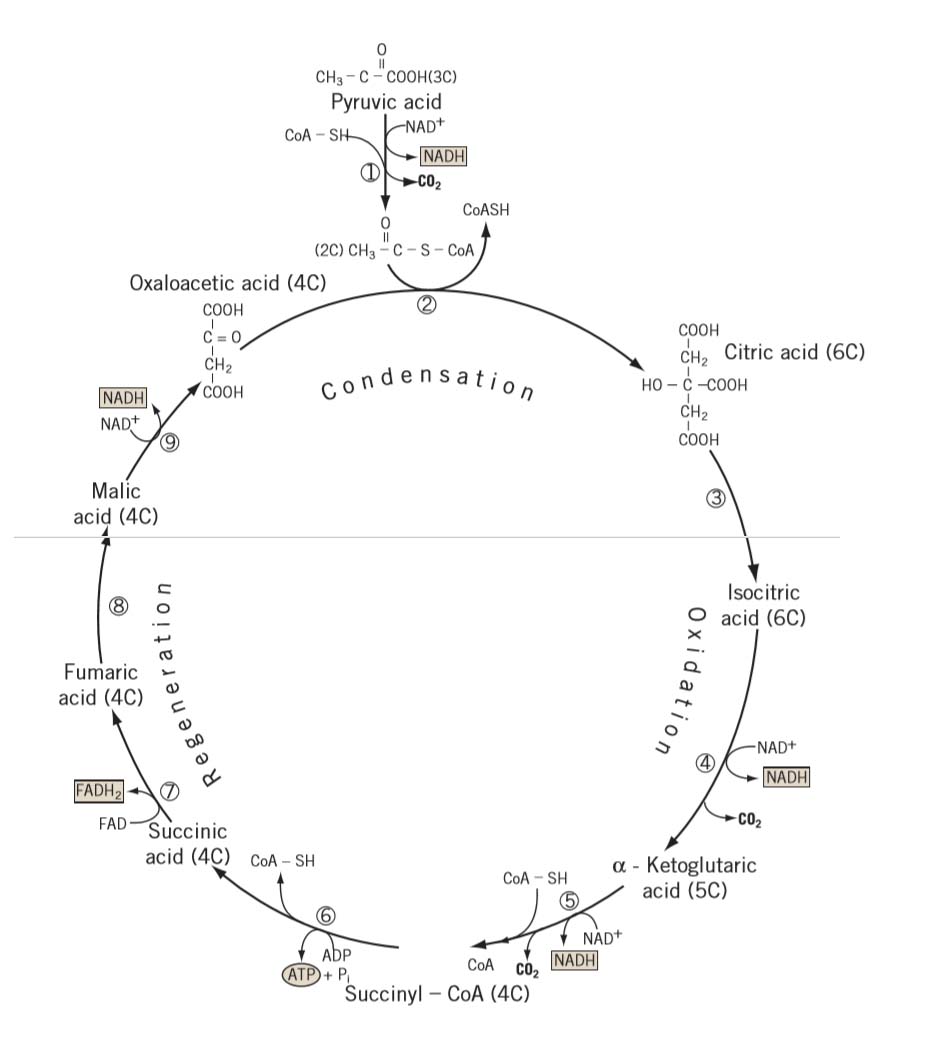
42 diagram of krebs cycle
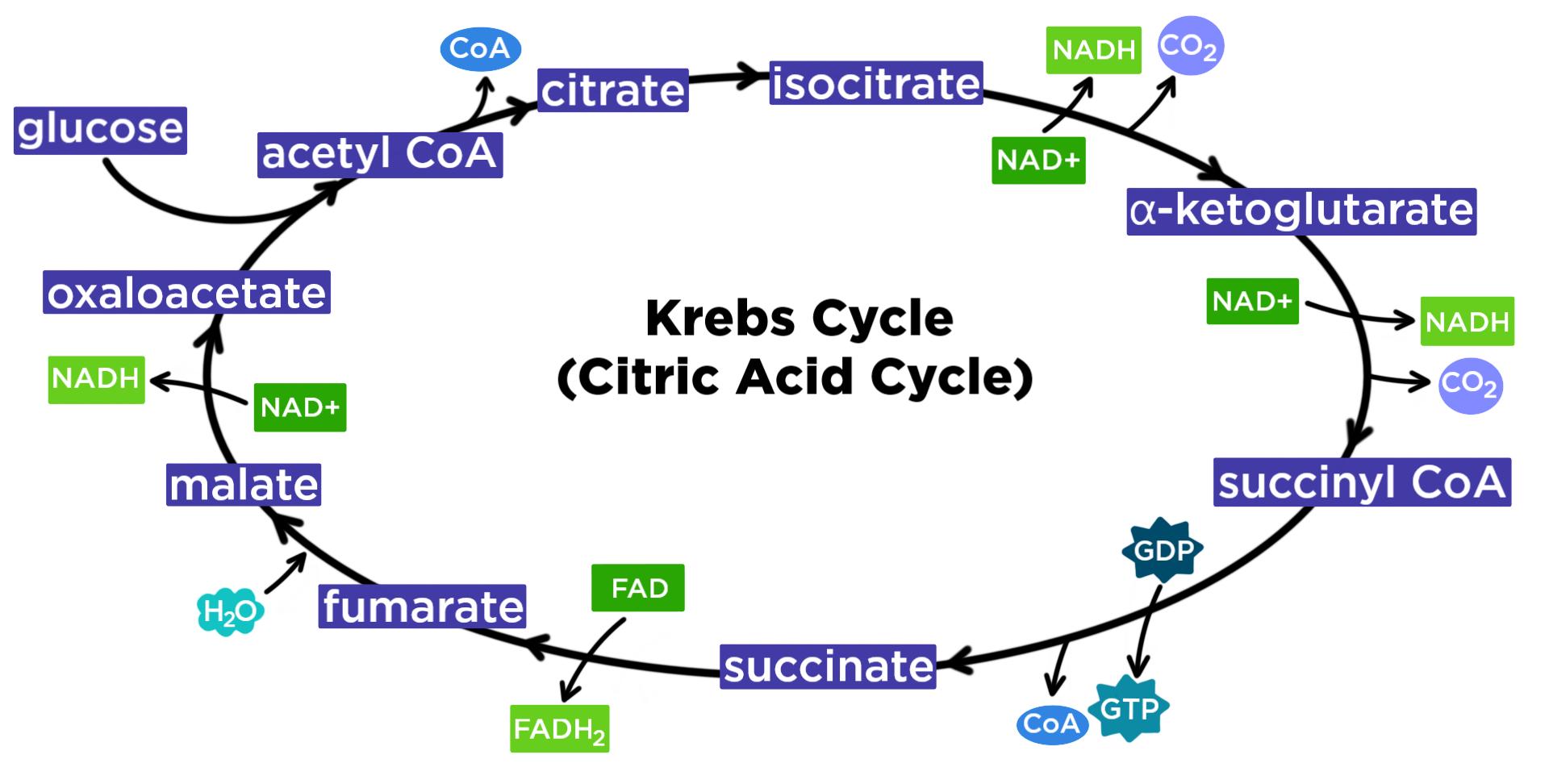
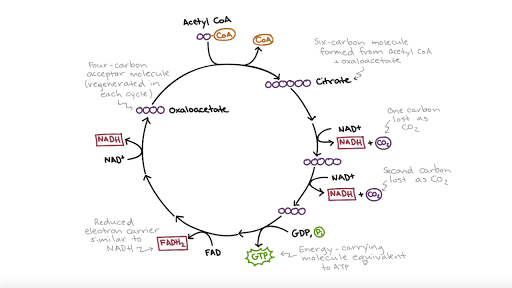
Krebs Cycle - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Krebs cycle The Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or the tricarboxylic acid cycle, is one of the most important reaction sequences in biochemistry. The Krebs cycle continuously recycles, reusing the substrates and enzymes with an overall reaction given by. Krebs Cycle: interactive lyrics, diagrams, and flashcards - learn-biology [q topic = "krebs cycle"]At the start of Krebs Acetyl-CoA's two carbons combine with oxaloacetate, a _____ carbon molecule. [q topic = "krebs cycle"]Oxidation of _____, along with removal of a CO2, produces one NADH. The resulting molecule is four carbon succinyl CoA.
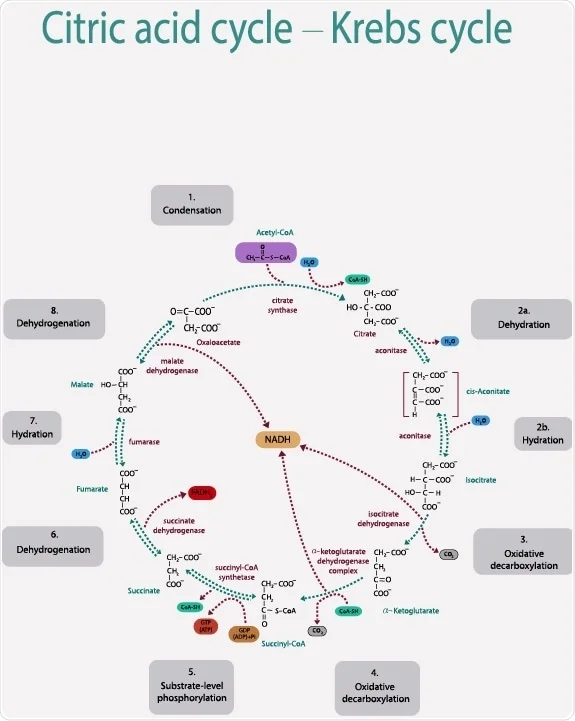
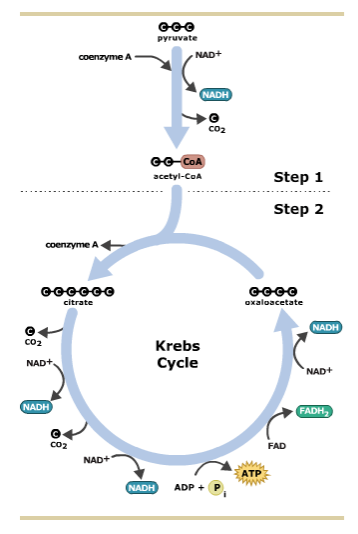
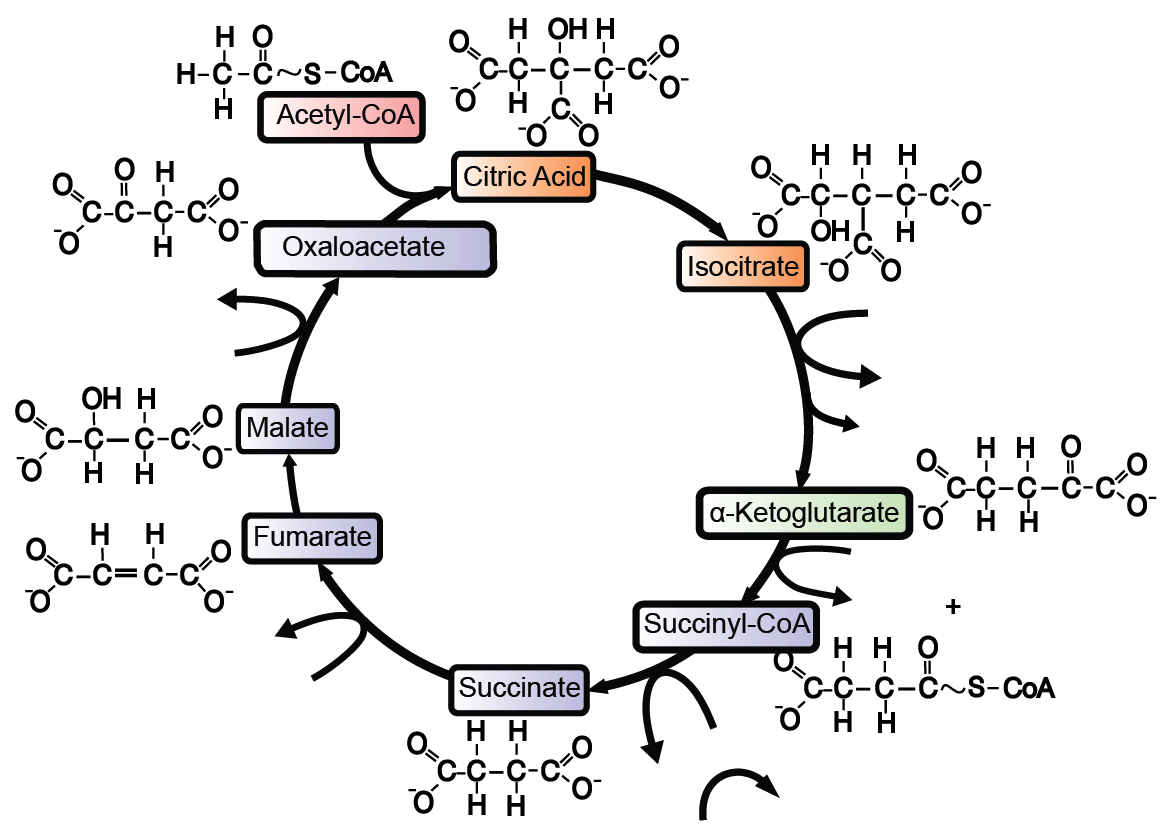
Figure 1.Krebs cycle diagram Full Krebs cycle diagram. The TCA cycle is usually described beginning with acetyl-CoA (top position). Follow the diagram clockwise in Where does the Krebs cycle take place? The TCA cycle was first observed in the muscle tissue of a pigeon. It takes place in all eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.

Diagram of krebs cycle
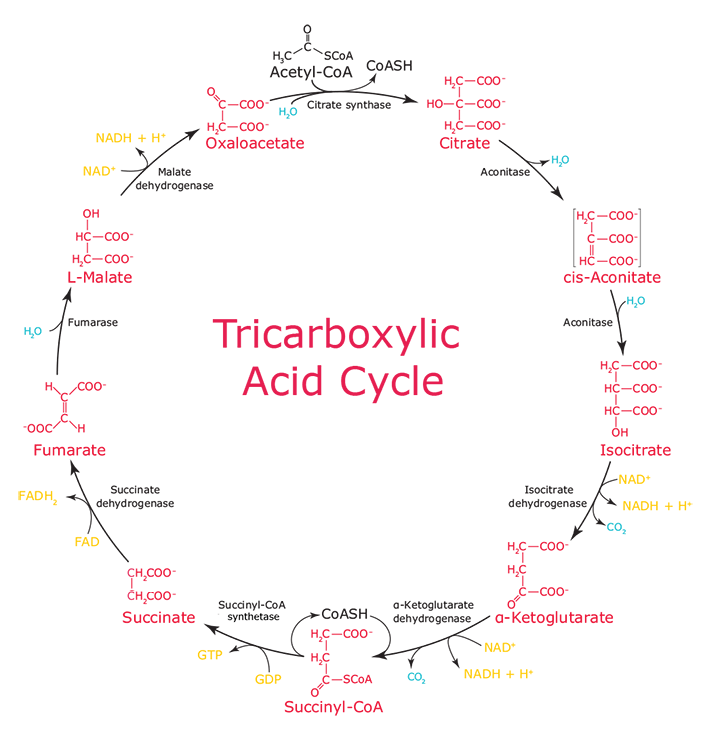
Citric acid cycle - Wikipedia The citric acid cycle (CAC) - also known as the TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle) or the Krebs cycle - is a series of chemical reactions to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Krebs cycle, mnemonics, steps, regulations - The Virtual Notebook The Krebs cycle occurs in mitochondria and all the enzymes are present in the mitochondrial matrix, either free or attached to the inner mitochondrial membrane and the cristae membrane. This process is aerobic because it requires oxygen as the final oxidant of the reduced enzymes. Krebs Cycle Diagrams | 101 Diagrams These cycle diagrams are designed to guide you in studying the acid cycle. This Krebs cycle is the oxidation of pyruvic acid into CO2 and water. This cycle is also called citric acid cycle because the cycle begins with the formation of citric acid.
Diagram of krebs cycle. Krebs' Cycle Intermediates | Nutrition Review The Krebs' cycle takes place inside the mitochondria or 'power plant' of cells and provides energy required for the organism to function. In simple terms, the Krebs' cycle metabolizes acetyl coenzyme A into citric acid and then runs through a complex series of biological oxidations, producing free... Structural Biochemistry/Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid cycle) - Wikibooks... The Citric Acid Cycle has eight-steps. Other name for citric acid cycle is tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle. The citric acid cycle is the central metabolic core of the cell. It is the final common pathway for oxidation — in other words harvesting high energy electrons--fuel molecules such as... Diagram of krebs cycle | Quizlet Start studying krebs cycle. Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools. (AKA citric acid or tricarboxylic acid cycle) catabolic pathway in which bonds of glucose and occasionally fats or lipids are broken down and reformed into ATP. Krebs Cycle Summary: Reactions, Products, Importance, Location The Krebs Cycle is one of the most crucial series of chemical reactions to take place in the human body. The products of the cycle play an essential role in maintaining energy levels and brain health. If you're experiencing brain fog, chronic fatigue, or a general lack of energy, the cause could be an...
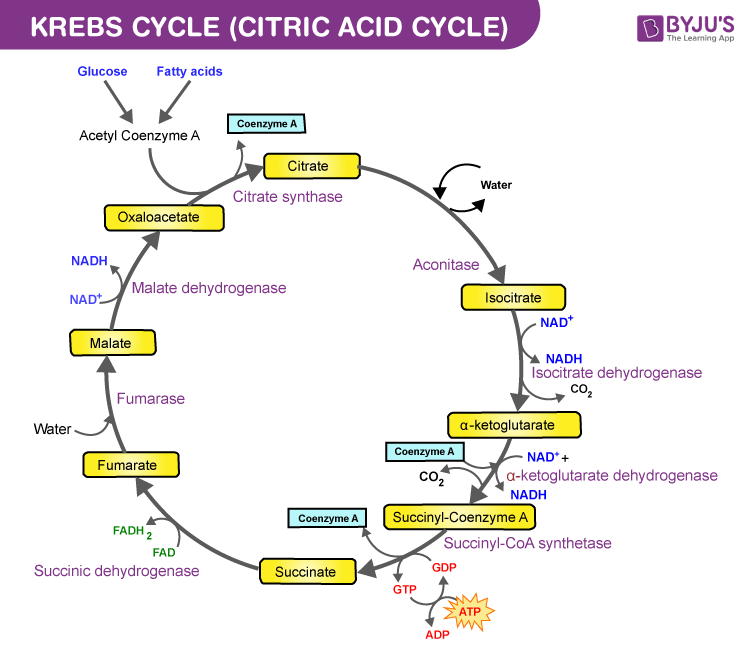
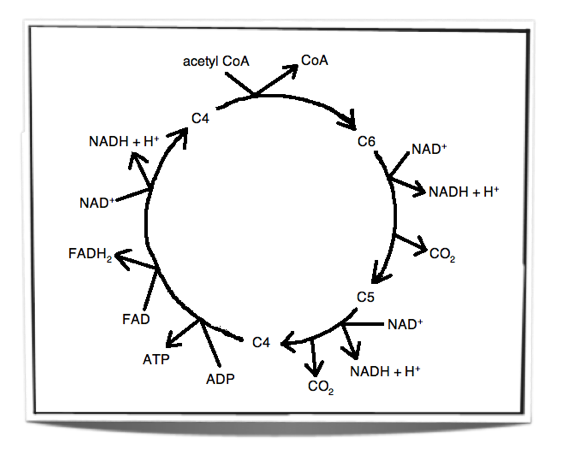
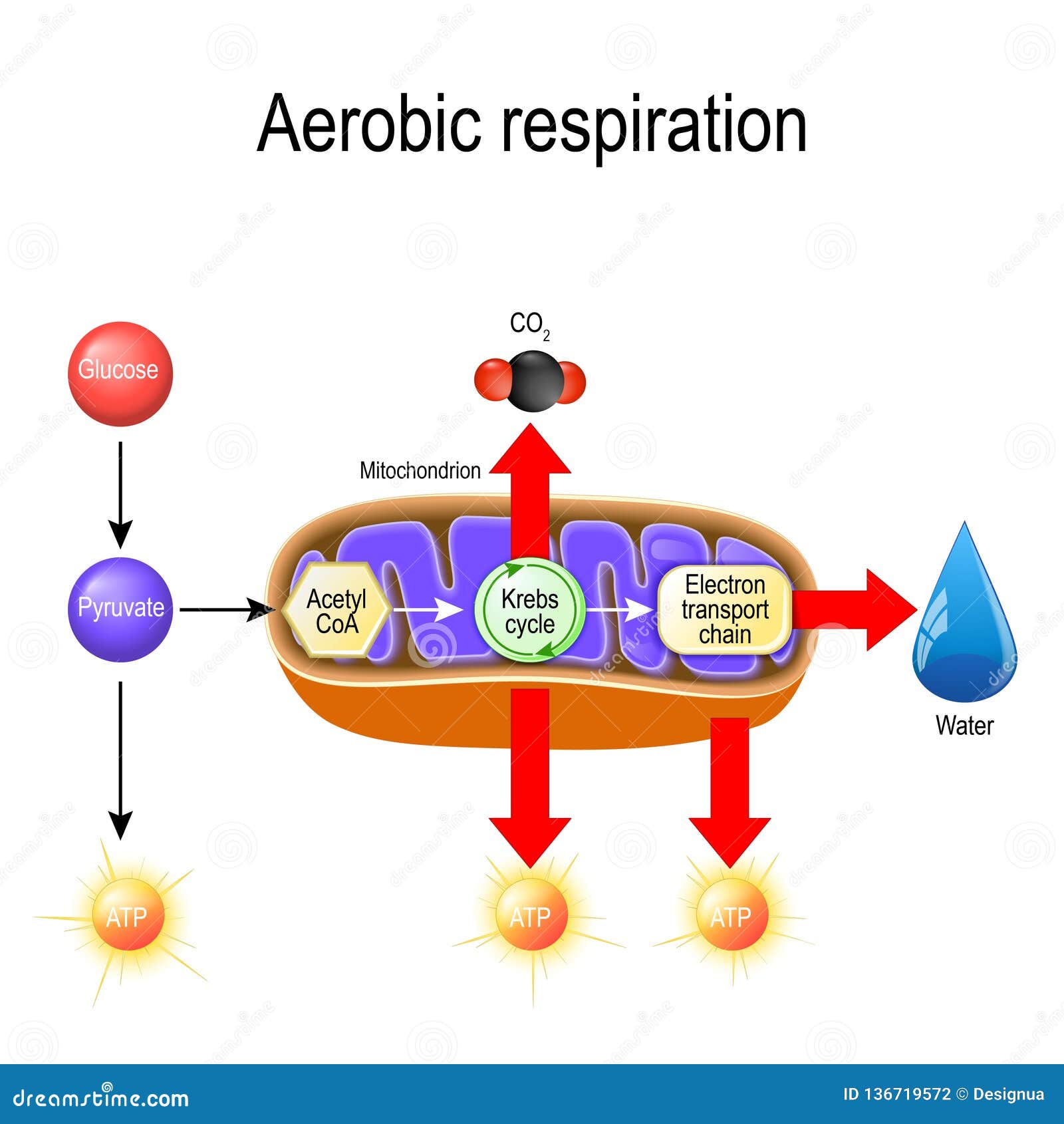
The TCA Cycle - Steps - Krebs Cycle - TeachMePhysiology Fig 1 - Diagram showing the steps of the TCA cycle. There are in fact no known defects of the TCA cycle that are compatible with life. This highlights the importance of this step in ATP production for sustaining life. Krebs Cycle | Encyclopedia.com Krebs Cycle The Krebs cycle [1] is a series of enzymatic reactions that catalyzes the aerobic metabolism of fuel molecules to carbon dioxide [2] and water, thereby generating energy for the production of adenosine triphosphate [3] (ATP) molecules. Krebs Cycle Overview - Wyzant Lessons The Krebs Cycle (also known as the Citric Acid or Tricarboxylic Acid (TCA) cycle) is the process through which aerobic cellular metabolism occurs. Because of these issues, tutors and students should exercise care when utilizing this summary and diagram to ensure that the language their... Krebs / citric acid cycle (video) | Khan Academy The Krebs cycle, or the citric acid cycle. And that actually takes place in the inner membrane, or I should say the inner space of these mitochondria. So this is just the way they happen to draw it. But this is the actual ATP that I drew in the diagram on the top. And then they have this Q group.
Krebs Cycle Steps with Diagram The Krebs cycle occurs in the Mitochondria of eukaryotic cells and in Prokaryotic cells (lacks mitochondria) or bacteria Krebs cycle takes place in the cytosol. Krebs Cycle Steps with Diagram. In the First step, the generated acetyl CoA is combined with the oxaloacetate and forms citrate with... Krebs Cycle ( Read ) | Biology | CK-12 Foundation Krebs Cycle. Loading... Found a content error? Krebs cycle. second stage of cellular respiration in which two pyruvate molecules from the first stage react to form ATP, NADH, and FADH2 in the presence of oxygen. What does the Krebs cycle produce? - Quora The Krebs cycle (or citric acid cycle) is a part of cellular respiration. Named after Hans Krebs, it is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic It's not; look at a diagram of the citric acid cycle online or in a text book - the link reaction comes before the cycle, and involves completely different... Krebs Cycle - Definition, Products and Location | Biology Dictionary The Krebs Cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle, is the second major step in the aerobic oxidation of glucose within living organisms. Krebs Cycle Overview. Most organisms use glucose as a major fuel source, but must break down this glucose and store the energy in ATP and other molecules.
The Krebs Cycle Made Easy | Sciencing The Krebs cycle supplies other benefits as well. Because it includes some eight reactions (and, correspondingly, nine enzymes) At this point you should avail yourself of a diagram detailing the Krebs cycle, as it is the only way to meaningfully follow along; see the Resources for an example.
tricarboxylic acid cycle | biochemistry | Britannica tricarboxylic acid cycle, (TCA cycle), also called Krebs cycle and citric acid cycle, the second stage of cellular respiration, the three-stage process by which living cells break down organic fuel molecules in the presence of oxygen to harvest the Alternate titles: Krebs cycle, TCA cycle, citric acid cycle.
Krebs cycle - The School of Biomedical Sciences Wiki The Krebs Cycle can also be called the Citric Acid Cycle (CAC) or the Tricarboxylic Acid (TCA) Cycle. This cycle takes place in the Mitochondrial matrix and is the primary step of aerobic processing within a cell.
The Citric Acid (Krebs) Cycle | Boundless Microbiology Krebs cycle: a series of enzymatic reactions that occurs in all aerobic organisms; it involves the oxidative metabolism of acetyl units and serves as the main source of cellular energy. mitochondria: in cell biology, a mitochondrion (plural mitochondria) is a membrane-enclosed organelle, often described...
Krebs Cycle The Krebs cycle uses the two molecules of pyruvic acid formed in glycolysis and yields high-energy molecules of NADH and flavin adenine dinucleotide The Krebs cycle occurs in the mitochondrion of a cell (see Figure 6-1). This sausage-shaped organelle possesses inner and outer membranes and...
Respiration: Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, and Electron... - ScienceAid Glycolysis. Krebs Cycle. Electron Transfer Chain. Questions and Answers. 5.2 Cristae and matrix correct in the diagram? I thought that they were supposed to the other way around? 5.3 Glycolysis, the link reaction, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain are all part of?
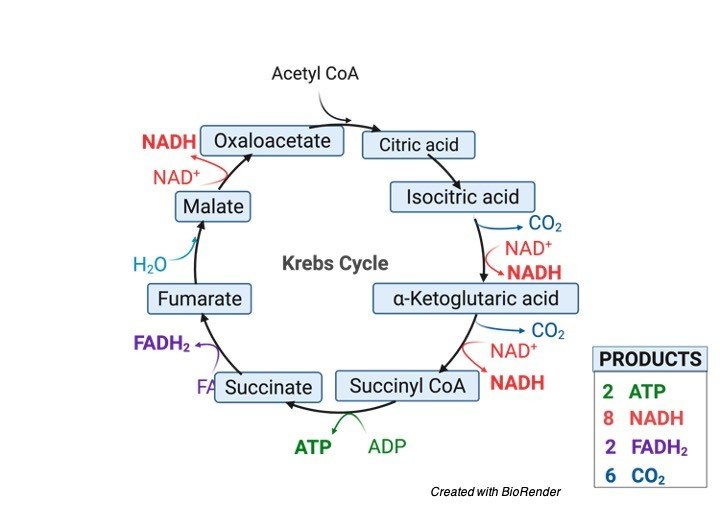
Citric Acid Cycle or Krebs Cycle Overview The Krebs cycle is the key set of reactions for aerobic cellular respiration. Some of the important functions of the cycle include: It is used to obtain chemical energy from proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. ATP is the energy molecule that is produced. The net ATP gain is 2 ATP per cycle...
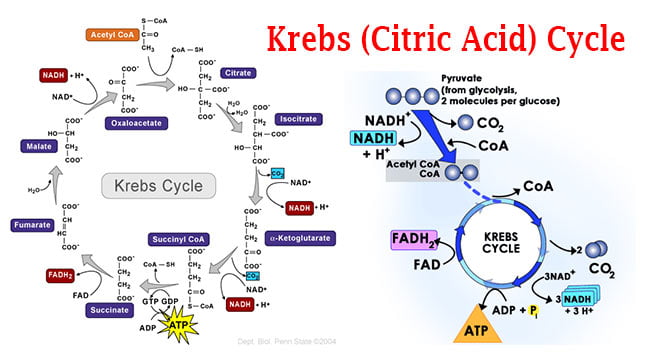
PDF The Citric Acid (Krebs, TCA) Cycle • The Krebs cycle contains two oxidative decarboxylation steps; this is the first one • The reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme Isocitrate dehydrogenase. • The reaction involves dehydrogenation to Oxalosuccinate, an unstable intermediate which spontaneously decarboxylates to give α-Ketoglutarate.
Krebs Cycle - Steps, Summary, Equation, Significance and Important... The Krebs cycle or Citric acid cycle is a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions occurring in the mitochondrial matrix, where acetyl-CoA is oxidized to form carbon dioxide and coenzymes are reduced, which generate ATP in the electron transport chain. Krebs cycle was named after Hans Krebs...
Krebs (Citric Acid) Cycle Steps by Steps... - Microbiology Info.com The Krebs Cycle is also the source for the precursors of many other molecules, and is therefore an amphibolic pathway (meaning it is both Reviewing the whole process, the Krebs cycle primarily transforms the acetyl group and water, into carbon dioxide and energized forms of the other reactants.
Krebs cycle / Citric acid cycle / TCA Cycle with steps and diagram Krebs cycle Steps. Oxidative Decarboxylation of pyruvate to Acetyl CoA. Step 1: Condensation of acetyl CoA with oxaloacetate. This cycle is also termed tricarboxylic acid (TCA) because it was then not certain whether citric acid or some other tricarboxylic acid (g., isocitric acid) was the first product of...
Krebs Cycle Diagrams | 101 Diagrams These cycle diagrams are designed to guide you in studying the acid cycle. This Krebs cycle is the oxidation of pyruvic acid into CO2 and water. This cycle is also called citric acid cycle because the cycle begins with the formation of citric acid.
Krebs cycle, mnemonics, steps, regulations - The Virtual Notebook The Krebs cycle occurs in mitochondria and all the enzymes are present in the mitochondrial matrix, either free or attached to the inner mitochondrial membrane and the cristae membrane. This process is aerobic because it requires oxygen as the final oxidant of the reduced enzymes.
Citric acid cycle - Wikipedia The citric acid cycle (CAC) - also known as the TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle) or the Krebs cycle - is a series of chemical reactions to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
























0 Response to "42 diagram of krebs cycle"
Post a Comment