40 inferior vena cava diagram
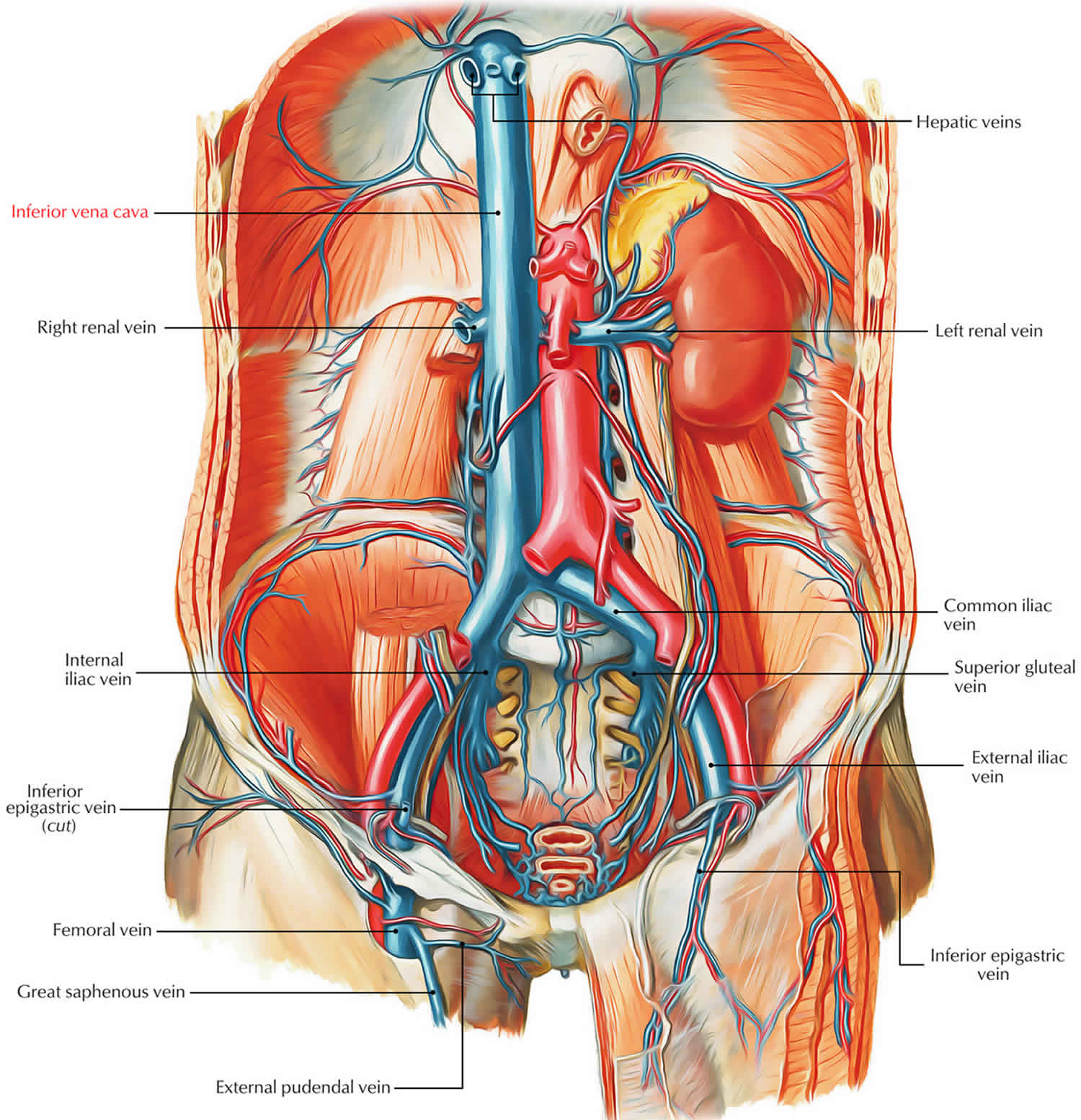
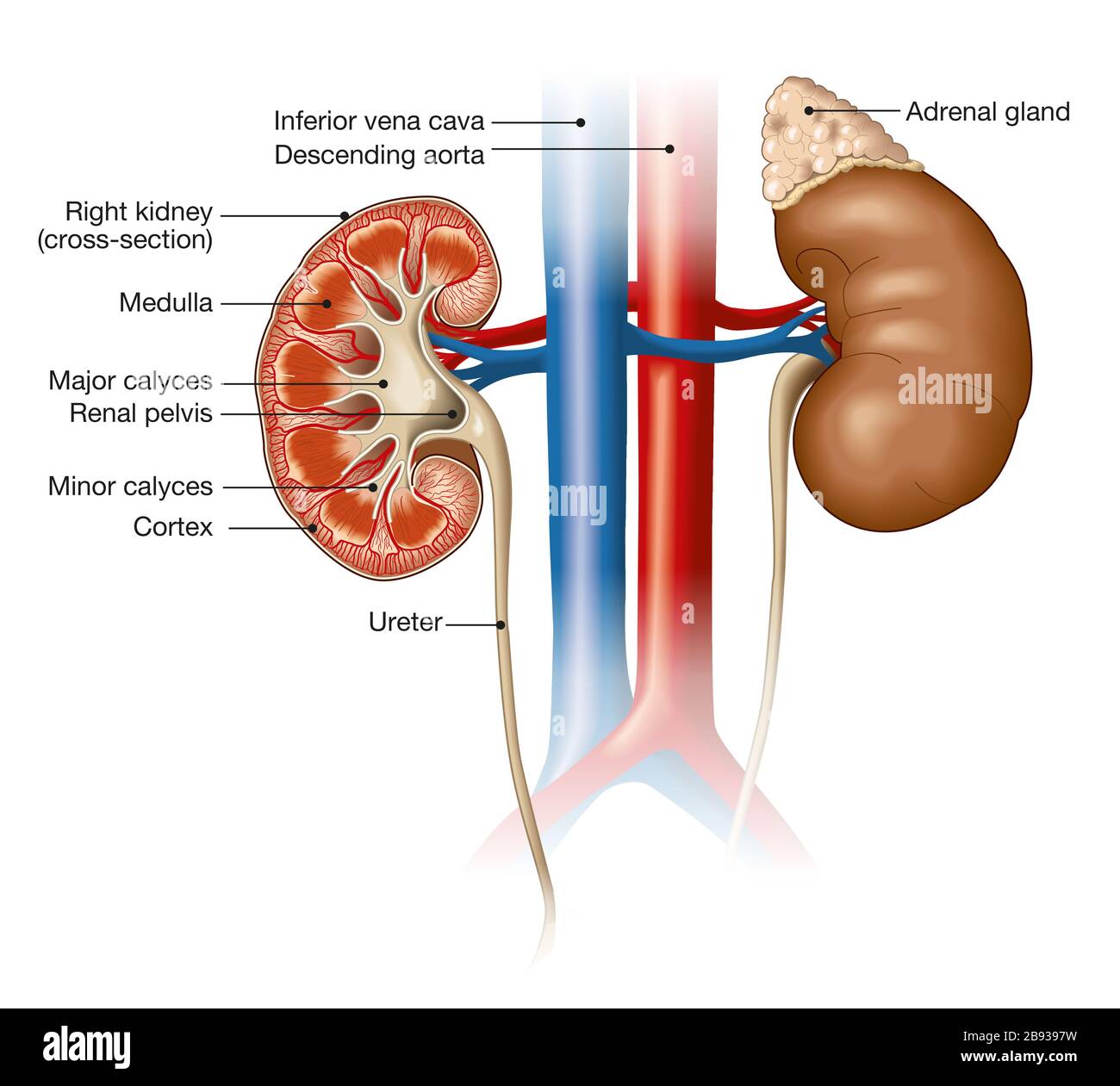
Inferior vena cava syndrome (IVCS) is a sequence of signs and symptoms that refers to obstruction or compression of the inferior vena cava (IVC). The pathophysiology of IVCS is similar to superior vena cava syndrome (SVCS) because of the presence of an underlying process that inhibits venous return to the right atrium. IVCS is not a primary diagnosis because it is often caused by other ... Inferior Vena Cava Diagram. In this image, you will find hepatic veins, inferior phrenic vein, portal vein, left renal vein, left suprarenal vein, left gonadal vein, right gonadal vein, right renal vein in it. You may also find right suprarenal vein, aorta, left common iliac vein, right common iliac vein, left external iliac vein, median sacral ...
The ultrasound can assess fluid responsiveness as measure the maximal inferior vena cava diameter, inferior vena cava inspiratory collapse, and internal jugular aspect ratio. Amongst these three, the measurement of the maximal inferior vena cava diameter was found to be the best estimate of the central venous pressure with an inferior vena cava ...
Inferior vena cava diagram
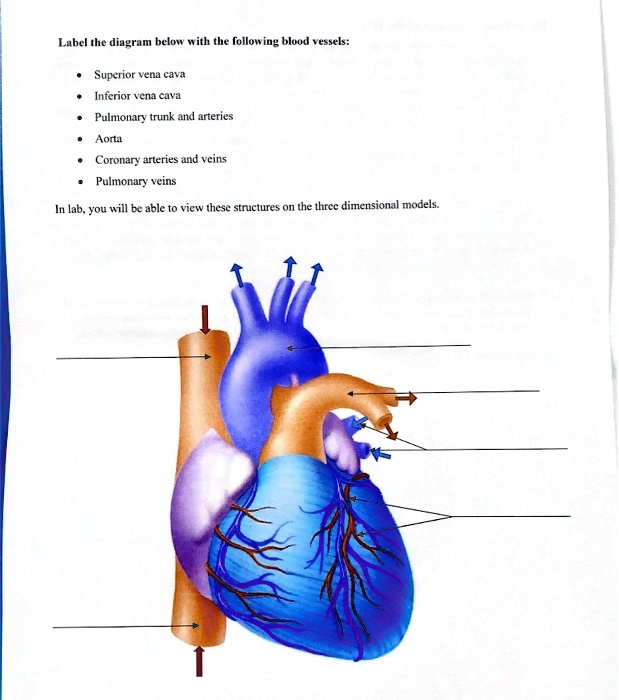
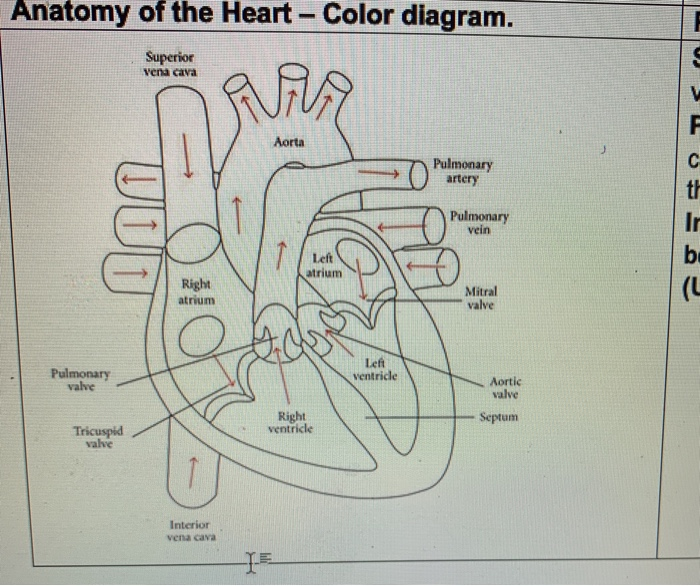
The inferior vena cava (IVC) (plural: inferior venae cavae) drains venous blood from the lower trunk, abdomen, pelvis and lower limbs to the right atrium of ...Missing: diagram | Must include: diagram Superior/Inferior Vena Cava. Now that we understand the blood flow to and from the heart, we can discuss the final structures. The first 2 structures are responsible for carrying deoxygenated blood from the body to the right side of the heart (right atrium). They are known as the superior vena cava and inferior vena cava. 15 Inferior Vena Cava Diagram. The inferior vena cava is the common convergence of venous drainage from all structures below the diaphragm. The inferior vena cava (ivc) drains venous blood from the lower trunk, abdomen, pelvis and lower limbs to the right atrium of the heart. In this image, you will find hepatic veins, inferior phrenic vein ...
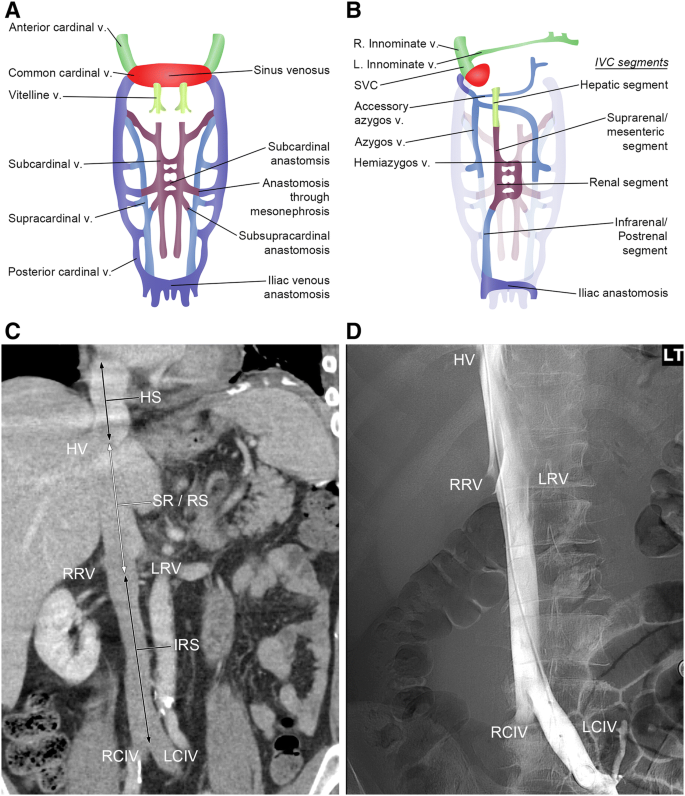
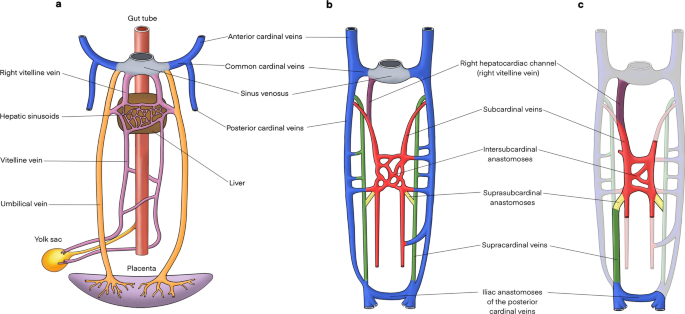
Inferior vena cava diagram. The inferior vena cava has a convoluted development during the 7-10 th weeks of gestation 4. posterior cardinal vein appears first but forms only the distal IVC i.e. iliac bifurcation. subcardinal veins (2) appear next, left subcardinal vein regresses, and right subcardinal vein forms the suprarenal IVC. Inferior Vena Cava- Takes deoxygenated blood from the kidney back to the heart. Renal Artery- Takes oxygenated blood from the Abdominal Aorta to the kidneys. Renal Vain- Takes deoxygenated blood from the kidney to the Inferior Vena Cava. Kidneys- Filter waste and water together into urine. Ureter- tubes that take the urine to the bladder. Vena Cava And Aorta Diagram. In this image, you will find phrenic artery, spleen, splenic artery, left renal artery, superior mesenteric artery, inferior mesenteric artery, left internal iliac artery in it. You may also find right external iliac artery, right common iliac artery, aorta, gonadal, right renal artery, common hepatic artery, left ... Inferior Vena Cava. The inferior vena cava is the largest vein in the human body. It collects blood from veins serving the tissues inferior to the heart and returns this blood to the right atrium of the heart. Although the vena cava is very large in diameter, its walls are incredibly thin due to the low pressure exerted by venous blood.
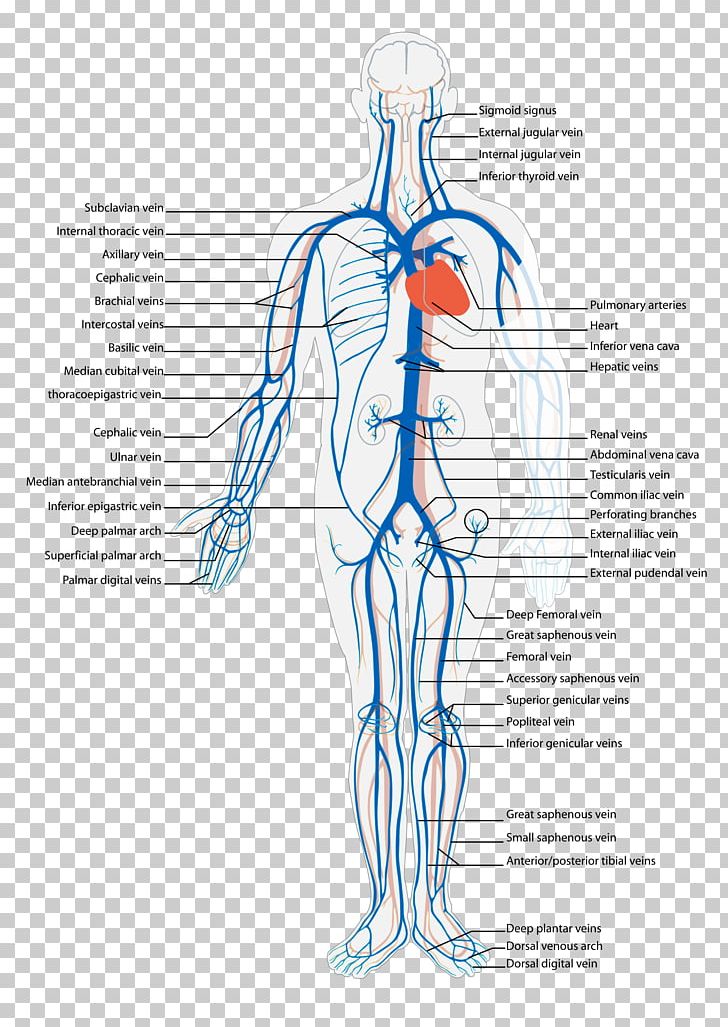
The inferior vena cava is formed by the joining of the common iliac veins which meet a little below the small of the back. The inferior vena cava travels along the spine, parallel to the aorta, and transports blood from the lower extremities of the body to the posterior region of the right atrium. The inferior vena cava (also known as IVC or the posterior vena cava) is a large vein that carries blood from the torso and lower body to the right side of the heart. From there the blood is pumped to the lungs to get oxygen before going to the left side of the heart to be pumped back out to the body. The IVC gets its name from its structure ... The inferior vena cava is the headmaster of the veins department. It collects all the blood from the abdomen, pelvis and lower limbs and carries it to the right atrium of the heart.. The IVC is formed by merging of the left and right common iliac veins at the L5 vertebral level, just in front of the aortic bifurcation.. The inferior vena cava then ascends to the right of the abdominal aorta ... by WD Tucker · 2020 · Cited by 4 — The inferior vena cava (IVC) is a large retroperitoneal vessel formed by the confluence of the right and left common iliac veins.Missing: diagram | Must include: diagram
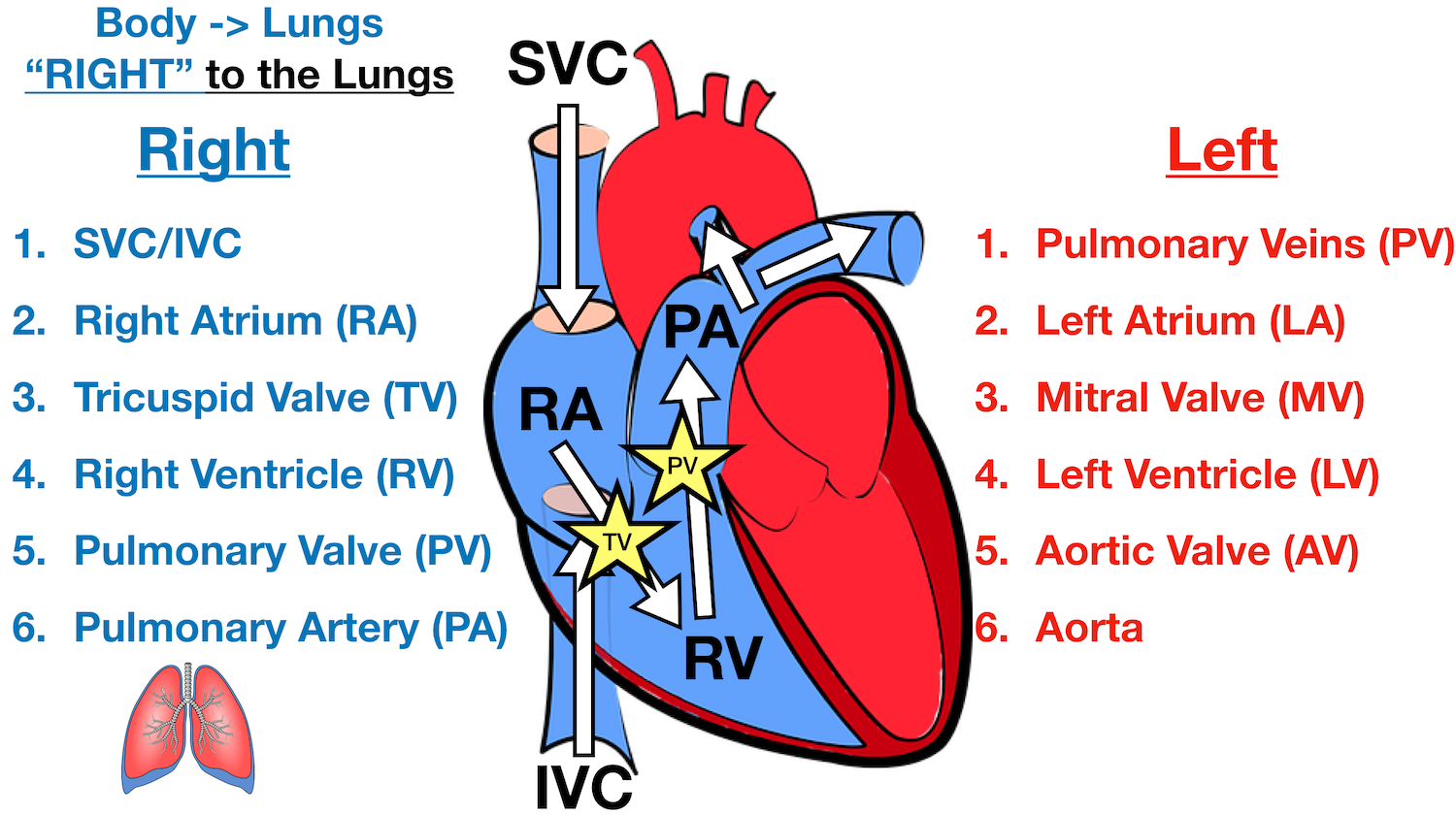
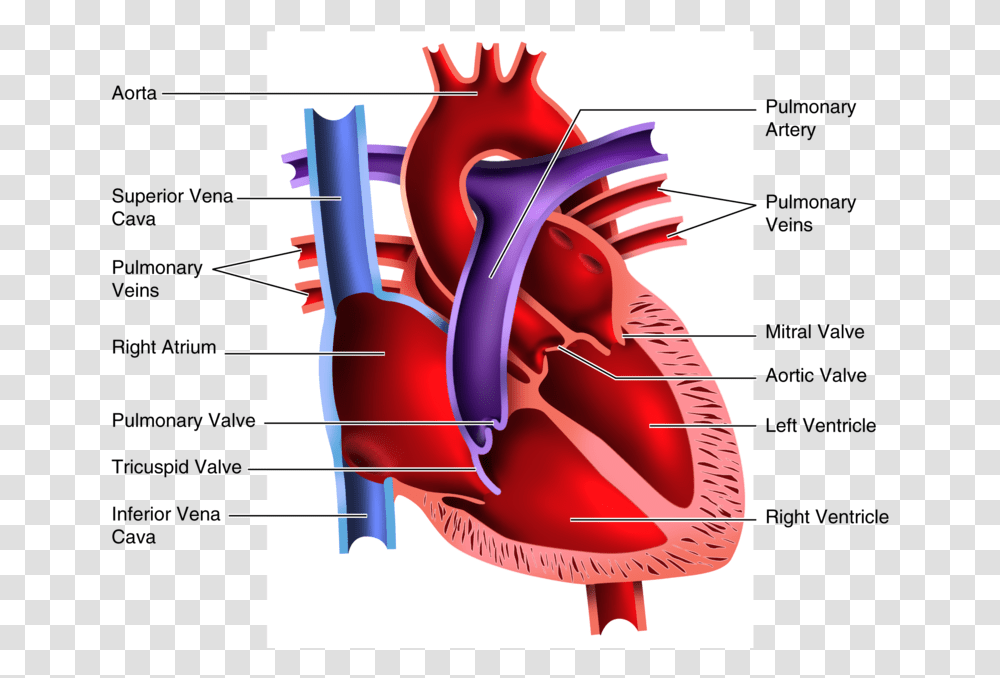
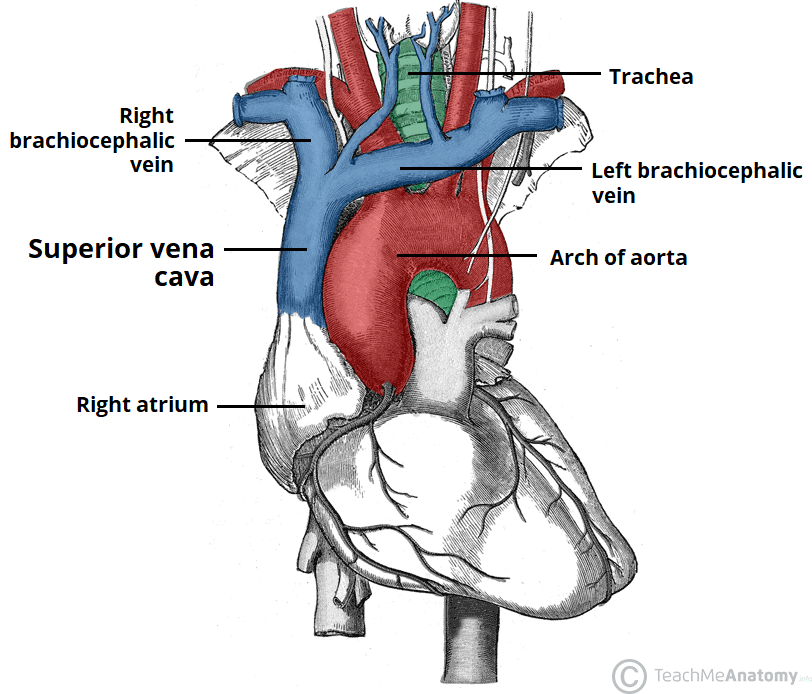
Superior Vena Cava & Inferior Vena Cava. The vena cava is the largest vein in the body that delivers oxygen-poor or deoxygenated blood to the right atrium of the heart. The superior vena cava comes from the upper part of the body, including the brain and arms, while the inferior vena cava comes from the abdominal area and legs. 3. Superior Vena Caval 4. Inferior Vena Caval: Variations of ASD. Atrial Septal Defects are divided into three different types on the basis of the position of the hole (or holes) in the atrial septum. The first type of ASD is known as ostium primum defect, or simply, primum (number 1 in the diagram). Locate the inferior vena cava and superior vena cava. 7. Use the scalpel to open the heart chambers: make an incision along the coronal plane, from the superior portion of the left ventricle to the superior portion of the right ventricle. Inferior Vena Cava Superior Vena Cava Posterior View Vena Cava = Singular Vena Cavae = Plural NOTICE the ... The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart.It is formed by the joining of the right and the left common iliac veins, usually at the level of the fifth lumbar vertebra.. The inferior vena cava is the lower ("inferior") of the two venae cavae, the two large veins that carry deoxygenated blood from ...
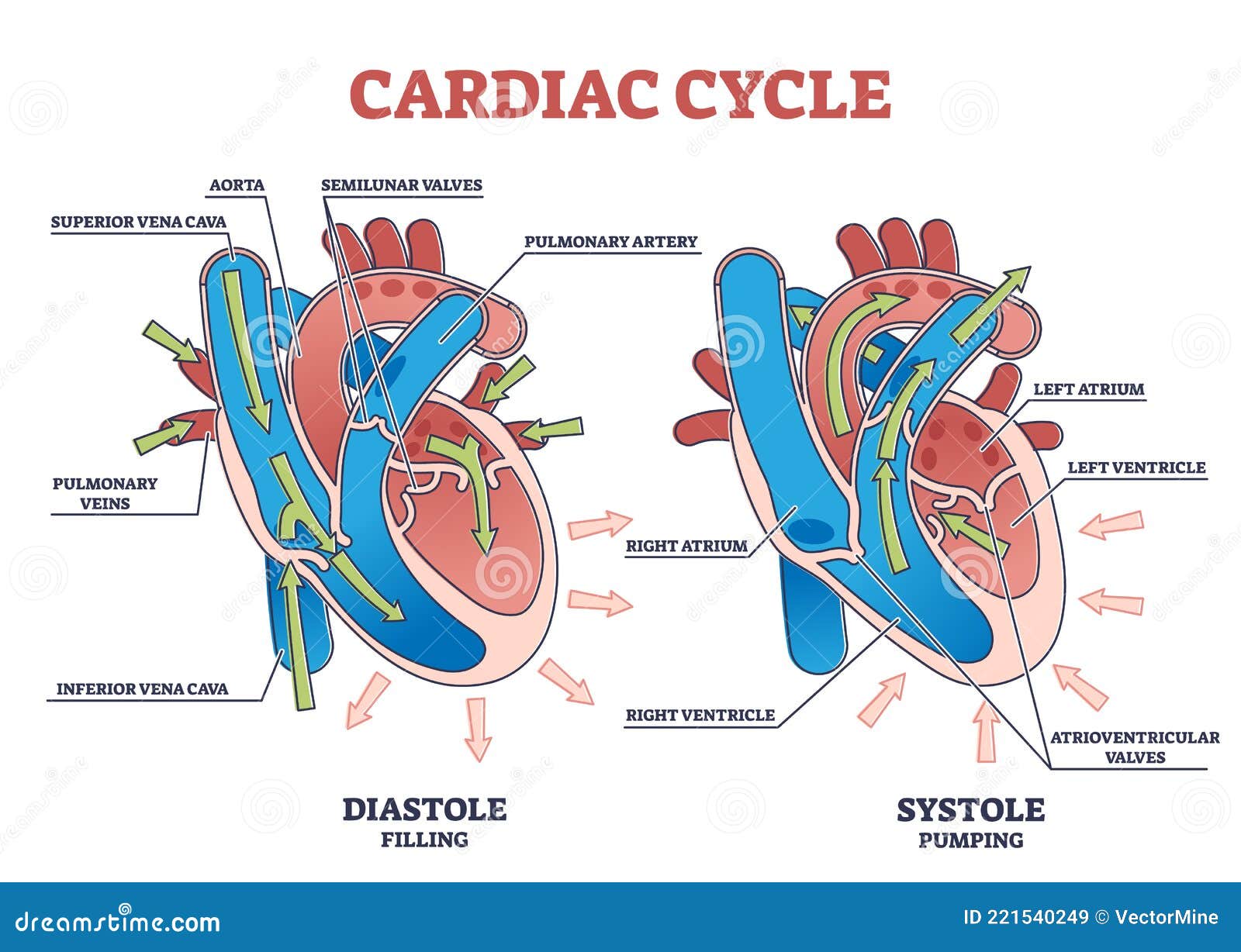
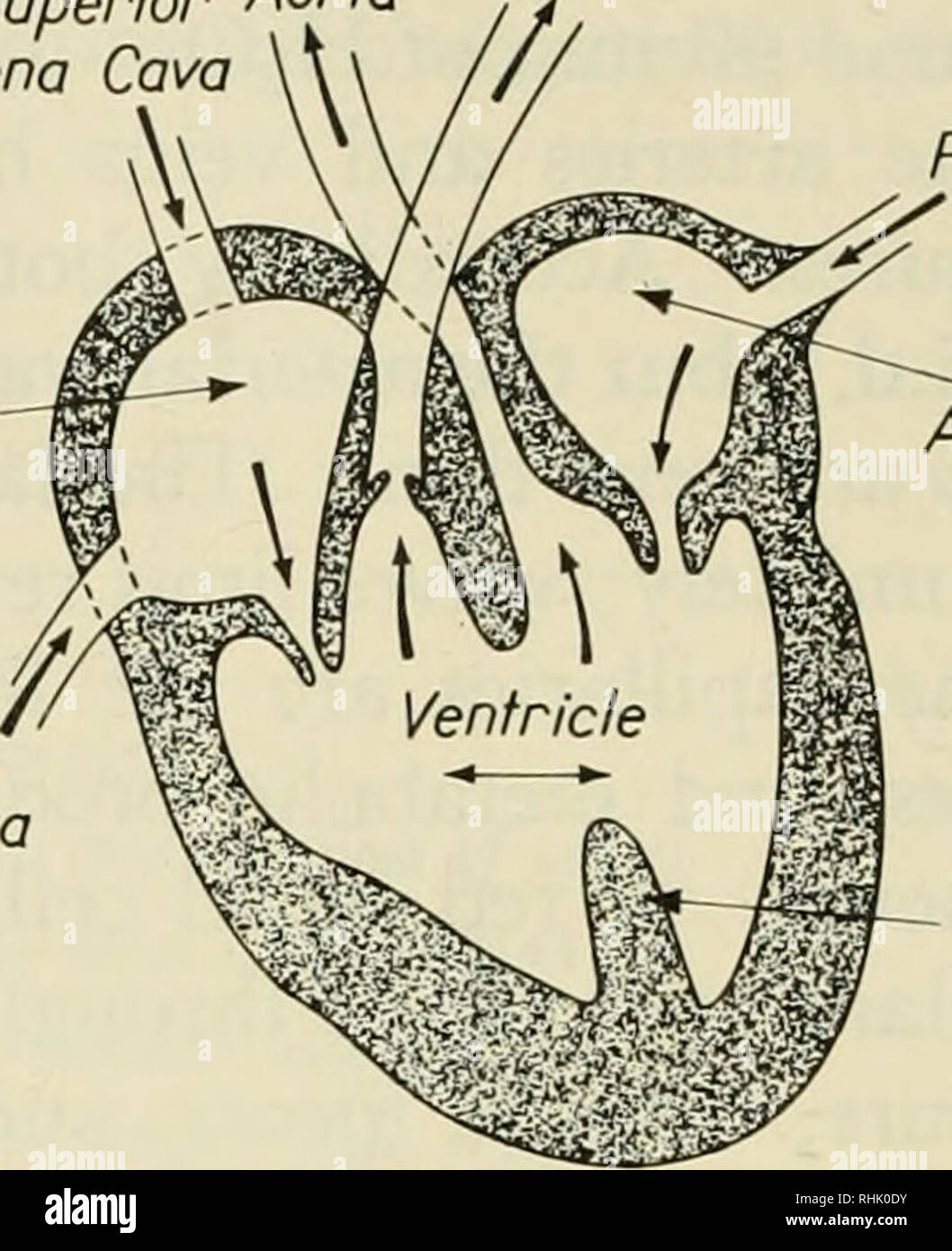
The pathway of blood flow through the heart begins as blood comes from the body and enters the heart through the superior and inferior vena cava indicated by the yellow star in the diagram below. Superior and inferior vena cavae and the coronary sinus 2. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood through the superior and inferior vena cavas ...
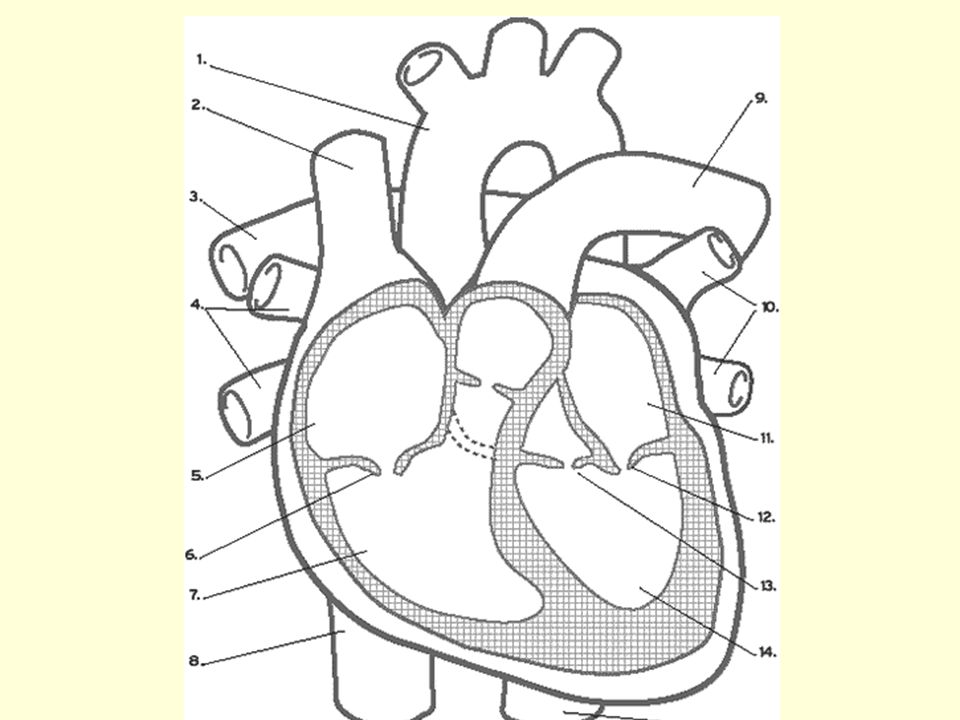
superior vena cava. inferior vena cava. right coronary artery. left coronary artery. posterior interventricular artery. anterior interventricular artery. circumflex artery. right marginal artery. small cardiac vein.
aorta; superior vena cava; inferior vena cava; pulmonary trunk; pulmonary veins ... match the structures and border of the heart with the letter indicator in the diagram. a-right border, b- sternal angle, c- sternum, d- left border, e- inferior border. openings of _____ are visible in the left atrium.
Overview of the inferior vena cava. The IVC is formed by the union of the right and left common iliac veins.It conveys systemic venous blood from the lower limbs and pelvis, the undersurface of the diaphragm and parts of the abdominal wall.The IVC does not drain blood from the gut.. Course of the IVC. The IVC begins in the abdomen at L5 and ends in the thorax at T8, where it enters the ...
The inferior vena cava is a large, valveless, venous trunk that receives blood from the legs, the back, and the walls and contents of the abdomen and pelvis ...
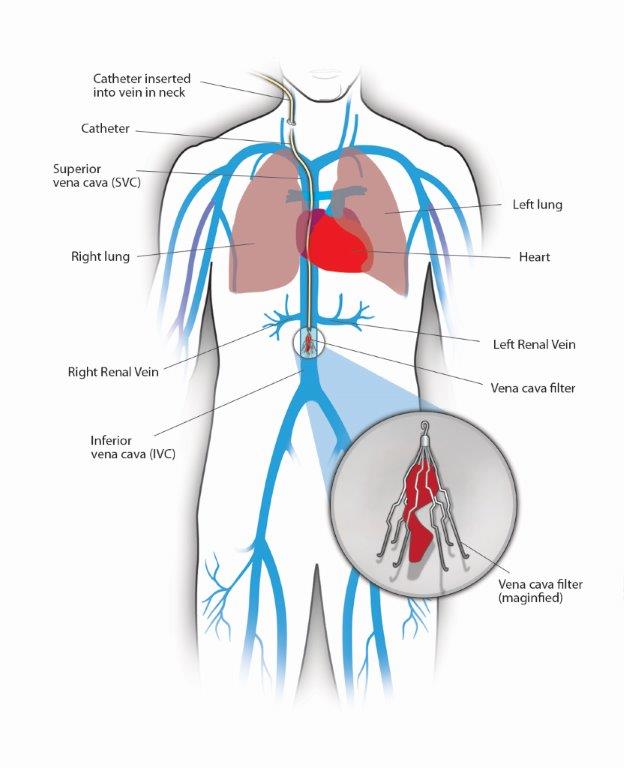
An inferior vena cava (IVC) filter is a small device that can stop blood clots from going up into the lungs. The inferior vena cava is a large vein in the middle of your body. The device is put in during a short surgery. Veins are the blood vessels that bring oxygen-poor blood and waste products back to the heart.
Inferior Vena Cava. The IVC, a single right-sided vessel in 97% of individuals, returns blood from all structures below the diaphragm to the right atrium of the heart. It is formed by the confluence of the two common iliac veins at the level of the fifth lumbar vertebra just to the right of midline.
Step 1 involves the superior vena cava (SVC) and inferior vena cava (IVC). They are the main blood vessels that carry the deoxygenated venous blood from the rest of the body to the right side of the heart, specifically the right atrium. The superior vena cava is located superiorly, and it carries the deoxygenated venous blood from the upper ...
The inferior vena cava (IVC) is the largest vein of the human body. It is located at the posterior abdominal wall on the right side of the aorta. The IVC’s function is to carry the venous blood from the lower limbs and abdominopelvic region to the heart.. The inferior vena cava anatomy is essential due to the vein’s great drainage area, which also makes it a hot topic for anatomy exams.
The inferior vena cava is also referred to as the posterior vena cava. The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries de-oxygenated blood from the lower body to the heart.
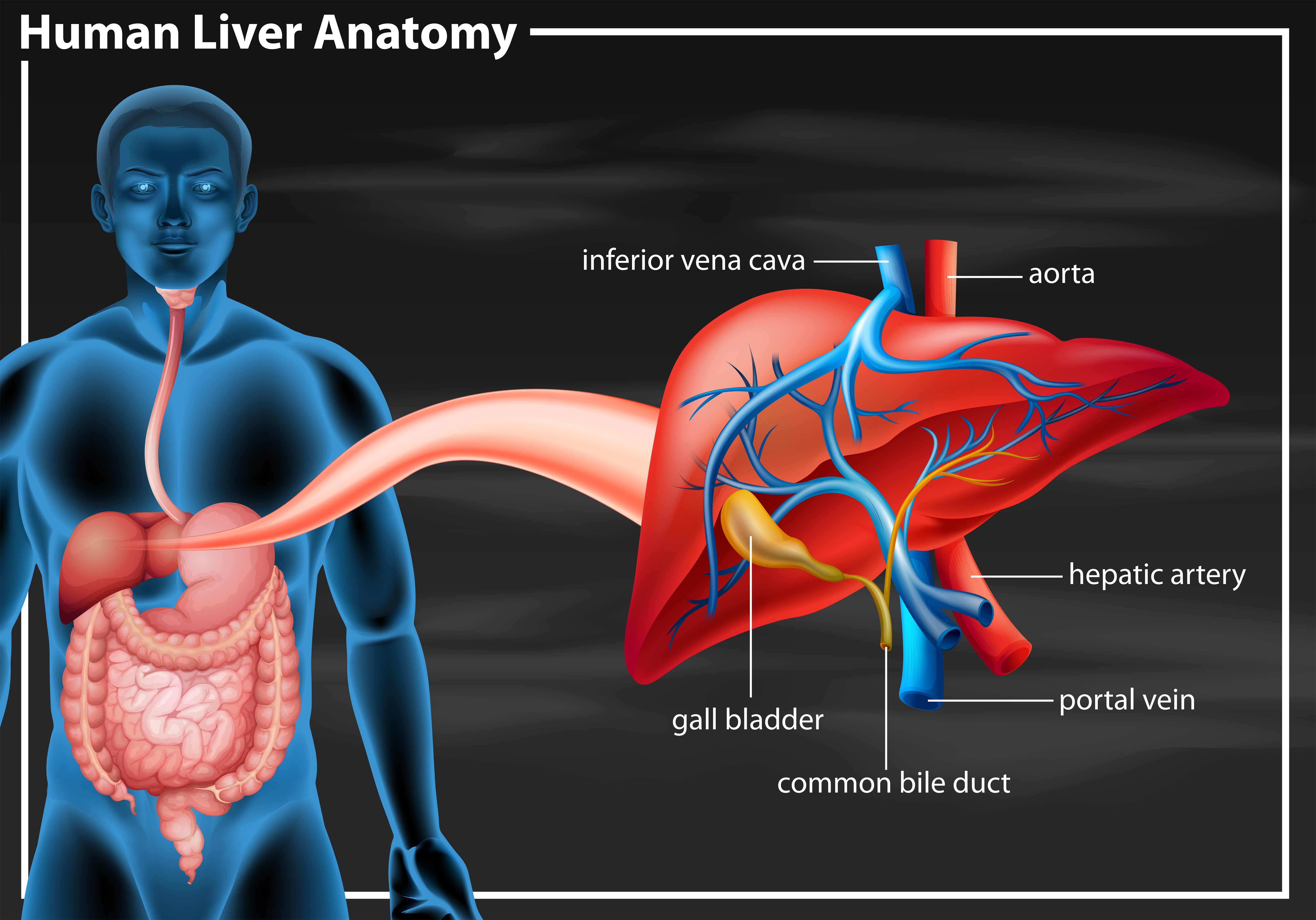
The hepatic veins carry oxygen-depleted blood from the liver to the inferior vena cava. They also transport blood that has been drained from the colon, pancreas, small intestine, and the stomach ...
3. The inferior vena cava carries blood from the lower part of the body to the right atrium. The hepatic vein drains the liver and enters the inferior vena cava near the diaphragm. 4. Renal veins drain the kidneys. 5. Genital veins lead from the gonads and enter the inferior vena cava. 6. The iliac and femoral veins drain the legs. 7.
The inferior vena cava runs along the vertebral bodies in the spine, and is formed by the joining of two leg veins in the lower body which fuse together in the vertebrae to form the inferior vena cava and continue up to the heart. These leg veins are called the iliac veins; the two branches join together and meet to form the inferior vena cava.
6 Inferior Vena Cava. The great vessels of the heart function to carry blood to and from the heart as it pumps, located largely within the middle mediastinum. In this article we will consider the structure and anatomical relationships of the aorta, pulmonary arteries and veins, and the superior and inferior vena cavae.
15 Inferior Vena Cava Diagram. The inferior vena cava is the common convergence of venous drainage from all structures below the diaphragm. The inferior vena cava (ivc) drains venous blood from the lower trunk, abdomen, pelvis and lower limbs to the right atrium of the heart. In this image, you will find hepatic veins, inferior phrenic vein ...
Superior/Inferior Vena Cava. Now that we understand the blood flow to and from the heart, we can discuss the final structures. The first 2 structures are responsible for carrying deoxygenated blood from the body to the right side of the heart (right atrium). They are known as the superior vena cava and inferior vena cava.
The inferior vena cava (IVC) (plural: inferior venae cavae) drains venous blood from the lower trunk, abdomen, pelvis and lower limbs to the right atrium of ...Missing: diagram | Must include: diagram























0 Response to "40 inferior vena cava diagram"
Post a Comment