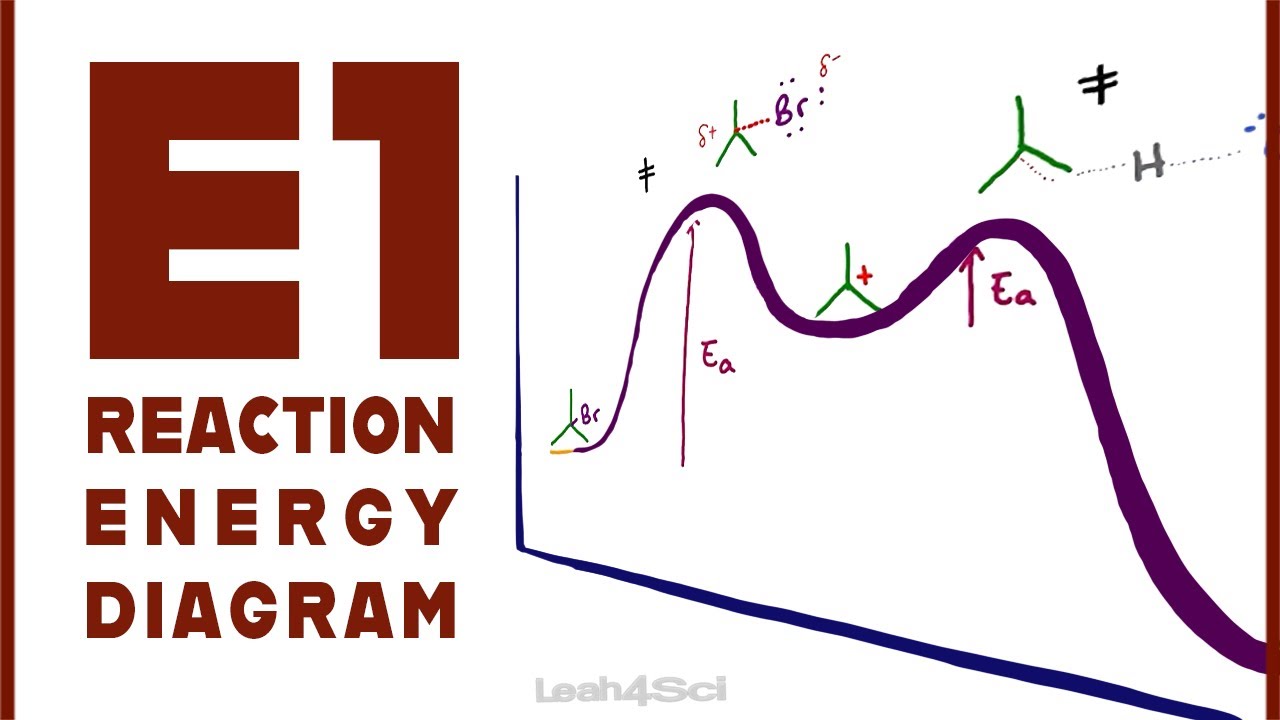
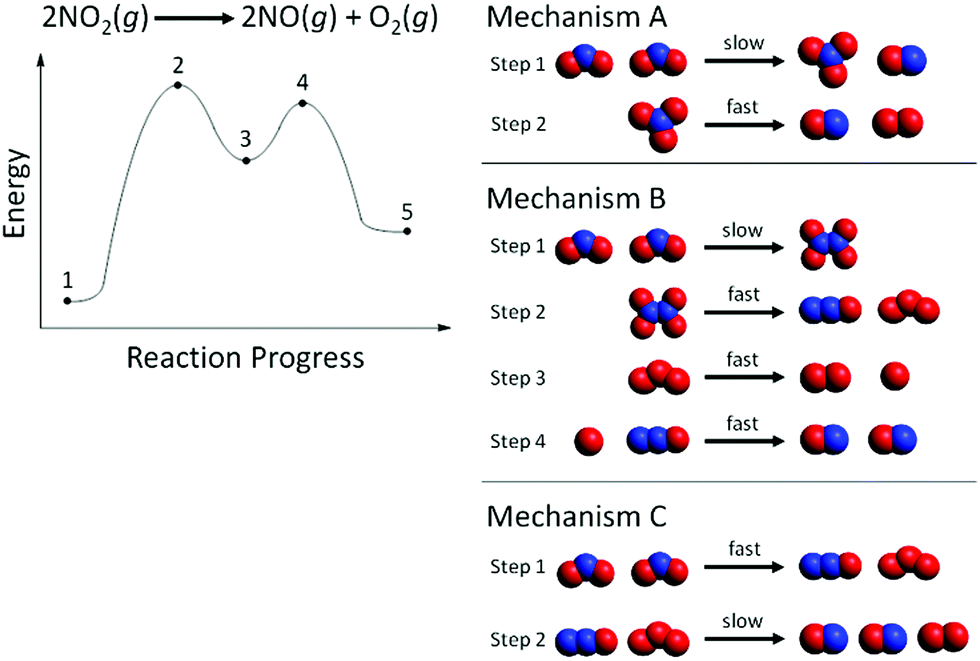
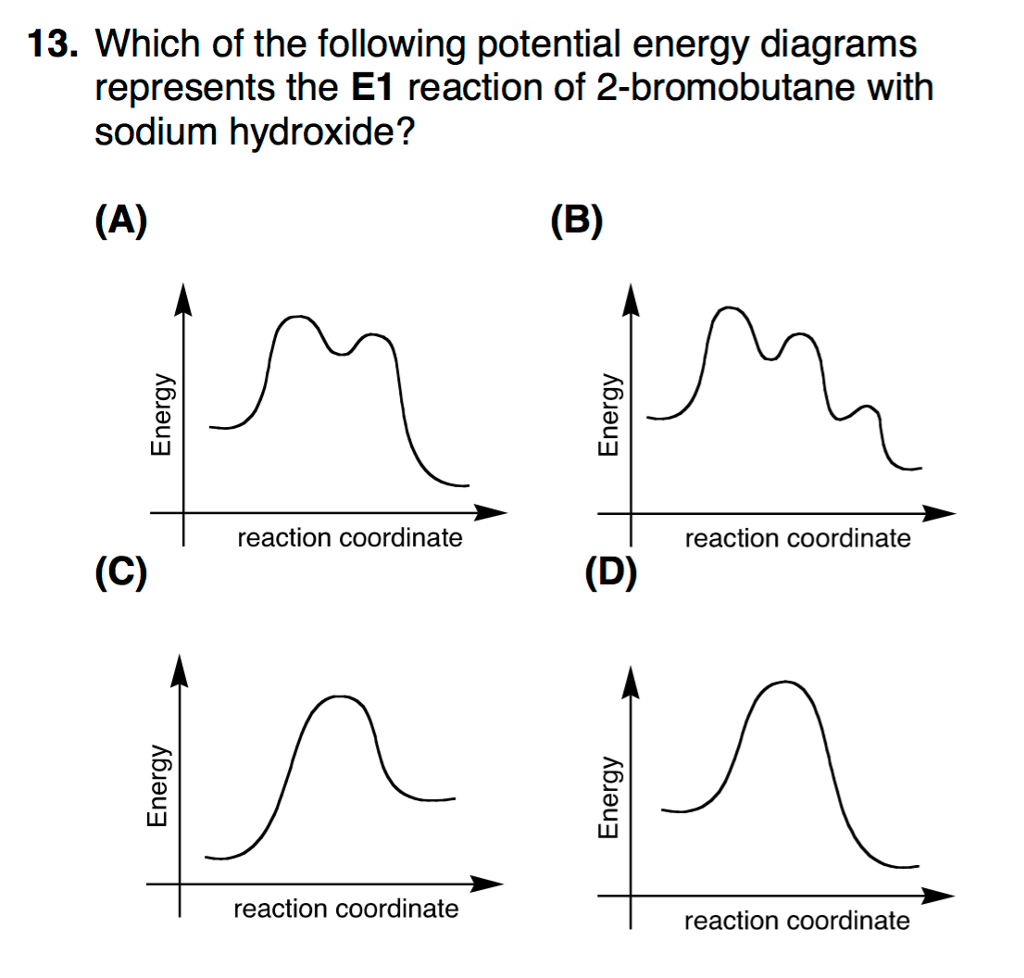
40 e1 reaction coordinate diagram
Organic Chemistry: E1 Reaction with Alkyl Halides ... This reaction is good but check out our new improved animation of the E1 reaction!The E1 reaction with an alkyl halide occurs in two steps. In the first ste... More O'Ferrall-Jencks plot - Wikipedia More O'Ferrall-Jencks plots are two-dimensional representations of multiple reaction coordinate potential energy surfaces for chemical reactions that involve simultaneous changes in two bonds.As such, they are a useful tool to explain or predict how changes in the reactants or reaction conditions can affect the position and geometry of the transition state of a reaction for which there are ...
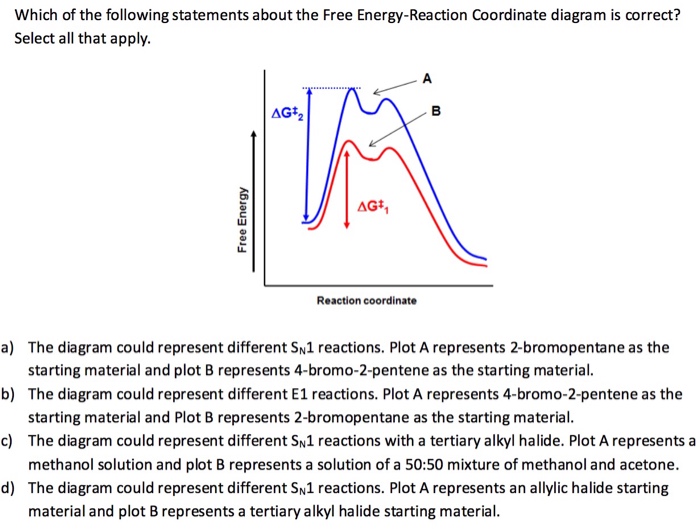
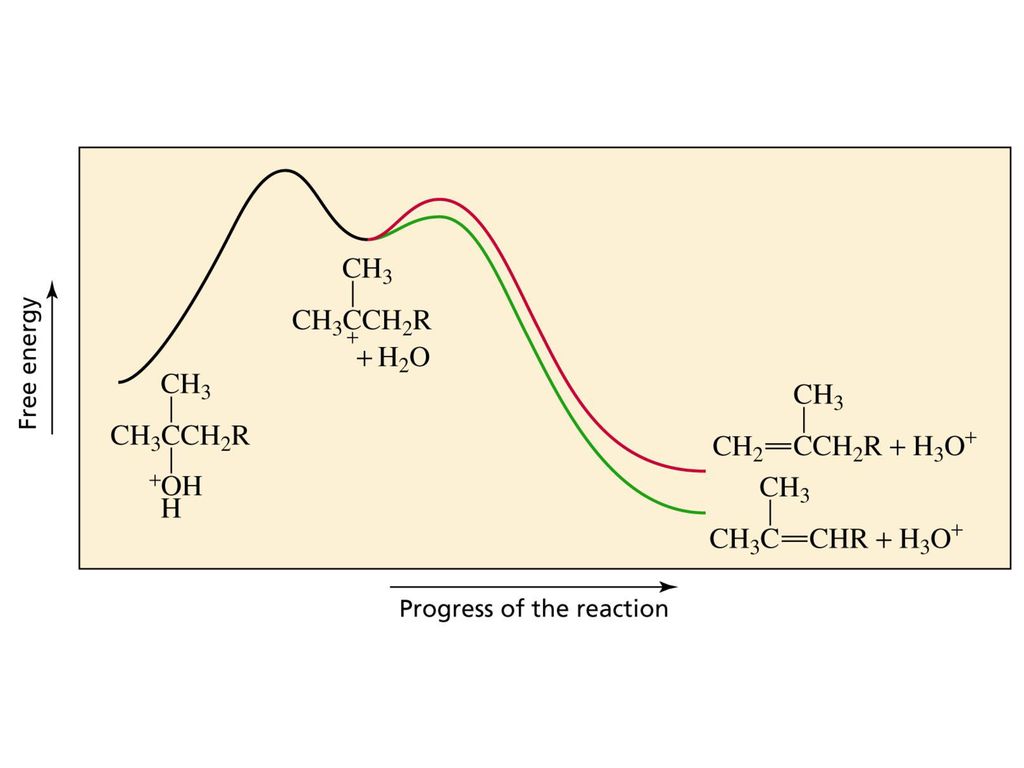
PDF 9.6 THE SN1 AND E1 REACTIONS - Macmillan Learning reaction coordinate Br Figure 9.11 Reaction free-energy diagram for the S N1-E1 solvolysis reaction of (CH 3) 3CBr with ethanol.The rate-limiting step,ionization of the alkyl halide (red curve),has the transition state of highest standard free energy.The

E1 reaction coordinate diagram
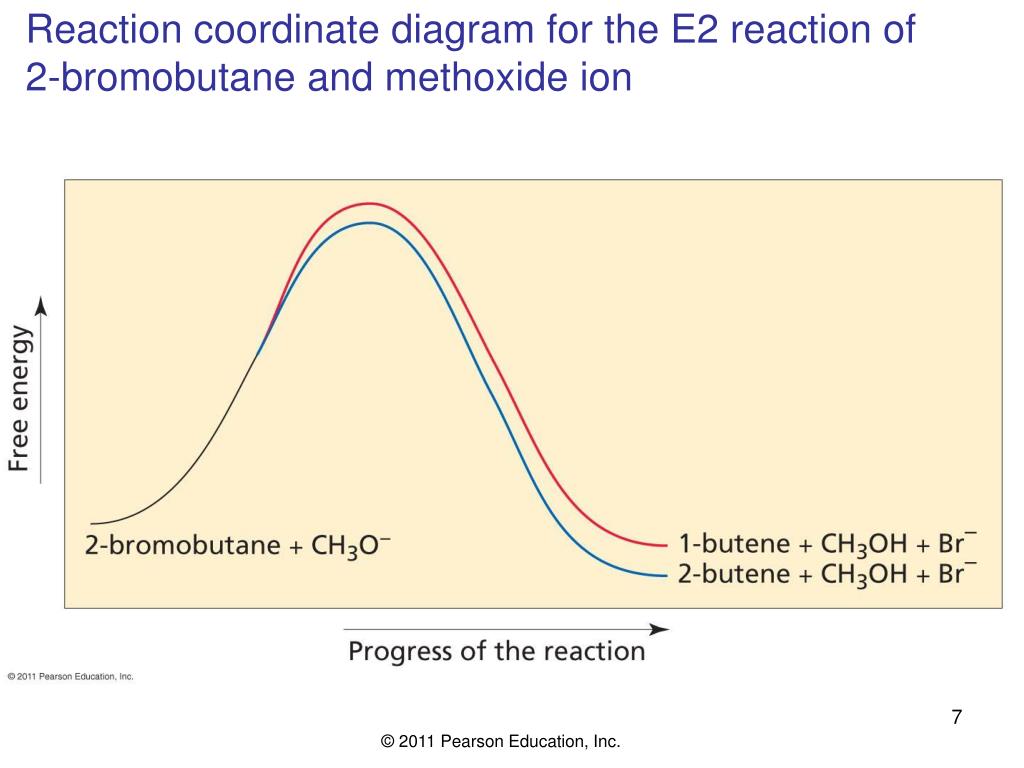
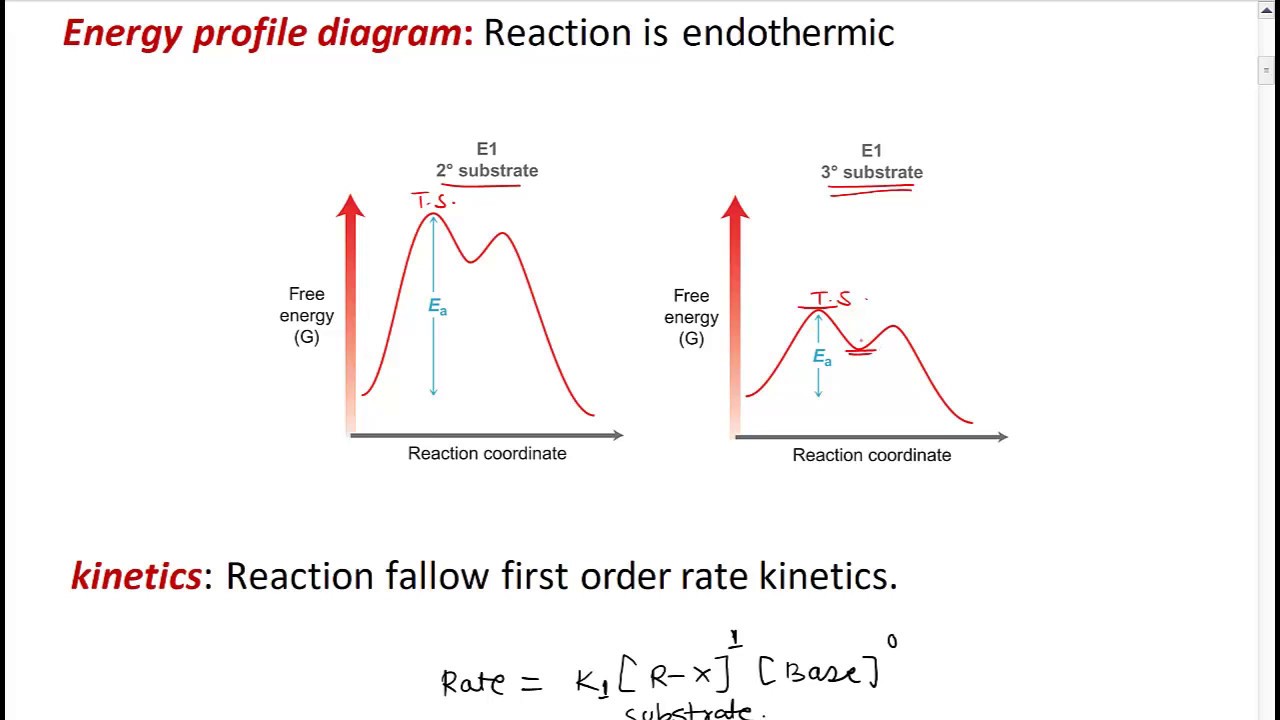
PDF Elimination Reactions - IIT Kanpur Factors Affectin g the Rate of an E1 Reaction The rate of an E1 reaction increases as the number of R groups on the carbon with the leaving group increases. Increasing rate of E1 reaction RCH 2 XR 2CH XR 3C X 1° 2° 3° + + + I i bili f b i RCH 2 R 2CH R 3C 1° 2° 3° ncreas ng sta ty o car ocat ons The strength of the base usually determines whether a reaction follows the E1 or E2 mechanism. PDF Dehydrohalogenation of Alkyl Halides E2 and E1 Reactions ... Reaction coordinate diagram for the E1 reaction of 2-chloro-2-methylbutane. Must consider possible carbocation rearrangement. Stereochemistry of the E1 Reaction. E1 Elimination from Cyclic Compounds E1 mechanism involves both syn and anti elimination. Summary & Applications (Synthesis) S N 1 / E1 vs. S N Sn1 Reaction Coordinate Diagram Sn1 Reaction Coordinate Diagram. SN1 reaction is a two step reaction as mentioned below: 1. Leaving group leaves first being solvolysed by solvent creating a carbocation intermediate. This is. whose proposed mechanism and free energy diagram are depicted Figures 1 and 2. Figure 2: Reaction coordinate diagram for an SN1 reaction1. 1. Identify the .
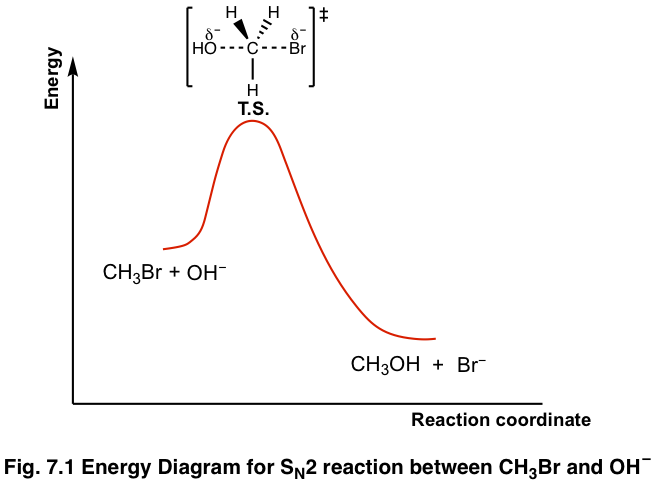
E1 reaction coordinate diagram. What is the Difference Between a Transition State and an ... On this diagram we see: the x-axis that is a reaction coordinate: a loosely defined term meaning the reaction progress in the general direction from the starting materials or reagents (SM) to the products (Pr). the energy curve describing the energy states of the components at a certain point in the reaction. Energy Diagrams: Describing Chemical Reactions Energy Diagrams: Describing Chemical Reactions. Energy changes accompany chemical reactions. Energy diagrams are quite useful in illustrating these changes on a continuous basis as the reaction proceeds. Terms such as "activation energy" (E a), "transition state" (*), and "enthalpy change" are easy to define by referring to a graph such as ... Energy Diagram For Sn2 SN2 reaction coordinate diagram. In this diagram, there are really only three parts: the reagents, the transition state, and the products. The transition state is the point in the reaction with the highest energy level, and the difference in energy between the reagents and transition state is called the activation energy (often abbreviated as Ea). CHEM 213 Chapter 8 - Alkyl Halides and Elimination ... The reaction coordinate vs. energy diagram has two energy barriers. The bond to the leaving group breaks before the π bond is formed. Select all statements that correctly describe a dehydrohalogenation reaction that proceeds via an E1 mechanism.
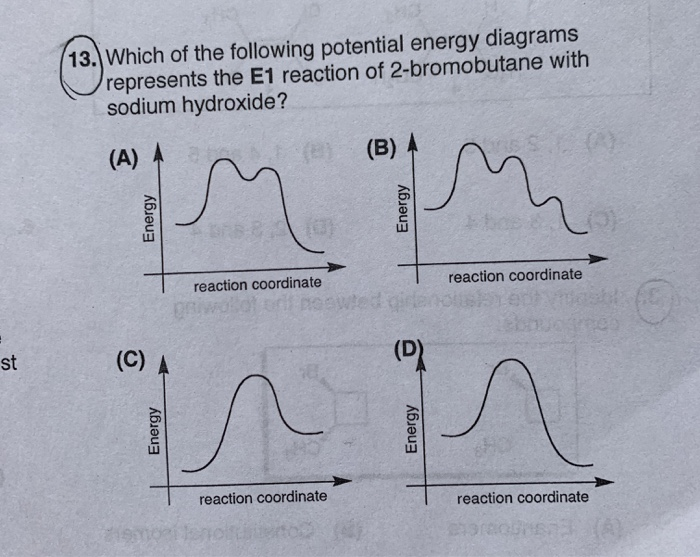
Ch 8 : SN2 mechanism - Faculty of Science This pathway is a concerted process (single step) as shown by the following reaction coordinate diagrams, where there is simultaneous attack of the nucleophile and displacement of the leaving group. The nucleophile attacks at the carbon with the partial positive charge as a result of the polar s bond to the electronegative atoms in the leaving group. Substitution and Elimination Reactions Flashcards - Quizlet Reaction Coordinate Diagram for E1 Types of Products in E2 reactions Zaitsev or major PDT (more substituted & Thermodynamically stable PDT). Hoffman or minor PDT (less substituted & less Thermodynamically stable PDT). How does a base affect regiochemistry? As size of B: increases, the stability of the PDT increases in Hoffman form. Solved Based upon the following energy diagram, is this ... Based upon the following energy diagram, is this reaction an E1 or an E2 elimination? reaction coordinate Question : Based upon the following energy diagram, is this reaction an E1 or an E2 elimination? reaction coordinate Elimination - SlideShare Reaction coordinate diagram for the E1 reaction of 2-chloro-2-methylbutane 46 © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. 47. Carbocation rearrangement © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
Solved Based upon the energy diagram shown, is this ... Based upon the energy diagram shown, is this reaction an E1 or an E2 elimination? free energy, kJ/mol reaction coordinate O E1 elimination O E2 elimination O It is impossible to determine from the diagram alone. The diagram suggests that it is not an elimination reaction. What substitution reaction mechanism is most likely for the conversion shown? PDF Eliminations Instead of substitution reactions, another ... Reaction Coordinate! S N 1! Potential energy! Reaction Coordinate! E1! S N 1 and E1 Reactions Have Identical Energy Diagrams for Rate Determining Step! Cl H CH3 3C H3C Cl H CH3 3C H3C CH3 H3C CH3 CH3 H3C CH3 OCH3 H CH3 3C H3C H2C CH3 CH3 B CH3OH Rate = k [substrate]! Rate = k [substrate]! 7.15: Characteristics of the E1 Reaction - Chemistry ... Regiochemistry & Stereochemistry of the E1 Reaction. The E1 reaction is regiospecific because it follows Zaitsev's rule that states the more substituted alkene is the major product. This infers that the hydrogen on the most substituted carbon is the most probable to be deprotonated, thus allowing for the most substituted alkene to be formed. Unlike E2 reactions, the E1 reaction is not stereospecific. SOLVED:(10 points) The reaction coordinate diagram below ... drew an energy diagram for the addition off HB are toe 1 19 That's the energy versus reaction. Coordinate. Starting materials spirals through this point on that girl. Let one curve on your diagram. Show the information off one Brumer contain the curve on the left would respond to the formacion off one bomber contain, which is at this point, and the curve on the right will respond to the ...
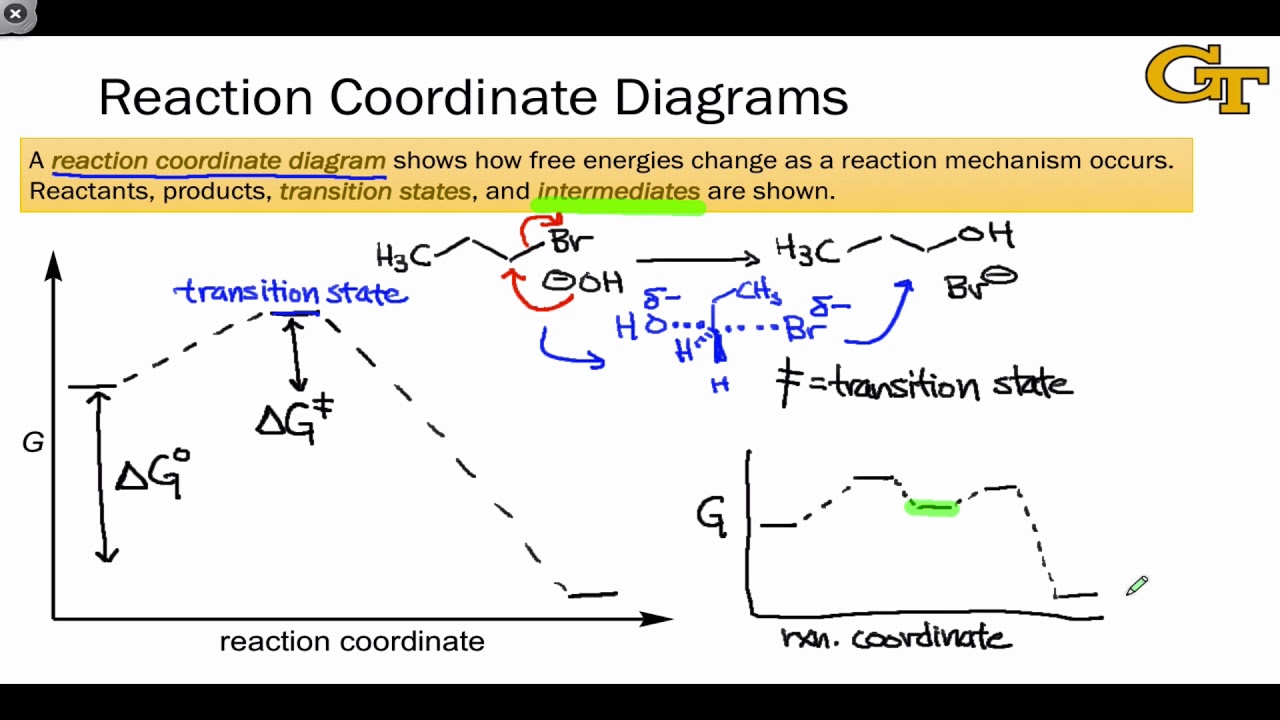
5.3. Reaction coordinate diagrams | Organic Chemistry 1 ... Reaction coordinate diagrams You may recall from general chemistry that it is often convenient to describe chemical reactions with energy diagrams. In an energy diagram, the vertical axis represents the overall energy of the reactants, while the horizontal axis is the ' reaction coordinate ', tracing from left to right the progress of the reaction from starting compounds to final products.
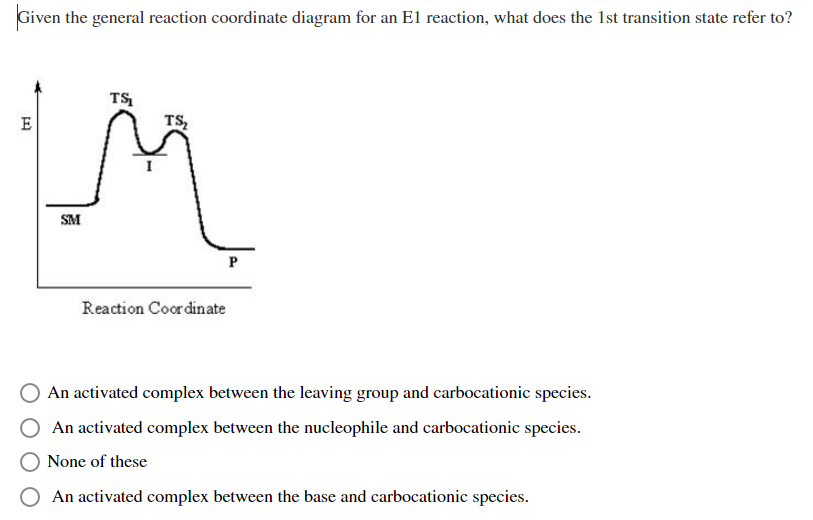
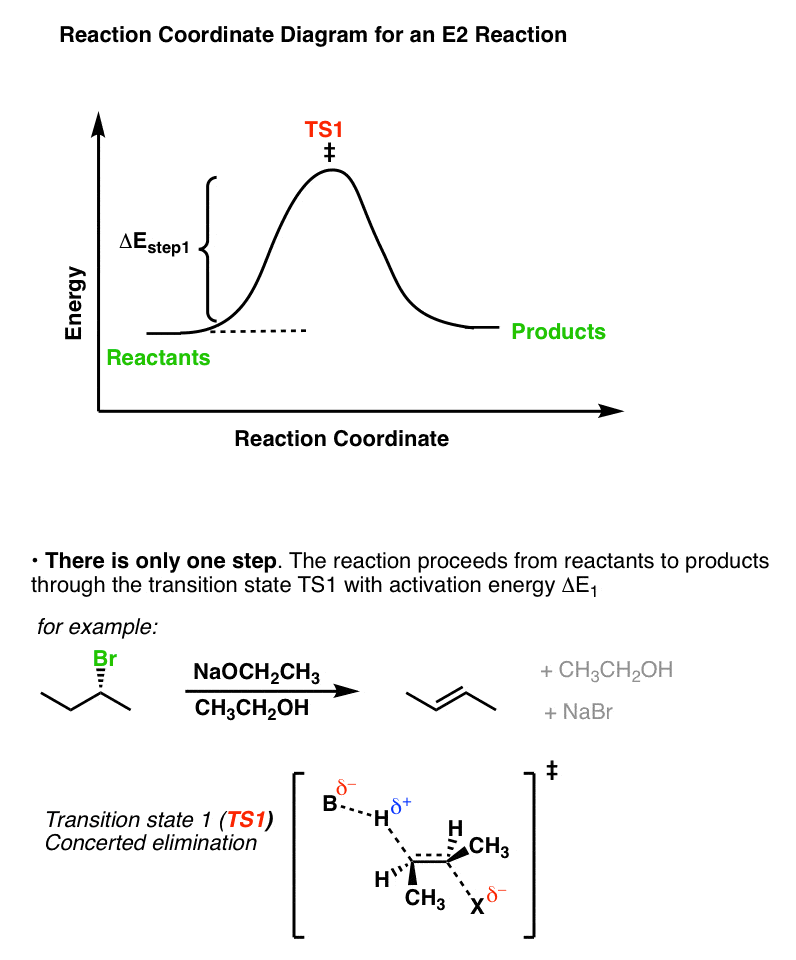
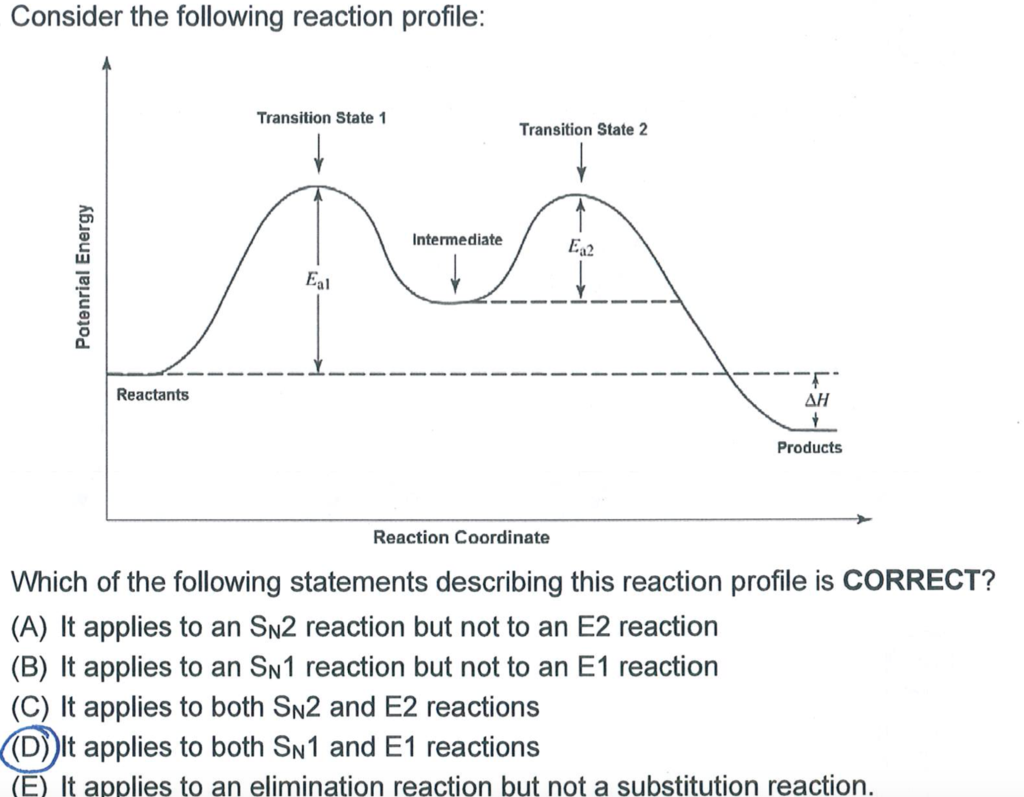
PDF SN2 S 1 - Massachusetts Institute of Technology reaction coordinate (E1) energy ‡ RDS ‡ R X R R R B - R R R R B H R R R R B - X - H R R R R B CHR 2 X R R δ− δ+ Bimolecular Unimolecular Substitution Elimination Generic Reaction-Energy Diagrams Predicting the Products: Substitution versus Elimination Is Nuc/Base strong? no Unimolecular Reaction Bimolecular yes Reaction Is Nuc/Base bulky? E2 yes no What kind of substrate? methyl or 1° S N2 3° yes mostly E1* 2°
8.5. Elimination reactions | Organic Chemistry 1: An open ... E1 Reactions. Unimolecular elimination (E1) is a reaction in which the removal of an HX substituent results in the formation of a double bond. It is similar to a unimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction (SN1) in particular because the rate determining step involves heterolysis (losing the leaving group) to form a carbocation intermediate. Because the rate determining (slow) step involves only one reactant, the reaction is unimolecular with a first order rate law.
E1 Reaction Mechanism and E1 Practice Problems E1 Reaction Mechanism and E1 Practice Problems. The E1 is a stepwise, unimolecular - 1st order elimination mechanism: The first, and the rate-determining step is the loss of the leaving group forming a carbocation which is then attacked by the base: This is similar to the S N 1 mechanism and differs only in that instead of a nucleophilic ...
Sn1 Reaction Coordinate Diagram or process an energy profile (or reaction coordinate diagram) is a theoretical. SN1 reaction is a two step reaction as mentioned below: 1. Leaving group leaves first being solvolysed by solvent creating a carbocation intermediate. This is. Figure 2 identifies these species in a reaction coordinate diagram like the one in the right-hand panel of Figure 1. Here the nucleophile is hydroxide ion.Reaction Bimolecular yes Reaction Is Nuc/Base bulky? E2 yes no What kind of substrate? methyl or 1 ...
E1 and E2 Reactions - Organic Chemistry | Socratic REACTION ORDER. We have a first-order and a second-order process associated with elimination. These are called #"E"1# and #"E"2#, respectively. First-order simply means the rate-limiting step involves one molecule only. Second-order would mean that the rate-limiting step involves two molecules. E1 REACTIONS vs. E2 REACTIONS. Some examples can be seen below.
PDF Energy/Reaction Coordinate Diagrams Energy/Reaction Coordinate! Diagrams! Thermodynamics, Kinetics ! Dr. Ron Rusay" A Reaction Coordinate (Energy) Diagram Thermodynamic Quantities Gibbs standard free energy change (ΔGo) Enthalphy (ΔHo): the heat given off or absorbed during a reaction Entropy (ΔSo): a measure of freedom of motion ΔGo = ΔHo - TΔSo ΔG,ΔH,ΔS, ΔE are state ...
PDF Elimination Reactions - University of Minnesota Potential Energy Diagram for E1 TS energy depends on carbocation rate-determining titi tt stability and leaving group quality. (Same as SN1.) H CH3 CH3 E transition state TS energy does not depend on the strength of the base. X H H a rate determining E - step reaction coordinate E1 and SN1 Frequently Occur Together (because they pass through a common intermediate)
Answered: Based upon the following energy… | bartleby Based upon the following energy diagram, is this reaction an E1 or an E2 elimination? reaction coordinate O E1 O E2 free energy, kJ/mol
Reaction Coordinate Diagrams - University of Illinois ... The diagram below is called a reaction coordinate diagram. It shows how the energy of the system changes during a chemical reaction. In this example, B is at a lower total energy than A. This is an exothermic reaction(heat is given off) and should be favorable from an energy standpoint.
E1 Reaction Coordinate Energy Diagram - YouTube presents: E1 Reaction Coordinate Energy Diagram with step by step mechanism, transition states and intermediates📺Watch Next...
Sn1 Reaction Coordinate Diagram Sn1 Reaction Coordinate Diagram. SN1 reaction is a two step reaction as mentioned below: 1. Leaving group leaves first being solvolysed by solvent creating a carbocation intermediate. This is. whose proposed mechanism and free energy diagram are depicted Figures 1 and 2. Figure 2: Reaction coordinate diagram for an SN1 reaction1. 1. Identify the .
PDF Dehydrohalogenation of Alkyl Halides E2 and E1 Reactions ... Reaction coordinate diagram for the E1 reaction of 2-chloro-2-methylbutane. Must consider possible carbocation rearrangement. Stereochemistry of the E1 Reaction. E1 Elimination from Cyclic Compounds E1 mechanism involves both syn and anti elimination. Summary & Applications (Synthesis) S N 1 / E1 vs. S N
PDF Elimination Reactions - IIT Kanpur Factors Affectin g the Rate of an E1 Reaction The rate of an E1 reaction increases as the number of R groups on the carbon with the leaving group increases. Increasing rate of E1 reaction RCH 2 XR 2CH XR 3C X 1° 2° 3° + + + I i bili f b i RCH 2 R 2CH R 3C 1° 2° 3° ncreas ng sta ty o car ocat ons The strength of the base usually determines whether a reaction follows the E1 or E2 mechanism.





















0 Response to "40 e1 reaction coordinate diagram"
Post a Comment