36 diabetic ketoacidosis pathophysiology diagram
Pathogenesis and Pathophysiology — Please see details of the pathophysiology outlined in the figure/flowchart below. Metabolic Derangements of DKA vs ...Non-compliance with insulin regimen: Lack of i...Precipitants: Mechanism(s)
Step 1 of the pathophysiology of diabetic ketoacidosis is there is not enough insulin. So normally in your body, your pancreas produces insulin, and insulin’s job is to grab onto glucose and move it into the cells so that the cells can use them for energy. But in the case of diabetic ketoacidosis, there isn’t enough insulin.
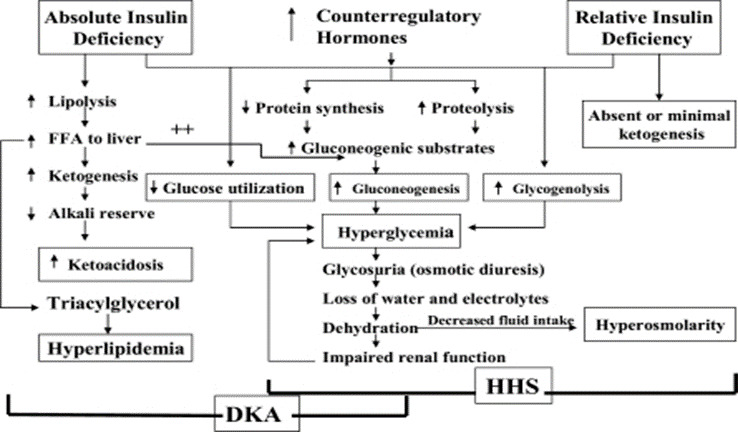
Download scientific diagram | Pathophysiology of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and of hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state (HHS) (modified from [16]). from ...
Diabetic ketoacidosis pathophysiology diagram
25 Jul 2020 — Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) pathophysiology finally explained with a simplified flowchart, and an easy mneumonic to remember management ...
24 Oct 2017 — Diabetic ketoacidosis (one of the hyperglycemic crises), DKA, pathophysiology, causes, clinical presentation (signs and symptoms) and ...
22.01.2018 · Diabetes Pathophysiology & Diseases Process (Diagram) Signs and symptoms of hyperglycemi a reported by patients with Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes include: Vaginal infections or discomfort. The complications of diabetes mellitus usually affect the heart, brain, legs, eyes, kidneys, nerves, and skin, resulting in angina, heart failure, strokes, leg ...
Diabetic ketoacidosis pathophysiology diagram.
Pathophysiology of DKA ... Insulin deficiency causes the body to metabolize triglycerides and amino acids instead of glucose for energy. Serum levels of glycerol ...
Diabetic Ketoacidosis Pathophysiology Diagram Diabetic Meal Plan For The Day Diabetic Foot And Leg Problems Diabetic Dog Throws Up Let Him Eat It Diabetic Food Carbs ...
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) ... Causes of Morbidity and Mortality: Cerebral edema, which occurs in 0.5 – 1 % of all episodes of DKA, is the most common cause of mortality in children with DKA, Cerebral edema usually develops 4 – 12 hours into treatment, but
19 Jan 2021 — DKA is a state of absolute or relative insulin deficiency aggravated by ensuing hyperglycemia, dehydration, and acidosis-producing derangements ...
13 Sept 2018 — Like hypoglycemia, by understanding the basic pathophysiology of DKA, there is no need to memorize signs and symptoms in order to recognize ...
31.03.2018 · Diabetic Ketoacidosis Pathophysiology Diagram. Home Diabetic Diagram Ketoacidosis Pathophysiology Diabetic Ketoacidosis Pathophysiology Diagram Diabetic Ketoacidosis Pathophysiology Diagram Diabetes Diet: Doctors Say New York City Big-Soda Ban is Just a Start created on behalf of the New York City Department of Health(Photo.New …
Pathophysiology of DKA Page 2 Diagram showing the mechanism of diabetic ketoacidosis Diagram of pathophysiology of diabetic ketoacidosis in a molecular level “On admission, serum potassium levels may be high or within reference range due to shift of potassium from intracellular to extracellular due to acidemia, insulin
Ketoacidosis is a metabolic state associated with pathologically high serum and urine concentrations of ketone bodies, namely acetone, acetoacetate, and beta-hydroxybutyrate. During catabolic states, fatty acids are metabolized to ketone bodies, which can be readily utilized for fuel by individual cells in the body. Of the three major ketone bodies, acetoacetic acid is the only true ketoacid ...
26.12.2017 · Diabetic Ketoacidosis (dka) Diabetic ketoacidosis is an acute metabolic complication of diabetes characterized by hyperglycemia, hyperketonemia, and metabolic acidosis. Hyperglycemia causes an osmotic diuresis with significant fluid and electrolyte loss. DKA occurs mostly in type 1 diabetes mellitus (DM). It causes nausea, vomiting, and abdominal …
Pathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis Diabetic ketoacidosis is one of the potentially life-threatening acute complications of diabetes mellitus. In the past, diabetic ketoacidosis was considered as the hallmark of Type I diabetes, but current data show that it can be also diagnosed in patients with type II diabetes mellitus.
Diabetic Ketoacidosis Pathophysiology Diagram Diabetes Diet: Doctors Say New York City Big-Soda Ban is Just a Start created on behalf of the New York City Department of Health(Photo.New York, NY Patient Service Diet Representative Jobs Jobs in New York, NY include Diet Aide, Patient Billing Representative, Patient ...
26.12.2017 · A A A Diabetic Ketoacidosis Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) results from dehydration during a state of relative insulin deficiency, associated with high blood levels of sugar level and organic acids called ketones. Diabetic ketoacidosis is associated with significant disturbances of the body's chemistry, which resolve with proper therapy. Diabetic …
Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Pathophysiology and Treatment Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), also known as diabetic acidosis or diabetic coma, is a severe complication of diabetes mellitus (DM; Michel, 2011). More commonly seen in patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D), DKA results when lipid breakdown generates a surplus of acidic
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY. Insulin deficiency, increased insulin counter-regulatory hormones (cortisol, glucagon, growth hormone, and catecholamines) and peripheral insulin resistance lead to hyperglycemia, dehydration, ketosis, and electrolyte imbalance which underlie the pathophysiology of DKA.
View 339095705-DKA-PATHO-DIAGRAM.pdf from BS NURSING NURS101 at Saint Louis University, Baguio City Main Campus - Bonifacio St., Baguio City. Pathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis NONMODIFIABLE

0 Response to "36 diabetic ketoacidosis pathophysiology diagram"
Post a Comment