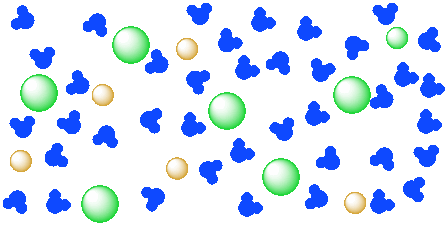
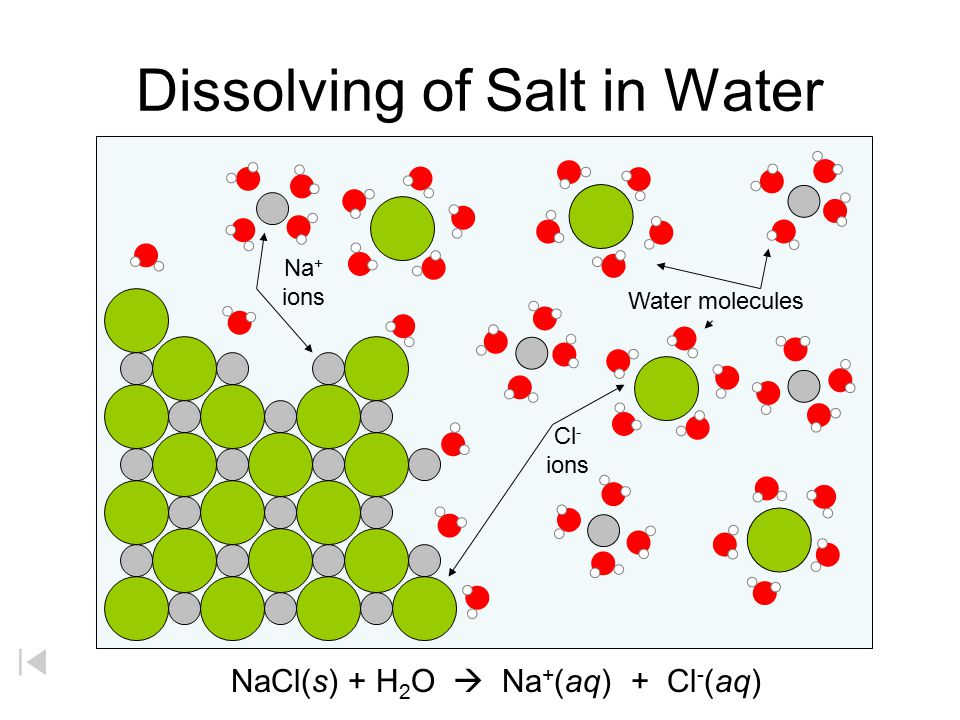
38 diagram of table salt dissolved in water
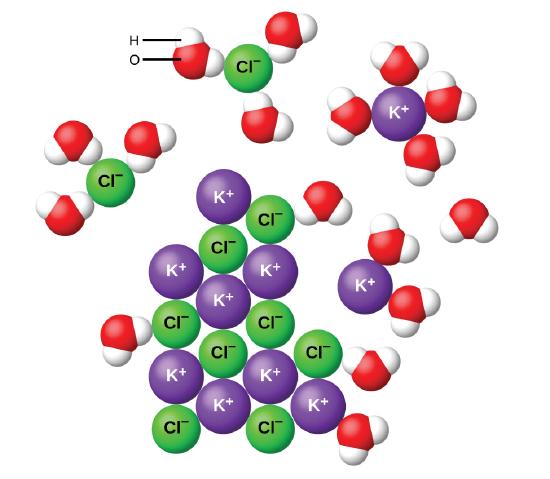
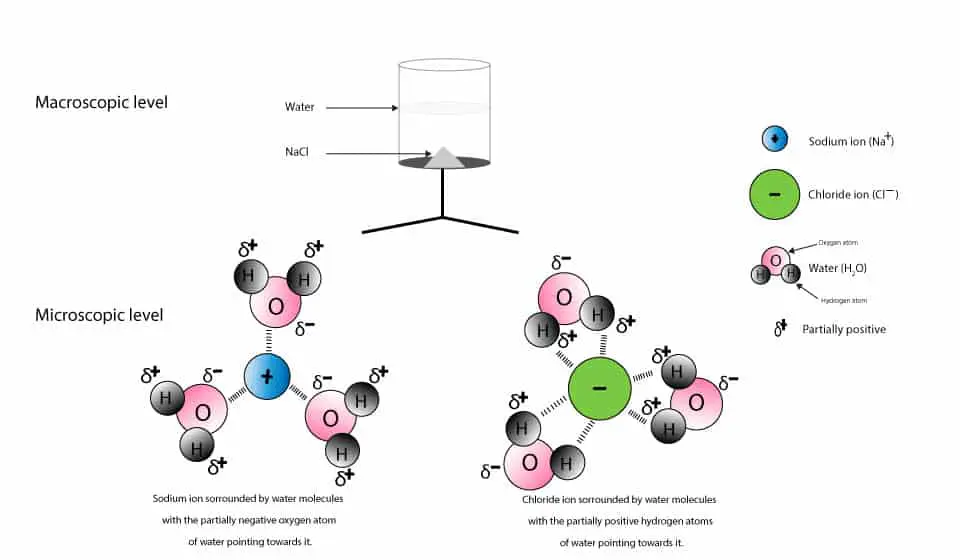
Water can dissolve salt because the positive part of water molecules attracts the negative chloride ions and the negative part of water molecules attracts the Project an image and have students model what happens when salt dissolves in water. Show students a series of four pictures to help explain... Therefore, dissolving salt in water is a chemical change. The reactant (sodium chloride, or NaCl) is different from the products (sodium cation and Thus, any ionic compound that is soluble in water would experience a chemical change. In contrast, dissolving a covalent compound like sugar does...
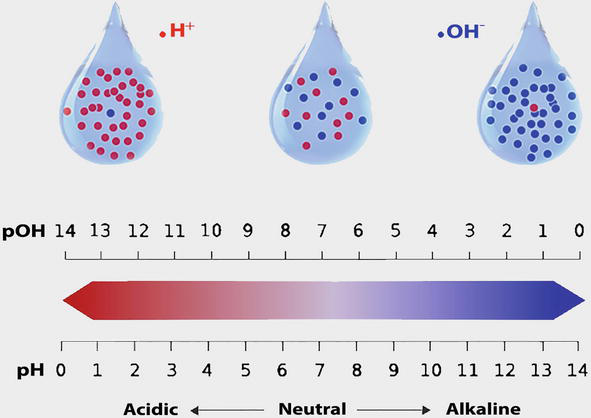
The table below lists the concentrations of free available residual chlorine in water samples taken from four swimming pools. Which of these pools has water ACIDS are substances that release H+ ions in aqueous solutions (when dissolved in water). They neutralize bases. Their pH < 7. The formula for...

Diagram of table salt dissolved in water
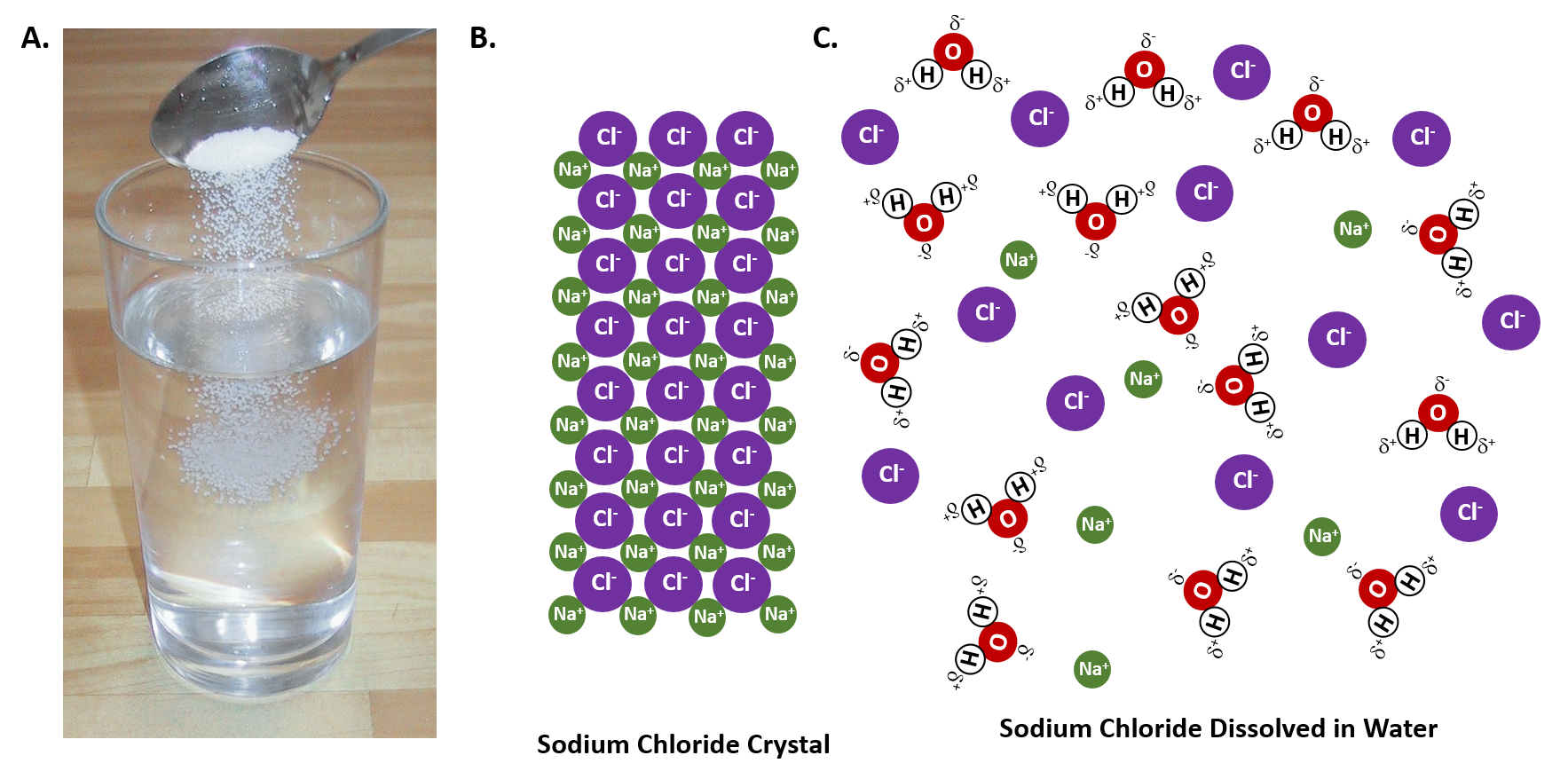
Pour the salt into the water. If the salt does not immediately dissolve, try mixing it with a spoon or spatula. You need water molecules to come in Add salt one gram at a time, stirring until it completely dissolves. Repeat until no more will dissolve. With table salt and pure water, you should get around... When sugar dissolves in water, the weak bonds between the individual sucrose molecules are broken, and these C12H22O11 molecules are released into These patterns form the basis for the rules outlined in the table below, which can guide predictions of whether a given salt will dissolve in water. Above is a diagram showing the general structure of water molecules in a body of water (in liquid state), the red spheres representing an atom Back to the point, when we dissolve table salt, an ionic compound, in water, the water molecules break away from the hydrogen bonds to solvate the ions.
Diagram of table salt dissolved in water. The solubility of sodium chloride or table salt is only slightly affected by temperature increase. Aside from this, salt also increases the temperature at which water boils. With 100 grams of almost-boiling water (around 200 to 212 degrees F), you can add around 40 grams of salt before it becomes... Table salt: Table salt, also known as granulated salt, is the most common type of salt. It is produced by washing away trace minerals from mined salt, then The open evaporation gives the salt a hollow pyramid shape that allows it to dissolve quickly in water (up to five times faster than table salt). Table salt, sea salt, kosher salt, and iodized salt (which is a form of table salt with iodine added to it) are the four main types of salts available to us. The salt dissolves in water, converting it into brine. This brine is then extracted and pumped into the purification plant, wherein magnesium, calcium... For solutions of various salts in water it has been found that temperature effects on solubility vary Continue heating until all of the salt has dissolved, but DO NOT ALLOW THE SOLUTION TO BOIL. Add another portion of water (see Table 1 for the amount ). To do this, measure the next quantity of...
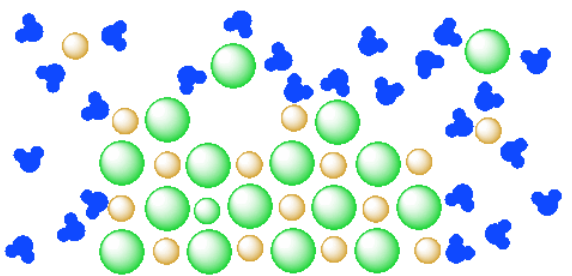
Table salt is just one type of salt and is water soluble. Other water-soluble salts include nitrates, chlorides, and sulfates. There are exceptions to the rule, though. A salt is considered insoluble if, by Purdue University's definition, it can dissolve in room temperature water to a concentration of... Water is a universal solvent and hence, it has many dissolved substances in it, mainly salts. In this video, we test 3 samples of water, namely, hard, tap... In the case of table salt mixed with water, Na and Cl atoms, initially bonded together in the form of a crystal, are dissolved by molecules of water. Learning goals. To illustrate the different stages in the dissolution of salt (sodium chloride) in water. To introduce electrostatic phenomena ( ionic charges... All naturally occurring water, even rain, contains substances dissolved in it. These substances will include salts such as sodium chloride, calcium The classification of water according to the quantity of dissolved substances in it is shown in Table 2 (National Research Council, 2004); Table 3 shows the...
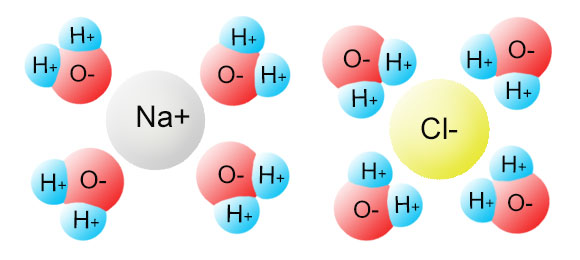
Table 1. Composition of dissolved salts in Standard mean ocean water at 25 °C and 101 325 Pa, where Z is the charge, M is the molar mass, X is the The total amount of salt (expressed in grams) dissolved in one kilogram of seawater is referred to as salinity (‰). Salinity is of great importance for... This diagram shows the positive and negative parts of a water molecule. It also depicts how a charge, such as on an ion (Na or Cl, for example) can At the molecular level, salt dissolves in water due to electrical charges and due to the fact that both water and salt compounds are polar, with positive and... Things like salt, sugar and coffee dissolve in water. They are soluble. They usually dissolve faster and better in warm or hot water. Two things that affect the speed at which a solid dissolves are temperature and the size of the grains of the solid. Caster sugar which is made of fine particles will... Every 100 g of table salt added to 1 kg of water adds 34±1 cm3 to the volume. Table 4. Other properties of NaCl-H2O mixtures at 15 ºC. 1. Phase diagram for water-sucrose solutions at 100 kPa. Glucose has a solubility of 47%wt in water at 15 ºC (i.e. up to 890 g of glucose can be dissolved in 1...
Total dissolved solids (TDS) is the term used to describe the inorganic salts and small amounts of organic matter present in solution in water. The principal constituents are usually calcium, magnesium, sodium, and potassium cations and carbonate, hydrogencarbonate, chloride, sulfate, and nitrate anions.
Ocean water is about 3.5% salt. That means that if the oceans dried up completely, enough salt would be left behind to build a 180-mile-tall, one About 90 percent of that salt would be sodium chloride, or ordinary table salt. Chlorine, sodium and the other major dissolved salts of the ocean are listed in...
Total Dissolved Solids, also known as TDS, are inorganic compounds found in water, such as salts, heavy metals, and some traces of organic compounds dissolved in water. Excluding the organic matters that are sometimes naturally present in water and the environment...
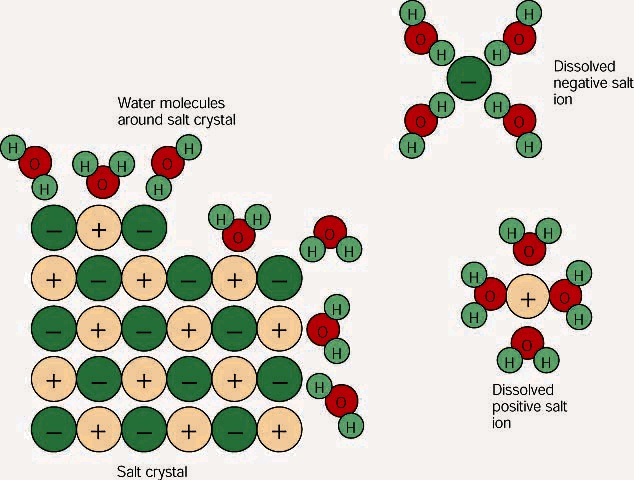
salt dissolves in water forming a solution. solute. gets dissolved. solvent. does the dissolving. a homogeneous mixture. b/c the components are indistinguishable. Aim: How do salts get dissolved by water? all ionic compounds; NaCl is the most common example. Refer to the diagram in today's...
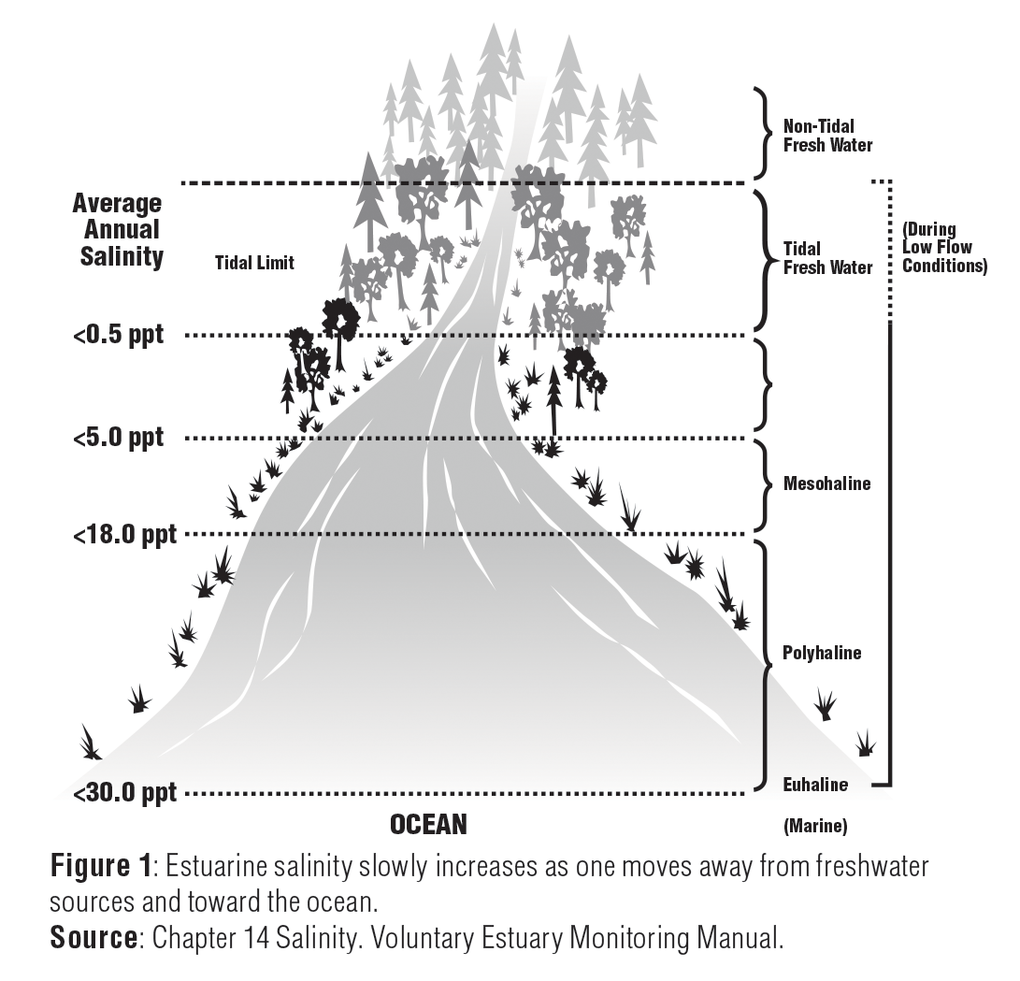
Salinity (/səˈlɪnɪti/) is the saltiness or amount of salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). This is usually measured in. (note that this is technically dimensionless).
Table 1.12. Dissolved salts in water. Component. Ocean water has a fairly consistent makeup, with 99% having between 33 and 37 PSU in dissolved salts. Generally, rain enters the water cycle as pure water then gains various dissolved minerals as it travels toward the ocean.
Salinity is the saltiness or measure of dissolved salt in water. 35 g dissolved salt / kg sea water = 35 ppt = 35 o/oo = 3.5% = 35000 ppm = 35000 mg/l. fresh water - official salt concentration limits in drinking water US: 1000 ppm. typical limit agriculture irrigation : 2000 ppm.
These dissolved solids (sea salts) give the ocean its salty taste. Amount of table salt dissolved in hot water Describe what would happen to the dissolved salt in the hot water if the hot water was chilled.
Table salt is a mineral composed mainly of sodium chloride (NaCl). This is a chemical compound, one of many salts. Salt in its natural form as a crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. When salt (sodium chloride) is mixed with water, the salt dissolves into the water, creating a saline solution.
Salts dissolve in water to produce an anion and a cation. These ions make up the basis of conductivity in water. Conductivity is a measure of water's capability to pass electrical flow. This ability is directly related to the concentration of ions in the water 1. These conductive ions come from dissolved salts...
Calculation of phase diagrams and salt precipitation can be done in easy to use software. This phase diagram shows the solubility of calcium sulfate in water at temperatures between 0 and 200 °C. Gypsum and anhydrite are the stable The salt therefore prefers to be dissolved at high pressure.
NaCl ( table salt) is an ionic compound as it is made up of positively charged sodium ion, which is bonded to the negatively charged chloride ion. Similarly, the positive part of NaCl is attracted by the negative part of the water molecule. Due to this, the table salt gets readily dissolved in water.
Above is a diagram showing the general structure of water molecules in a body of water (in liquid state), the red spheres representing an atom Back to the point, when we dissolve table salt, an ionic compound, in water, the water molecules break away from the hydrogen bonds to solvate the ions.
When sugar dissolves in water, the weak bonds between the individual sucrose molecules are broken, and these C12H22O11 molecules are released into These patterns form the basis for the rules outlined in the table below, which can guide predictions of whether a given salt will dissolve in water.
Pour the salt into the water. If the salt does not immediately dissolve, try mixing it with a spoon or spatula. You need water molecules to come in Add salt one gram at a time, stirring until it completely dissolves. Repeat until no more will dissolve. With table salt and pure water, you should get around...















0 Response to "38 diagram of table salt dissolved in water"
Post a Comment