38 pathway of light through the eye diagram
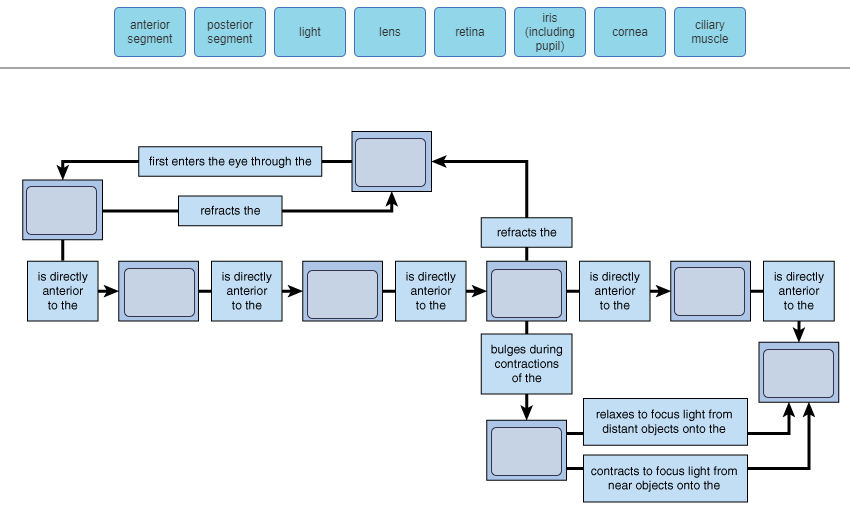
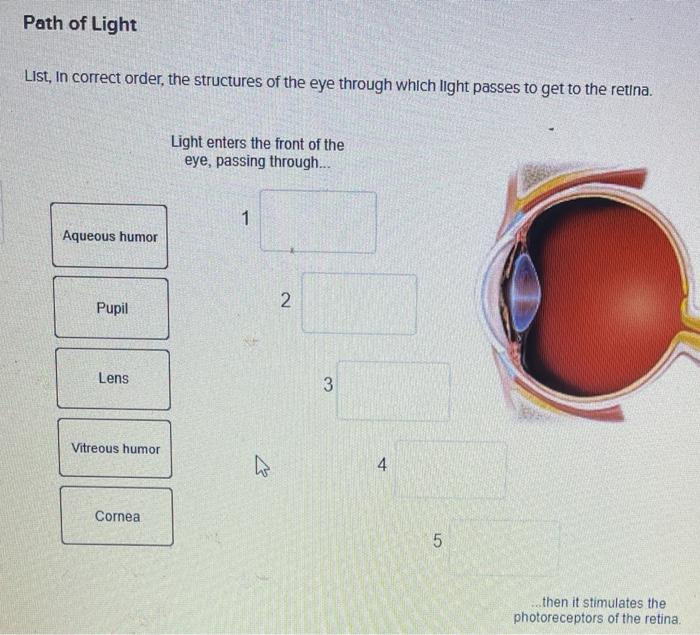
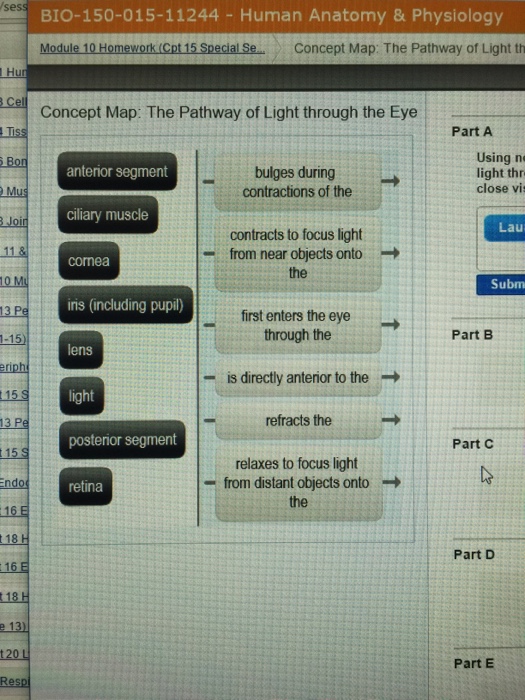
Question: Concept Map: The Pathway of Light through the Eye Complete the Concept Map to trace the pathway of light through the eye to the retina and explain how light is focused for distant or close vision. This problem has been solved! See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading. It is mainly responsible for vision, differentiation of colour (the human eye can differentiate approximately 10 – 12 million colours) and maintaining the biological clock of the human body. The human eye can be compared to a camera as both works by gathering, focusing and transmitting the light through the lens for creating an image of an ...
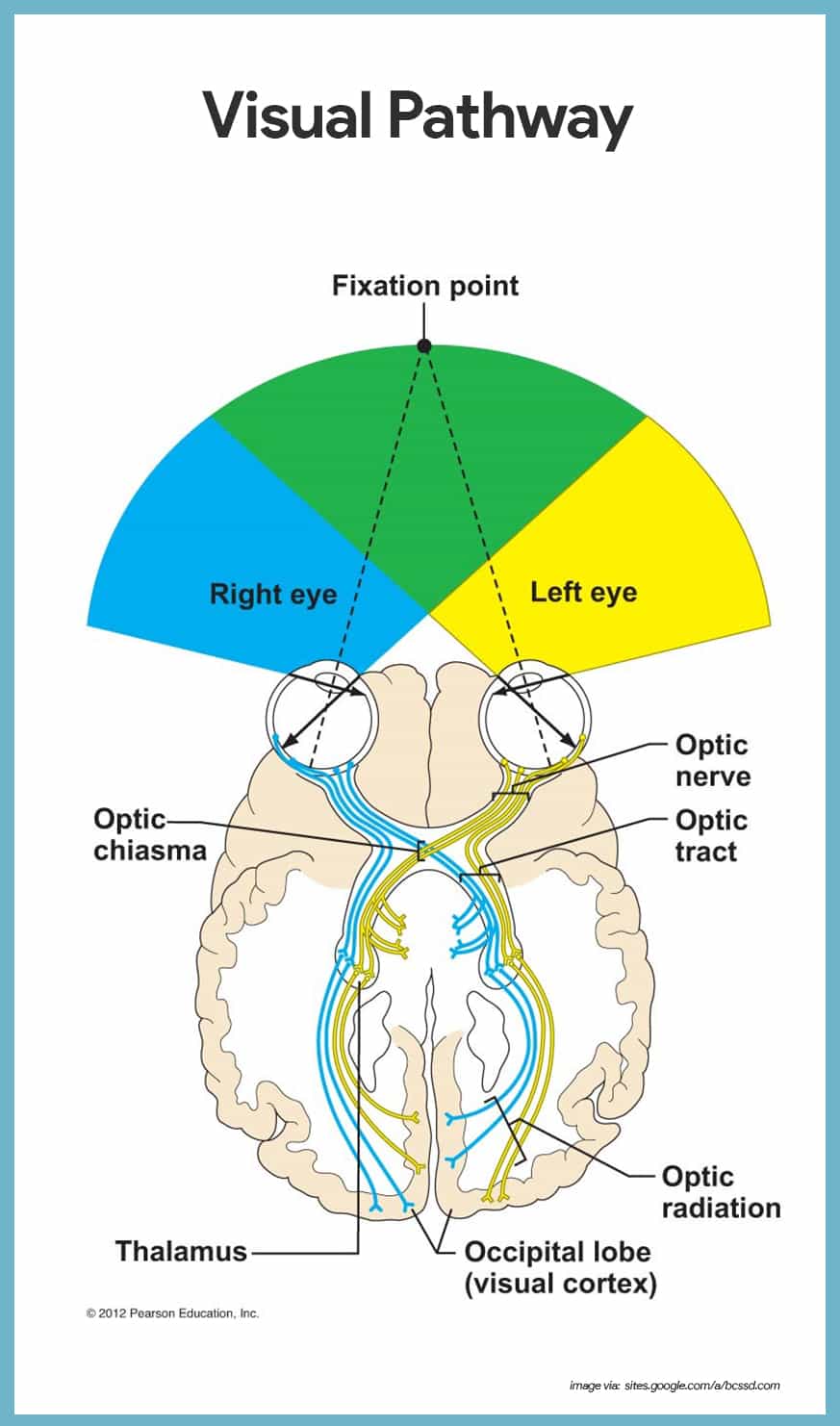
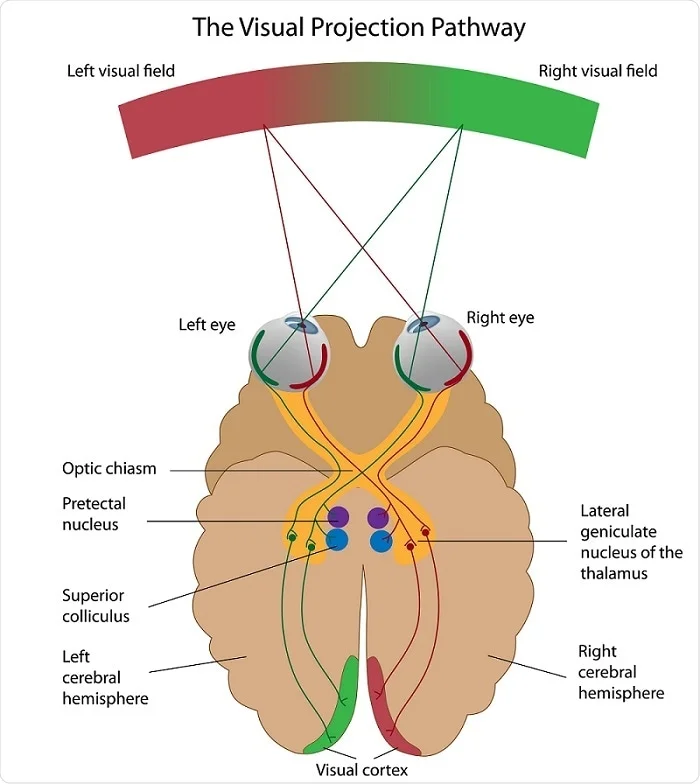
The eyes act as the initial point of contact through which photons pass to access the visual pathway. The visual pathway refers to the anatomical structures responsible for the conversion of light energy into electrical action potentials that can be interpreted by the brain. It begins at the retina and terminates at the primary visual cortex ...
Pathway of light through the eye diagram
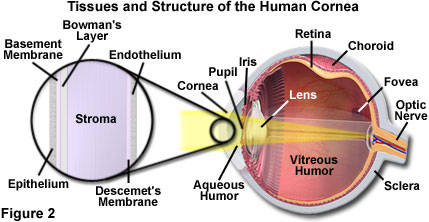
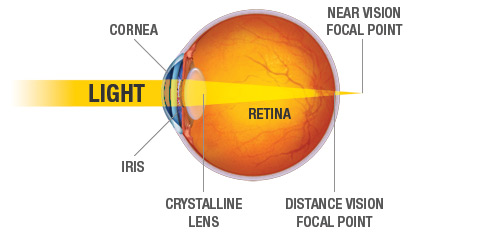
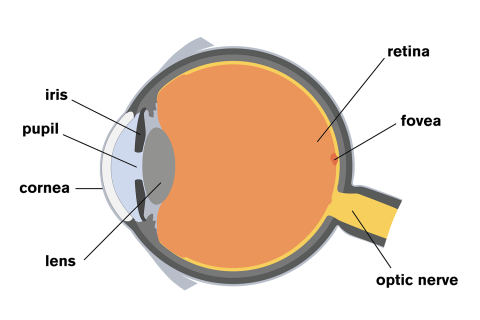
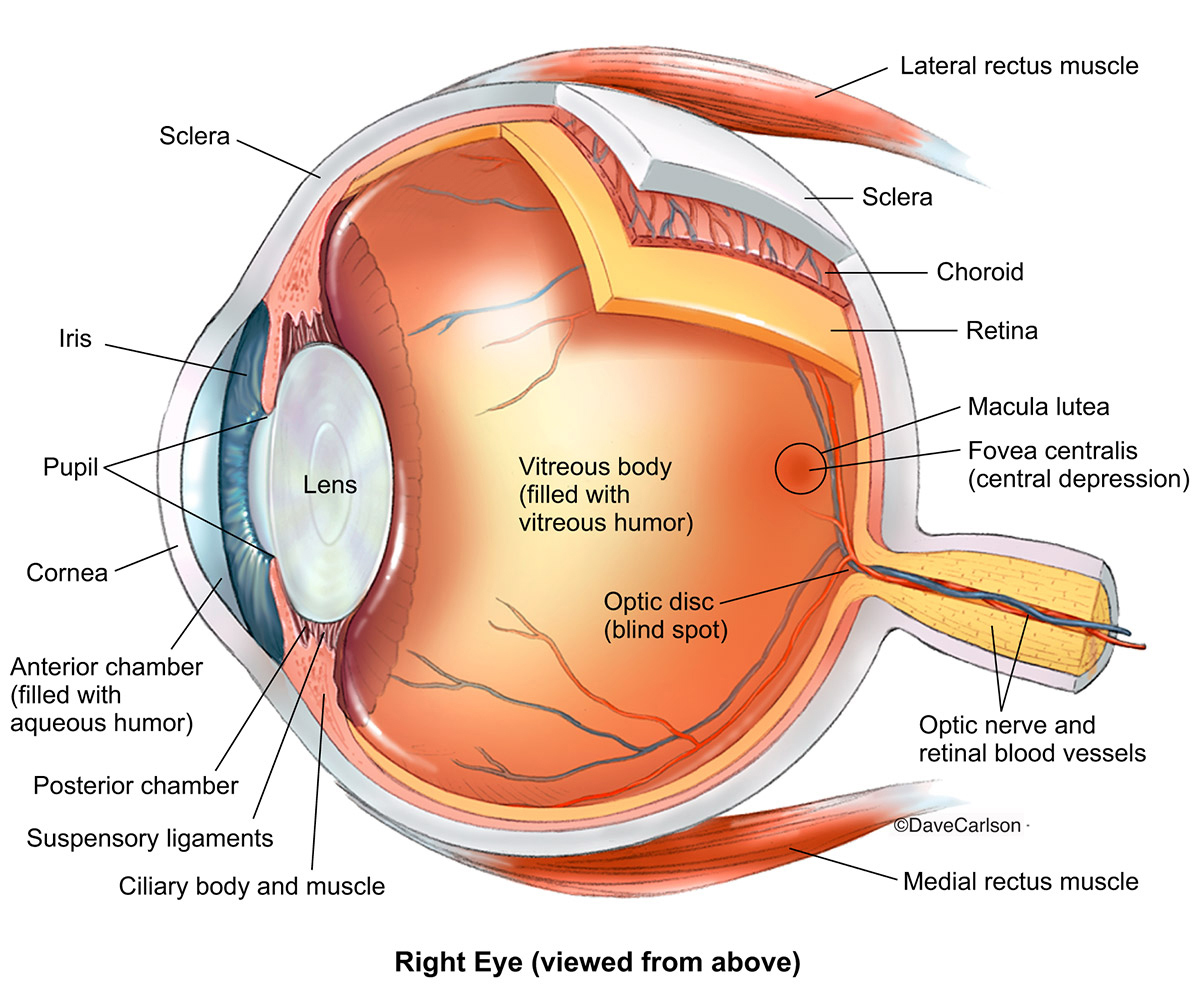
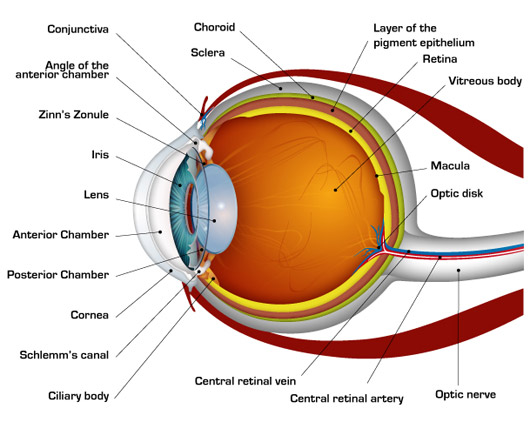
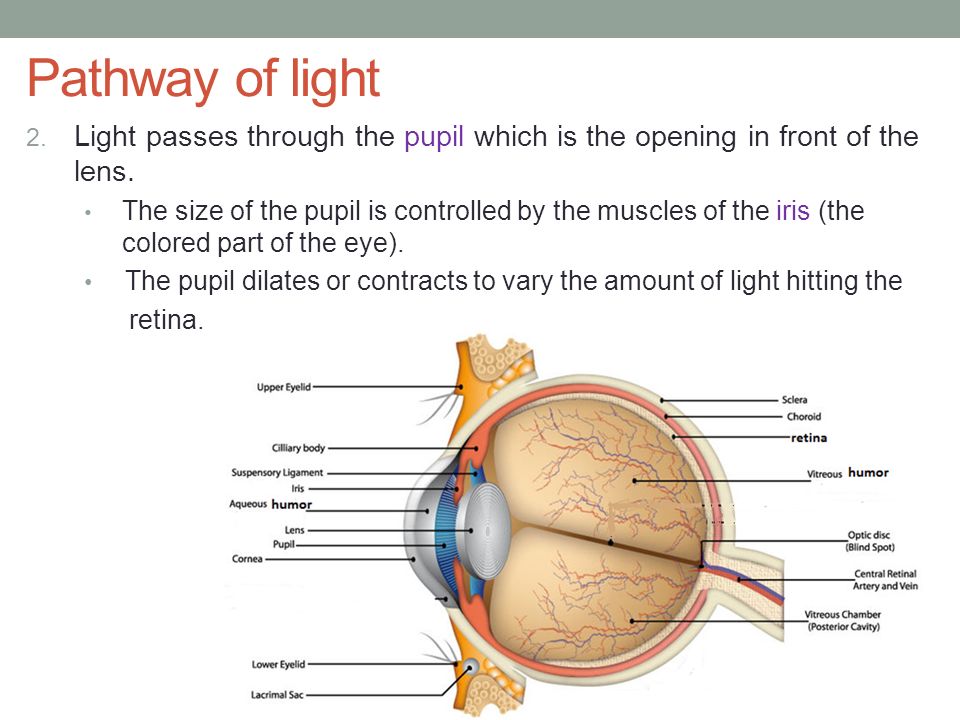
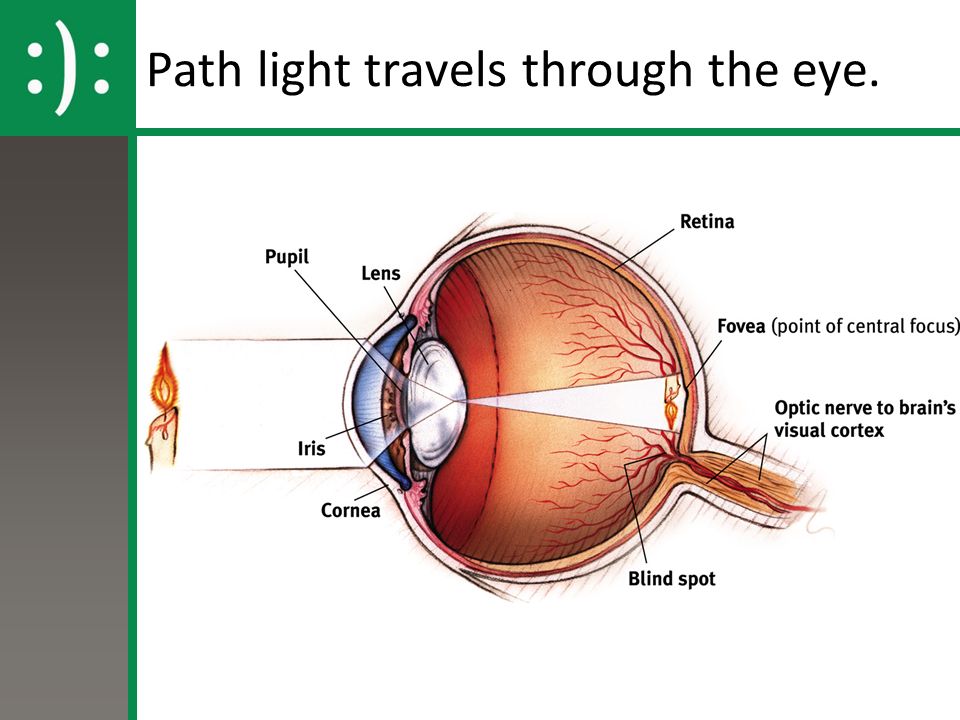
(a) Table 4.1 describes some of the functions of the parts of the eye. Complete the table by: • naming the parts of the eye • using the letters on Fig. 4.1 to identify the parts of the eye. Table 4.1 function name of part letter on Fig. 4.1 carries impulses to the brain focuses light onto the back of the eye The refraction of light through the human eye. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. Email. Chemical and physical sciences practice passage questions. Practice: Understanding cardiac pressure-volume curves. Practice: Imaging tissue structures using muon tomography. 1. Light rays enter the eye through the cornea, the clear front “window” of the eye. The cornea’s refractive power bends the light rays in such a way that they pass freely through the pupil the opening in the center of the iris through which light enters the eye. The iris works like a shutter in a camera.
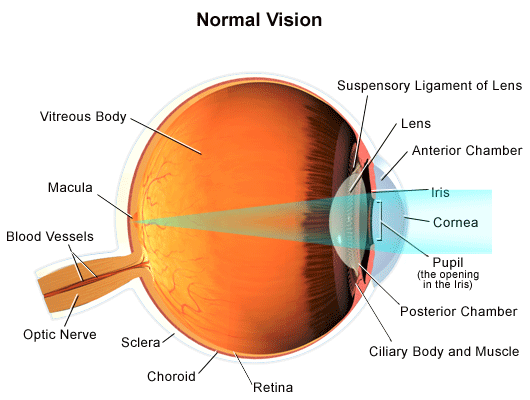
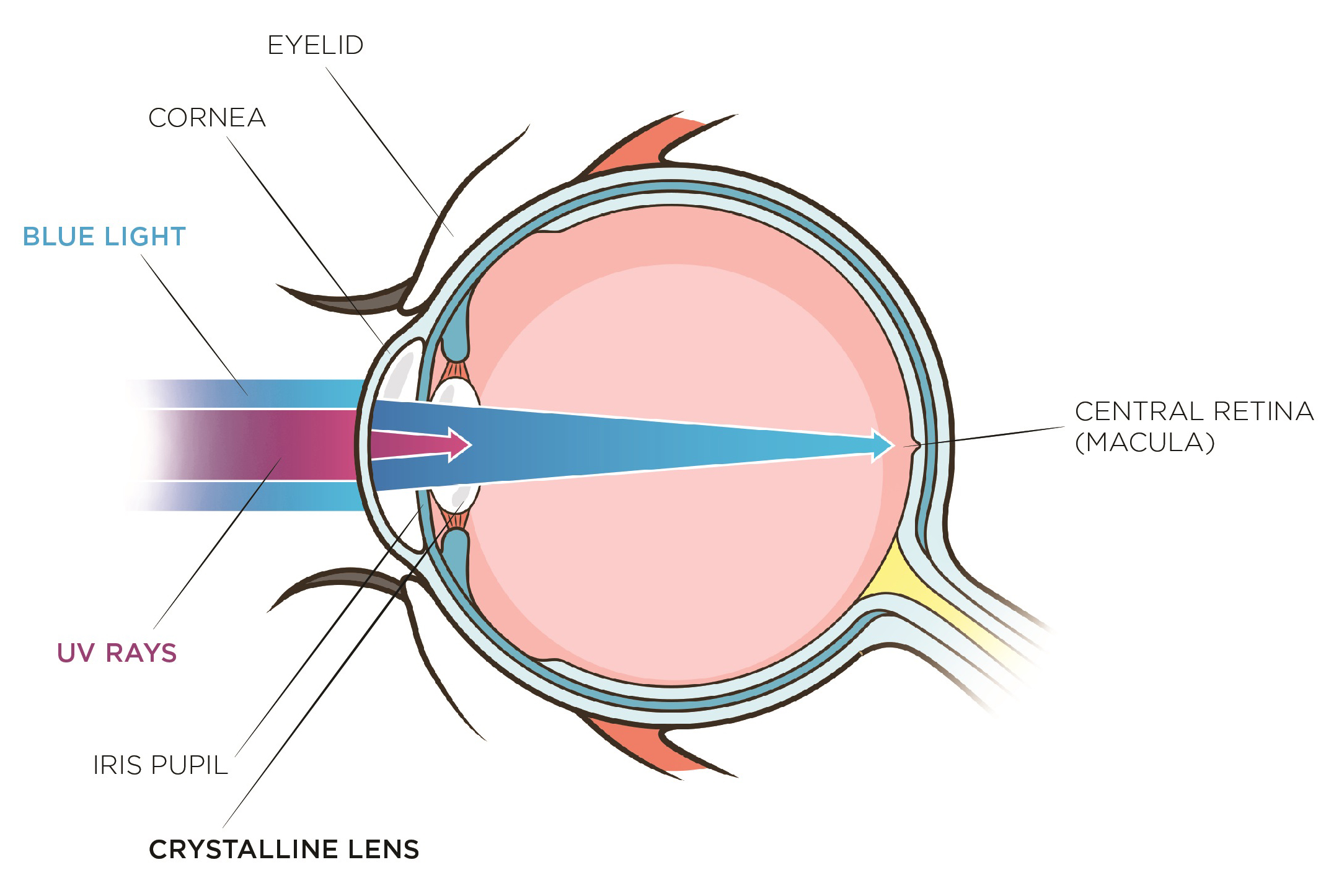
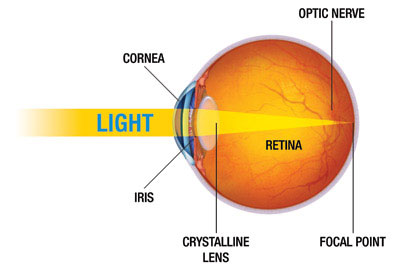
Pathway of light through the eye diagram. The path of light through the eye begins with the objects viewed and how they produce, reflect or alter light in various ways. When your eyes receive light, it begins a second journey through the eye's optical parts that adjust and focus light to the nerves that carry images to your brain. Pathway of light through the eye (Cornea image (Aqueous Humor image … ... Recieves the light and processes it. Here the image is most clear focused. ... Help to see ... Parts of the Eye Cornea: imagine two corn muffins over your eyes. Iris: gives your eye its color and is also a muscle that gets smaller when there is a lot of light around you and it gets bigger when there is not much light around you. Use the notion that Irish makes many people think of the colorful green things like leprechauns, Light passes through the front of the eye (cornea) to the lens. The cornea and the lens help to focus the light rays onto the back of the eye (retina). The ...
The iris allows more light into the eye (enlarging or dilating the pupil) when ... other nerve fibers (called the visual pathway) to the back of the brain, ... 15 Jun 2018 — Explanation: · 1. Cornea · 2. Aqueous Humor · 3. Pupil · 4. Lens · 5. Vitreous Humor · 6. Retina. Here's a diagram of the eye to follow along: https:/ ...1 answer · See below. Explanation: Light's path through the eye from the outside to the retina is as follows: 1. Cornea 2. Aqueous Humor 3. Pupil 4. ... What is normal vision? · Light enters the eye through the cornea. · From the cornea, the light passes through the pupil. · From there, it then hits the lens. · Next ... The eye is one of the most important of the receptors. It provides us with information on dimensions, colours and the distance of objects in our environment. 1. Light rays from an object enter the transparent cornea. 2. The cornea ‘bends’ (refracts) the light rays in towards one another. 3.
All the different parts of your eyes work together to help you see. First, light passes through the cornea (the clear front layer of the eye). The visual pathway's primary task of converting light information into a picture of the outside world is moderated by neurons of the visual cortex. The optic nerve transmits the signals of the eye to the brain. In the eye, the visual pathway begins when light passes through the cornea, pupil, and lens, where it is inverted and projected onto ... 1. Light rays enter the eye through the cornea, the clear front “window” of the eye. The cornea’s refractive power bends the light rays in such a way that they pass freely through the pupil the opening in the center of the iris through which light enters the eye. The iris works like a shutter in a camera. The refraction of light through the human eye. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. Email. Chemical and physical sciences practice passage questions. Practice: Understanding cardiac pressure-volume curves. Practice: Imaging tissue structures using muon tomography.

Molecular Expressions Microscopy Primer Physics Of Light And Color Human Vision And Color Perception
(a) Table 4.1 describes some of the functions of the parts of the eye. Complete the table by: • naming the parts of the eye • using the letters on Fig. 4.1 to identify the parts of the eye. Table 4.1 function name of part letter on Fig. 4.1 carries impulses to the brain focuses light onto the back of the eye

Solved Which Of The Following Gives The Correct Path For Light Rays Entering The Human Eye A Sclera Retina Choroid Lens Cornea B Fovea Centralis Pupil Aqueous Humor Lens C Cornea Pupil Lens

Anatomy And Physiology Of The Human Eye Effects Of Mucopolysaccharidoses Disease On Structure And Function A Review Willoughby 2010 Clinical Amp Experimental Ophthalmology Wiley Online Library
















0 Response to "38 pathway of light through the eye diagram"
Post a Comment