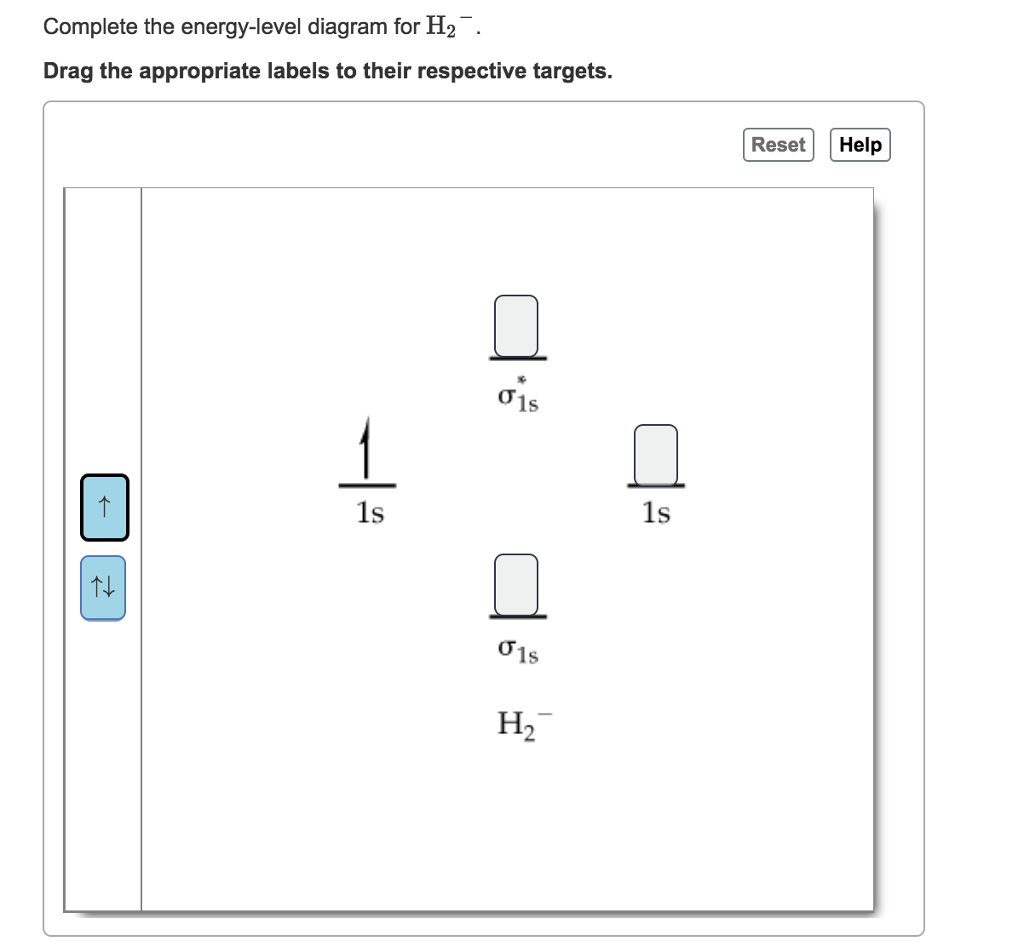
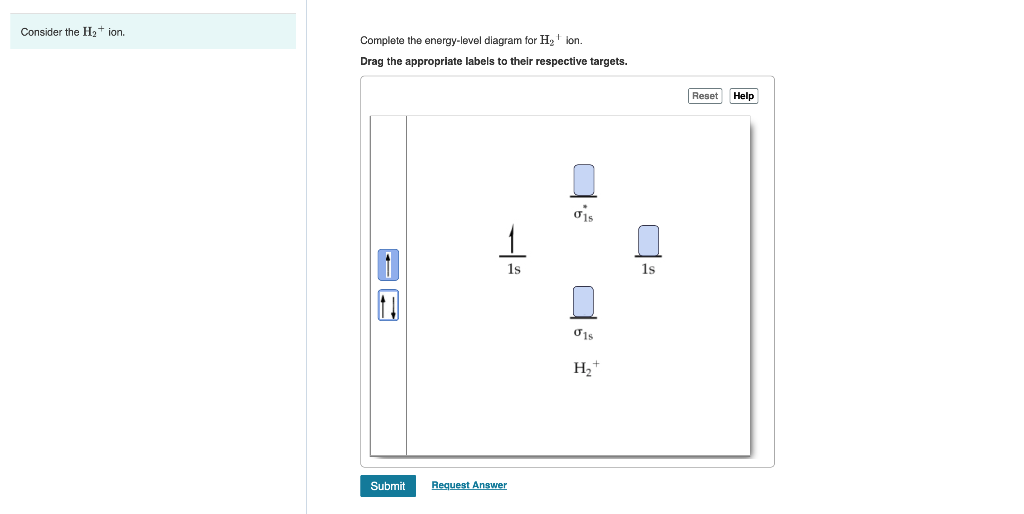
39 complete the energy-level diagram for h2−.
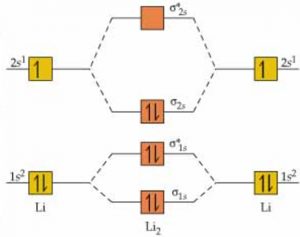
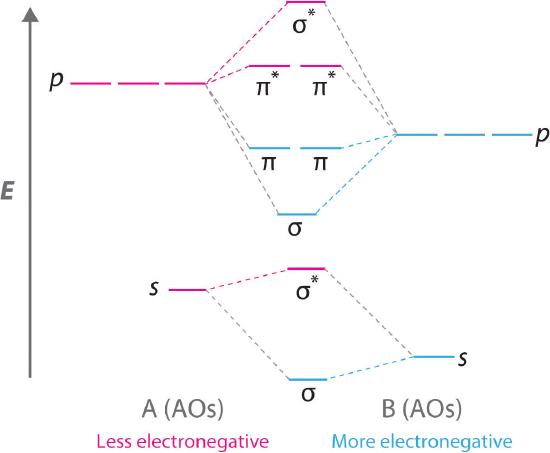
Answer to Draw an MO energy diagram and predict the bond order of Be2+ and Be2−. Do you expect these molecules to exist in the. From the above MO diagram we can see that number of elctrons in the bonding and antibonding orbital is same and hence Be does not form Be2 molecule(for. Show transcribed image text Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2 and then identify the bond order. Click within the blue boxes to add electrons%(15). The molecular orbital energy-level diagram shown in Figure 13 also applies (with changes of detail in the energies of the molecular orbitals) to the hypothetical species He 2. However, this species has four valence electrons, and its ...
a) Carefully complete the energy diagram by drawing a curve that accurately shows the progress of the reaction, beginning at the reactants, moving through the transition state, and ending at the final products. When adding the products to the diagram, be sure to use an energy level that is appropriate relative to the energy level of the reactants

Complete the energy-level diagram for h2−.
Fig. 20: Quantized energy levels (E. n . for n 2= 0 − 4) in red. Also, in green the position probability distribution |w. n (x)| the photon energies in black-body radiation and photo-electric effect, then the electron energies in the atom) is what gave quantum mechanics its name. However, as we saw from the scattering problems in the previous chapter, the quantization of energies is not a ... The energy level diagram for CO2 in Figure 5.25 can be used as a guide, with the orbitals of Be higher in energy than those of C and the orbitals of F lower in energy than those of O. Calculated molecular orbital shapes are below, for comparison for those of CO2 in Figure 5.25. Answer to: what is the energy-level diagram for H2−.1 answer · Top answer: Hey there!We are asked to draw the energy-level diagram or the molecular orbital energy diagram for H2-.An H2 molecule has two electrons and a charge ...
Complete the energy-level diagram for h2−.. The heat of solution ΔHsoln of CaCl2 is −82.8 kJ/mol. since of heat of solution is negative, energy is released in this dissolving process. ΔHsoln=-q (calorimeter)-q (soln) q (calorimeter) = heat gained by calormeter. q (soln) = heat gained by solution. Assuming heat is not lost to the calorimeter, q (cal) = 0. Draw this out using an energy level diagram: 2 He2 has bond order 0 [(2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+. 2,. H−.A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. diagram for CO2 in ... Transcribed Image Textfrom this Question. Complete the energy-level diagram for H2 Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets Reset Help σ1s 1s 1s 14 1s H2. functions are called energy eigenfunctions and the corresponding values of energy are the energy eigenvalues. Notice that the probability density for an energy eigenfunction is independent of time: Ψ(x,t)2=Ψ∗(x,t)Ψ(x,t)=ψ∗(x)eiωtψ(x)e−iωt=ψ(x)2.(7.11) Thus, energy eigenfunctions are called stationary states.
The ground state energy level of the electron in a hydrogen atom is −13.6 eV, which is equivalent to an ultraviolet photon of roughly 91 nm wavelength.. The energy levels of hydrogen can be calculated fairly accurately using the Bohr model of the atom, which conceptualizes the electron as "orbiting" the proton in analogy to the Earth's orbit of the Sun. ΔG298D = −34 kJ mol−1 12.0 g H2 × 2 2 1 mol H 2.0 g H × 2 1 mol reaction 3 mol H × 34 kJ 1 mol reaction-= -68 kJ One point is earned for the correct stoichiometry. One point is earned for the correct answer. (c) Given that ΔH298D for the reaction is −92.2 kJ mol−1, which is larger, the total bond dissociation energy The energy can be released as one quantum of energy, as the electron returns to its ground state (say, from n = 5 to n = 1), or it can be released as two or more smaller quanta as the electron falls to an intermediate state, then to the ground state (say, from n = 5 to n = 4, emitting one quantum, then to n = 1, emitting a second quantum). The first ionization energy (Ei1) is the energy associated with the removal of an electron from the neutral gaseous atom. The reaction is represented for the generalized atom X as X→X^+ + e− The amount of energy required to remove an electron is related to the effective nuclear charge and the stability of the electron configuration of the atom.
Each hydrogen atom contributes one electron, and thus, H− 2 has three electrons while H+ 2 has one. Each hydrogen atom contributes one 1s atomic orbital, and thus, the orbitals overlap according to MO theory to form one σ1s and one σ* 1s MO by conservation of orbitals. If you calculate their bond order, you get: BOH+ 2 = 1 2(Bonding − ... (iii) Complete the energy level diagram for the combustion of ethanol. On the completed diagram, label: • activation energy • overall energy change. (3) (Total 12 marks) Q10. Methane (CH 4) is used as a fuel. (a) The displayed structure of methane is: Draw a ring around a part of the displayed structure that represents a covalent bond. (1) (b) Why is methane a compound? Tick one. box ... -iE jt/h-, the average value of the energy does not vary with time but the expectation values of other properties do vary with time. 3. A particle is confined to a one-dimensional box of length L having infinitely high walls and is in its lowest quantum state. Calculate: < x>, < x2>, < p>, and < p2>. Using the 2> − < A > 2)1/2, to define the H−. Bond order = 1. 2 (electrons in bonding orbitals - electrons in antibonding orbitals) Draw a complete MO diagram for all the bonds in ethene.The energy-level diagram for He2 is shown above, the two electrons in each of the 1s atomic orbital give total of 4 electrons in this molecule.
Click here to get an answer to your question ✍️ 6. Draw the molecular orbital energy level diagram of H2.
N b = 2 , Na =0. Bond order = 1. Positive value of bond order indicates that H 2 molecule is stable.. Bond order value of 1 means that two hydrogen atoms are connected by a single bond.. Greater value of bond order for H 2 molecule than H 2 + ion shows that two H 2 molecule is more stable than H 2 +.. Bond length of H 2 is smaller than that of H 2 + ion.. As no unpaired electron is present ...
A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single Energy Level Diagrams He2 has bond order 0 [ (2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+. According to the molecular orbital theory, in a supposed He2 molecule, both the if we draw its MOT DIAGRAM, 2 e's enter the Bonding molecular Orbital and 2 .
c. O2−, F−, N3− F- O2- N3-all isoelectronic with Ne; size dictated by number of protons 8.88 Rank the ions in each set in order of decreasing size, and explain your ranking: a. Se2−, S2−, O2− Se2- S2- O2- all isoelectronic with noble gases; size dictated by shell number b.
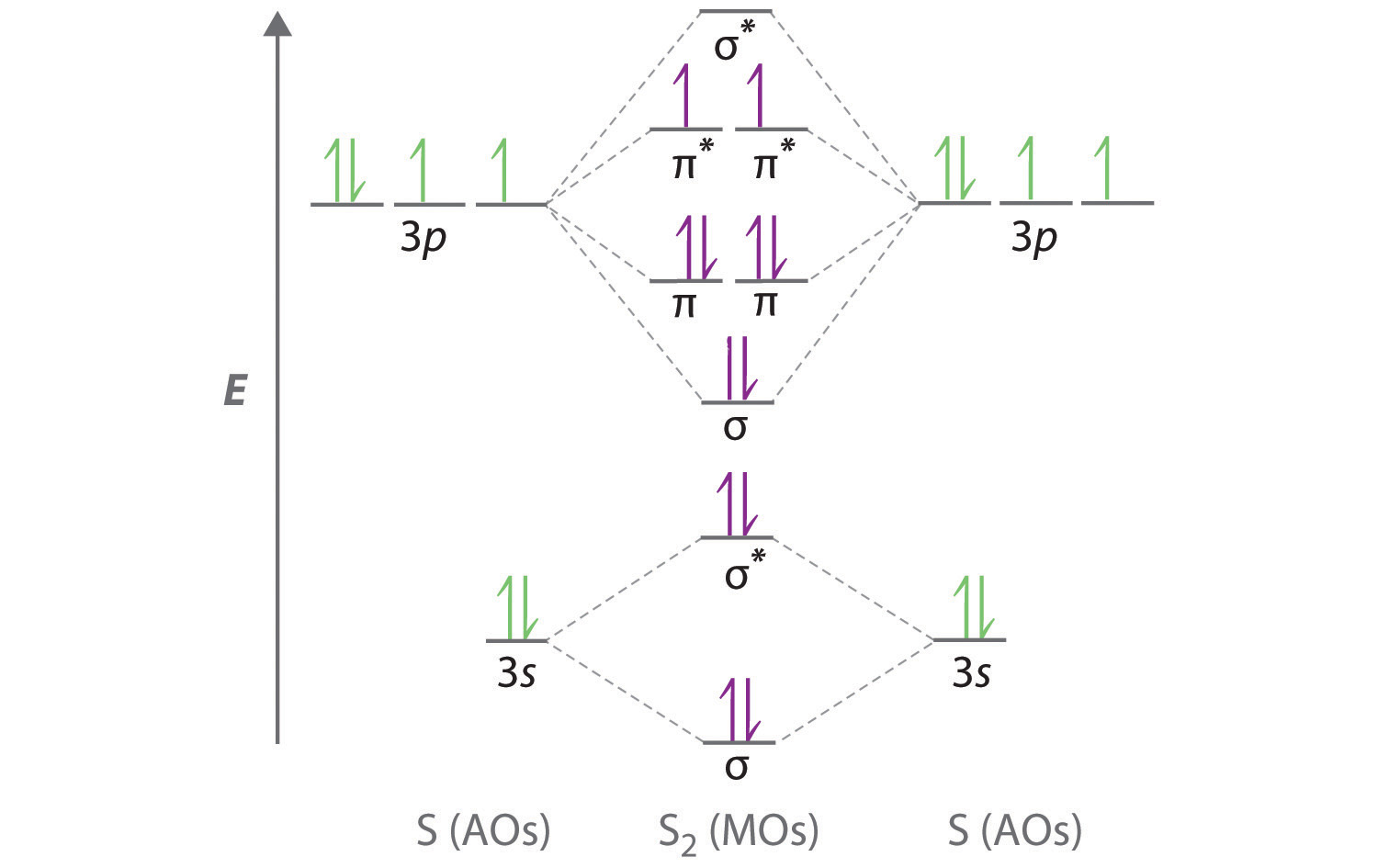
Precise energies of the H2, D2, and HD levels are calculated from highly accurate ab initio potential energy curves that include relativistic, radiative, and empirical non-adiabatic corrections.
The energy and wavelength of light are related by the equation E=hc/λ where E is energy in J, h is Planck's constant (6.626×10−34 J-s6.626×10−34 J-s) c is the speed of light (2.998×108 m/s2.998×108 m/s), and λ is the wavelength in m. Convert the wavelength from nanometers to meters using the relationship that 1 m=1×109 nm1 m=1×109 nm
Hey, guys. So for this next problem were given this molecular orbital diagram and were asked to figure out which electrons in this diagram contribute to the ...1 answer · Top answer: 1/2
Energy Level Diagram For Molecular Orbitals Chemical Bonding And Molecular Structure Chemistry Class 11
e, and therefore µc2 is the rest energy of the electron. Eq. (11.33) shows that the typical scale of the energy levels in the H atom is 10−4 the rest energy of the electron. This justifies the nonrelativistic treatment of the H atom that we have used here. Clearly
Solid State ChemiStry and itS appliCation 2014 Anthony R. West
The free-energy change, ΔG, for this reaction varies with temperature as shown in. G / kJT / K Δ mol− 1 298 −592.5 288 −594.2 273 −596.7 260 −598.8 240 −602.2 Use these data to plot a graph of free-energy change against temperature on the grid below. Calculate the gradient of the line on your graph and hence calculate the
Complete An Mo Energy Diagram For H2 . carefully complete the energy diagram by drawing a curve, complete the mo energy diagram for the n2+ ion, complete the energy-level diagram for h2−, complete the sentences to describe the energy diagram shown, complete the diagram showing the uses of geothermal energy, complete the energy-level diagram for h2+ ion, complete a qualitative energy diagram ...
COCl (g) + Cl (g) → COCl2 (g) (fast, with k3 its rate constant) Write the rate law for each elementary reaction: reaction 1, reverse. rate = k-1 * [Cl]^2. The reaction of CO with Cl2 gives phosgene (COCl2), a nerve gas that was used in World War I. Use the mechanism shown here to complete the following exercises.
.bmp)
A Draw The Energy Diagram For H2 Be2 N2 O2 B What Is Meant By The Term Bond Order Chemistry 8057743 Meritnation Com
integers between −Jto J. Vibrations With ψ(r) given by Eq. 9 and the Hamiltonian by Eq. 4, the radial part of Eq. 6 becomes " − ¯h2 2µ d2 dr2 + ¯h2 2µr2 J(J+1)+ V(r) # χ(r) = Eχ(r) (10) The term (¯h2/2µr2) J(J+1) gives the rota-tional energy. Because this energy turns out to be small compared to the total energy E, the ...
The energy levels are enumerated using a principal quantum number n, an integer that must be greater or equal to one: En = − e2 2a 0 1 n2, n= 1,2,.... (2.1.3) Note that H(0) is a non-relativistic Hamiltonian: the speed of light does not enter in it, and the kinetic term is that of Newtonian mechanics. The energy scale relevant to the 25
Other articles where molecular orbital energy-level diagram is discussed: chemical bonding: Molecular orbitals of H2 and He2: The molecular orbital ...
Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
The C −Br bond is weaker than the C−Cl bond. The H −Cl bond is weaker than the H−Br bond. Chlorine is more reactive than bromine. (1) (Total 15 marks) Q3.A student investigated the rate of reaction of magnesium and hydrochloric acid. Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) MgCl 2 (aq) + H 2 (g)
−1652 kJ/mol divided by 4 = 413 kJ --- that's the bond enthalpy of a C−H bond Note that bond enthalpies are expressed as a positive value (energy put into the bond to break it), so I ignored the minus sign on the 1652 value. For the second reaction, note that six C−H bonds are formed and one C−C bond is formed. 413 times 6 = 2478
Answer to Draw an MO energy diagram and predict the bond order of Be2+ and Be2−. Do you expect these molecules to exist in the. Even rather simple molecular orbital (MO) theory can be used to predict which we start reading from the bottom of the diagram because this is how MO diagrams are constructed, Diberyllium, Be2, has a bond order of zero and is unknown.
Answer to: what is the energy-level diagram for H2−.1 answer · Top answer: Hey there!We are asked to draw the energy-level diagram or the molecular orbital energy diagram for H2-.An H2 molecule has two electrons and a charge ...
The energy level diagram for CO2 in Figure 5.25 can be used as a guide, with the orbitals of Be higher in energy than those of C and the orbitals of F lower in energy than those of O. Calculated molecular orbital shapes are below, for comparison for those of CO2 in Figure 5.25.
Fig. 20: Quantized energy levels (E. n . for n 2= 0 − 4) in red. Also, in green the position probability distribution |w. n (x)| the photon energies in black-body radiation and photo-electric effect, then the electron energies in the atom) is what gave quantum mechanics its name. However, as we saw from the scattering problems in the previous chapter, the quantization of energies is not a ...

Photocatalysts Based On Organic Semiconductors With Tunable Energy Levels For Solar Fuel Applications Kosco 2020 Advanced Energy Materials Wiley Online Library
Crystals Free Full Text Role Of The Potential Barrier In The Electrical Performance Of The Graphene Sic Interface Html

Scielo Brasil Explaining The Geometry Of Simple Molecules Using Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagrams Built By Using Symmetry Principles Explaining The Geometry Of Simple Molecules Using Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagrams Built












0 Response to "39 complete the energy-level diagram for h2−."
Post a Comment