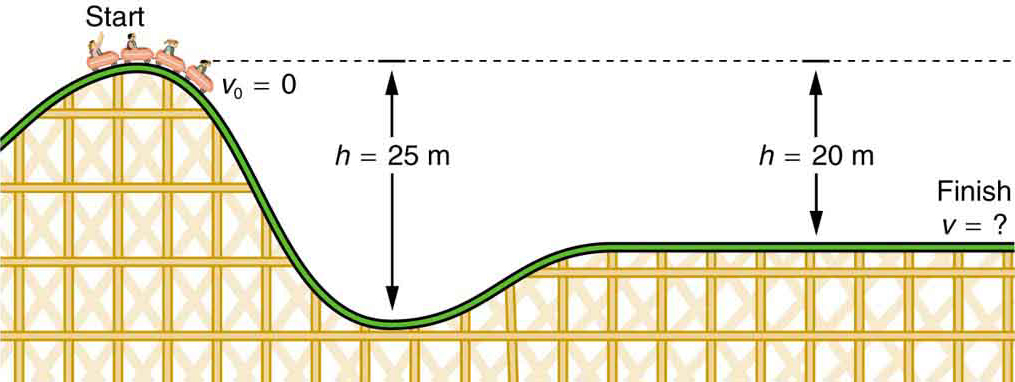
40 (figure 1) is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at a.
The figure shows the potential energy diagram for a 500 g ... Question: The figure shows the potential energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at A. a. What is the particle's speed at B? b.What is the particle's speed at C? c.What is... FIGURE is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g | StudySoup FIGURE is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at A. What are the particle's speeds at B, C, and D?FIGURE Solution 26EStep 1az:We are going to find the speed of the particle at the points B, C, and D.The mass of the particle m = 500 g = 0.5 kgThe energy of the particle when it
The figure is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g ... The figure is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at A. What are the particle speeds at point B, C and D? orchidlocust372 The figure is the potential-energy diagram for a 15 g particle that is released from rest at x = 6 m. (a) Will the particle move to the right or to the left? Explain your answer.

(figure 1) is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at a.
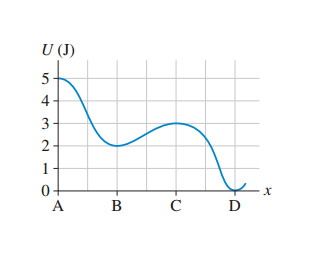
Answered: (Figure 1) is the potential-energy… | bartleby Transcribed Image Text: I Revie (Figure 1) is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at A. Part A What is the particle's speed at B? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. OneClass: The figure is the potential-energy diagram for a ... The figure is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at A. What are the particle's speeds at B, C, and D? silverferret259 The figure is the potential-energy diagram for a 15 g particle that is released from rest at x = 6 m. (a) Will the particle move to the right or to the left? Explain your answer. What is the maximum speed of a 3.40g particle that ... For the potential-energy diagram in (Figure 1), what is the maximum speed of a 5.0 g particle that oscillates between x = 2.0 mm and x = 8.0 mm? parabola starts at 5,2 and ends at 5,8 with the bottom at 1,4 Physics The speed of a transverse wave on a string is 450m/s, while the wavelength is 0.18m. The amplitude is 2.0mm.
(figure 1) is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at a.. 8.4 Potential Energy Diagrams and Stability | University ... Find the potential energy of a particle due to this force when it is at a distance x from the wall, assuming the potential energy at the wall to be zero. Show Solution A single force F (x) = −4.0x F ( x) = − 4.0 x (in newtons) acts on a 1.0-kg body. When x= 3.5m, x = 3.5 m, the speed of the body is 4.0 m/s. What is its speed at x =2.0m? x = 2.0 m? 1. || FIGURE EX10.25 is the potential-energy diagram for a ... FIGURE EX10.25 is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at A. What are the particle's speeds at B, C, and D? In FIGURE EX10.26, what is the maximum speed of a 2.0 g particle that oscillates between x = 2.0... Potential Energy Graphs and Motion Learning Goal To be ... Potential Energy Graphs and Motion Learning Goal: To be able to interpret potential energy diagrams and predict the corresponding motion of a particle. Potential energy diagrams for a particle are useful in predicting the motion of that particle. These diagrams allow one to determine the direction of the force acting on the particle at any point, the points of stable and unstable equilibrium ... Solved The figure is the potential-energy diagram for a ... The figure is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 gparticle that is released from rest at A. What are the particle's speeds at B, C, and D? Expert Answer 100% (23 ratings) We will assume conservation of energy here. PE + KE = Total Energy At … View the full answer Previous question Next question
PDF M10 KNIG9404 ISM C10 - pshs.psd202.org (b) The turning points for the particle with total energy (TE) shown are at 2 mx = and 8 mx =. (c) The particle could remain at rest in stable equilibrium at 3 mx = and 6 mx =. The particle could also remain at rest in unstable equilibrium at 1 mx = and 4 mx =. 10.14. The problem can be divided into three parts: (1) from when the first ball is ... Online Quiz 11 Flashcards | Quizlet The potential energy of a particle m = 0.20 kg moving along the x axis is given by U (x) = 8x2 + 2x4, where U is in joules and x is in meters. Use a calculator to solve the equation. If the particle has a speed of 5.0 m/s when it is at x = 1.0 m. Find the speed of the particle when it is at the origin. 11.2 m/s. Homework Problems 8 - Copy.pdf - 8 Mechanical Energy ... (Knight Problem 10.25) FIGURE EX10.25 is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at A. What are the particle's speeds What are the particle's speeds at B, C, and D? 8 Chapter Review - General Physics Using Calculus I Find the potential energy of a particle subjected to this force when the particle is at a distance D from P, assuming the potential energy to be zero when the particle is at P. 74 . An object of mass 10 kg is released at point A , slides to the bottom of the 30 ° 30° incline, then collides with a horizontal massless spring, compressing it a ...
8.4 Potential Energy Diagrams and Stability - University ... Interpreting a one-dimensional potential energy diagram allows you to obtain qualitative, and some quantitative, information about the motion of a particle. At a turning point, the potential energy equals the mechanical energy and the kinetic energy is zero, indicating that the direction of the velocity reverses there. C9-11 Flashcards - Quizlet The work-energy theorem implies that four times more work must be done on the heavier block than on the lighter block. Since the same force is applied to both blocks, the heavier block must be pushed through four times the distance as the lighter block. 4K for the heavier, K for the lighter K = 1/2mv^2 Kf - Ki = W = F*s PDF Problem set 8 key - CSU, Chico The particle with a mass of 500 g is released from rest at A. That is, at A. Since we can draw a horizontal TE line through The distance from the PE curve to the TE line is the particle's kinetic energy. These values are transformed as the position changes, causing the particle to speed up or slow down, but the sum does not change. Potential-energy diagram help - Physics Forums Dec 6, 2006 #1 fsm 88 0 I am given a potential-energy diagram with the vertical axis is potential-energy and the horizontal axis is x. The mass of the particle is 500g. They are asking the velocities of b, c, and d. I am completely lost. I can't even find an example in the book. This isn't good : ( Answers and Replies Dec 6, 2006 #2 berkeman Mentor

29 Is The Potential Energy Diagram For A 500 G Particle That Is Released From Rest At A ...
Solved Item 6 Part A (Figure 1) is the potential-energy ... Question: Item 6 Part A (Figure 1) is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at A What is the particle's speed at B? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units UValue Units Submit Part B What is the particle's speed at C?

Is The Potential Energy Diagram For A 20 G Particle That Is Released From Rest At X 10 M ...
PDF Exam 2 Solutions The graph shows the potential energy of an object acted upon by a conservative ... Then the total time to rest: t 3= (ω 3−ω 1) α = (0−500 rev/min)(1 min/ 60 s) 1.67 rev/s2 =5 s so the additional time was 2 s ... If the block is released from rest 2.0 m above the floor, what ...
The figure shows the potential energy of a 400g particle as ... Nov 25, 2016 · The potential energy (PE) value in the figure when x = 2 is 8 J Because it is known that ME = 12 J, particle velocity can be found from the kinetic energy equation KE = ME - PE KE = 12 - 8 KE = 4 J the particle's maximum speed The maximum particle velocity occurs when PE = 0 and KE = ME The lowest particle velocity occurs when KE = 0 and PE = ME
MMP: Ch. 10 Flashcards | Quizlet is the potential-energy diagram for a 35g particle that is released from rest at x = 1.0 m. Will the particle move to the right (in the positive x-direction) or to the left (in the negative x-direction), and why? What is the particle's maximum speed? At what position does the particle have maximum speed? Where are the turning points of the motion?
Solved (Figure 1) is the potential-energy diagram for a ... Question: (Figure 1) is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at A. V Part A What is the particle's speed at B2 Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate unit HA ? UB Value Units Figure Submit Request Answer 1 of 1 Part B U (J) What is the particle's speed at C?
SOLVED:is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g ... We've got a potential energy diagram for a particle, and I'm just going to sketch that right here and that. That points a, B, C and D and 1234 When AIDS at five b, it's down to two C. It's up to three d of zero, and I can actually curves up again right there. And I know that it's released from rest at point A.
In the figure shown the potential energy U of a particle ... The potential energy of a particle in a certain field is given by U= r 2a − rb , where a and b are positive constants and r is the distance from the centre of the field. The distance of particle in the stable equilibrium position is Hard View solution > Potential energy curve is shown in figure. Point at stable equilibrium is : Hard View solution >
The figure is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g ... 8. The figure is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from. rest at A. What is the particle's speed at C? What is the acceleration of the object at.



0 Response to "40 (figure 1) is the potential-energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at a."
Post a Comment