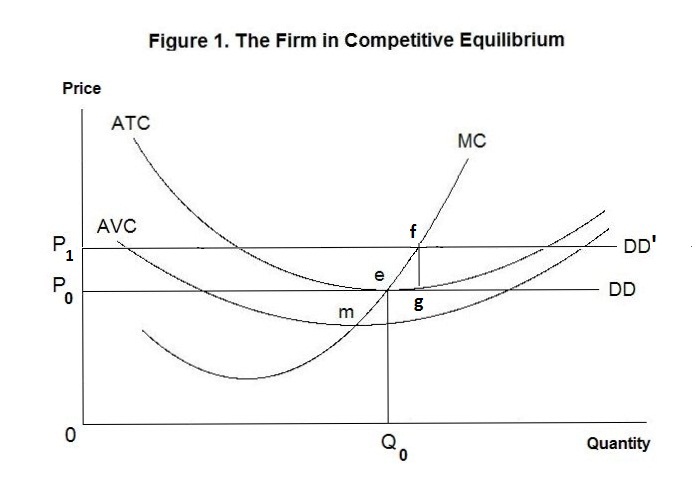
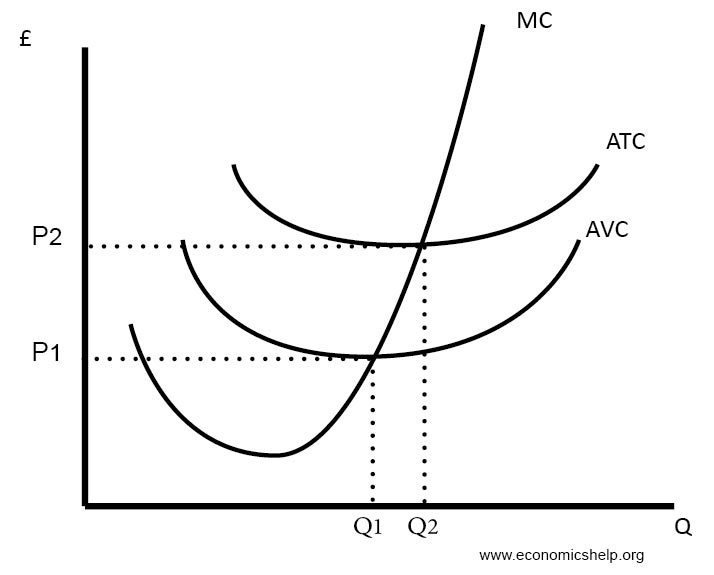
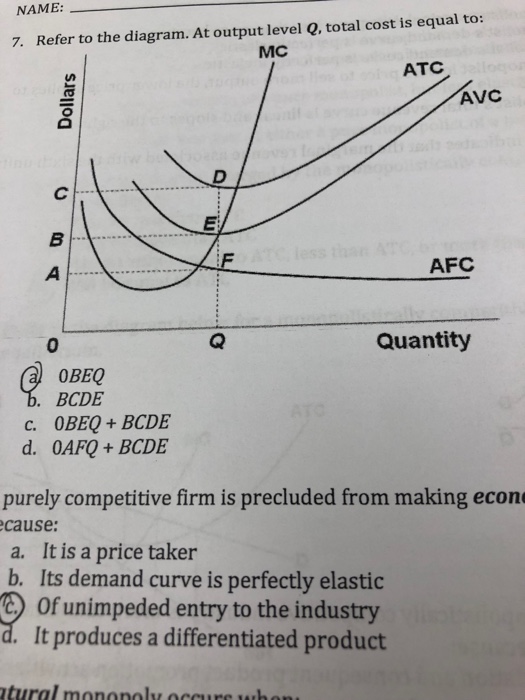
38 refer to the diagram. at output level q, average fixed cost
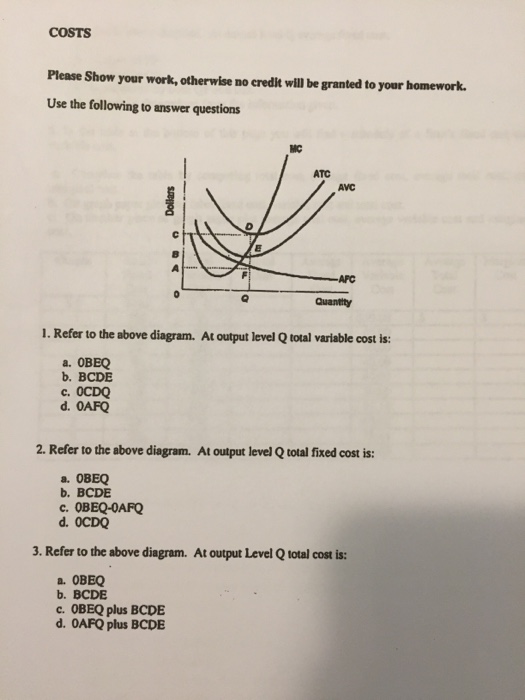
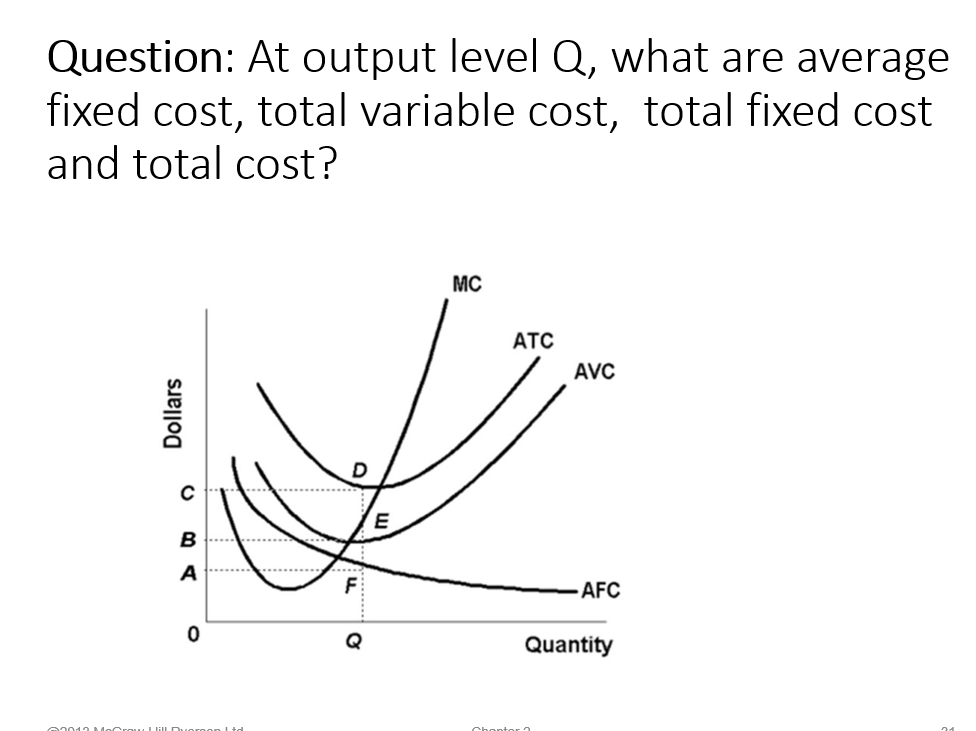
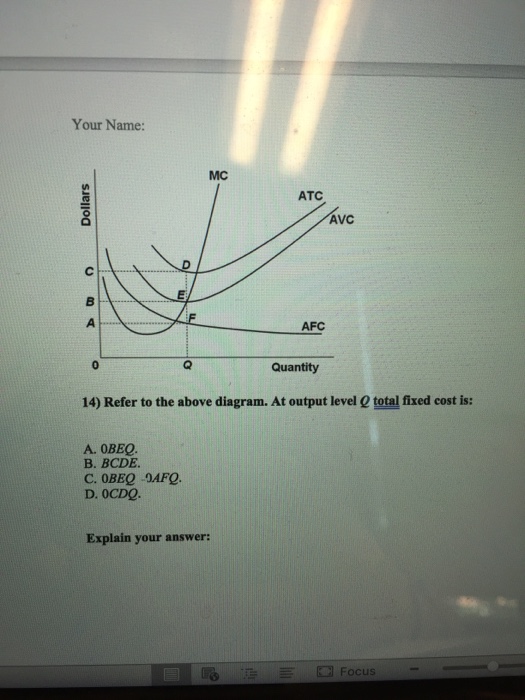
Refer to the above data. The marginal cost of producing the sixth unit of output: A. is $24. B. is $12. C. is $16. D. ... Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q average fixed cost: A. is equal to EF. B. is equal to QE. C. is measured by both QF and ED. D. cannot be determined from the information given. ... At output level Q total cost is: 0BEQ + BCDE. Refer to the diagram. At output level Q average fixed cost: is measured by both QF and ED. Assume that in the short run a firm is producing 100 units of output, has average total costs of $200, and has average variable costs of $150. The firm's total fixed costs are: $5,000.
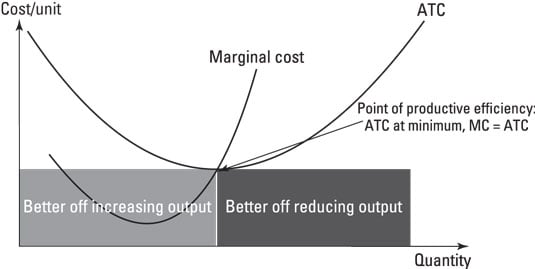
Refer to the diagram. At output level Q: Multiple Choice marginal product is falling. ... Average total cost is the difference between average variable cost and average fixed cost. Marginal cost measures the cost per unit of output associated with any level of production.

Refer to the diagram. at output level q, average fixed cost
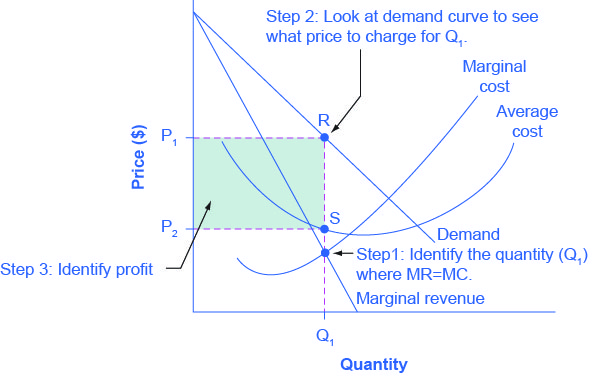
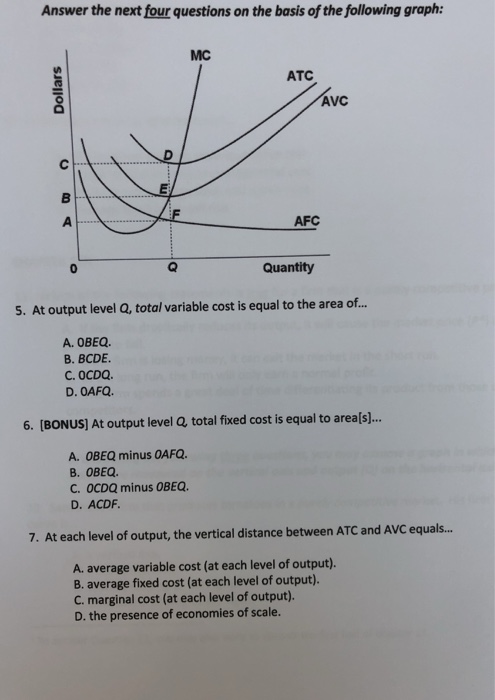
C) marginal cost at each level of output. B) the average fixed cost at each level of output. D) the presence of economies of scale. 21. Marginal cost: A) equals both average variable cost and average total cost at their respective minimums. B) is the difference between total cost and total variable cost. its output to Q 1 . 14) Refer to Figure 13 -14. It is possible to lower the average cost of production by expanding output beyond Q 0 to Q 1 . Why wouldn't a firm expand its output to Q 1 ? 14) A) Demand is not sufficient for consumers to buy Q 1 . B) The firm's marginal revenue would be negative at Q 1 . At output level Q average fixed cost: A. is equal to EF B. is equal to QE C. is measured by both QF and ED D. cannot be determined from the information given. 60. Refer to the above diagram.
Refer to the diagram. at output level q, average fixed cost. represents the same cost level prior to the wage change. - To produce the same level of output, Q 0, the firm will produce on a lower isocost line ( C1) at a point B. - The slope of the new isocost line represents the lower wage relative to the rental rate of capital. Q0 0 A L K C C0/w 1 L0 L1 0/w 0 C1/w 1 K0 K1 B Refer to the diagram. At output level Q average fixed cost: Click card to see definition 👆. Tap card to see definition 👆. is equal to <i>QE</i>. Click again to see term 👆. Tap again to see term 👆. Refer to the data. Diminishing returns begin to occur with the hiring of the _________ unit of labor. Use this information to answer the following questions. Refer to the diagram at output level q average fixed cost. Assume that in the short run a firm is producing 100 units of output has average total costs of 200 and average variable costs of 150. At output level q average fixed cost. At output level q total fixed cost is. a. Total cost=ATC*Q b. Total revenue=P*Q c. Variable cost=AVC*Q d. Profit or loss=(P-ATC)*Q Briefly explain whether the firm will continue to produce in the short run. Answer: The firm should continue to produce in the short run. That's because that when firm produce the output level where MR=MC (output level Q), price is greater than average ...
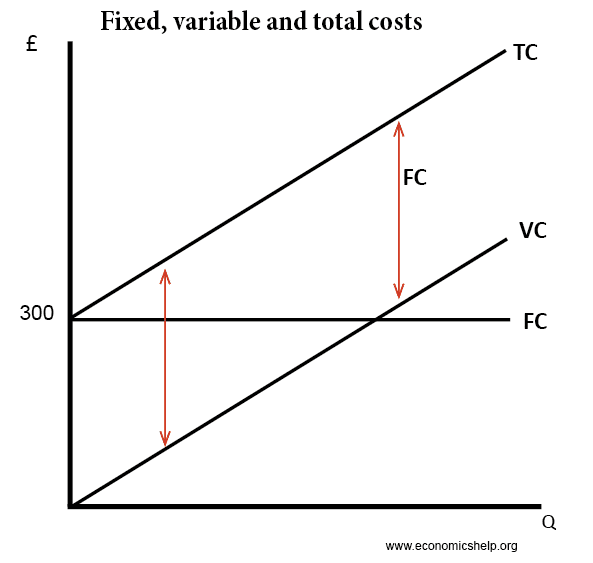
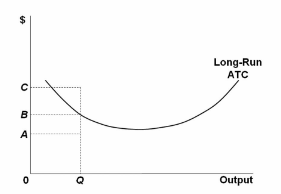
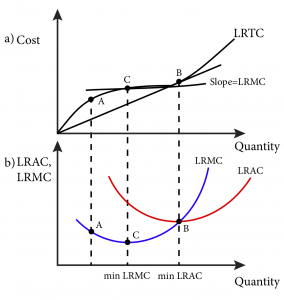
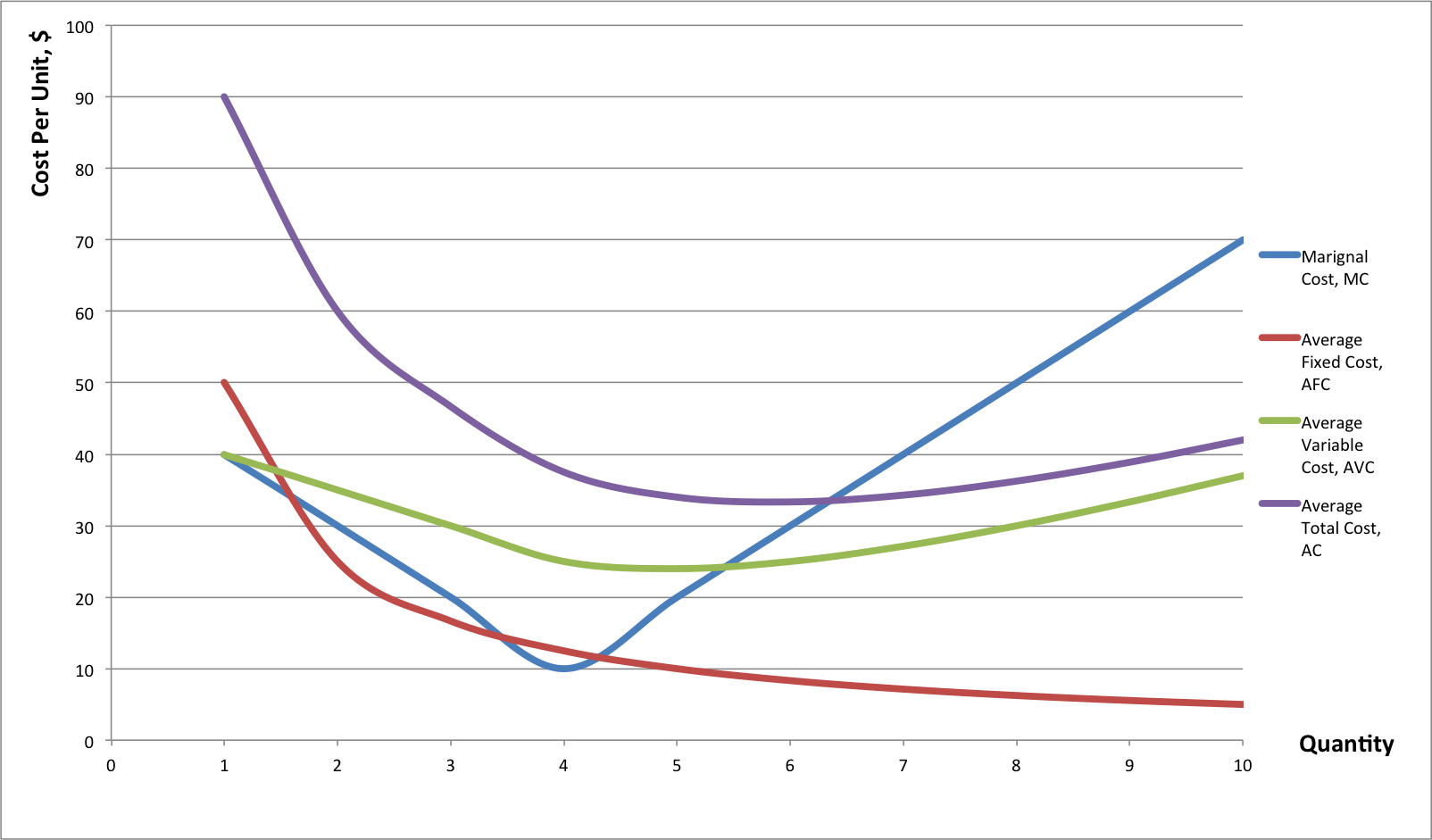
Refer to the above diagram showing the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's total cost: not 10 (b) Given a total cost function, 2 TC(Q) = Q + 10Q + 100 where Q represents quantity of output produced. (i) Find the expressions for the variable cost, fixed cost, average cost, average variable cost, and average fixed cost. 5 (ii) At what output level (Q) is the average cost lowest? Also find the minimum average cost. 5 OR Refer to the diagram above. The vertical distance between ATC and AVC reflects: A) the law of diminishing returns. B) the average fixed cost at each level of output. C) marginal cost at each level of output. D) the presence of economies of scale. Average Fixed Cost: The average fixed cost shows the mean fixed cost when producing one unit of output. Unlike total fixed costs, the average fixed cost is not constant.
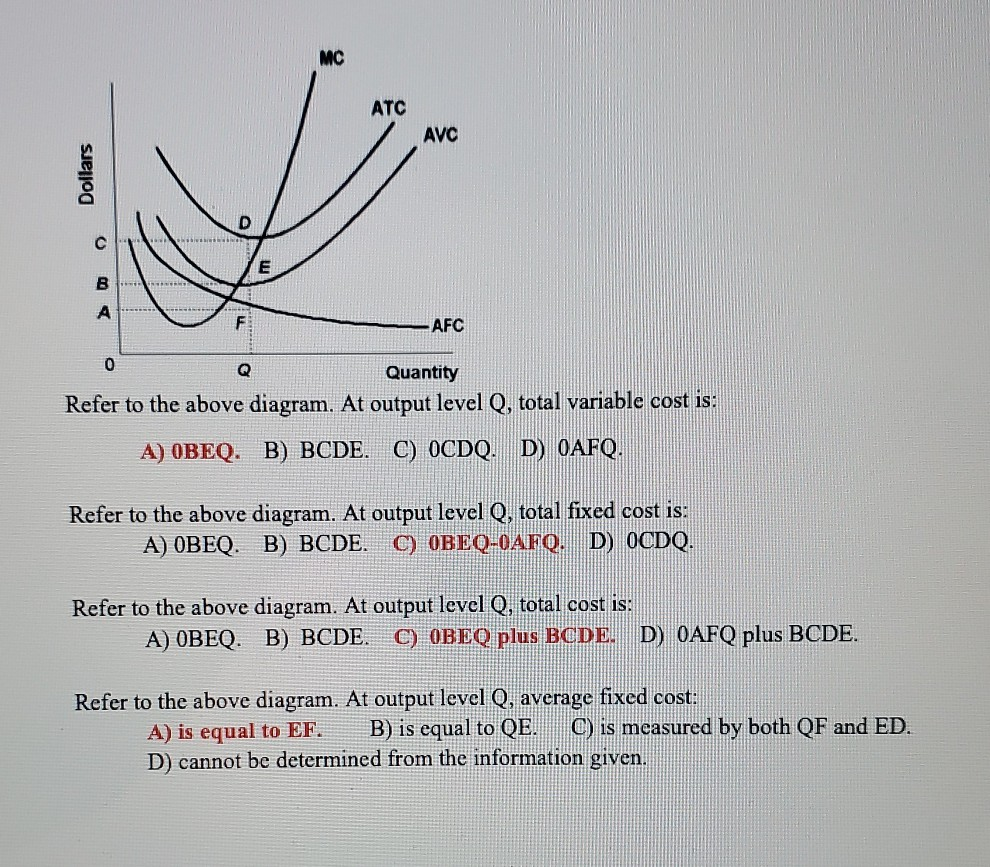
Refer to the diagram. At output level Q, total variable cost is. 0BEQ. If average variable cost is $74 and total fixed cost is $100 at 5 units of output, then average total cost at this output level is. $94. output Total Cost 0 $ 400 1 900 2 1,300 3 1,600 4 2,000 5 2,500 6 3,100 View Homework Help - ECONHW10Sols139.pdf from ECONOMICS ECOS1001 at The University of Sydney. 269. Award: 1.00 point Refer to the provided graph of cost curves. Total xed cost at output level Q2 is Average Fixed Cost Formula and Example. AFC = Total fixed cost/Output (Q) If the fixed cost of a pen factory is ₹5,000/- and it produces 500 pens, then the average fixed price will be ₹10/- per unit. Similarly, if the factory produces 1,000 pens, then the cost of a unit will be ₹5/-, and if the total production is 5,000 pens, then the ... The total variable cost or the variable cost or prime cost or direct cost or special cost is the one that varies with the level of output. It can be 0 at 0 levels of output. For example, wages of temporary laborers, cost of raw material, electricity, etc.
Oct 19, 2021 · Refer to the diagram. at output level q total fixed cost is: At calculation level q total fixed cost is. Together successive quantities of one source labor are added to fixed amounts of other resources capital beyond some allude the resulting extra or marginal output will certainly decline.
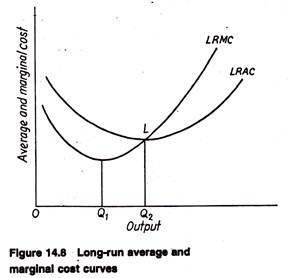
1. the level of output that coincides with the intersection of the MC and AVC curves. 2. minimization of the AFC in the production of any good. 3. the production of the product-mix most desired by consumers. 4. the production of a good at the lowest average total cost. 5. If the price of product Y is $25 and its marginal cost is $18: 1.
177. Refer to the above diagram. For output level Q, per unit costs of B are: A) unobtainable and imply the inefficient use of resources. B) unobtainable, given resource prices and the current state of technology. C) obtainable, but imply the inefficient use of resources. D) obtainable and imply least-cost production of this output. Answer: D
Get the detailed answer: Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q, the total fixed cost is: a. 0BEQ b. BCDE c. 0BEQ - 0AFQ d. 0CDQ
36) Refer to Figure 7.1. At output level Q2 . A) average fixed cost is increasing. B) average variable cost equals average fixed cost. C) marginal cost is negative. D) average total cost is negative. E) none of the above . Answer: B. Diff: 1. Section: 7.2. 37) Refer to Figure 7.1. At output level Q3 . A) average fixed cost reaches its minimum.
Question 2. Answer the next question (s) on the basis of the following output data for a firm. Assume that the amounts of all non-labor resources are fixed. Refer to the above data. Diminishing marginal returns become evident with the addition of the: a. sixth worker. b. fourth worker. c. third worker.
Refer to the diagram At output level Q total variable cost is A 0BEQ B BCDE C from ECONOMICS 111 at Middle East Technical University
At output level Q, average fixed cost _____. a. is equal to (the length of line segment) EF. b. is equal to QE. c. is equal to both QF and ED.
The marginal cost is constant at $0.10 for all cookies produce Refer to Scenario 1. The total cost to produce 50 cookies is. A. $20. B. $25. C. $50. D. $60. E. ... Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q average fixed cost: A. A. is equal to EF. B. B. is equal to QE. C. C. is measured by both QF and ED. ...
the average fixed cost at each level of output. Answer the question on the basis of the following output data for a firm. Assume that the amounts of all non labor resources are fixed. ... Refer to the diagram. At output level Q, total variable cost is. 0 BEQ. If a technological advance increases a firm's labor productivity, we would expect its.
Q. The diagram shows the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's economic profit. answer choices . is zero. is $400. is $200. ... Q. Refer to the diagram. At output level Q2, answer choices
Refer to the Diagram. at Output Level Q total Cost is: profit maximization to obtain the profit maximizing output quantity we start by recognizing that profit is equal to total revenue tr minus total cost tc given a table of logic gate in electronics a logic gate is an idealized or physical device implementing a boolean function that is it performs a logical operation on one or more
A) Average total cost is the difference between average variable cost and average fixed cost. B) Marginal cost measures the cost per unit of output associated with any level of production. C) When marginal product rises, marginal cost must also rise.
Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q total cost is: A. OBEQ. B. BCDE. C. OBEQ plus BCDE. D.OAFQ plus BCDE. 4. Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q average fixed cost: A. is equal to EF. B. is equal to QE. C. is measured by both QF and ED. D. cannot be determined from the information given. 5. Refer to the above diagram.
At output level Q average fixed cost: A. is equal to EF B. is equal to QE C. is measured by both QF and ED D. cannot be determined from the information given. 60. Refer to the above diagram.
its output to Q 1 . 14) Refer to Figure 13 -14. It is possible to lower the average cost of production by expanding output beyond Q 0 to Q 1 . Why wouldn't a firm expand its output to Q 1 ? 14) A) Demand is not sufficient for consumers to buy Q 1 . B) The firm's marginal revenue would be negative at Q 1 .
C) marginal cost at each level of output. B) the average fixed cost at each level of output. D) the presence of economies of scale. 21. Marginal cost: A) equals both average variable cost and average total cost at their respective minimums. B) is the difference between total cost and total variable cost.

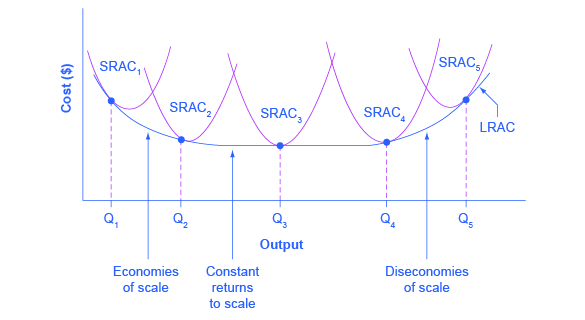


/MinimumEfficientScaleMES2-c9372fffba0a4a1ab4ab0175600afdb6.png)






0 Response to "38 refer to the diagram. at output level q, average fixed cost"
Post a Comment