37 space time diagram tutorial
Q-circuit Tutorial Bryan Eastin, Steven T. Flammia Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, New Mexico 87131–1156, USA Q-circuit is a list of macros that greatly simplifies the construction of quantum circuit diagrams (QCDs) in LATEX with the help of the XY-pic package. This tutorial should help the reader ac- 24 Dec 2020 — What is more, these diagrams give both axes the same units by scaling the vertical axis by the speed of light, c. The resulting representation ...
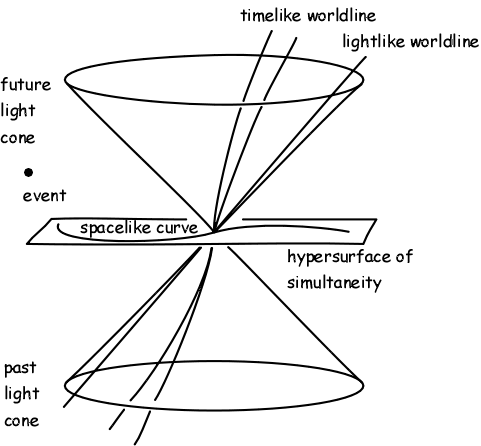
In the jargon of spacetime diagrams, the green point on Tom’s and Sarah’s plots is an event and the red or blue trajectories are worldlines. An event is anything that can be characterized by a single point on a spacetime diagram (or on a position vs time graph). An event must have both a time and a place, and
Space time diagram tutorial
The two events may also be shown in "real time" by pressing the buttons " Play worldline t" or " Play worldline t'". The two events will then appear in space and time (given time unit = 1 second). Below the animation is a more detailed tutorial and some examples and excercises. This is called a time-space diagram Traffic Flow Basics-Trajectory Plots . Time (t) (x) Consider a horizontal “slice” of the diagram Traffic Flow Basics-Trajectory Plots (2) The number of trajectories crossing this line is the number of vehicles passing a fixed point on the road. The tutorial Grover’s search shows you how to build and run Grover search, one of the most popular quantum computing algorithms and offers a nice example of a Q# program that can be used to solve real problems with quantum computing. Set up Azure Quantum recommends more ways to learn Q# and quantum programming.
Space time diagram tutorial. 1. In this diagram, which events (out of A, B, C and D) occur at the same time? Which events occur at the same place? 2. One division of the space axis corresponds to 1 meter. Construct a world line of the particle that is resting at 2 m from the reference event. time space A D B C O. time space { A point on the spacetime diagram is called an event. This is a point in space at a speci c moment in time. { The vertical value of this event is the time as measured by observer 1. { The horizontal value event is the position of the event as measured by observer 1. { Take a line from the event, parallel to the space axis of observer 2. Previous Lesson. Current Lesson. Next Lesson. Basic Mechanics. Description of Motion, Galilean. Relativity Principle. Introduction to spacetime diagrams.24 pages The time-space diagram is a visual tool for engineers to analyze a coordination strategy and modify timing plans. The main components in a time-space diagram that are inputs include individual intersection locations, cycle length, splits, offset, left turn phasing (on the arterial in the direction of the diagram), and speed limit.
In a spacetime diagram like is being used the observers frame of reference O has the non-prime axes t and x and light will always move moving at a 45 degree angle and the observer will always be on their t axis. When we look at the spaceship that is moving at 0.5c they are in O' and we are in O. A good way to keep track of these concepts is the space-time diagram. A space-time diagram is nothing more than a graph showing the position of objects as a ... Figure 7: Diagram for showing time dilation for events located at a fixed point in frame S. Now we want to show that the measurement of time intervals in the S frame are not the same as those in the S0frame using Minkowski diagrams. In Figure 7 we mark two events, A and B, located at the same point in space but different points in time, in the ...
The tutorial Grover’s search shows you how to build and run Grover search, one of the most popular quantum computing algorithms and offers a nice example of a Q# program that can be used to solve real problems with quantum computing. Set up Azure Quantum recommends more ways to learn Q# and quantum programming. This is called a time-space diagram Traffic Flow Basics-Trajectory Plots . Time (t) (x) Consider a horizontal “slice” of the diagram Traffic Flow Basics-Trajectory Plots (2) The number of trajectories crossing this line is the number of vehicles passing a fixed point on the road. The two events may also be shown in "real time" by pressing the buttons " Play worldline t" or " Play worldline t'". The two events will then appear in space and time (given time unit = 1 second). Below the animation is a more detailed tutorial and some examples and excercises.


0 Response to "37 space time diagram tutorial"
Post a Comment