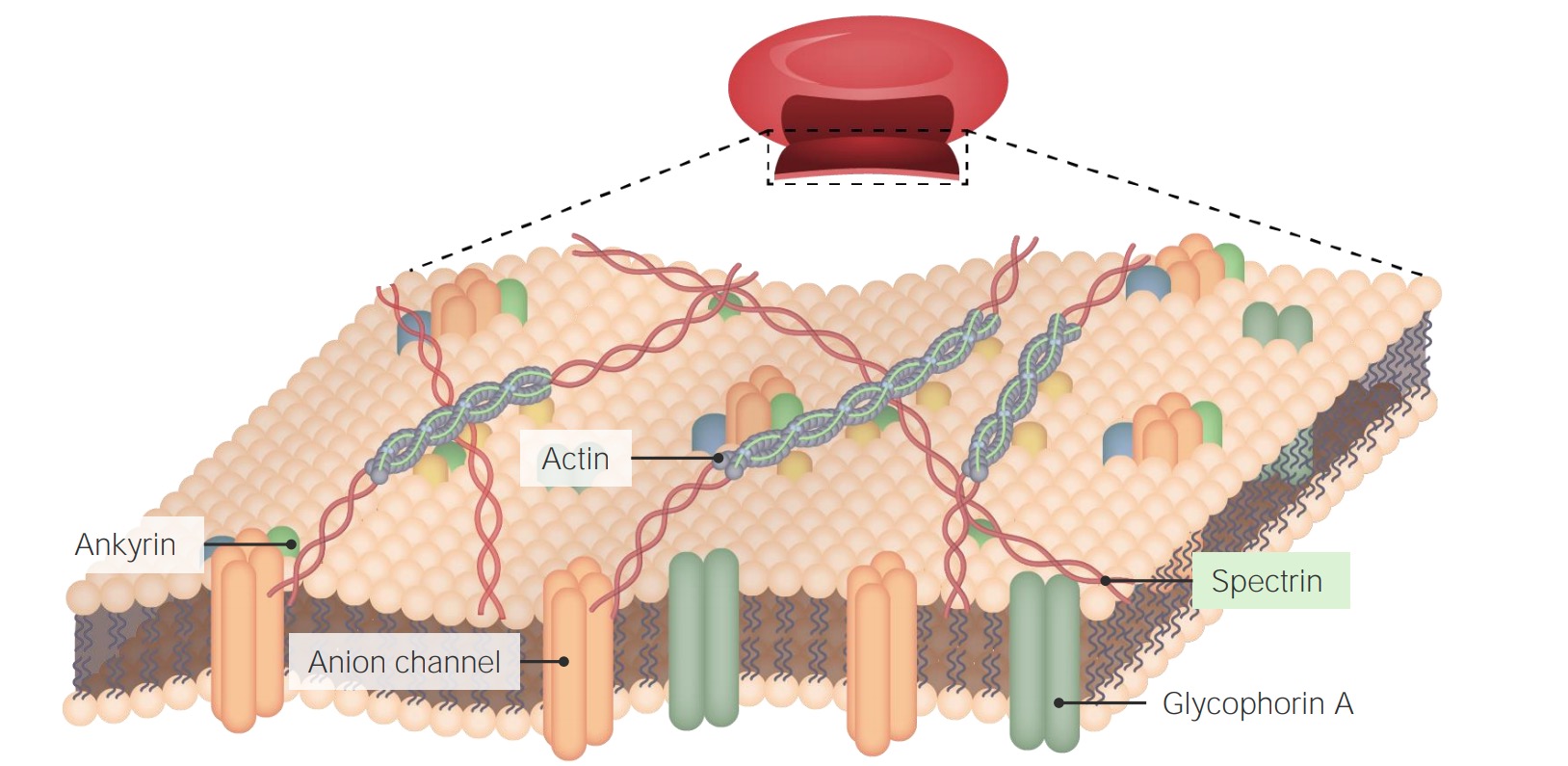
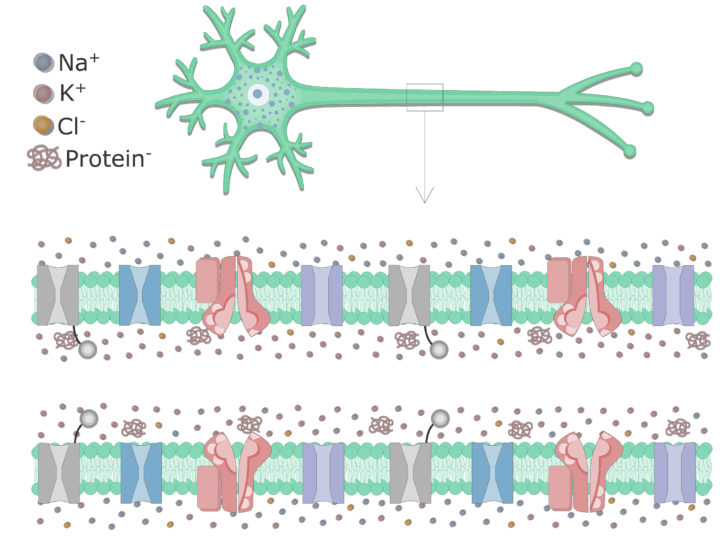
39 diagram of the cell membrane of the axon
Axons - Physiopedia Original Editor - Lucinda hampton. Top Contributors - Lucinda hampton and Kim Jackson. Axons are the elongated portion of the neurone located in the centre of the cell between the soma and axon terminals. Each neuron in your brain has an axon that snakes away from the main part of the cell. Cell Membrane Function and Structure The cell membrane is a thin, semi-permeable barrier that surrounds and encloses the contents of a cell. It protects the integrity of the cell along with supporting the cell and helping to maintain the cell's shape. Proteins and lipids are the major components of the cell membrane.
Axon - Wikipedia An axon (from Greek ἄξων áxōn, axis), or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences), is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action potentials away from the nerve cell body.
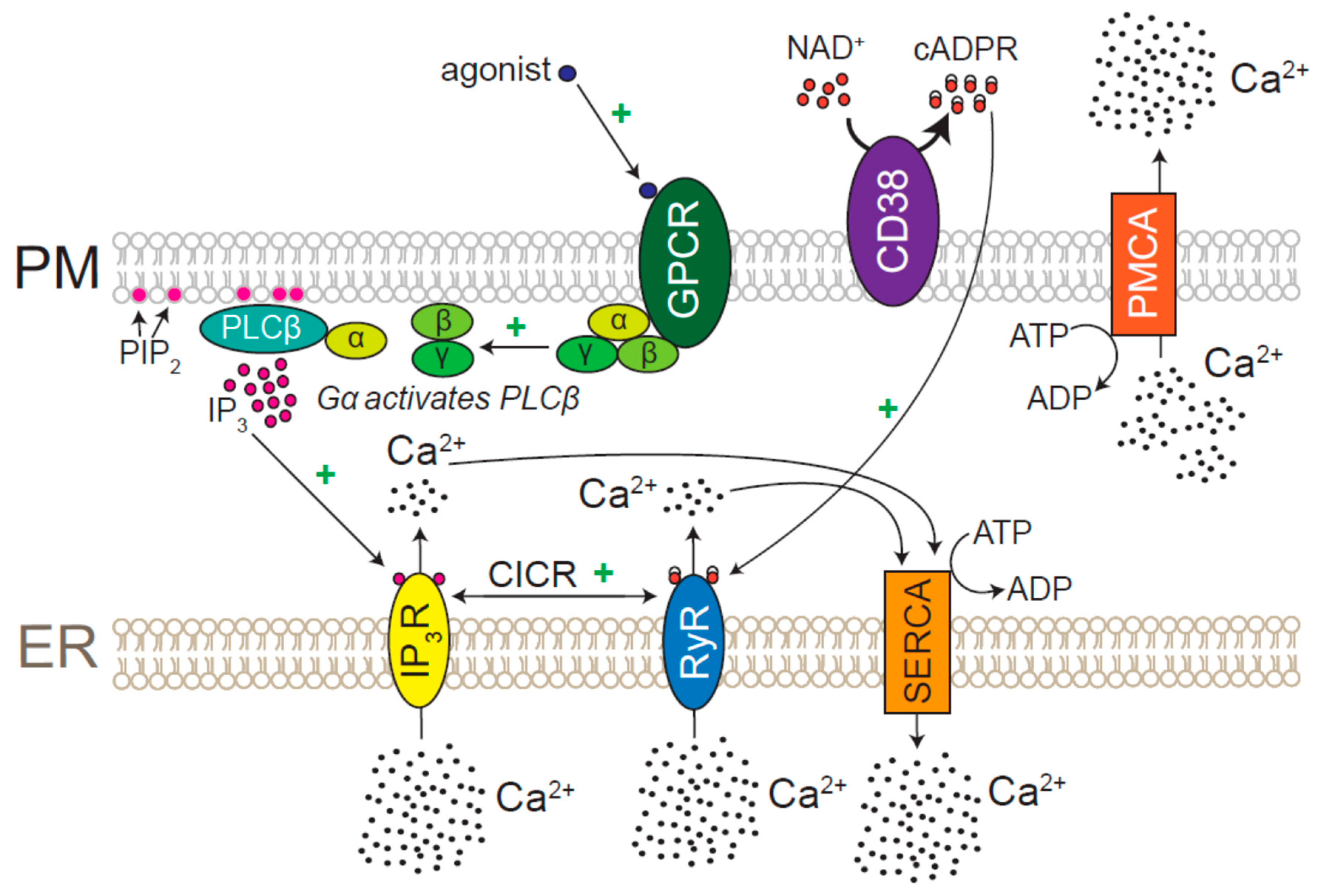
Diagram of the cell membrane of the axon
Axon Terminal - The Definitive Guide | Biology Dictionary The axon terminal, also known as the synaptic/ terminal bouton, is the most distal portion of a neuron's axon and is critical for neural communication. When action potentials reach the axon terminal, calcium floods the neuron, allowing synaptic vesicles to fuse with the membrane and release stored... Axon - Structure and Functions - GetBodySmart Sep 22, 2017 · Axon – Structure and Functions. All neurons have a cytoplasmic process called an axon (nerve fiber), which conducts electrochemical impulses or action potentials. Axons most commonly attach to one side a neuron cell body (soma, perikaryon), at a cone-shaped region called the axon hillock. Electrochemical events in the cell body summate in the ... Structure of Cell - Membrane, Cytoplasm, and Organelles - Earth's Lab All the living things are made up ofcells The human body is made up of about 75 trillion cells, the tiniest living systems that exist. Body cells can be categorized into about 300 types, such as...
Diagram of the cell membrane of the axon. Cell Structure | The Cell Surface Membrane The RER consists of interconnected membranous sacs (cisternae) - unit membrane enclosing a fluid-filled lumen. The function of the RER is the synthesis, storage and transport of proteins around the cell. The proteins are manufactured by the ribosomes, 10 nm diameter particles that stud the outside... What is an intuitive way of explaining how myelin speeds up... - Quora Signal propagation along the membrane of myelinated axons is achieved via long jumps of the action potential. Action potentials are generated only in The passive diffusion of membrane depolarization triggers other action potentials in either adjacent cell membrane in nonmyelinated nerve fibers or... Action potential - Wikipedia In physiology, an action potential (AP) occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls: this depolarization then causes adjacent locations to similarly depolarize. Action potentials occur in several types of animal cells, called excitable cells, which include neurons, muscle cells, endocrine cells and in some plant cells. Modeling of the axon membrane skeleton structure and implications... To determine the possible implication of the differing actin cytoskeleton structure, we determined the stiffness of the plasma membrane of neuronal subcompartments using atomic force microscopy (AFM). We found that axons are almost ~6 fold stiffer than the soma and ~2 fold stiffer than dendrites.
Histology, Axon - PubMed The cell membrane of Schwann cells is arranged around the axon, forming a double membrane structure (mesaxon), which elongates and wraps itself in a spiral, in concentric layers, around the axon itself. a) Axon hillock - The part of the axon which remains attached to the... Parts of a Neuron Diagram. Although they have a characteristic elongated shape, they vary widely Besides the three major parts, there is the presence of axon terminal and synapse at the end of the The cell body is also the largest part of a neuron enclosed by a cell membrane that protects the cell... Functions of the Cell Membrane - TeachMePhysiology Cell membranes are an essential component of the cell, providing separation between the intracellular and extracellular environment. An example of this specialisation can be seen in the different parts of a nerve; the cell membrane in the axon is specialised for electrical conduction whereas the end of... Cell Membranes | Function, Structure, Model, Facts & Notes The structure of the cell membrane is described by the fluid mosaic model, a universally accepted model of the plasma membrane. They are mostly seen in the membranes of nerve cells. The hydrophobic chains of such lipids have an even number of fatty acids.
The Axon Initial Segment: An Updated Viewpoint | Journal of... At the base of axons sits a unique compartment called the axon initial segment (AIS). The AIS generates and shapes the action potential before it is propagated along the axon. Neuronal excitability thus depends crucially on the AIS composition and position, and these adapt to developmental and... Dendrite - Wikipedia The cell membrane of neurons covers the axons, cell body, dendrites, etc. The protein channels can differ between chemical species in the amount of required activation voltage and the activation duration. Action potentials in animal cells are generated by either sodium-gated or calcium-gated ion channels in the plasma membrane. These channels ... Developmental mechanism of the periodic membrane skeleton in axons The brain contains hundred types of neurons, but they are all variations on the same basic structure. Each neuron consists of a cell body that is covered in short protrusions called dendrites and a long thin structure called the axon. The dendrites receive incoming signals from neighboring neurons and they... Electrical properties of cell membranes - Scholarpedia The fundamental unit of all biological life is the cell, a mass of biomolecules in watery solution surrounded by a cell membrane. One of the characteristic features of a living cell is that it controls the exchange of electrically charged ions across the cell membrane and therefore the electrical potential...
The Hodgkin-Huxley Model - McGill University membrane potential is close to the potassium equilibrium value during rest, but rose to zero during activity. Bernstein reasoned that the activity caused the membrane to degrade, but this was proved incorrect in 1938. During the year of 1938, Hodgkin collaborated with Cole to directly measure the membrane voltage [9].
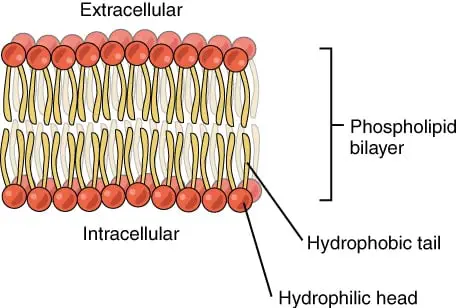
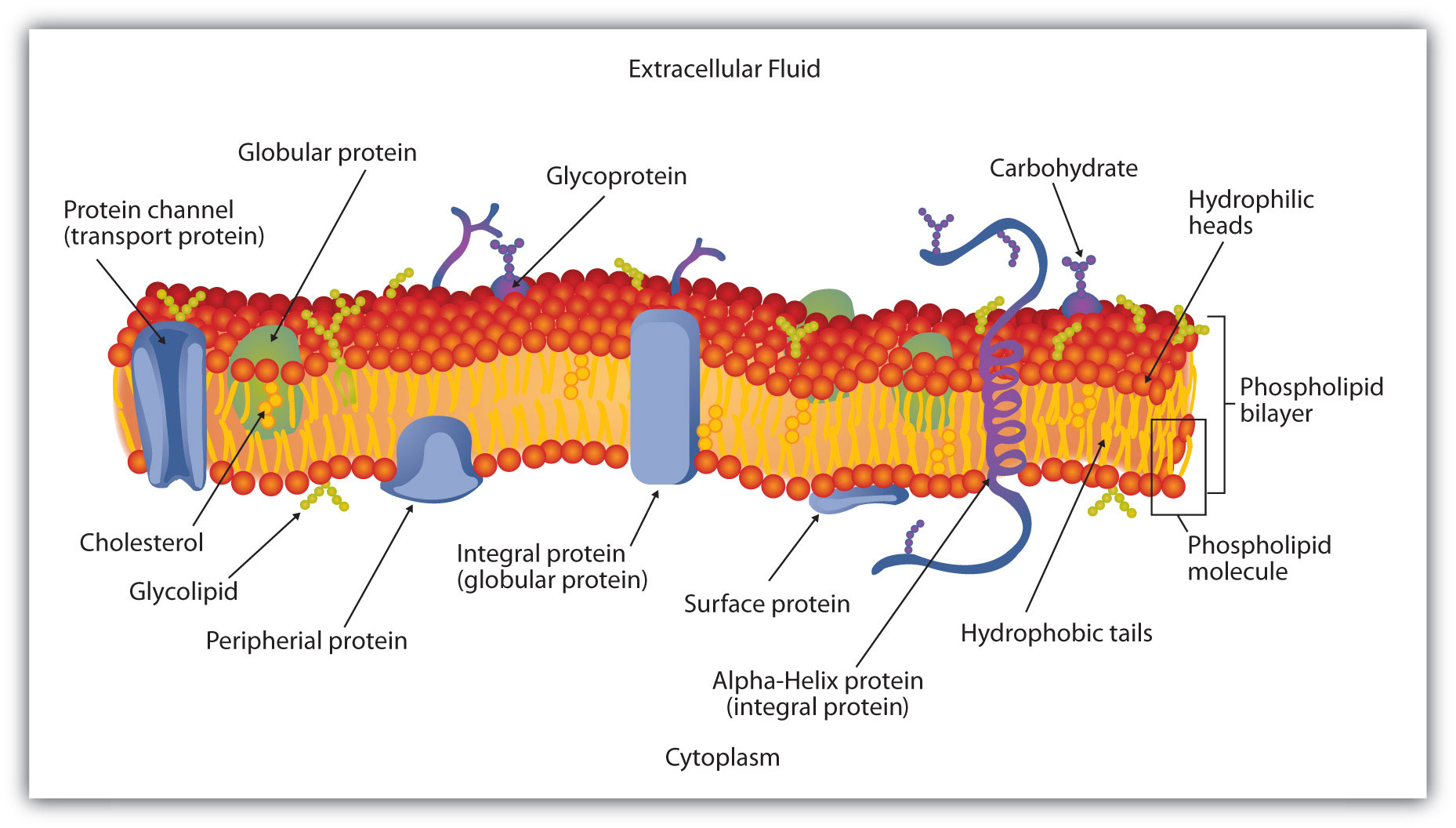
Figure: Diagram of Cell (Plasma) Membrane The plasma membrane, also known as the cell surface membrane or plasmalemma, defines the boundary of the cell. It is a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that encloses every living cell. It regulates the movement of materials into and out of the cell and facilitates electrical signaling...
Axon Structure And Function - Nerve Cell - MCAT Content Topic: Nerve Cell. Axon is a tube-like structure that carries neural signals away from the cell body via the axon terminals. The cell body contains the axon hillock that collects signals from many synapses. The axon hillock serves as a junction between the cell body and an axon. The axon then delivers these collected signals to specialized ...
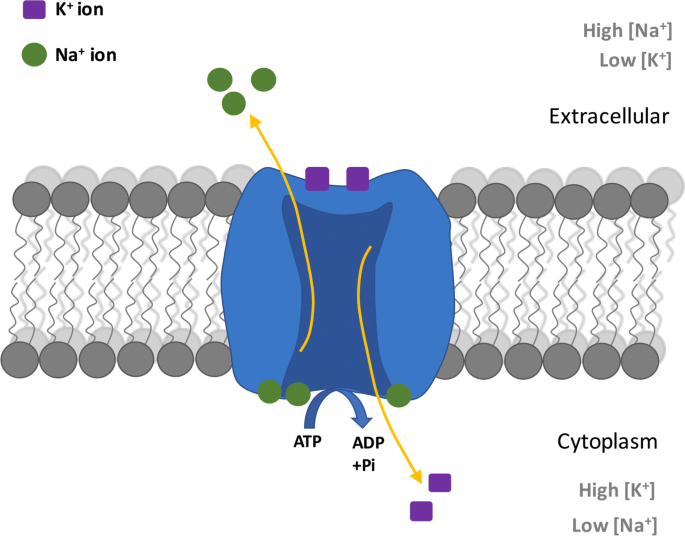
Neuron Diagram, Structure & Function | What Is a Neuron ... Feb 07, 2022 · In the axon diagram shown below, ... The cell membrane of the neuron creates a charge imbalance across the membrane by pumping sodium ions out of the cell, and potassium ions into the cell. Every ...
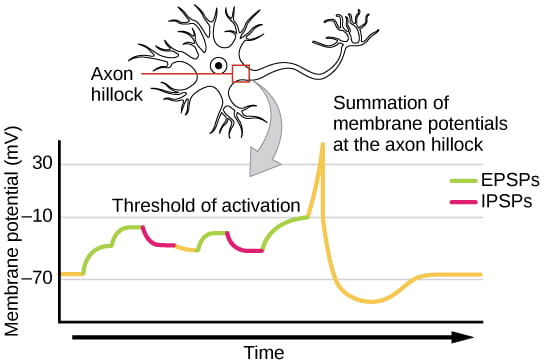
Action potential - Definition, Steps, Phases | Kenhub After reviewing the roles of ions, we can now define the threshold potential more precisely as the value of the membrane potential at which the voltage-gated sodium channels open. An action potential propagates along the cell membrane of an axon until it reaches the terminal button.
Neuroscience/Cellular Neurobiology/Cells of the Brain - Wikibooks... The cellular basis for the nervous system lies in two classes of cells, neurons and glia. Neuronal cells function as the information processing and transfer cells, while glial cells are generally considered support cells (though this is not a rigid statement.)
Structure of the Cell Membrane | Biology for Majors I A cell's plasma membrane defines the cell, outlines its borders, and determines the nature of its interaction with its environment. For example, myelin, an outgrowth of specialized cells' membrane that insulates the peripheral nerves' axons, contains only 18 percent protein and 76 percent lipid.
Structure and Function of Axons and Dendrites - WikiLectures The axon is the long projection of a nerve that can reach a length of tenths of centimeters, that conveys electrical impulses from the dendrites/soma of the neuron to the next neuron. They have a high variability of branching pattern and extent (characteristic for individual neuronal types)...
What Is an Axon Membrane? (with pictures) - Info Bloom Mar 11, 2022 · The structure and chemical properties of the axon membrane is what enables it to contain an electrical charge, to force its flow in one direction, and to transfer the signal to other cells of the body. For the most part, for most types of nerve cells, the axon is insulated within a protective sheath called myelin.
Axon Initial Segment Cytoskeleton: Architecture, Development, and... The functional and morphological polarity of neurons depend on the asymmetric distribution of specific molecules to the axonal and somatodendritic domains. The establishment of molecular asymmetry between these domains is fundamental to axon specification during early neuron development.
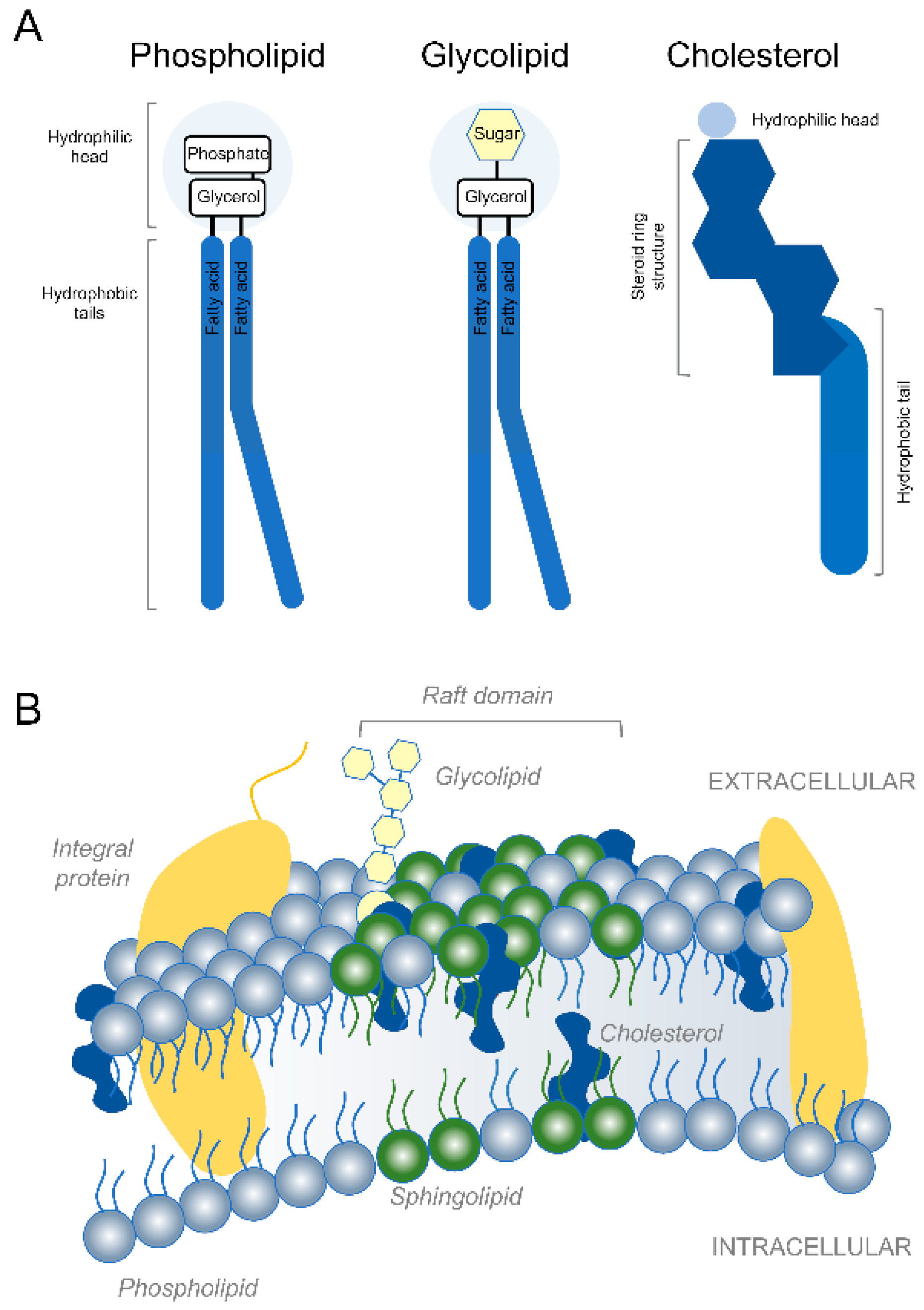
Fluid Mosaic Model of the Cell Membrane A cell membrane is the thin, fragile and outermost barrier that separates the internal contents of a cell from the external. For the majority of cells, the cell membrane consists of three main components. These include glycerol, two fatty acid chains as well as a phosphate group.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Crayfish Giant Axon Preparation The giant axon is the largest of 8-10 third-order giant axons arising in the stellate ganglion that innervate the circular muscles of the mantle, contractions of which underlie the rapid jet propulsion mode of squid swimming behavior ( Fig. 1 A ). Each giant axon originates from the fusion of many...
Frontiers | Axonal Membranes and Their Domains: Assembly and... Here, we review the intricate organization of axonal membrane domains that facilitate rapid action potential conduction underlying communication between complex neuronal circuits. Two critical excitable domains of vertebrate axons are the axon initial segment (AIS) and the nodes of Ranvier...
Human Body Axon Diagram - Studying Diagrams Mar 14, 2022 · No need to register buy now. Axon terminals dendrites cell body axon chandelier axon terminals dendritic tree cell body axon A B FIGURE 1-7A and B Chandelier neurons. Preview this quiz on Quizizz. Posted on June 7 2016 by admin. Draw a diagram of the cell membrane of the axon. Find the perfect human body organs diagram stock photo.
neuron | Glial cells The number of dendrites on a neuron varies. They are called afferent processes because they transmit impulses to the neuron cell body. There is only one axon that projects from each cell body. It is usually elongated and because it carries impulses away from the cell body, it is called an efferent process.
Diagram of 4.3.5 Changes in the potential difference across the axon... - Rapid depolarisation of the membrane takes place and the inside becomes +40mV relative to the outside - the action potential! ... - Positive ions diffuse out and are also pumped out of the axon. - This stage is called the refractory period as the membrane cannot be depolarised again until the...
The Structure of the Cell Membrane The cell membrane (or plasma...) The carbohydrates are found on the outer surface of all eukaryotic cell membranes, and are attached to the membrane proteins or sometimes to the phospholipids. Proteins with carbohydrates attached are called glycoproteins, while phospholipids with carbohydrates attached are called glycolipids.
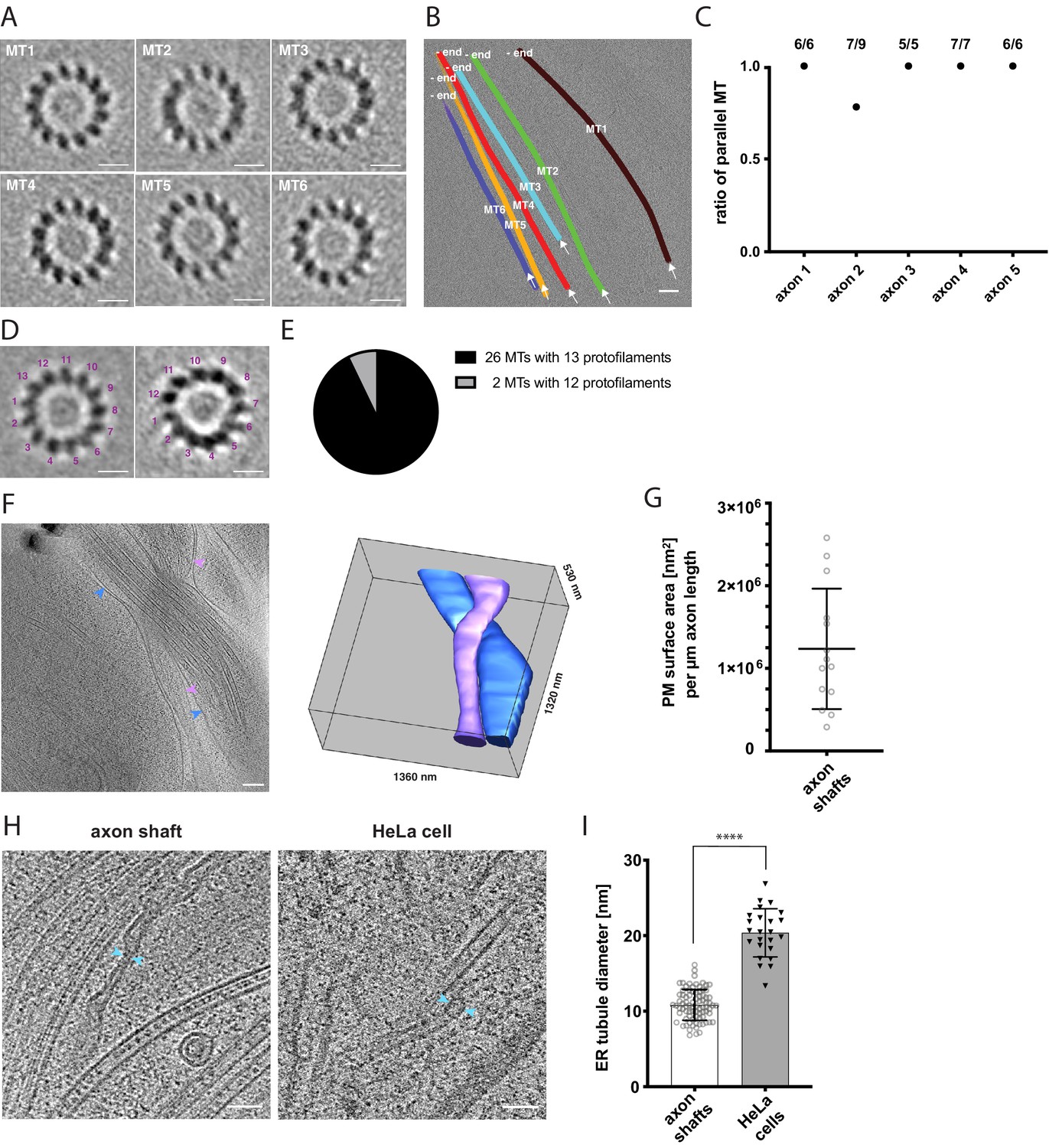
PDF Calcium Influx through Plasma-Membrane Nanoruptures Drives Axon... Calcium accumulates in the axoplasm because nanoscale ruptures of the axonal plasma membrane provide an entry path for extracellular calcium. Axon loss is a key determinant of persistent functional decits in the common neuroinammatory condition multiple sclerosis (Fri-ese et al., 2014).
Electrical Model of a Cell Membrane - Electrophysiology of the Cell... The various ionic gradients across the membrane provide a form of stored electrical energy, much like that It is helpful to model the electrical behavior of cell membranes by a circuit diagram (see Fig. Electrodes in the form of thin wires can be inserted into the axon to clamp the axon membrane...
Cell Structure - Biology Online Tutorial Integral membrane proteins span the entire width of the membrane, thus crossing through both the Cell organelles are the little workhouses within the cell. All the functions of life take place in each individual cell. Microtubules are present in the axons and long dendrite projections of nerve cells.
Structure of Cell - Membrane, Cytoplasm, and Organelles - Earth's Lab All the living things are made up ofcells The human body is made up of about 75 trillion cells, the tiniest living systems that exist. Body cells can be categorized into about 300 types, such as...
Axon - Structure and Functions - GetBodySmart Sep 22, 2017 · Axon – Structure and Functions. All neurons have a cytoplasmic process called an axon (nerve fiber), which conducts electrochemical impulses or action potentials. Axons most commonly attach to one side a neuron cell body (soma, perikaryon), at a cone-shaped region called the axon hillock. Electrochemical events in the cell body summate in the ...
Axon Terminal - The Definitive Guide | Biology Dictionary The axon terminal, also known as the synaptic/ terminal bouton, is the most distal portion of a neuron's axon and is critical for neural communication. When action potentials reach the axon terminal, calcium floods the neuron, allowing synaptic vesicles to fuse with the membrane and release stored...
























0 Response to "39 diagram of the cell membrane of the axon"
Post a Comment