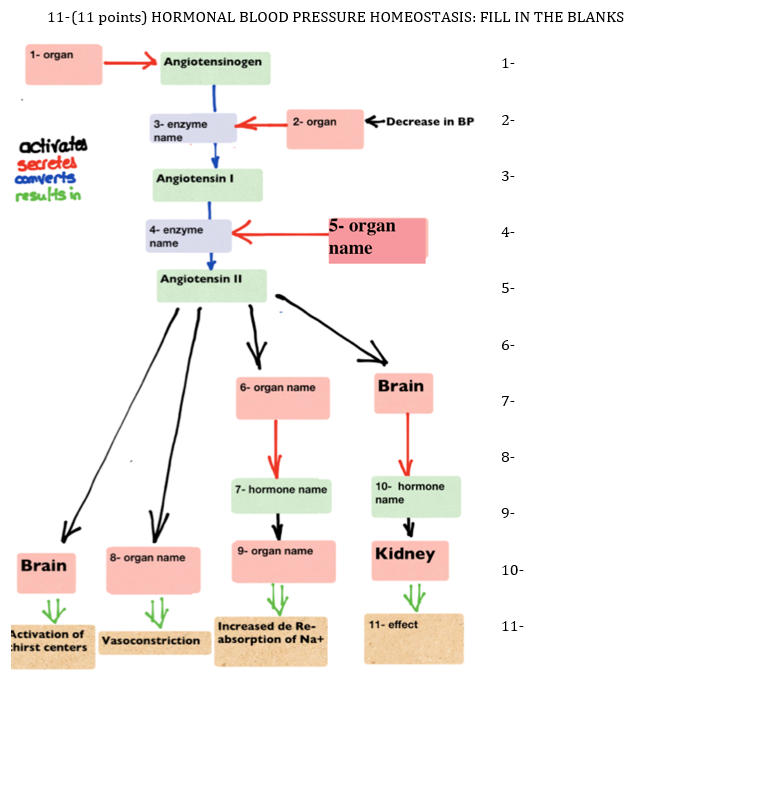
41 blood pressure homeostasis diagram
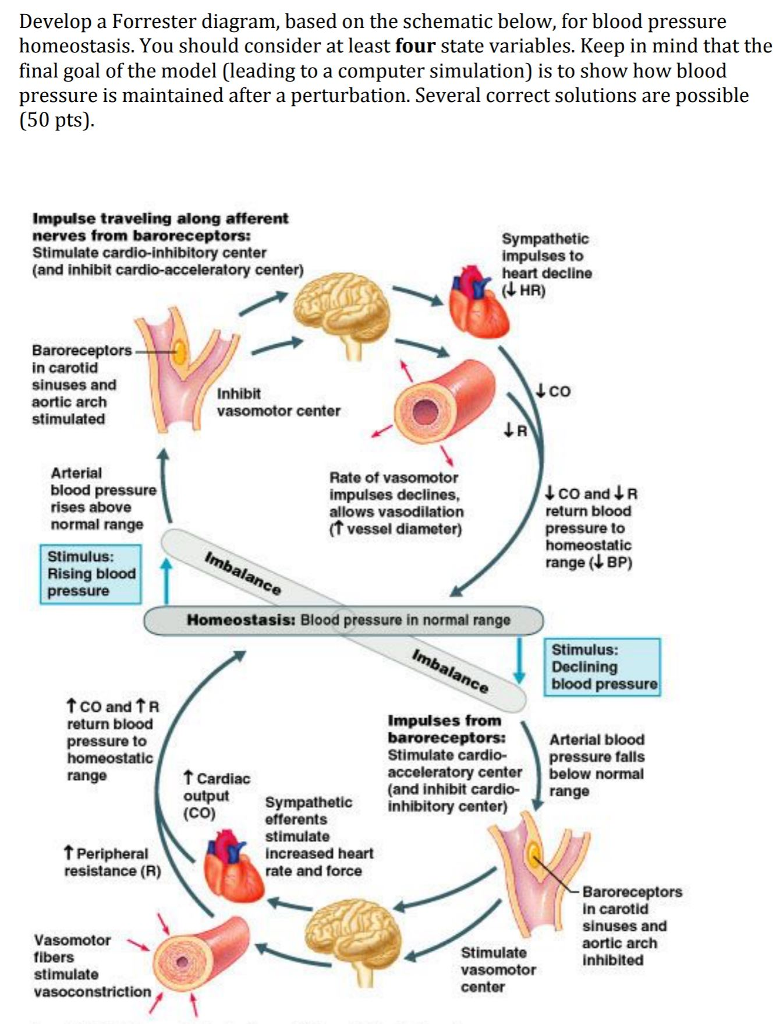
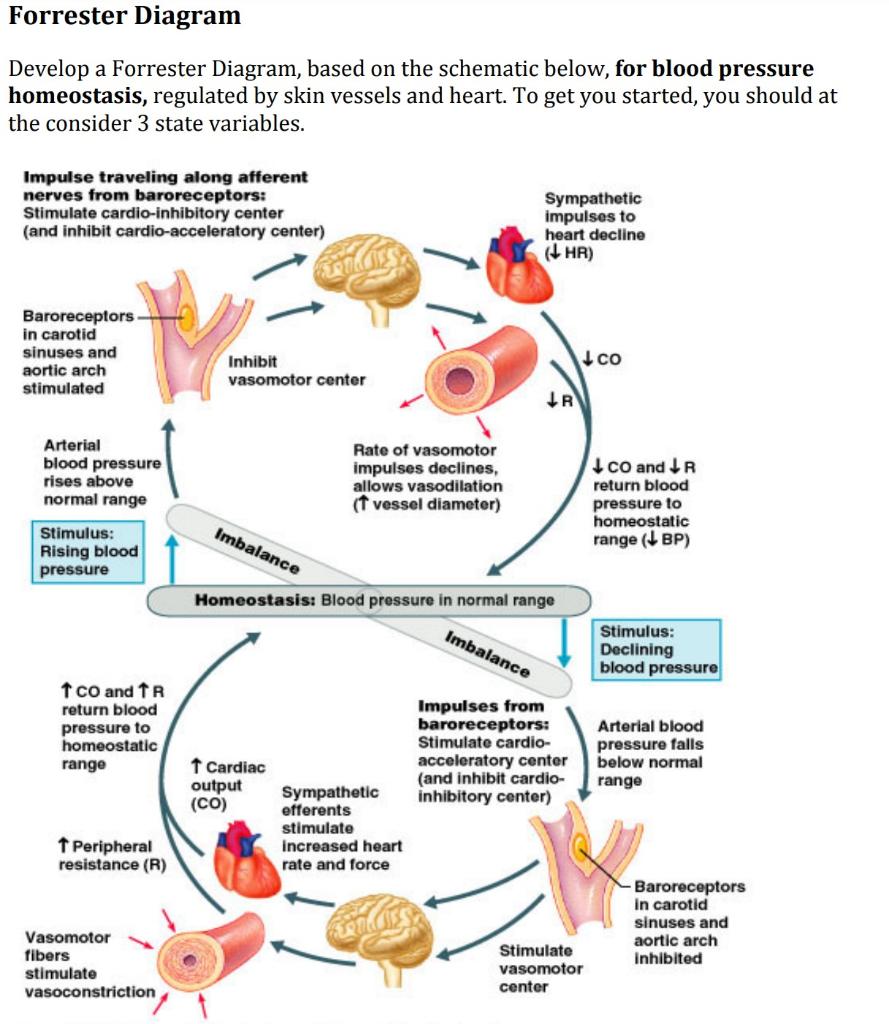
Forrester Diagram Develop a Forrester Diagram, based on the schematic below, for blood pressure homeostasis, regulated by skin vessels and heart. To get you started, you should at the consider 3 state variables. Impulse traveling along afferent nerves from baroreceptors: Stimulate cardio-inhibitory center (and inhibit cardio-acceleratory center ... The optimal diastolic blood pressure is 80 mmHg. Many factors can affect blood pressure, such as hormones, stress, exercise, eating, sitting, and standing. Blood flow through the body is regulated by the size of blood vessels, by the action of smooth muscle, by one-way valves, and by the fluid pressure of the blood itself.
Osmosis Blood Pressure Regulation high-yield notes offers clear overviews with striking illustrations, tables, and diagrams. Make learning more manageable.
Blood pressure homeostasis diagram
blood gas analysis laboratory studies of arterial and venous blood for the purpose of measuring oxygen and carbon dioxide levels and pressure or tension, and hydrogen ion concentration (pH). (See accompanying table.) Analyses of blood gases provide the following information:ƒ Pa O 2 —partial pressure (P) of oxygen (O 2) in the arterial blood (a) Sa O 2 —percentage of available hemoglobin ... Endothelin (ET) peptides and their receptors are intimately involved in the physiological control of systemic blood pressure and body Na homeostasis, ... Homeostasis, however, is the process by which internal variables, such as body temperature, blood pressure, etc., are kept within a range of values appropriate to the system. When a stimulus changes one of these internal variables, it creates a detected signal that the body will respond to as part of its ability to carry out homeostasis.
Blood pressure homeostasis diagram. An important aspect of homeostasis is maintaining a normal body temperature. Describe the homeostatic feedback system that would be activated in response to a decreased external temperature. Yes, homeostasis is important to keep everything in the body balanced. The temperature of the body is around 37ºC at all times. B. Blood Pressure Homeostasis Use the terms in bulleted list to complete the schematic diagram of blood pressure homeostasis in Figure 29.8. • ADH • aldosterone • blood pressure ln o bluow • blood volume • cardiac output • sympathetic nerves nl beblaoo 2gvd one nl HOMEOSTASIS oold odi motl anoruh Normal BP and volume lo llew ods nidiw asd stem dioom f Yon vaW vishs st to asmal sdi ... The diagram consists of nodes, representing body systems producing physiological variations, and arcs connecting nodes, representing the mediators of these variations, viz. hormones, mechanical effects exerted by blood volume and pressure changes, and nerve signal conduction and neurotransmitter release. Blood pressure regulation is a complex process, regulated by several mechanisms that work in unison to maintain homeostasis. Rapid adjustments in blood pressure are typically neurally mediated by the baroreceptor reflex. Intermediate and long term regulation of blood pressure is predominantly mediated by vasoactive compounds.
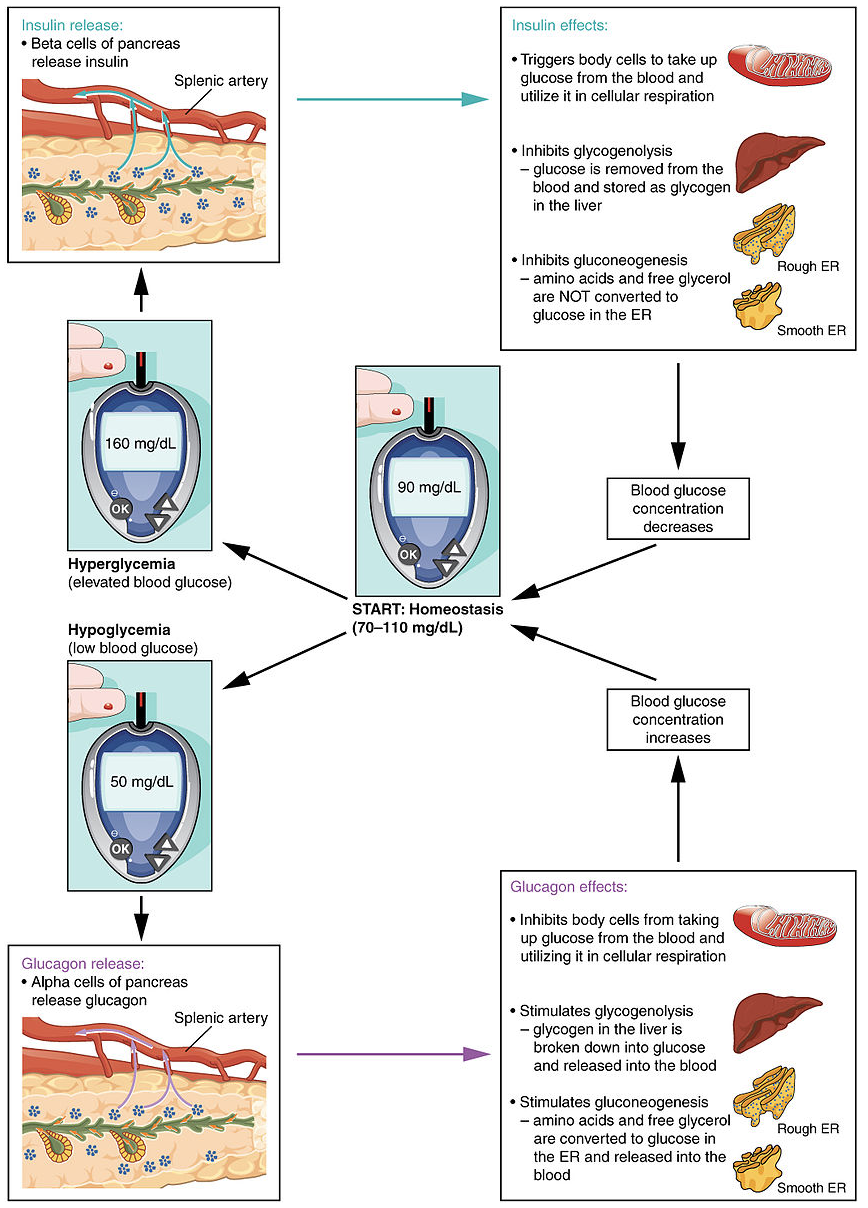
Effectors: Glucose homeostasis • Liver and skeletal muscle and other bodily tissues • Important for constant supply of glucose to the brain • High blood sugar (hyperglycaemia) is undesirable because it causes tissue damage (nephropathy [kidney disease], neuropathy [nerve damage], retinopathy [eye disease]). Blood pressure homeostasis 2.4 Blood Pressure Regulation . Homeostasis: Homeostasis is defined as the condition of constancy of the "internal environment" in terms of its cells, tissues, and organs. Thus in blood pressure regulation, homeostasis will tend to stabilize the blood pressure, maintaining it at a steady resting state. The diagram consists of nodes, representing body systems producing physiological variations, and arcs connecting nodes, representing the ... Question: Use the terms to complete the schematic diagram of blood pressure homeostasis. ADH blood volume aldosterone cardiac output blood pressure sympathetic ...
Blood Glucose Homeostasis Glucose is the transport carbohydrate in animals, and its concentration in the blood affects every cell in the body. Its concentration is therefore strictly controlled within the range 0.8 - 1g per dm3 of blood, and very low levels (hypoglycaemia) or very high levels (hyperglycaemia) are both serious and can lead to death. Blood Pressure Diagram - With the assistance of this high blood pressure chart, you can identify if the blood pressure is great or if you need to make some dietary or workout modifications to decrease it.. The sum of the systolic and diastolic blood pressures is what you'll see on your high blood pressure display. As your heart beats, your systolic high blood pressure increases ... Adjustments of blood pressure, metabolism, and body temperature are all negative feedback. Key Terms. homeostasis: The ability of a system or ... Anatomy and physiology of blood pressure Why regulating blood pressure is so important Factors that affect the functioning of the baroreceptor reflex Regulation of the blood pressure is a vital physiological process enabling the body to respond to immediately changing demands such as 'fight or flight', or resting The physiology of blood

Frontiers Role Of A2 Adrenoceptors In Hypertension Focus On Renal Sympathetic Neurotransmitter Release Inflammation And Sodium Homeostasis Physiology
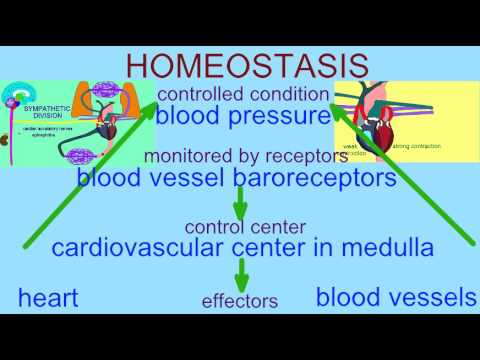
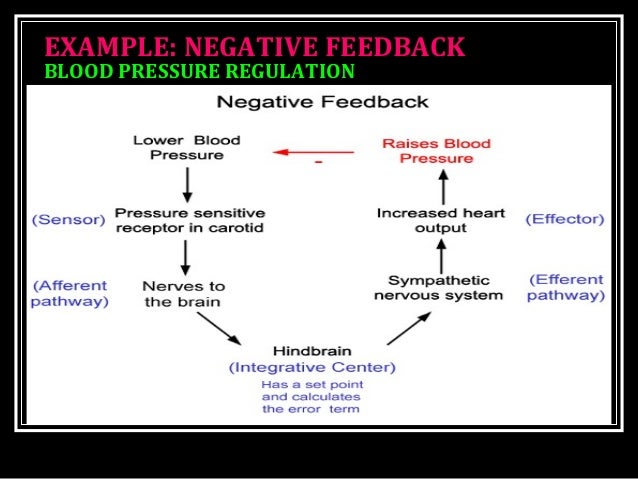
When the cardiovascular center in the medulla oblongata receives this input, it triggers a reflex that maintains homeostasis (Figure 2): When blood pressure rises too high, the baroreceptors fire at a higher rate and trigger parasympathetic stimulation of the heart. As a result, cardiac output falls. Sympathetic stimulation of the peripheral ...

The Roles Of V1a Vasopressin Receptors In Blood Pressure Homeostasis A Review Of Studies On V1a Receptor Knockout Mice Semantic Scholar
The diagram on the left is a general model showing how the components interact to maintain homeostasis. The diagram on the right shows the example of body temperature. From the diagrams, you can see that maintaining homeostasis involves feedback, which is data that feeds back to control a response. ... but it will also lower your blood pressure ...
Combined, these activities cause blood pressure to rise. Figure 20.4.2 - Baroreceptor Reflexes for Maintaining Vascular Homeostasis: Increased blood pressure results in increased rates of baroreceptor firing, whereas decreased blood pressure results in slower rates of fire, both initiating the homeostatic mechanism to restore blood pressure.
the blood and lymphatic system and is known as 'the body's internal environment' (Tortora and Anagnostakos, 2003). The body is said to be in homeostasis when its internal environment contains: l Optimum levels of gases, ions, water and nutrients; l Is at optimal temperature; l Has optimal pressure for the health of cells.
Cardiovascular center: identify the relationship between blood pressure and neural activity in the cardiovascular center on block diagram. Feedback to the PNS and SNS from the cardiovascular center, which receives input from baroreceptors, prevents a sudden decrease in SNS activity from having a lasting effect on blood pressure.
Homeostasis is a core concept necessary for understanding the many regulatory mechanisms in physiology. ... blood pressure and body temperature are sensed variables. Baroreceptors and thermoreceptors exist within the system and provide the value of the pressure or temperature to the regulatory mechanism. ... For example, textbook diagrams ...
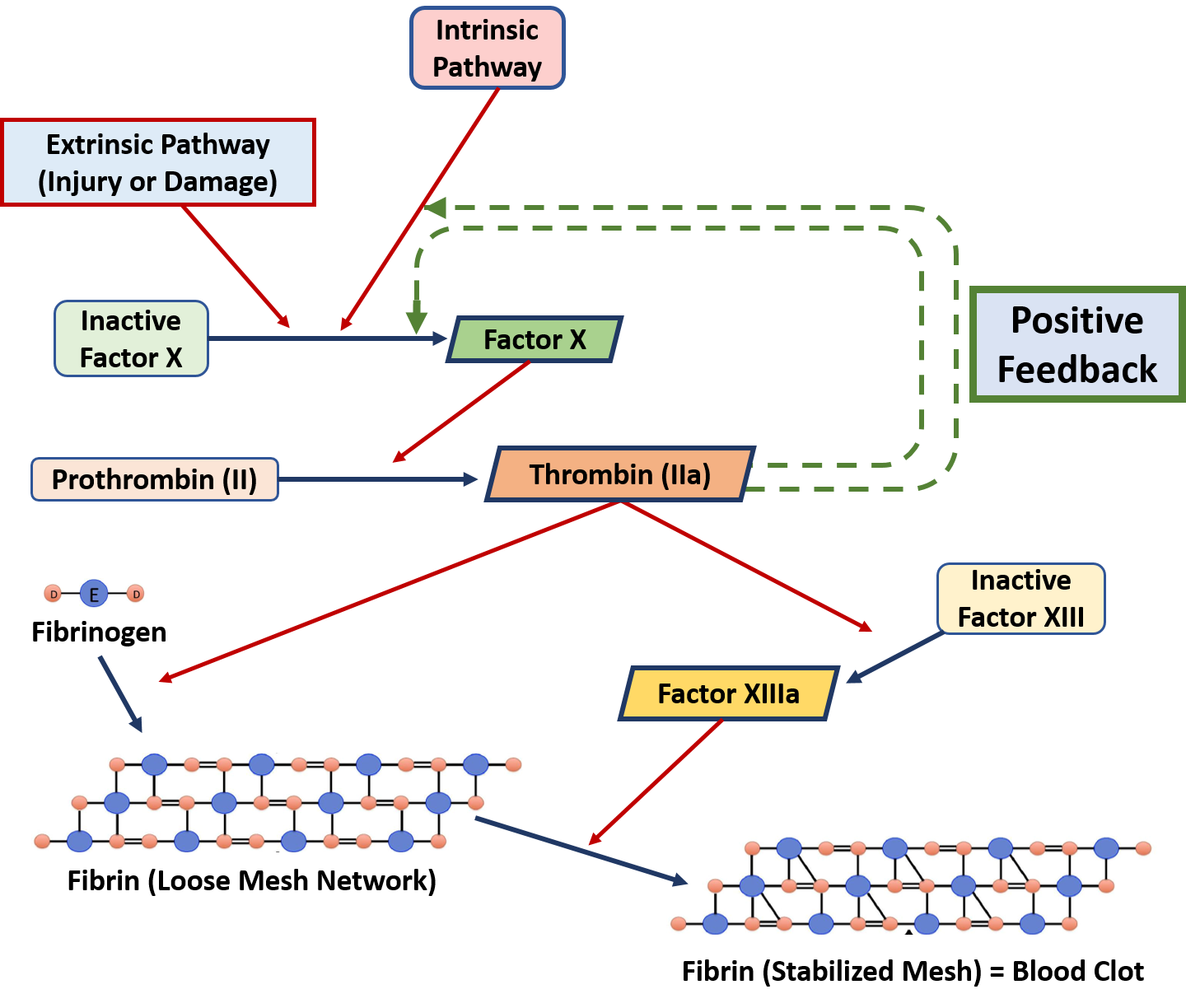
Response in the opposite direction as the stimulus. Maintains homeostasis. (Thermoregulation) Response in the same direction as the stimuli. Occurs with childbirth, blood clotting, and generation of nerve signals . Essay: Describe all of the components of the two types of feedback loops and describe how each works.
The autonomic nervous system plays a critical role in the regulation of vascular homeostasis. The primary regulatory sites include the cardiovascular centers in ...
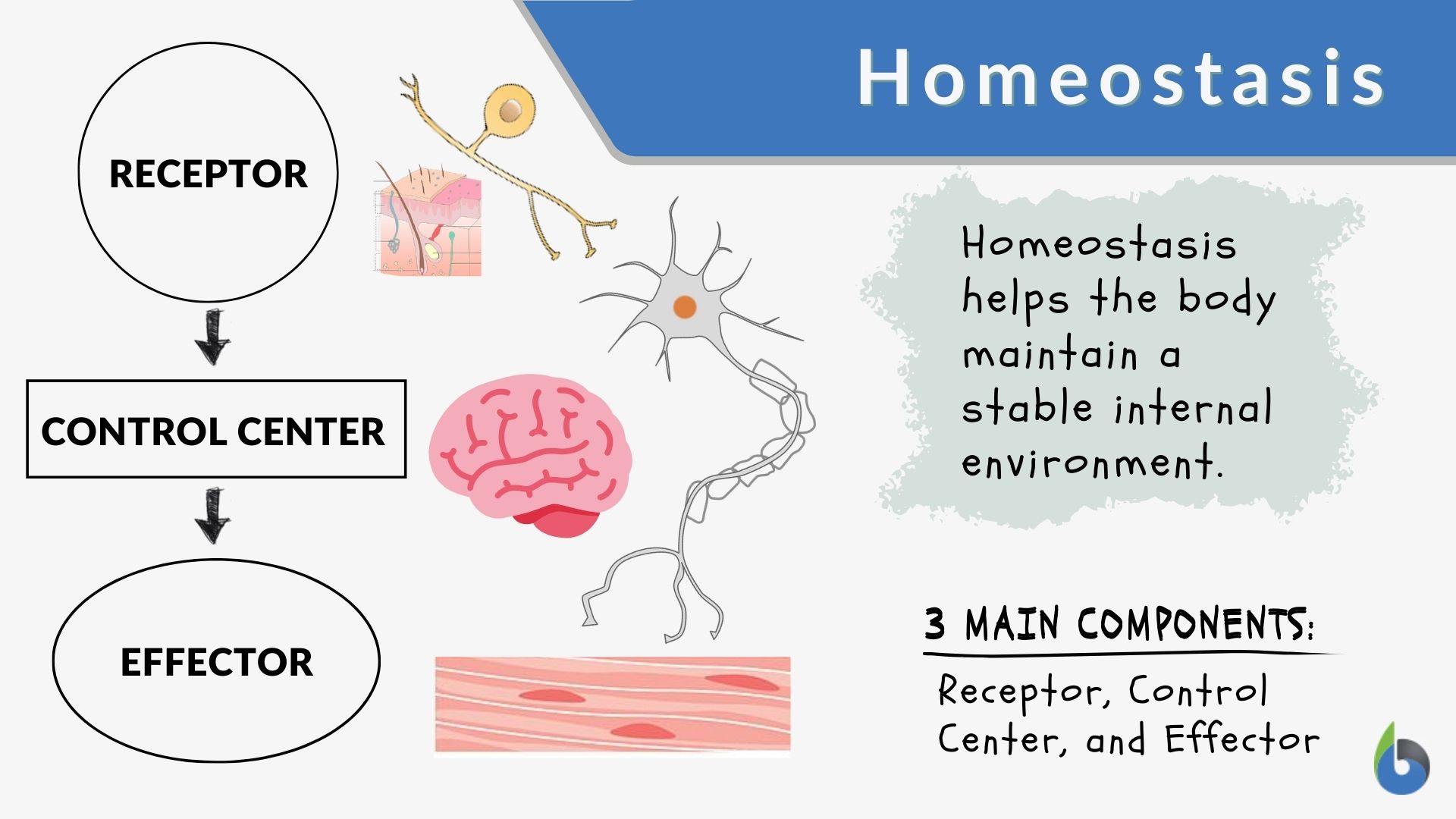
Homeostasis is the ability of the body to maintain an internal environment that is constant, regardless of outside influences. The body controls blood pressure, temperature, respiration and even blood glucose levels by using several internal mechanisms to keep things constant.
Homeostasis refers to the maintenance of relatively constant internal conditions. For example, your body shivers to maintain a relatively constant body temperature when the external environment gets colder. To maintain homeostasis, your body adapts two types of feedback mechanisms: Negative feedback occurs when a change in a
Leptin Dried Plum Weight Loss Hologram Penurun Berat Badan Alami Buah Plum Kering Pelangsing Shopee Indonesia
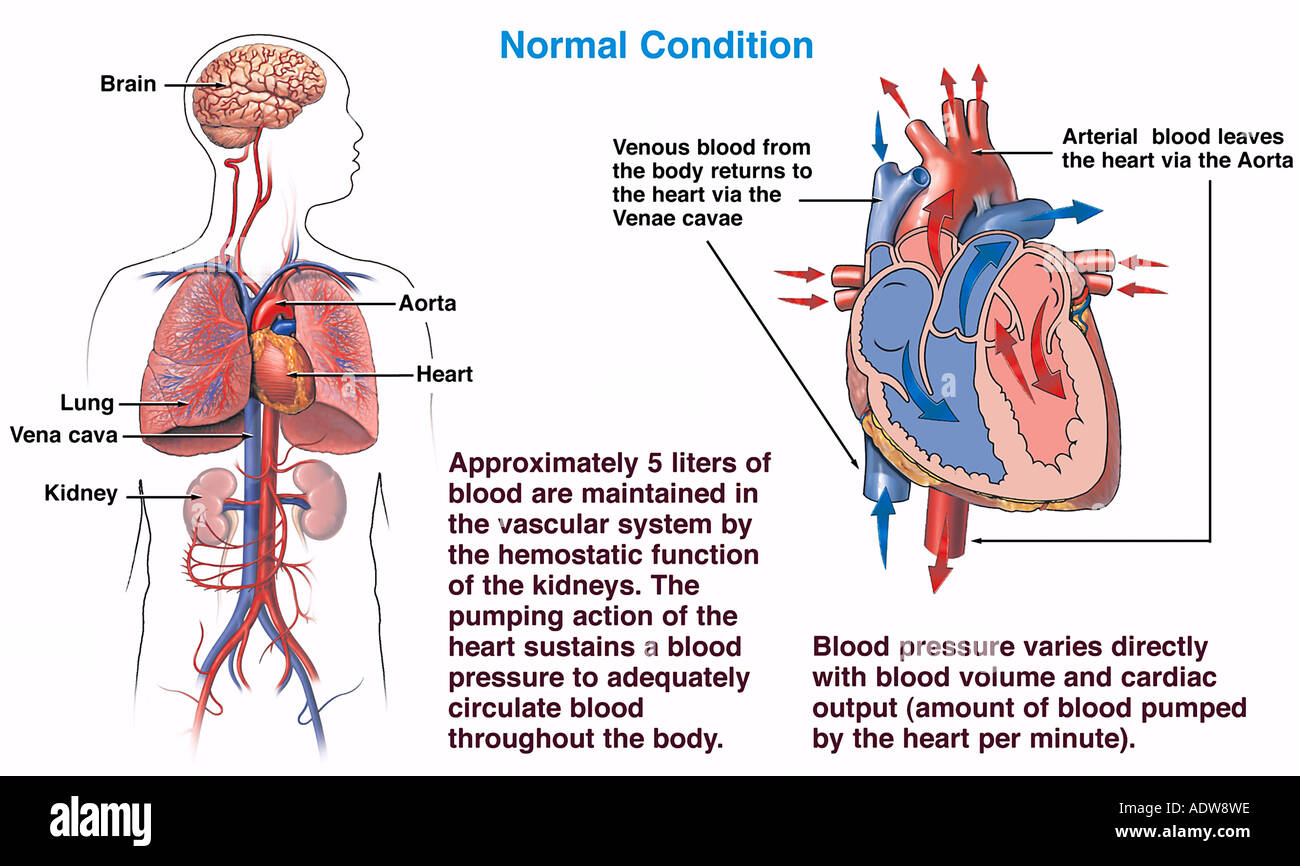
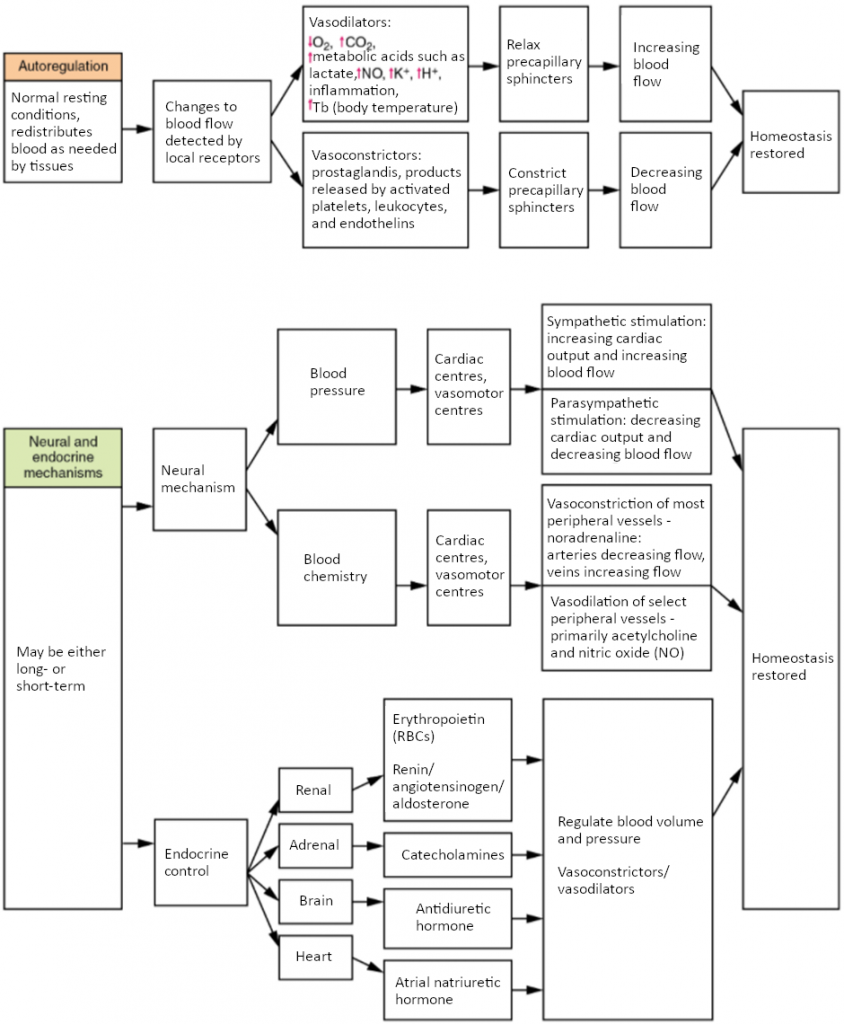
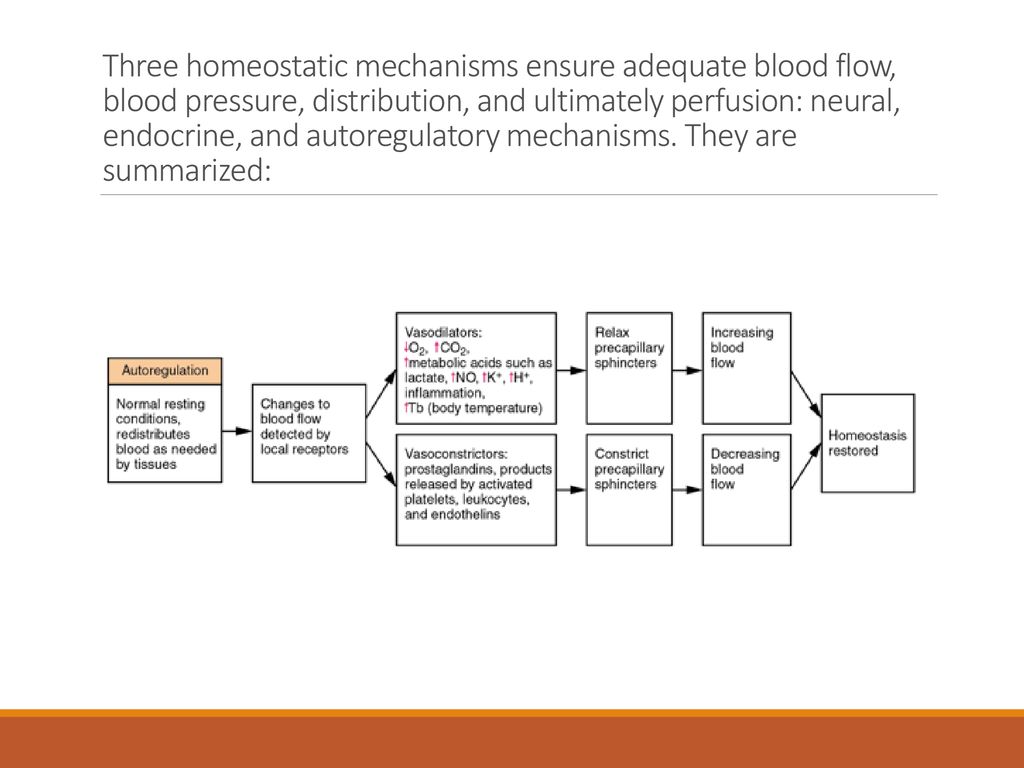
Abstract. The circulatory system is a closed-loop system in which cardiac output is dependent upon adequate venous return. Distribution of this output to the various organ systems in amounts appropriate to their needs is accomplished by constriction or relaxation of vascular smooth muscle.
Start studying 29.8: Blood pressure homeostasis. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
HOMEOSTASIS BLOOD PRESSURE REGULATION. 3,367 views3.3K views. Aug 23, 2014. 15. Dislike. Share. Save. Walter Jahn. Walter Jahn.
Maintaining homeostasis requires that the body continuously monitor its internal conditions. From body temperature to blood pressure to levels of certain nutrients, each physiological condition has a particular set point. A set point is the physiological value around which the normal range fluctuates.
Homepage / blood pressure homeostasis diagram. Tag: blood pressure homeostasis diagram. Blood Pressure. Blood Pressure Diagram. Blood Pressure Diagram - With the assistance of this high blood pressure chart, you can identify if the blood pressure is Continue reading. Pages. About Us; Contact;
Blood pressure is maintained in normal ranges through a process called homeostasis, which sends out chemicals andsignals to either relax or tighten the blood vessels to make blood pressure go up or down when needed. This happens through a blood pressure feedback loop that tells the body how to maintain your blood pressure where it needs to be.
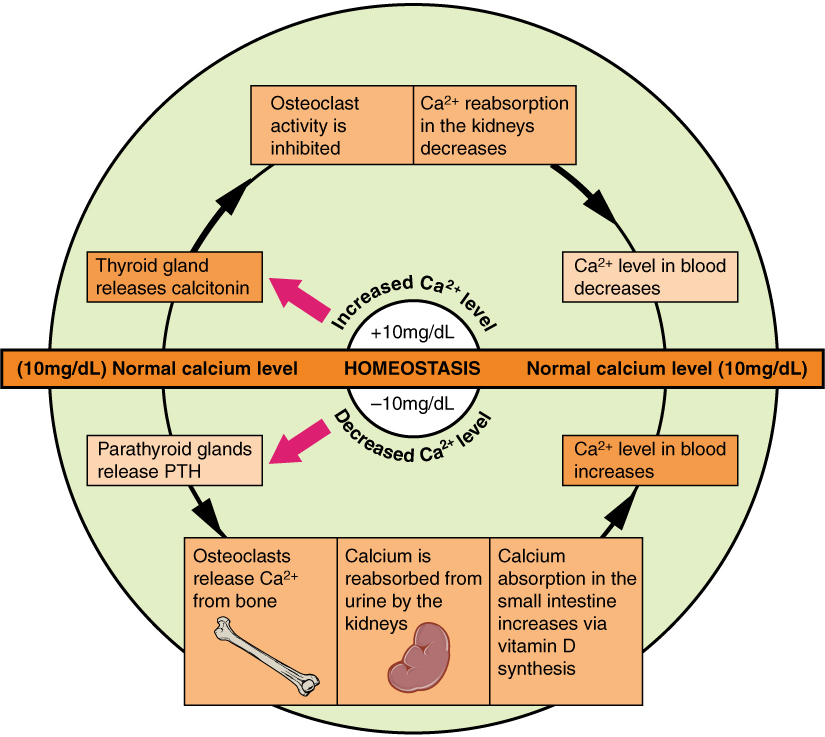
Calcium homeostasis, i.e., maintaining a blood calcium level of about 10 mg/dL, is critical for normal body functions. Hypocalcemia can result in problems with blood coagulation, muscle contraction, nerve functioning, and bone strength. Hypercalcemia can result in lethargy, sluggish reflexes, constipation and loss of appetite, confusion, and coma.
the blood volume and therefore blood pressure. • Label the diagram on the top of the next page. Interactive Physiology 8 Page 29. Short-Term Effect of Osmolarity on BP • A short-term effect of increased osmolarity is the excitation of the thirst center in the hypothalamus. The thirst center stimulates the individual to drink more water and thus
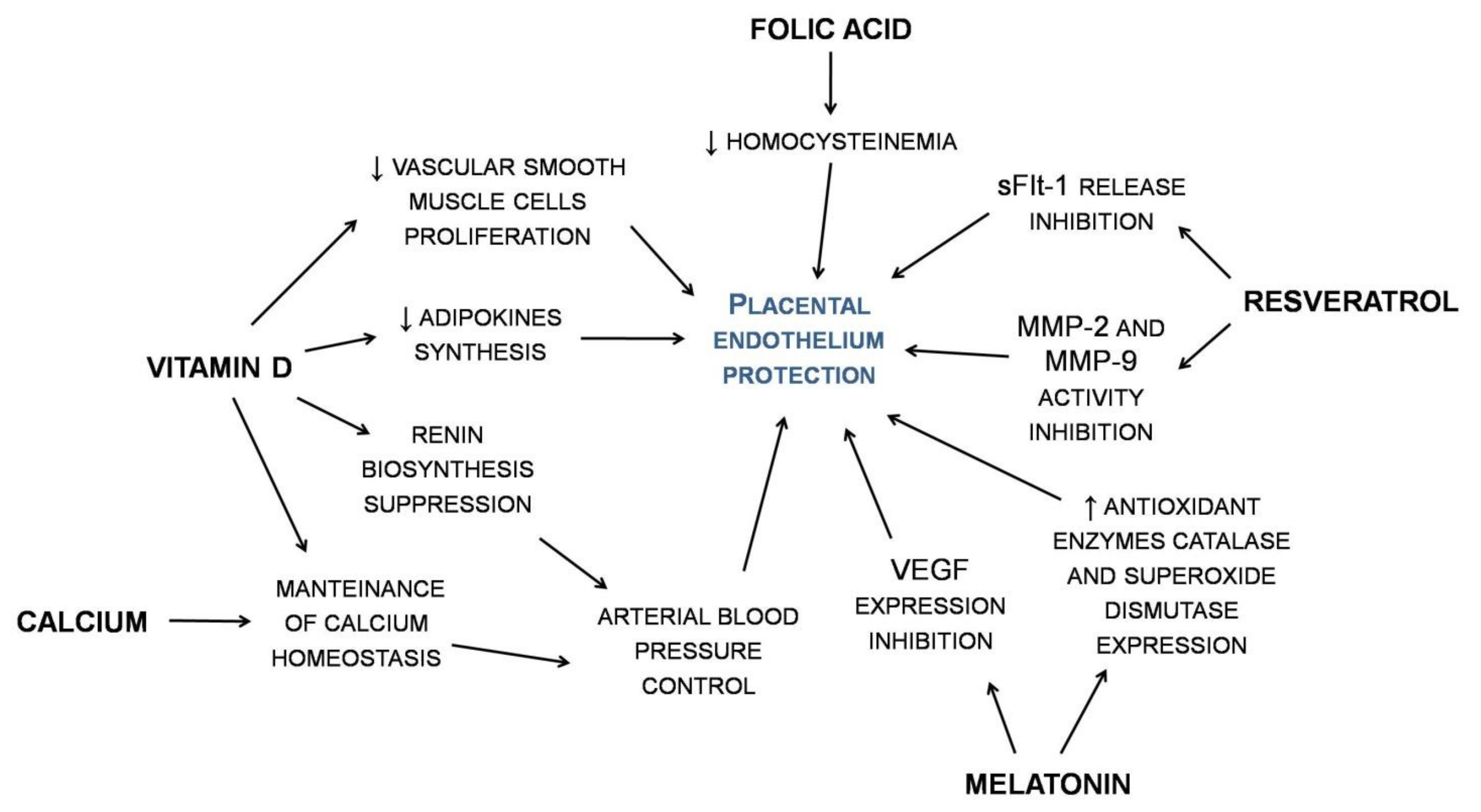
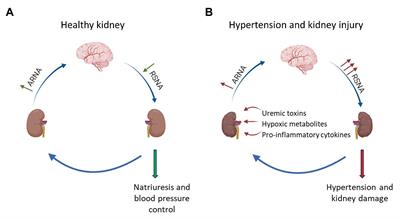
Nutrients Free Full Text Nutraceuticals And Hypertensive Disorders In Pregnancy The Available Clinical Evidence
Homeostasis, however, is the process by which internal variables, such as body temperature, blood pressure, etc., are kept within a range of values appropriate to the system. When a stimulus changes one of these internal variables, it creates a detected signal that the body will respond to as part of its ability to carry out homeostasis.
Endothelin (ET) peptides and their receptors are intimately involved in the physiological control of systemic blood pressure and body Na homeostasis, ...
blood gas analysis laboratory studies of arterial and venous blood for the purpose of measuring oxygen and carbon dioxide levels and pressure or tension, and hydrogen ion concentration (pH). (See accompanying table.) Analyses of blood gases provide the following information:ƒ Pa O 2 —partial pressure (P) of oxygen (O 2) in the arterial blood (a) Sa O 2 —percentage of available hemoglobin ...
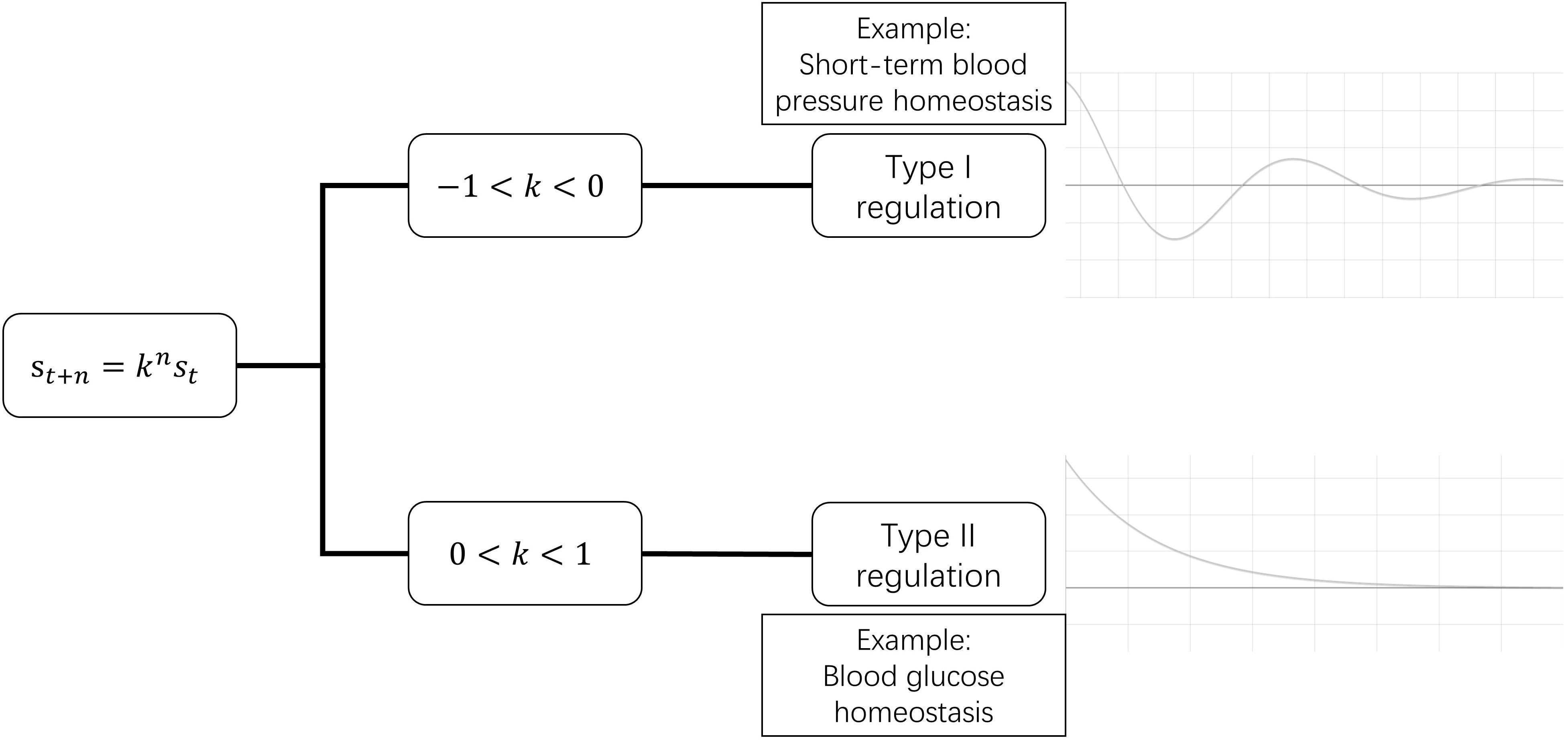
Frontiers Depiction Of Physiological Homeostasis By Self Coupled System And Its Significance Physiology

Hypertension Lecture 4 Shaesta Naseem Hypertension Definition Blood Pressure Is A Function Of Cardiac Output And Peripheral Vascular Resistance Blood Ppt Download
















0 Response to "41 blood pressure homeostasis diagram"
Post a Comment