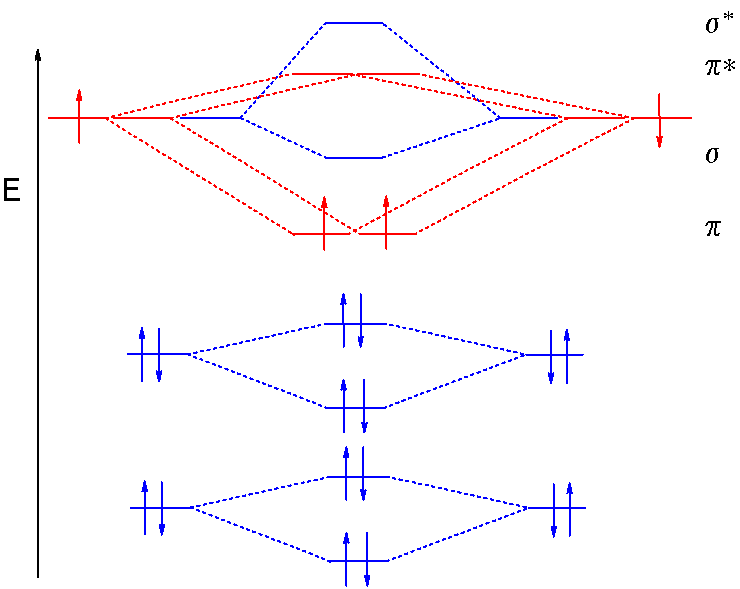
Molecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of molecular orbital (MO) energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center, flanked by constituent atomic orbital (AO) energy levels for comparison, with the energy levels increasing from the bottom to the top. Lines, often dashed diagonal lines, connect MO levels with their constituent AO levels.
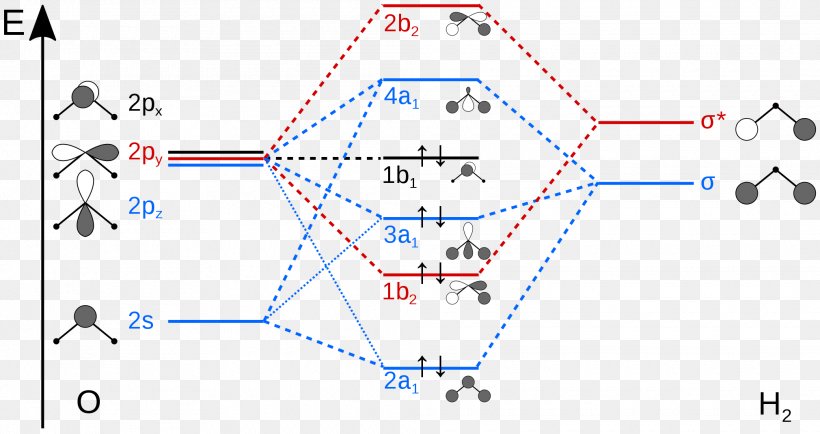
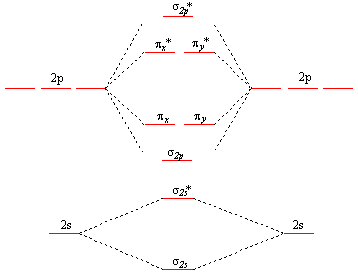
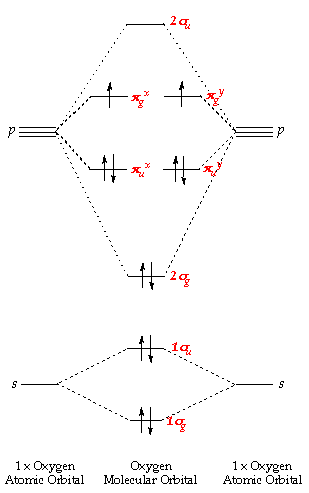
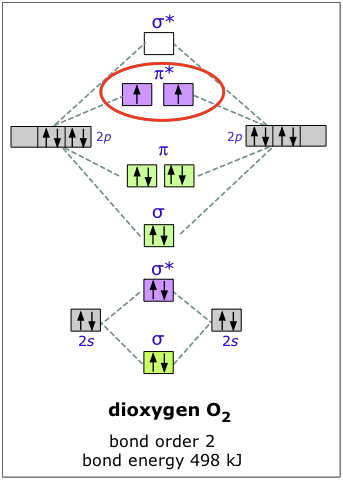
Molecular Orbital Theory - Purdue University Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ...
Carbon Monoxide Molecular Orbital Diagram Explanation A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. . combinations such as CO and NO show that the 3σg MO is higher in energy. Click on the CO molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals.
› 2017/02/16Molecular Orbitals of The Allyl Cation, Allyl Radical, and ... Feb 16, 2017 · How To Draw The Molecular Orbitals of The Allyl Cation, Allyl Radical And Allyl Anion. Drawing the molecular orbitals of a pi system like allyl (3 conjugated p-orbitals) is a bit like construction: build the house (orbitals) first, and fill it with people (electrons) second.
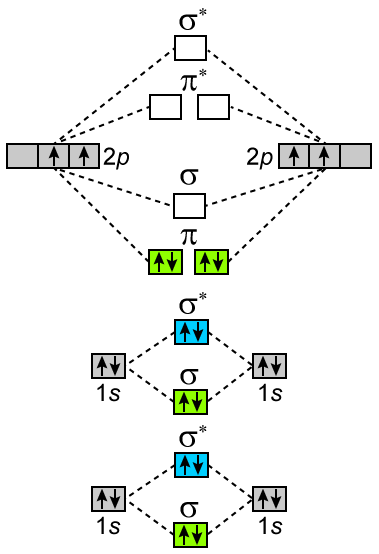
What is the molecular orbital diagram for C−2? - Socratic The lowest energy unoccupied molecular orbital is 2pσ, so that is where the extra electron will be added. The electron configuration of the neutral C2 molecule is -- I'll use the notation given to you in the diagram. C2:(1sσ)2(1s* σ)2(2sσ)2(2s* σ)2(2pπ)4. The electron configuration of the C− 2 ion will be.
PDF Miessler-Fischer-Tarr5e SM Ch 05 CM molecular orbitals in the diagram ... carbon: Carbon's remaining 2p orbitals are nonbonding. b. Linear CH2 is a paramagnetic diradical, with one electron in each of the px and py orbitals of carbon. (A bent singlet state, with all electrons paired, is also known, with a calculated
Molecular orbitals in Carbon Monoxide - ChemTube3D Home / Structure and Bonding / Atomic Orbitals / Molecular orbitals in Carbon Monoxide. Molecular orbitals in Carbon Monoxide. CONTROLS > Click on the CO molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. Explore bonding orbitals in other small molecules.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Orbital_hybridisationOrbital hybridisation - Wikipedia In ethylene the two carbon atoms form a σ bond by overlapping one sp 2 orbital from each carbon atom. The π bond between the carbon atoms perpendicular to the molecular plane is formed by 2p–2p overlap. Each carbon atom forms covalent C–H bonds with two hydrogens by s–sp 2 overlap, all with 120° bond angles. The hydrogen–carbon bonds ...
Molecular orbital diagram - Infogalactic: the planetary ... Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of molecular orbital (MO) energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center, flanked by constituent atomic orbital (AO) energy levels for comparison, with the energy levels increasing from the bottom to the top. Lines, often dashed diagonal lines, connect MO levels with their constituent AO levels.
Co2+ Orbital Diagram - schematron.org The second diagram corrects this by realizing there are two unused p orbitals on the carbon. The valence electron configuration of "O" is ["He"] 2s^2 2p^4. To accommodate the two lone pairs and the bonding pair, it will also form three equivalent sp^2 hybrid orbitals.
PDF MO Diagrams for Linear and Bent Molecules Molecular Orbitals for Larger Molecules 1. Determine point group of molecule (if linear, use D2h and C2v instead of D∞h or C∞v) 2. Assign x, y, z coordinates (z axis is principal axis; if non-linear, y axes of outer atoms point to central atom)3. Find the characters of the reducible representationfor the combination of
Lecture B8 Molecular Orbital Theory, Part 3 diagrams for heteronuclear diatomics: 0. Draw the vacuum level. 1. Put the atomic orbitals for each bonding partner in your diagram. Position the HOAO based ...50 pages
PDF ORBITALS and MOLECULAR REPRESENTATION CARBON ORBITALS 18 BENZENE C 6 H 6 This picture illustrates the delocalization of the six 2p electrons in the benzene molecule. These six electons are shared collectively among all six of the carbon atoms. ORBITALS AND MOLECULAR REPRESENTATION
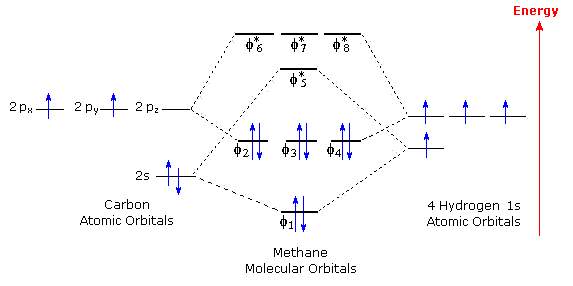
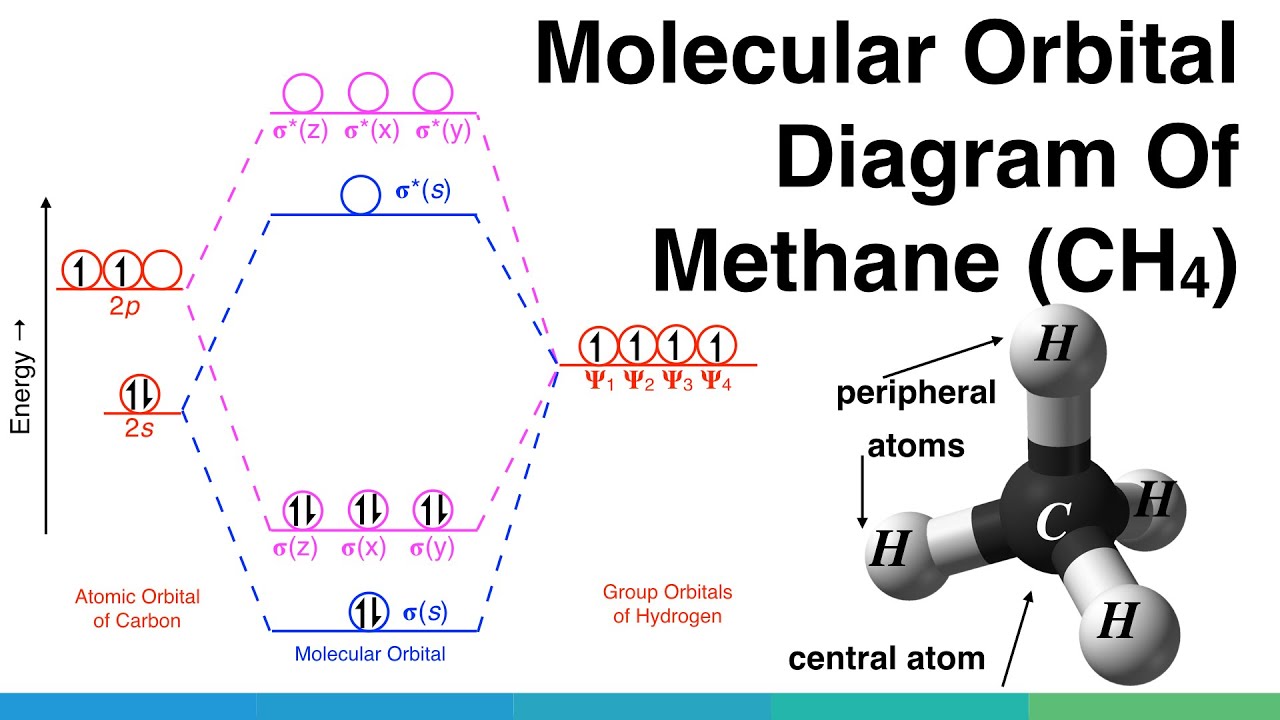
Polyatomic Species | Molecular Orbital Theory | Chemogenesis Introduction: Methane, CH 4. Using the carbon and hydrogen atomic orbitals, methane, CH 4, is constructed by overlapping the carbon's one 2s and three 2p AOs with the four hydrogen 1s AOs.. Methane's MOs have a topology similar to the AOs of carbon, but the structure can be very difficult to visualise, so the methane MO construction diagrams A, B and C (below) are shown with the AOs and MOs ...
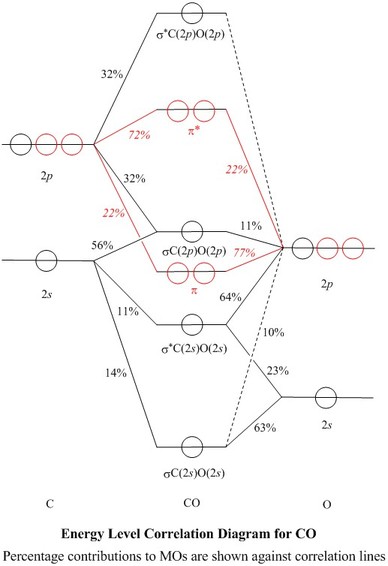
Molecular Orbitals for Carbon Monoxide - Newcastle University Molecular Orbitals for CO. Jmol models of wavefunctions calculated at the RHF/3-21G* level. To view a model, click on a molecular orbital in the energy level correlation diagram shown The results displayed may be switched between those from a low level of calculation and those from a high level.
Explanation of the missing 1-s orbital electrons of carbon ... $\begingroup$ $99.9999...99$ % of the four atomic orbitals $1s$ of $\ce{H}$ are forming molecular orbitals with the $2s$ and $2p$ of the carbon atom. The rest, $0.000..01$ % is forming a dim molecular orbital with the $1s$ of the carbon. As a result, this molecular orbital is not different from the $1s$ of the carbon atom. $\endgroup$ -
Molecular Orbital Diagram of Carbon Molecule - Nature of ... Molecular Orbital Diagram of Carbon Molecule Video Lecture from Chapter Nature of Chemical Bond of Subject Chemistry Class 11 for HSC, IIT JEE, CBSE & NEET.W...
Atomic and Molecular Orbitals - Michigan State University Atomic and Molecular Orbitals. A more detailed model of covalent bonding requires a consideration of valence shell atomic orbitals. For second period elements such as carbon, nitrogen and oxygen, these orbitals have been designated 2 s, 2p x, 2p y & 2p z. The spatial distribution of electrons occupying each of these orbitals is shown in the ...
















0 Response to "40 carbon molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment