38 molecular orbital diagram for ne2 2+
Molecular Orbital Diagram Of N2, N2 Ions And Li2 Molecule. ... ne2, etc). one is for the elements up to nitrogen. the pi(2p) bonding orbitals are lower than the sigma(2p) bonding orbitals. n2(2 ) has a bonding order of 2, which predicts that ... Draw the molecular orbital (MO) electron diagram for the Ne2 molecule. Be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in the molecule, including any core electrons. Energy ; Question: O STRUCTURE AND BONDING Drawing the MO energy diagram for a Period 2 homodiat... Draw the molecular orbital (MO) electron diagram for the Ne2 molecule.
Dec 28, 2018 · Even rather simple molecular orbital (MO) theory can be used to predict from the bottom of the diagram because this is how MO diagrams are constructed, from N2, O2, F2, Ne2 the complexity of the molecular orbitals develop in two ways. Page 1. MO Diagrams for Elements Li2 through Ne2. (Don't memorize.) Li2 through N2. O2 through Ne2.

Molecular orbital diagram for ne2 2+
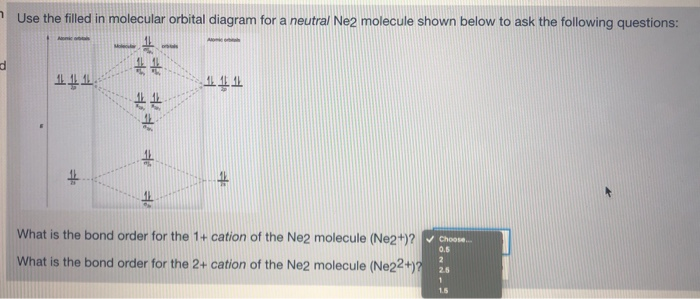
A) O2^2-B) Ne2^2+ C) O2^2+ D) F2^2+ E) None of the above are paramagnetic; 3) Draw the molecular orbital diagram needed, and determine which of the following is paramagnetic. A) B2^2+ B) B2^2-C) N2^2+ D) C2^2-E) B2; 4) Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories: Valence Bond Theory and Molecular… For Ne2, construct three molecular orbital diagrams, one each for the neutral molecule, the +1 cation, and the -1 anion. Give each MO an appropriate label. Determine the electron configuration and bond order for each, and rank the three species in order of increasing bond order. Rationalize the trend in bond order in terms of bond strength.
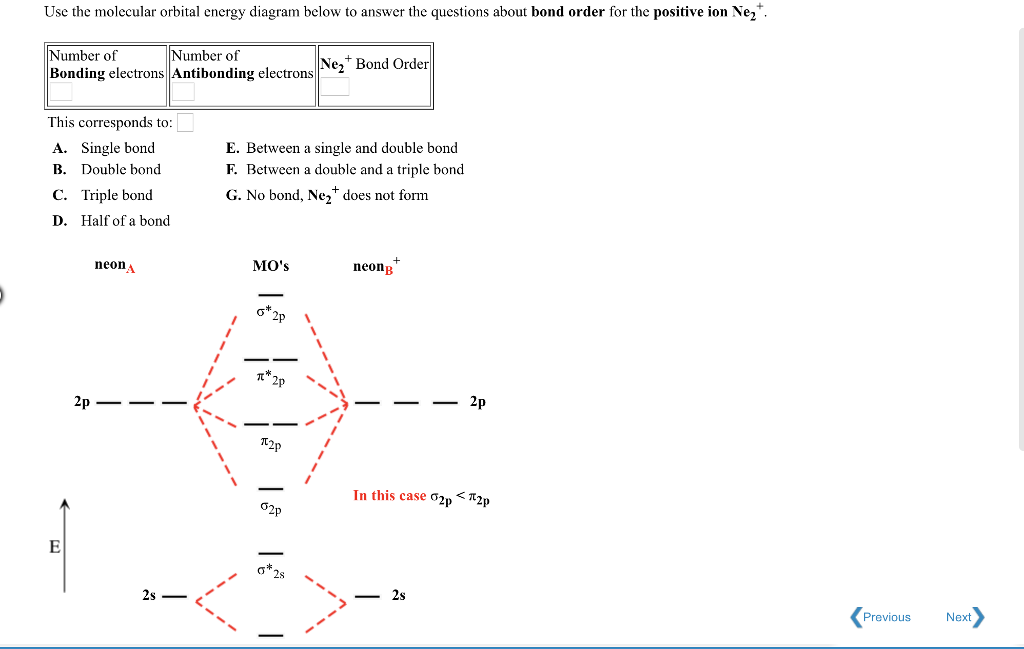
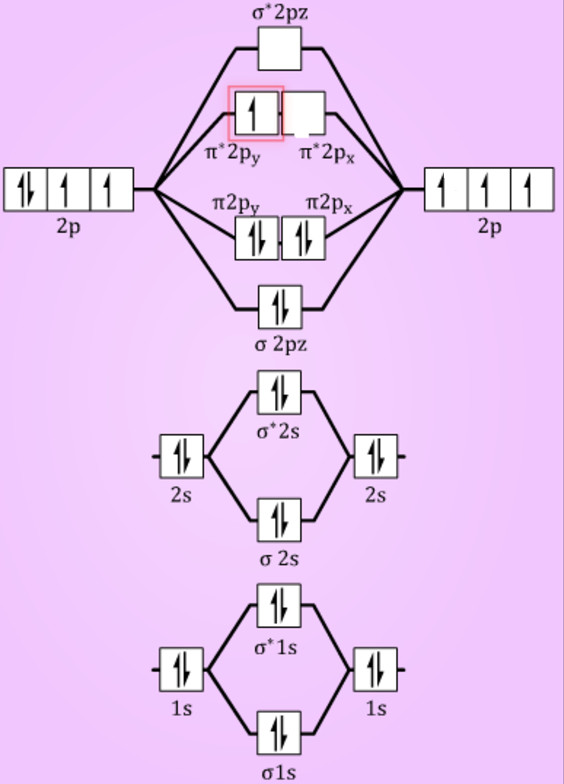
Molecular orbital diagram for ne2 2+. To form the 2+ ion, the uppermost electrons in the sigma* 2p orbital are removed, making it isoelectronic with F2, so it has a bond order of 1 and should be ... LCAO MO Energy Diagram for H2 Energy H-H ∆E1 ∆E2 • ∆E2> ∆E1, so the antibonding orbital is always more anti-bonding than the bonding orbital is bonding H2molecule: two 1s atomic orbitals combine to make one bonding and one antibonding molecular orbital. Ha Hb A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single Energy Level Diagrams He2 has bond order 0 [ (2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+. According to the molecular orbital theory, in a supposed He2 molecule, both the if we draw its MOT DIAGRAM, 2 e's enter the Bonding molecular Orbital and 2 . From Molecular Orbital Diagram, which is most stable? A. F2 2-B. Ne2 2+ C. O2 2+ D. F2 E. F2 2+ C. O2 2+ Choose the compound below that should have the highest melting point according to the ionic bonding model. A. CaS B. NaCl C. RbI D. MgO E. AlN. E. AlN.
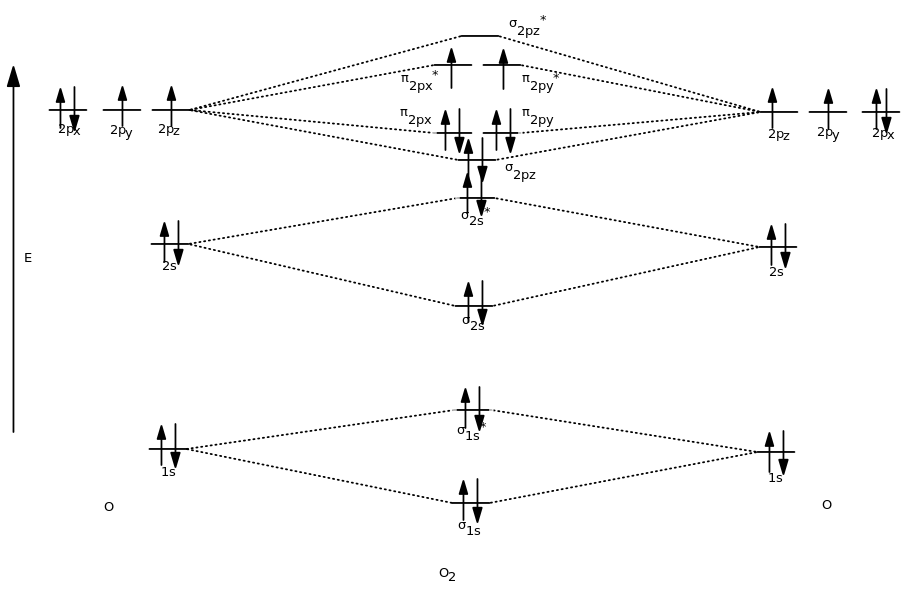
This picture shows the molecular orbital diagram of N 2 − . Orbitals represented by ∗ are antibonding orbitals and the orbitals without ∗ are bonding orbitals. Bond order can be calculated by the formula: Bond order = bonding electrons - antibonding electrons 2 As it can be seen from the MOT of O 2 , The electrons in the highest occupied molecular orbital are unpaired therefore it is paramagnetic in nature. Also, the bond order can be calculated as [N b − N a ] / 2 = [1 0 − 6] / 2 = 2. Therefore there is a double bond present as O = O. Explain your answer here in addition to providing the bond order values. We are asked to determine the bond order from the molecular orbital diagram of Ne2 and to check whether the calculated bond order agrees with the Lewis structure of Ne2. Part A. Draw the Lewis Structure of Ne2. Part B. Determine the bond order from the molecular orbital ... The lowest energy unoccupied molecular orbital is 2pσ, so that is where the extra electron will be added. The electron configuration of the neutral C2 molecule is -- I'll use the notation given to you in the diagram. C2:(1sσ)2(1s* σ)2(2sσ)2(2s* σ)2(2pπ)4. The electron configuration of the C− 2 ion will be.
0:21 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Oxygen Molecule3:30 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Florine Molecule5:25 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Neon MoleculeSo as we d... Answer (1 of 2): First let me make it clear that Ne, which is Neon, is a noble gas. Noble gases rarely form compounds and they don't exist as molecules in their pure form. So, Neon, as a gas, exists as only Ne and not as Ne2 (Oxygen, Hydrogen, Nitrogen are some of the many gases that exist as mol... Answer to For Ne2, construct three molecular orbital diagrams, one each for the neutral molecule, the +1 cation, and the -1 anion. Find an answer to your question Draw and explain the molecular orbital diagram of Ne2. On the basis of molecular orbital diagram, explain.Molecular orbital (MO) diagram for N2 and N2^-up vote 16 down vote favorite. 2. The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
the pi(2p) bonding orbitals are LOWER than the sigma(2p) bonding orbitals.N2(2-) has a bonding order of 2, which predicts that there will be a stable double ...
There are two MO diagrams you need to memorize for diatoms (N2, O2, Ne2, etc).One is for the elements up to Nitrogen. The other is for AFTER nitrogen (start...
A molecular orbital can hold two electrons, so both electrons in the H 2 molecule are in the [latex]\sigma[/latex] 1s bonding orbital; the electron configuration is [latex]{\left({\sigma}_{1s}\right)}^{2}.[/latex] We represent this configuration by a molecular orbital energy diagram (Figure 7.7.10) in which a single upward arrow indicates one ...
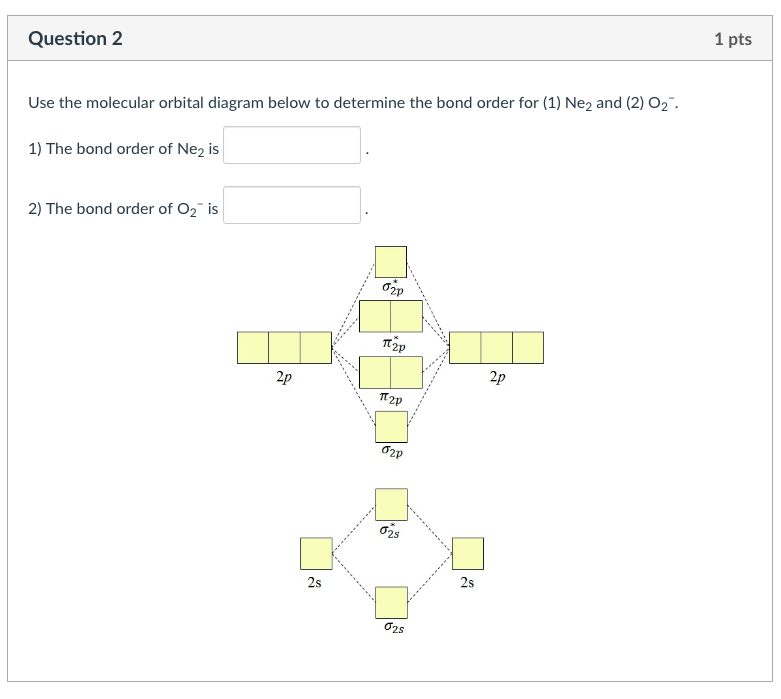
Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Question 2 1 pts Use the molecular orbital diagram below to determine the bond order for (1) Ne2 and (2) 02 1) The bond order of Ne2 is 2) The bond order of O2 is 2p 2p t2p 2p 2s 2s 2s 2s.
So here we're looking at the molecular orbital theory to describe bonding. So the first example, we have a C. Two plus, we've got 11 electrons and we can ...
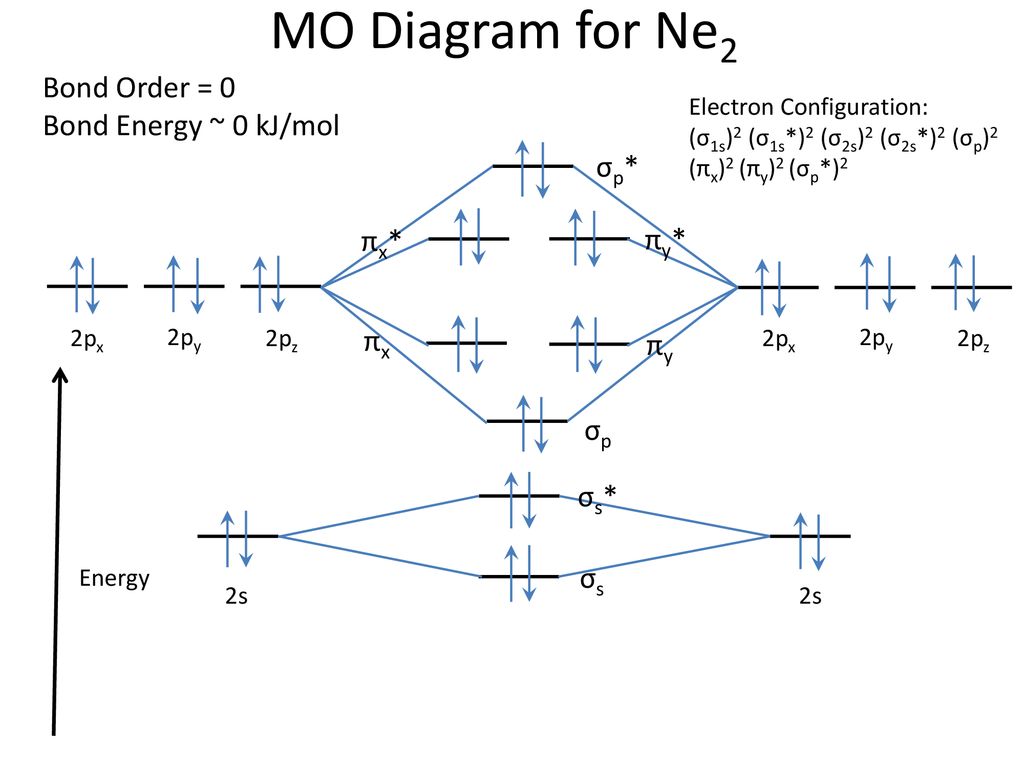
Use the molecular orbital energy level diagram to show that N2 would be expected to have a triple bond, F2 , a single bond and Ne2 , no bond. Hard Open in App Solution Verified by Toppr Formation of N2 molecule: Electronic Configuration, σ1s2<σ∗1s2<σ2s2<σ∗2s2<[π2px2 =π2px2 ]<<σ2pz2 Bond order = (Nb −Na )/2=(10−4)/2=3
Molecular Orbital Diagram of O 2 Chapter 9 Section 6 When filling the MO levels, you have to: Count the number of valence electrons, Start with the lower energy orbitals first, Follow Hund's rule, and Pt t th t Dr. A. Al-Saadi 19 Put not more than two electrons in one MO. Molecular Orbital Diagram of N 2 Chapter 9 Section 6
Molecular orbital diagram of N 2 BO = [Nb-Na] = [10-4] = 3 Since all the electrons in nitrogen are paired, it is diamagnetic molecule. Answered by | 13th Jun, 2016, 04:45: PM. Concept Videos. Molecular Orbital Theory - Part 1.
According to Molecular Orbital theory, only those molecule can exists which have net positive bond order while the molecules with negative or. Answer to For Ne2, construct three molecular orbital diagrams, one each for the neutral molecule, the +1 cation, and the -1 anion. © Prof Adam J Bridgeman | close window.
A) F2; B) F2^2+ C) Ne2^2+ D) O2^2+ E) F2^2-2) Use molecular orbital diagrams to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. A) O2^2-B) Ne2^2+ C) O2^2+ D) F2^2+ E) None of the above are paramagnetic; 3) Draw the molecular orbital diagram needed, and determine which of the following is paramagnetic. 10 5 molecular orbital theory chemistry libretexts.
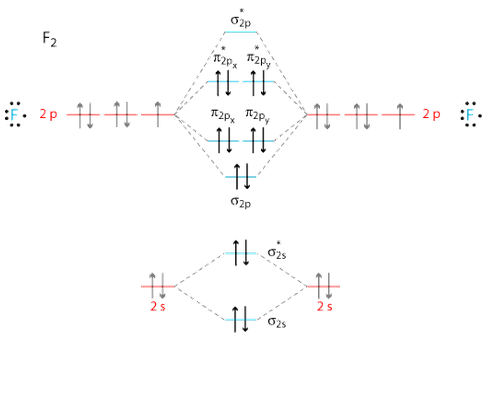
Determine the bond order from the molecular orbital diagram of N 2, F 2, and Ne 2. Does the bond order calculated agree with what you would draw for the Lewis structures of these molecules? Explain your answer here in addition to providing the bond order values. Learn this topic by watching MO Theory: Bond Order Concept Videos.
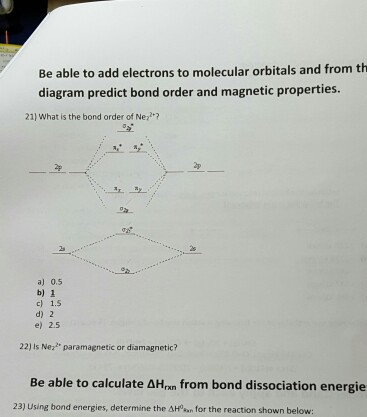
what is the bond order of Ne2 2+. i know its 1 but I do not know how to use this diagram. can someone explain this? Show transcribed image text. Expert Answer.
for each of the following molecules f2no ne2 a draw a molecular orbital diagram b determine the bond order of the molecule c is the molecule diamagnetic or paramagnetic d how stable do you think the m
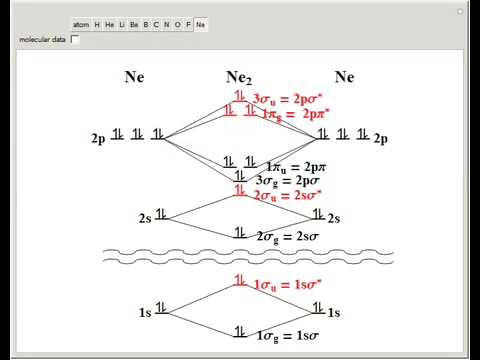
Ne2 (20) = σ1s2 σ*1s2, σ2s2 σ*2s2, σpx2. π 2py2 2π* 2py2π*2py2 2pz2 σ*. 2px2. B.O = 1/2 (10 - 10) = 0. Ne2 cannot exist because its bond ...
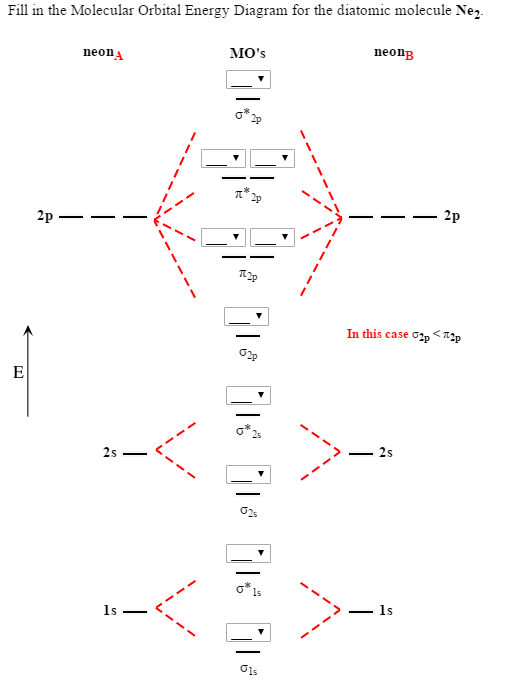
Molecular orbital diagram ne2.If ne 2 did form, it would be diamagnetic. Once you have the molecular orbitals and their energy ordering the ground state configuration is found by applying the pauli principle, the what is the molecular orbital diagram for the diatomic neon molecule, ne2?
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ...
Mar 17, 2019 · Even rather simple molecular orbital (MO) theory can be used to predict from the bottom of the diagram because this is how MO diagrams are constructed, from N2, O2, F2, Ne2 the complexity of the molecular orbitals develop in two ways.Draw the molecular orbital diagram for Ne 2 + and determine if the bond between the two atoms will be stable.
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
Question: Is Ne2 2+ paramagnetic or diamagnetic? To understand this answer you have to know about molecular orbital (MO) theory of bonding. You can learn about it and its application to 2nd row elements here: The Central Science, Chapter 9, Section 8. Within that document is this diagram:
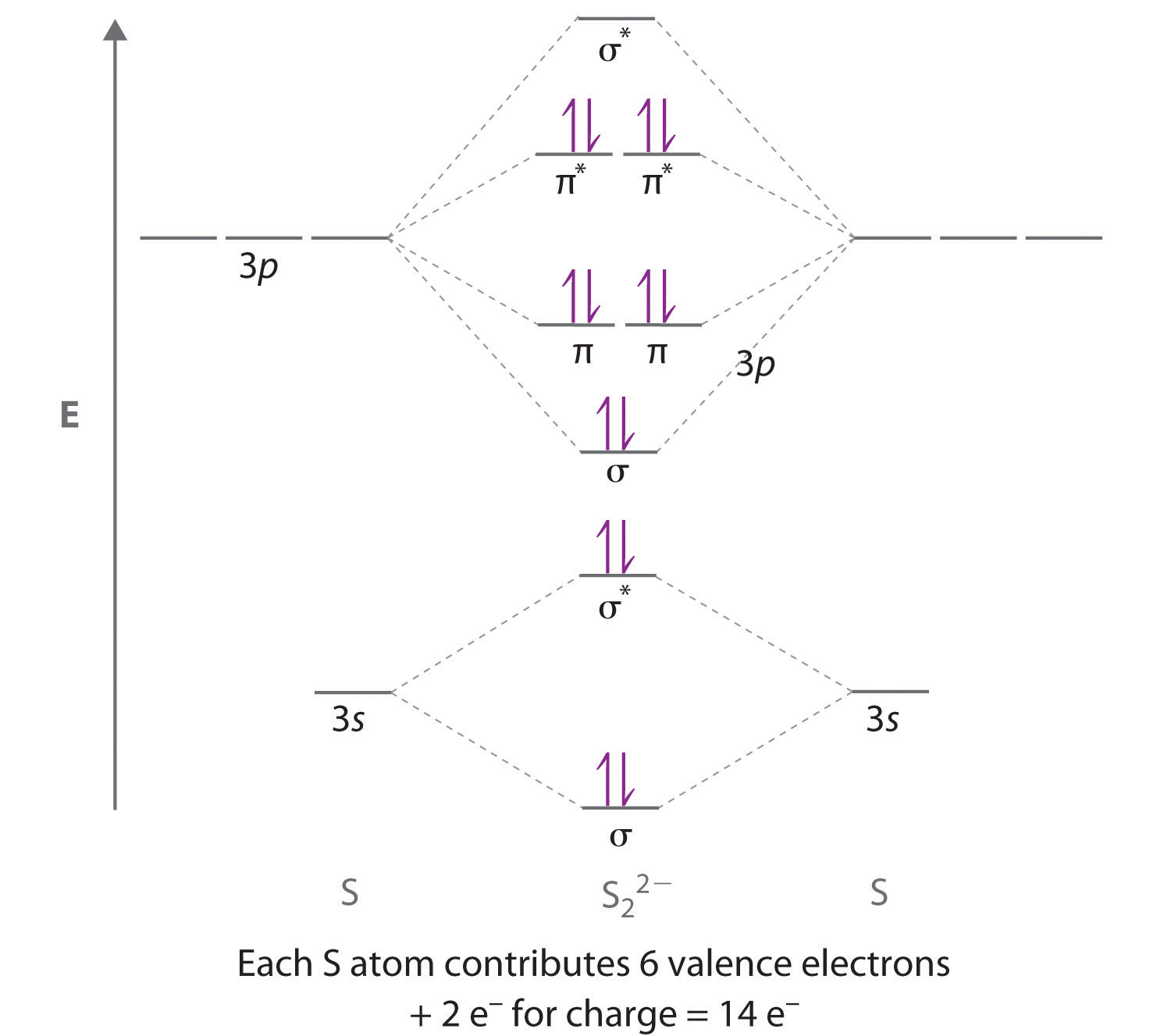
Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals. Then we rank them in order of increasing energy. We can ignore the 1s orbitals, because they do not contain the valence electrons. Each boron atom has one 2s and three 2p valence orbitals. The 2s orbitals will overlap to form 2sσ and 2sσ ...
For Ne2, construct three molecular orbital diagrams, one each for the neutral molecule, the +1 cation, and the -1 anion. Give each MO an appropriate label. Determine the electron configuration and bond order for each, and rank the three species in order of increasing bond order. Rationalize the trend in bond order in terms of bond strength.
Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories: Valence Bond Theory and Molecular…
A) O2^2-B) Ne2^2+ C) O2^2+ D) F2^2+ E) None of the above are paramagnetic; 3) Draw the molecular orbital diagram needed, and determine which of the following is paramagnetic. A) B2^2+ B) B2^2-C) N2^2+ D) C2^2-E) B2; 4) Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable.

![Expert Answer] Draw the molecular orbital diagram for F2 and ...](https://hi-static.z-dn.net/files/dae/d7baa23a1d4a2ea2c90e0a703e2fd41d.jpg)







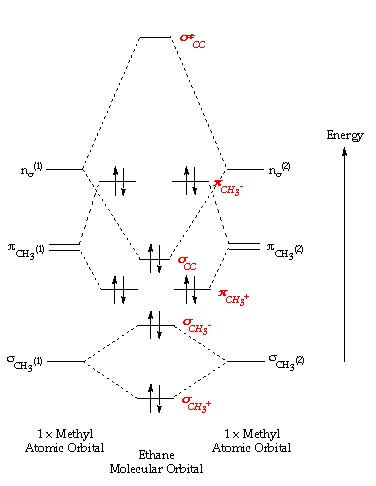

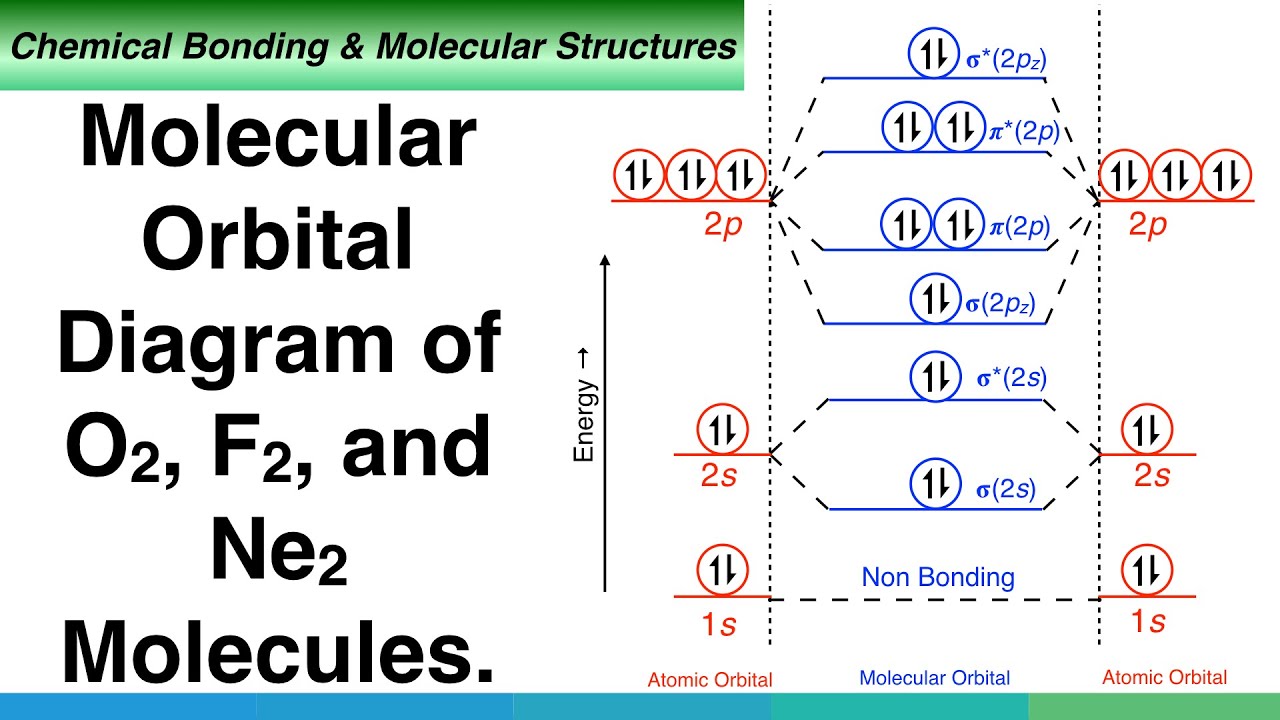

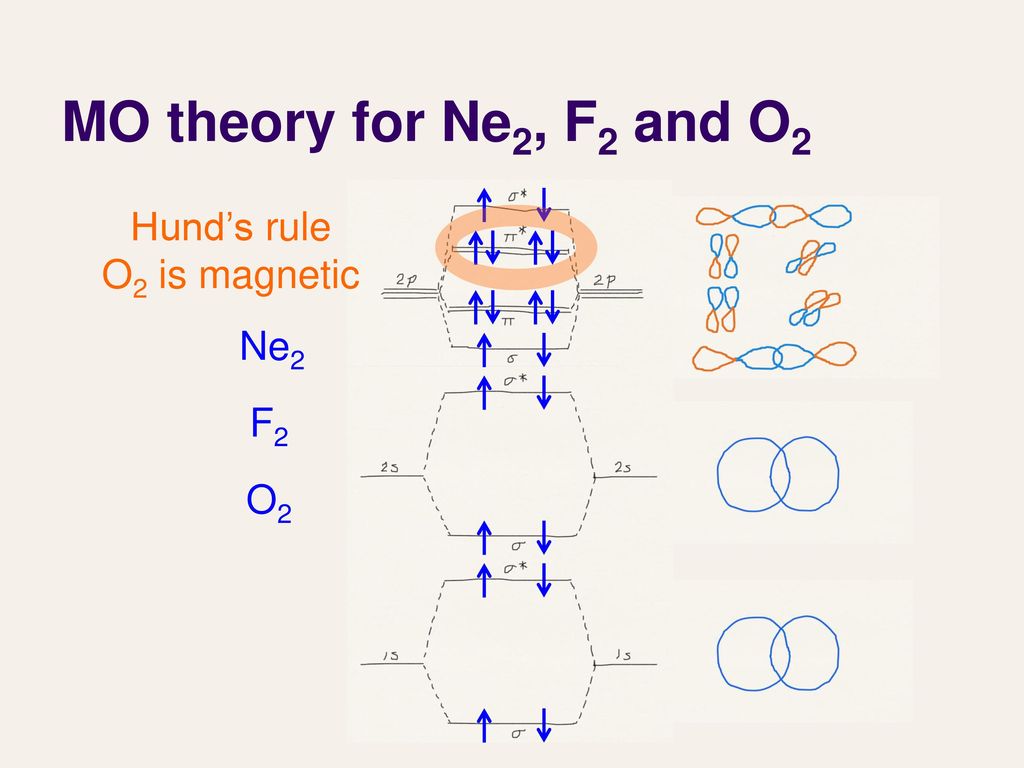
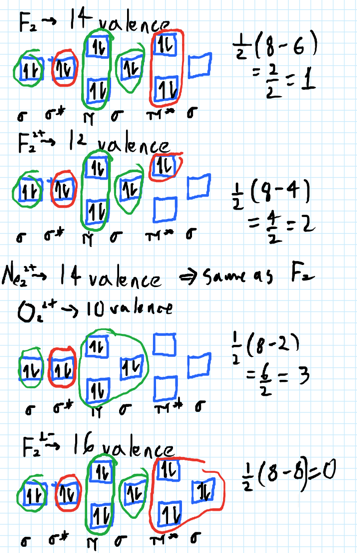
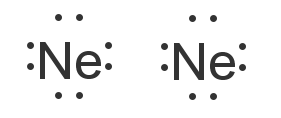

0 Response to "38 molecular orbital diagram for ne2 2+"
Post a Comment